标签:行数据 场景 throws 意思 readline 就是 iter 有一个 循环
假如有一个二维数组,里面只存了少数的值,然后我们需要将这个数组持久化到磁盘文件,在此之前请先想想,既然只存了少数的值,那么代表着这个二维数组的大部分位置都是没有值的,那么没有值的这些位置都是无意义的,我们不必要将这些没有值的位置都存储到磁盘中,那么这个时候为了解决类似这种问题,稀疏数组诞生了!
先来给刚才的二维数组画一个图:
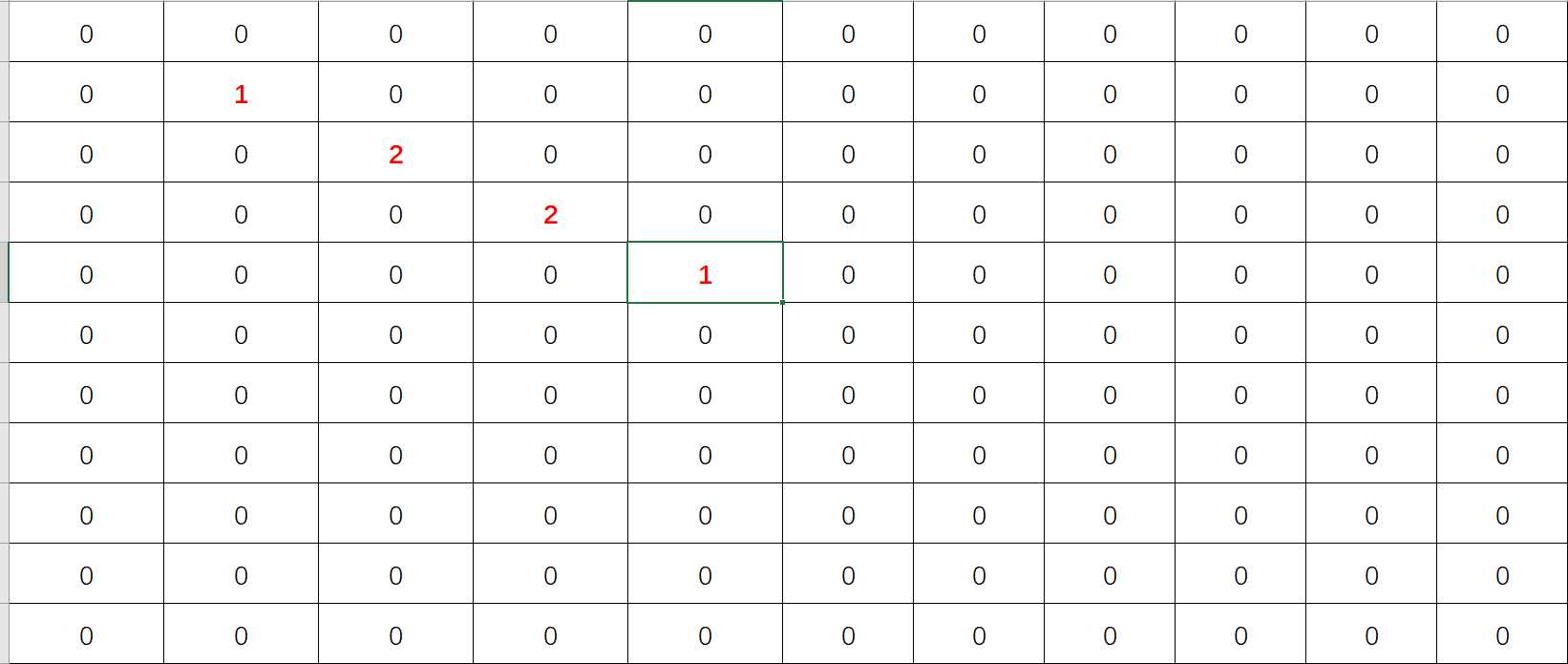
假设这我们需要保存到磁盘的那个二维数组,用Java代码表示为:int [][] = new int[11][11];
我们对这个二维数组认为,只要不为0的值就是有意义的值。
现在这个二维数组中有值的数据用红色标注了出来,现在我们需要将这么一个二维数组存储到磁盘文件中,但是这个二维数组中有太多的空值,存储到磁盘的时候会浪费一些空间,那么这个时候就可以应用稀疏数组。
根据刚才的二维数组图,我们应用稀疏数组后,稀疏数组的图为:
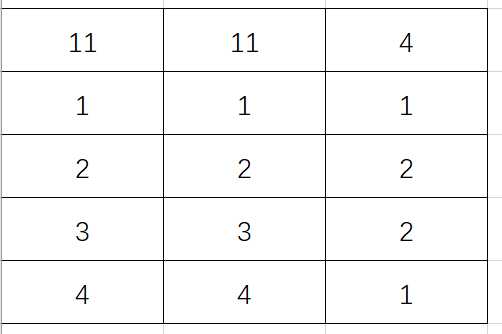
这个稀疏数组在Java代码中表示为:int [][] = new int[5][3];
解释一下这个稀疏数组立面值的意思:
稀疏数组中第一行数据意义为:原二维数组的行,原二维数组的列,原二维数组中共有多少有意义的值
其余行数据意义为:原二维数组中数据有意义的行、列、值,需要注意的是存储的行、列都是下标
利用这种方式将原二维数组转换为一个稀疏数组,然后再将稀疏数组存入到磁盘,需要读取时,读取到稀疏数组,然后再转换为二维数组。
如将原二维数组直接存入到磁盘,则为11*11,现转换为稀疏数组只需要5*3,所以稀疏数组在这种场景下还是有很大的用处的。
1 /** 2 * @author 自在仙 3 * @create 2020年04月12 20:15 4 */ 5 public class Test { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 8 /*创建一个二维数组*/ 9 int[][] chess1 = new int[11][11]; 10 chess1[1][2] = 1; 11 chess1[2][3] = 2; 12 /*展示一下原来的二维数组*/ 13 show(chess1); 14 15 /*因为稀疏数组的总行数取决于原二维数组有有意义的值+1,所以我们要先计算出原二维数组中有多少个有意义的值*/ 16 /*获得稀疏数组的总有效数据个数*/ 17 int sum = 0; 18 /*循环遍历原二维数组,计算总有意义值的个数*/ 19 for (int[] ints : chess1) { 20 for (int anInt : ints) { 21 /*如果不等于0,那么我们认为其有意义*/ 22 if (anInt != 0) { 23 sum++; 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 28 /* 29 * 创建我们的稀疏数组, 30 * 第一个大小为sum+1,为什么要+1,因为第一行记录的是原二维数组的行和列,所以需要多占一行 31 * 第二个大小固定为3,因为我们存储的是行、列、值,所以固定的是三个 32 * */ 33 int[][] sparse = new int[sum + 1][3]; 34 35 /*第一列存储的是原二维数组的长度和有效值数量*/ 36 /*原二维数组行*/ 37 sparse[0][0] = chess1.length; 38 /*原二维数组列*/ 39 sparse[0][1] = chess1[0].length; 40 /*共有多少个值*/ 41 sparse[0][2] = sum; 42 43 /*遍历原二维数组,将其有意义的数据存放至稀疏数组中去*/ 44 int sparseIndex = 1; 45 for (int i = 0; i < chess1.length; i++) { 46 for (int j = 0; j < chess1[i].length; j++) { 47 /*如果不为0则是有意义的,存放*/ 48 if (chess1[i][j] != 0) { 49 sparse[sparseIndex][0] = i; 50 sparse[sparseIndex][1] = j; 51 sparse[sparseIndex][2] = chess1[i][j]; 52 53 sparseIndex++; 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 System.out.println("----------------"); 58 /*二维数组到稀疏数组存放完了,展示一下*/ 59 show(sparse); 60 /*稀疏数组就转圜完了*/ 61 62 63 /*------------------------------然后再由稀疏数组转换为二维数组-------------------------------------*/ 64 /*创建二维数组,行和列都是存储在稀疏数组的第一行中*/ 65 int[][] chess2 = new int[sparse[0][0]][sparse[0][1]]; 66 /*然后将稀疏数组中其他数据填充到二维数组中*/ 67 for (int i = 1; i < sparse.length; i++) { 68 /*稀疏数组第一个元素是行,第二个是列,第三个是实际的值*/ 69 chess2[sparse[i][0]][sparse[i][1]] = sparse[i][2]; 70 } 71 /*这样就把稀疏数组转换回了二维数组*/ 72 System.out.println("-------------------------------"); 73 /*转换回二维数组后再展示一下*/ 74 show(chess2); 75 } 76 77 78 /*打印数组的方法*/ 79 public static void show(int[][] array) { 80 for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { 81 for (int j = 0; j < array[i].length; j++) { 82 System.out.print(array[i][j] + "\t"); 83 } 84 System.out.println(); 85 } 86 } 87 }
只要能写出上面的简单使用,这个存文件读取就没问题的
1 /** 2 * @author 自在仙 3 * @create 2020年04月12 22:07 4 */ 5 public class Test2 { 6 7 /* 8 * 练习: 9 * 将二维数组转换为稀疏数组,然后存入文件,然后再读取为稀疏数组,然后再转换为二维数组 10 * */ 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 13 /*原二维数组*/ 14 int[][] chess = new int[12][12]; 15 chess[1][2] = 2; 16 chess[2][3] = 1; 17 chess[3][4] = 2; 18 19 System.out.println("----------原数组---------"); 20 showArray(chess); 21 22 /*转换为稀疏数组*/ 23 /*先拿到原数组的总有效值数量*/ 24 int sum = 0; 25 for (int[] ints : chess) { 26 for (int anInt : ints) { 27 if (anInt != 0) { 28 sum++; 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 /*得到一个稀疏数组,然后将原数组中的内容转到稀疏数组中*/ 33 int[][] sparse = new int[sum + 1][3]; 34 sparse[0][0] = chess.length; 35 sparse[0][1] = chess[0].length; 36 sparse[0][2] = sum; 37 int sparseIndex = 1; 38 for (int i = 0; i < chess.length; i++) { 39 for (int i1 = 0; i1 < chess[i].length; i1++) { 40 if (chess[i][i1] != 0) { 41 /*第一个存原二维数组的行。*/ 42 sparse[sparseIndex][0] = i; 43 /*第二个存原二维数组的列*/ 44 sparse[sparseIndex][1] = i1; 45 /*第三个存实际的值*/ 46 sparse[sparseIndex][2] = chess[i][i1]; 47 sparseIndex++; 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 System.out.println("----------稀疏数组---------"); 52 showArray(sparse); 53 54 /*----------------------开始存入文件--------------------------*/ 55 /*获得文件地址*/ 56 String test2TextPath = Test2.class.getClassLoader().getResource("test2.txt").getPath(); 57 File file = new File(test2TextPath); 58 if (!file.exists()) { 59 file.createNewFile(); 60 } 61 /*获得输出流写文件*/ 62 BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file)); 63 for (int[] ints : sparse) { 64 /* 65 * 写入格式为 66 * 11 11 5 67 * 1 1 2 68 * 每行的元素之间间隔一个空格,行与行之间换行 69 * */ 70 bufferedWriter.write(ints[0] + " " + ints[1] + " " + ints[2]); 71 bufferedWriter.newLine(); 72 bufferedWriter.flush(); 73 } 74 bufferedWriter.close(); 75 System.out.println("稀疏数组已经存入文件:" + file.getAbsolutePath()); 76 /*------------------------开始文件中读取稀疏数组--------------------------*/ 77 /*读取稀疏数组文件到数组中*/ 78 BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); 79 String readDataTemp = null; 80 /*记录总行数,方便创建稀疏数组*/ 81 int indexTemp = 0; 82 while ((readDataTemp = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) { 83 indexTemp++; 84 } 85 /*读取完一次后,关闭,重新读取文件*/ 86 bufferedReader.close(); 87 /*重新赋值读取文件*/ 88 bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); 89 /*根据上方获得的总记录数,创建稀疏数组*/ 90 int[][] sparse2 = new int[indexTemp][3]; 91 /*记录每次添加的索引*/ 92 indexTemp = 0; 93 /*读取到数据后填充到稀疏数组中*/ 94 while ((readDataTemp = bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) { 95 System.out.println("readDataTemp:" + readDataTemp); 96 /*每一行的数据都进行拆分,*/ 97 String[] s = readDataTemp.split(" "); 98 /*分别填充到三列中*/ 99 sparse2[indexTemp][0] = Integer.valueOf(s[0]); 100 sparse2[indexTemp][1] = Integer.valueOf(s[1]); 101 sparse2[indexTemp][2] = Integer.valueOf(s[2]); 102 indexTemp++; 103 } 104 System.out.println("----------读取文件中的稀疏数组---------"); 105 showArray(sparse2); 106 107 /*------------------------将读取到的稀疏数组转换为二维数组----------------------------*/ 108 /*将读取到的稀疏数组转换为二维数组*/ 109 int[][] chess2 = new int[sparse2[0][0]][sparse2[0][1]]; 110 for (int i = 1; i < sparse2.length; i++) { 111 chess2[sparse2[i][0]][sparse2[i][1]] = sparse2[i][2]; 112 } 113 System.out.println("----------转换为二维数组---------"); 114 showArray(chess2); 115 } 116 117 /*打印数组的方法*/ 118 public static void showArray(int[][] array) { 119 for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { 120 for (int j = 0; j < array[i].length; j++) { 121 System.out.print(array[i][j] + " "); 122 } 123 System.out.println(); 124 } 125 } 126 }
标签:行数据 场景 throws 意思 readline 就是 iter 有一个 循环
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/daihang2366/p/12688796.html