标签:两个栈 出栈 最小 put NPU top tin else lan
以蓝书为学习参考,进行的栈的学习
例题1:
实现一个栈,支持Push,Pop和GetMin(查询栈中最小的值)在O(1)完成
算法实现思路:
建立两个栈,A存原本的数据,B存以栈底开头的每段数据的最小值
Push(X),在A中插入X,在B中插入min(B的栈顶数据,X)。执行GetMin只需要输出B.top()即可
例题2:

Input 8 I 2 I -1 I 1 Q 3 L D R Q 2 Output 2 3
//对顶栈算法
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int INF = -0x3F3F3F3F;
const int MAXN = 1000010;
// int s1[MAXN];
// int s2[MAXN];
int sum[MAXN]; //前x个数的和
int f[MAXN]; //前x个数中连续最大和
int main () {
int cas;
while(scanf("%d",&cas)!=EOF) {
memset(sum, 0, sizeof(sum));
memset(f, INF, sizeof f);
int pos1 = 0;
// int pos2 = 0;
stack<int> s1;
stack<int> s2;
while(cas--) {
string s;
s.resize(5);
scanf("%s", &s[0]);
if(s[0] == ‘I‘) {
// cin >> s1[++pos1];
int temp;
scanf("%d", &temp);
// cout << 666 << " " << temp << endl;
s1.push(temp);
pos1++;
sum[pos1] = sum[pos1 - 1] + temp;
f[pos1] = max(f[pos1 - 1], sum[pos1]);
// cout << pos1 << " III" << f[pos1] << endl;
}
else if(s[0] == ‘D‘) {
// pos1--;
if(s1.empty())
continue;
pos1--;
s1.pop();
}
else if(s[0] == ‘L‘) {
if(s1.empty())
continue;
// if(pos1 != 0) {
// s2[++pos2] = s1[pos1--];
// }
pos1--;
int temp = s1.top();
s1.pop();
s2.push(temp);
}
else if(s[0] == ‘R‘) {
if(!s2.empty()) {
// s1[++pos1] = s2[pos2--];
// sum[pos1] = sum[pos1 - 1] + s1[pos1];
// f[pos1] = max(f[pos1 - 1], sum[pos1]);
int temp = s2.top();
s2.pop();
s1.push(temp);
pos1++;
sum[pos1] = sum[pos1 - 1] + temp;
f[pos1] = max(f[pos1 - 1], sum[pos1]);
}
}
else if(s[0] == ‘Q‘) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("%d\n", f[x]);
}
}
}
}
例题三:进出栈序列问题
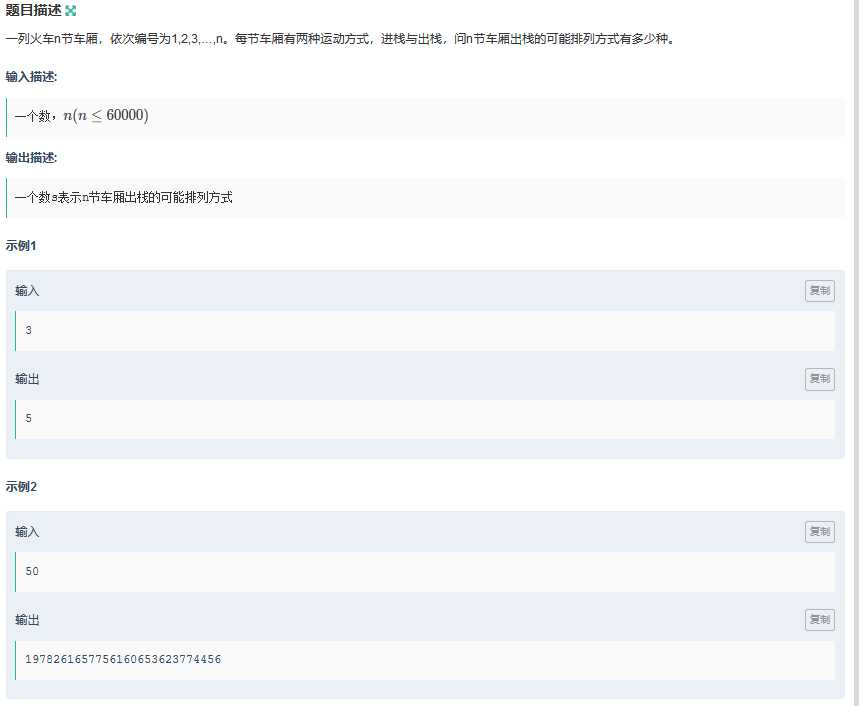
利用Catalan数定义计算 C(2N, N) / (N + 1) 涉及数论计算知识。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fir(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++)
#define ll long long
const ll M=1e9;//M为压位的最大值
ll a[60004],l,sum[120004];
int n;
void Prime(int b,int f)
{
for(int j=2;j*j<=b && b!=1;j++)//质因数分解.
