标签:ble 运算符优先级 case too 简易 panel public 简易计算器 优先级
本文记录了笔者的第一个Java程序,基于Java抽象窗口工具(abstract window toolkit , AWT)和Swing(Swing属于Java Foundation Classes的一部分)实现的建议计算器,由于笔者经验有限,初学Java,代码略带bug,无法实现7+5×8之类式子的计算,只能实现算术运算符按从高到低的式子运算,部分代码略显冗杂,希望大家在评论区积极讨论完善代码!
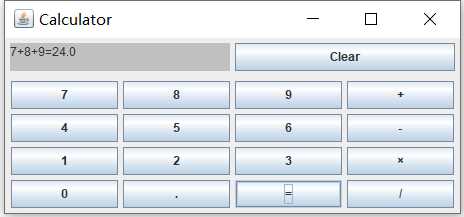
计算器示意图
一、代码相关知识简介
JFrame(框架)
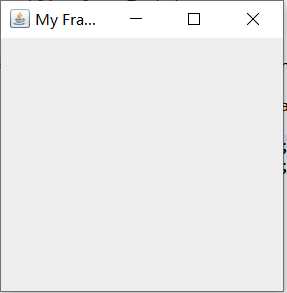
使用JFrame frame = new JFrame("My Frame");可以创建一个名为My Frame的windows框架
import javax.swing.*; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub JFrame frame = new JFrame("My Frame"); frame.setSize(300,300); frame.setVisible(true); } }
JButton(按钮)
使用JButton b = new JButtton("My Button");可创建一个按钮组件。
import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class Test { JFrame frame; public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub JFrame frame = new JFrame("My Frame"); JButton b = new JButton("My Button"); frame.getContentPane().add(b,BorderLayout.CENTER); //将按钮放在frame框架中央 frame.setSize(300,300); frame.setVisible(true); } }
JPanel(面板)
面板是一个容器,与顶层容器不同,JPanel不能独立存在,必须放在其他容器的内部,下面代码创建了含有一个按钮的红色面板。
import java.awt.*; import javax.swing.*; public class Test { JFrame frame; public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub JFrame frame = new JFrame("My Frame"); JButton b = new JButton("My Button"); JPanel panel = new JPanel(); panel.add(b); panel.setBackground(Color.red); frame.getContentPane().add(panel,BorderLayout.SOUTH); //将面板放在frame框架南方 frame.setSize(300,300); frame.setVisible(true); } }
JTextArea(文本输入框)
使用 JTextArea 类可实现一个文本域,其常用构造方法如下。
①JTextArea():创建一个默认的文本域。
②JTextArea(int rows,int columns):创建一个具有指定行数和列数的文本域。
③JTextArea(String text):创建一个包含指定文本的文本域。
④JTextArea(String text,int rows,int columns):创建一个既包含指定文本,又包含指定行数和列数的多行文本域。
出相关组件介绍外与实现计算器还需对布局有简单了解,本文仅使用GridLayout布局管理器,因此只对此做出介绍,若读者需要还可自行理解其他布局管理器。
GridLayout是一种网络式的布局管理器,将容器空间化为几行几列的形式网格,可将每个组件放在其中一格。
GridLayout定义在java.awt包中,有如下三种构造方法 public GridLayout() public GridLayout(int rows , int cols) //定义的布局有rows行cools列 public GridLayout(int rows , int cols,int h , int w) ////定义的布局有rows行cools列,水平间距为h,垂直间距为w
二、计算器功能,可实现加、减、乘、除功能,但由于笔者目前能力有限,若使用加、减、乘、除混合功能时需按运算符优先级,从高到小输入式子如7×8+5而不能按5+7×8输入,源代码如下:
import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; public class Calculator implements ActionListener{ JFrame frame; JButton b1,b2,b3,b4,b5,b6,b7,b8,b9,ba,bd,be,bf,bg,bh,b0,Clear; JTextArea ta; String Textcontent ="",sum=""; double result=0; public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Calculator cl = new Calculator(); cl.go(); } public void go() { frame = new JFrame("Calculator"); ta = new JTextArea(1,20); //设置文本框大小为1行20列 ta.setBackground(Color.lightGray); JPanel cp = new JPanel(); cp.setLayout(new GridLayout(4,4,5,5)); //四行四列,边距为5 JPanel c = new JPanel(); c.setLayout(new GridLayout(1,2,5,5)); //一行两列,边距为5 b0 = new JButton("0"); b0.addActionListener(this); //为每个按钮添加监听接口 b1 = new JButton("1"); b1.addActionListener(this); b2 = new JButton("2"); b2.addActionListener(this); b3 = new JButton("3"); b3.addActionListener(this); b4 = new JButton("4"); b4.addActionListener(this); b5 = new JButton("5"); b5.addActionListener(this); b6 = new JButton("6"); b6.addActionListener(this); b7 = new JButton("7"); b7.addActionListener(this); b8 = new JButton("8"); b8.addActionListener(this); b9 = new JButton("9"); b9.addActionListener(this); ba = new JButton("."); ba.addActionListener(this); bd = new JButton("+"); bd.addActionListener(this); be = new JButton("-"); be.addActionListener(this); bf = new JButton("×"); bf.addActionListener(this); bg = new JButton("/"); bg.addActionListener(this); bh = new JButton("="); bh.addActionListener(this); Clear= new JButton("Clear"); Clear.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){ public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { Textcontent =""; result=0; sum=""; ta.setText(""); } }); c.add(ta); c.add(Clear); c.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(5, 5, 5, 5)); cp.add(b7); cp.add(b8); cp.add(b9); cp.add(bd); cp.add(b4); cp.add(b5); cp.add(b6); cp.add(be); cp.add(b1); cp.add(b2); cp.add(b3); cp.add(bf); cp.add(b0); cp.add(ba); cp.add(bh); cp.add(bg); cp.setBorder(BorderFactory.createEmptyBorder(5, 5, 5, 5)); Container f = frame.getContentPane(); f.add(c,BorderLayout.NORTH); f.add(cp,BorderLayout.SOUTH); frame.pack(); frame.setVisible(true); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { String content = e.getActionCommand(); ta.append(e.getActionCommand()); getTextContent(content); } public void getTextContent(String content) { if(content.equals("+")||content.equals("-")||content.equals("×")||content.equals("/")) { Textcontent = Textcontent+" "+content+" "; } else if(content.equals("=")) { Textcontent = Textcontent+" "+content; sum=GetResult(Textcontent); } else { Textcontent = Textcontent+content; } ta.append(sum); } public String GetResult(String Textcontent) { String n=Textcontent; String []content=n.split(" "); result = Double.valueOf(content[0]); for(int i=1;i<content.length;i++) { switch(content[i]) { case "+": result = result+Double.valueOf(content[i+1]); break; case "-": result = result-Double.valueOf(content[i+1]); break; case "×": result = result*Double.valueOf(content[i+1]); break; case "/": result = result/Double.valueOf(content[i+1]); break; case "=": break; } } return result+""; } }
标签:ble 运算符优先级 case too 简易 panel public 简易计算器 优先级
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/24Zeng/p/12708151.html