标签:code end bsp xsd comm spring容器 setting 设计模式 位置
1、新建一个web项目
2、导入jar包:四个核心(bean、core、context、expression),一个依赖
spring-framework-3.0.2.RELEASE-dependencies:集成了很多jar包,是最新版本。
spring-framework-4.2.4.RELEASE:与spring相关,目录结构如下:
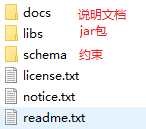
(1)导入Spring的核心包:它们是Spring其它功能的基础(四个核心包)
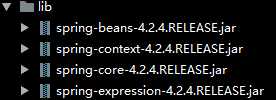
(2)导入日志文件相关的jar包:(依赖包)
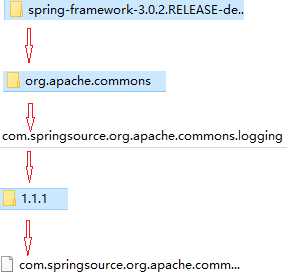
spring-framework-3.0.2.RELEASE-dependencies\org.apache.commons\com.springsource.org.apache.commons.logging\1.1.1
另外一个日志文件相关的包(支持老版本):
spring-framework-3.0.2.RELEASE-dependencies\org.apache.log4j\com.springsource.org.apache.log4j\1.2.15
3、IoC入门案例
(1)IoC(Inverse of Control)
IoC被称为控制反转,它是一种设计模式,实质上是将对象的创建方式进行反转。传统的资源获取方式是组件向容器发起请求,容器返回资源。在IoC模式下是容器主动地将资源推送给它所管理的组件,组件以合理的方式来接收资源即可。(将对象的创建交给了Spring)
(2)创建一个对象(Student):
package pers.zhb.domain;
public class Student {
private String snum;
private String sname;
private String sex;
public String getSnum() {
return snum;
}
public void setSnum(String snum) {
this.snum = snum;
}
public String getSname() {
return sname;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"snum=‘" + snum + ‘\‘‘ +
", sname=‘" + sname + ‘\‘‘ +
", sex=‘" + sex + ‘\‘‘ +
‘}‘;
}
}
(3)创建配置文件:
位置:任意(这里放在src目录下)
名字:任意(这里用applicationContext)
导入外部约束(IDEA):
File下选择Settings:
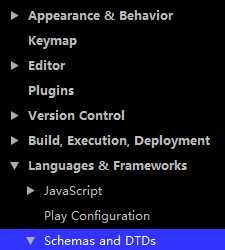
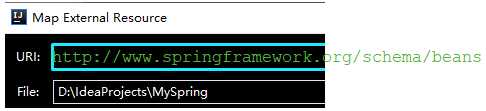
URI填入网络地址,File填入约束文件在本地的路径,然后点击确定配置完成。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd ">
</beans>
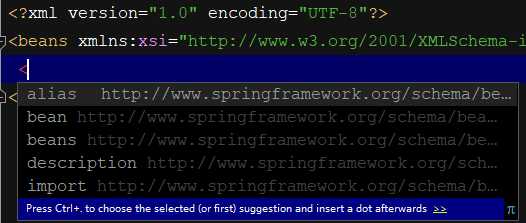
有提示即表明约束导入成功。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd "> <bean name="student" class="pers.zhb.domain.Student"> </bean> </beans>
以上的配置文件的作用是将Student对象交给Spring容器管理:
bean:配置需要创建的对象
name:用于以后从后spring容器中获得实例时使用
class:需要创建实例类的全限定名
(5)测试:
创建测试类:
public class Test {
public void test1(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//创建容器对象
Student student=(Student)applicationContext.getBean("student");
student.setSname("zhai");
student.setSnum("202012");
student.setSex("nv");
System.out.println(student);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Test test=new Test();
test.test1();
}
}
创建Spring的容器对象后将Student对象从容器中取出,通过set方法对对象进行赋值,打印结果如下:

4、spring与传统方式创建对象的对比
(1)spring方式:
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");//创建容器对象 Student student=(Student)applicationContext.getBean("student");
直接从容器中获取即可。
(2)传统方式:
Student student=new Student(); student.setSname("zhang"); student.setSnum("202019"); student.setSex("nan"); System.out.println(student);
标签:code end bsp xsd comm spring容器 setting 设计模式 位置
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhai1997/p/12590957.html