while(b%j==0)
{
sum[j]+=f;
b/=j;
}
if(b)
sum[b]+=f;
}
void High(ll c)
{
for(int i=1;i<=l;i++)
a[i]*=c;
for(int i=1;i<=l;i++)
a[i+1]+=a[i]/M,a[i]%=M;//我们需要压缩位置快速处理
while(a[l+1])
++l;
}
int main()
{
a[1]=1,l=1;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)//对于两个组合数相除,我们这道题目必须使用快速的质因数分解法,去处理.
Prime(n+i,1);
for(int i=2;i<=n+1;i++)
Prime(i,-1);
for(int i=2;i<=2*n;i++)
for(ll j=0;j<sum[i];++j)
High(i);//高精度
printf("%lld",a[l]);
for(ll i=l-1;i;--i)
printf("%09lld",a[i]);//输出
return 0;
}
例题四:

PS:改日研究研究我上面的算法==哪儿出错了(感觉出了玄学错误)
// // #include <bits/stdc++.h>
// #include <cstdio>
// #include <algorithm>
// using namespace std;
// typedef long long ll;
// const int MAXN = 100010;
// ll a[MAXN];
// int main () {
// int n;
// while((scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) && n) {
// //memset(a, 0, sizeof a);
// for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// scanf("%lld", &a[i]);
// }
// ll p;
// a[n + 1] = p = 0;
// ll s[MAXN];ll w[MAXN];
// s[0] = a[0];
// w[0] = 1;
// ll ans = 0;
// for(int i = 1; i <= n + 1; ++i) {
// if(a[i] > s[p]) {
// s[++p] = a[i];
// w[p] = 1;
// }
// else {
// ll width = 0;
// while(s[p] > a[i]) {
// width += w[p];
// ans = max(ans, (ll)width * s[p]);
// --p;
// }
// s[++p] = a[i];
// w[p] = width + 1;
// }
// }
// printf("%ld\n", ans);
// }
// }
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll Maxn = 1e6 + 5;
stack <int> s;
int n, x;
ll a[Maxn], m, ans, Right[Maxn], Left[Maxn];
int main () {
while (~scanf ("%d", &n), n) {
ans = 0;
a[0] = -1;
a[n + 1] = -1;
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf ("%lld", &a[i]);
}
while (!s.empty()) {
s.pop();
}
//从左向右
s.push(0);
for (ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (x = s.top(); a[x] >= a[i]; x = s.top()) {
s.pop();
}
Left[i] = x + 1;
s.push(i);
}
while (!s.empty()) {
s.pop();
}
//从右至左
s.push(n + 1);
for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
for (x = s.top(); a[x] >= a[i]; x = s.top()) {
s.pop();
}
Right[i] = x - 1;
s.push(i);
if ((Right[i] - Left[i] + 1) * a[i] > ans) {
ans = (Right[i] - Left[i] + 1) * a[i];
}
}
printf ("%lld\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
标签:两个栈 出栈 最小 put NPU top tin else lan
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lightac/p/12571165.html