标签:color += open reverse 算法 roc numpy height 智能
A*算法是一种启发式搜索算法,它的关键在于,每次从open表中选取结点时,要按特定的策略选取。该策略如下所述:
引入估值函数![]() , f(n)是结点n的函数,f(n)越小,就意味着从初始状态节点S通过结点n的路径长度的估值最短。简而言之,f(n)越小,则通过结点n的路径是最佳路径的可能性越大。
, f(n)是结点n的函数,f(n)越小,就意味着从初始状态节点S通过结点n的路径长度的估值最短。简而言之,f(n)越小,则通过结点n的路径是最佳路径的可能性越大。
因此,从open表中选取结点之前,我们先以f(n)为指标对open表中的所有节点进行排序,然后选取f(n)最小者即可。
具体地,在本题中

以下是完整代码
1 # from queue import Queue 2 from 八数码问题BFS import move0 # move0函数参考上一篇博文:https://www.cnblogs.com/vivlalib/p/12557518.html 3 import numpy as np 4 import time 5 6 class Node: 7 def __init__(self, state, parent, operator): 8 self.state = state 9 self.parent = parent 10 self.operator = operator 11 def operate(self, dir): # 操作算符 12 new_state = move0(self.state, dir) 13 if new_state is False: 14 return None 15 else: 16 return Node(new_state, self, dir) # 以self为父 17 def islegal(self): # 检查结点的合法性, 根据实际问题改变 18 return self 19 def traverse(self): 20 cur = self 21 res = [] 22 while cur is not None: 23 # print(cur.state) 24 res.append(cur) 25 cur = cur.parent 26 # res.pop() 27 return res 28 def depth(self): # 当前结点到根节点的距离,根据实际问题改变 29 return len(self.traverse()) - 1 30 31 def findn(state, n): # 在state中寻找n的位置 32 for i in range(len(state)): 33 for j in range(len(state)): 34 if state[i][j] == n: 35 ind0 = [i, j] 36 return ind0 37 def manhattan(pos1, pos2): # pos1, pos2 are like [x, y] 38 return abs(pos1[0] - pos2[0]) + abs(pos1[1] - pos2[1]) 39 40 41 def distance0(state1, state2): # 自己乱写的距离函数,很慢 15s 42 state1 = np.array(state1) 43 state2 = np.array(state2) 44 ret = np.sum(np.abs(state1-state2)) # ∑|state1[i] - state2[i]| 对应维度差的绝对值之和,即曼哈顿距离 45 return ret 46 47 def distance(state1, state2): # 这里使用曼哈顿距离, 0.21s 48 49 posn1, posn2 = [], [] 50 for n in range(9): # 分别在state1与state2中查找0到9的位置 51 posn1.append(findn(state1, n)) 52 posn2.append(findn(state2, n)) 53 dsum = 0 54 for i in range(9): 55 dsum += manhattan(posn1[i], posn2[i]) 56 return dsum 57 58 59 60 61 def f(node:Node, goal_state): # 估价函数 62 """ 63 公式表示为: f(n)=g(n)+h(n), 64 其中 f(n) 是从初始点经由节点n到目标点的估价函数, 65 g(n) 是在状态空间中从初始节点到n节点的实际代价, 66 h(n) 是从n到目标节点最佳路径的估计代价。 67 :param node: 68 :return: 69 """ 70 cur_state = np.array(node.state) 71 goal_state = np.array(goal_state) 72 gn = node.depth() 73 hn = distance(cur_state, goal_state) 74 return gn + hn 75 76 77 def showinfo(node: Node): # 用于搜索成功后的输出 78 nlist = node.traverse() 79 nlist.reverse() 80 for n in nlist: 81 if n.operator is not None: 82 print(n.operator) 83 print(n.state) 84 85 86 def Astar(init_state, goal_state): 87 dirs = [‘up‘, ‘down‘, ‘left‘, ‘right‘] 88 open = [] # open表 89 closed = [] 90 root = Node(init_state, None, None) # 起始状态,根节点 91 open.append(root) 92 while open: # 若open表为空,退出循环 93 open.sort(key=lambda x: f(x, goal_state)) 94 node = open.pop(0) # 选出open表中f(n)最小者 95 closed.append(node) 96 # 扩展 97 for dir in dirs: 98 node_tmp = node.operate(dir) # 以dir为方向拓展结点 99 # 新节点合法 100 if node_tmp is not None and node_tmp not in closed: 101 open.append(node_tmp) 102 if node_tmp.state == goal_state: # node_tmp 是目标结点? 103 print(‘搜索成功。‘) 104 showinfo(node_tmp) 105 return True 106 return False 107 108 goalss = [[1, 2, 3], 109 [8, 0, 4], 110 [7, 6, 5]] 111 goal = [[2,0,3], 112 [1,8,4], 113 [7,6,5]] 114 init = [[2,8,3], 115 [1,0,4], 116 [7,6,5]] 117 118 goal = [[1, 2, 3], 119 [8, 0, 4], 120 [7, 6, 5]] 121 122 init = [[2,8,0], 123 [1,6,3], 124 [7,5,4]] 125 if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: 126 127 print(Astar(init,goal)) 128 print(time.process_time())
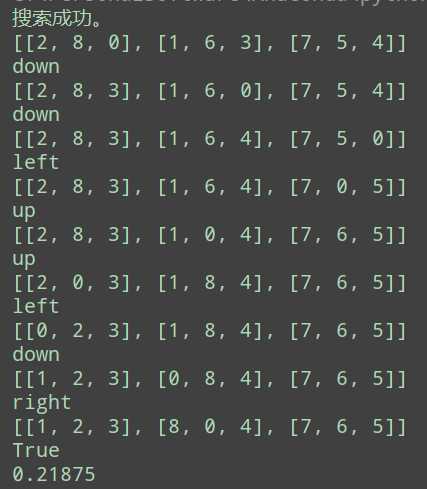
运行结果如下:
标签:color += open reverse 算法 roc numpy height 智能
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/vivlalib/p/12567524.html