标签:ons 位置 方法 规则 很多 new 分析 opera 最小
哈夫曼编码是一种贪心算法和二叉树结合的字符编码方式,具有广泛的应用背景,最直观的是文件压缩。本文主要讲述如何用哈夫曼编解码实现文件的压缩和解压,并给出代码实现。
哈夫曼树又称作最优树,是一种带权路径长度最短的树,而通过哈夫曼树构造出的编码方式称作哈夫曼编码。
也就是说哈夫曼编码是一个通过哈夫曼树进行的一种编码,一般情况下,以字符 “0” 与 “1” 表示。编码的实现过程很简单,只要实现哈夫曼树,通过遍历哈夫曼树,这里我们从根节点开始向下遍历,如果
下个节点是左孩子,则在字符串后面追加 “0”,如果为其右孩子,则在字符串后追加 “1”。结束条件为当前节点为叶子节点,得到的字符串就是叶子节点对应的字符的编码。
根据贪心算法的思想实现,把字符出现频率较多的字符用稍微短一点的编码,而出现频率较少的字符用稍微长一点的编码。哈夫曼树就是按照这种思想实现,下面将举例分析创建哈夫曼树的具体过程。
下面表格的每一行分别对应字符及出现频率,根据这些信息就能创建一棵哈夫曼树。
| 字符 | 出现频率 | 编码 | 总二进制位数 |
| a | 500 | 1 | 500 |
| b | 250 | 01 | 500 |
| c | 120 | 001 | 360 |
| d | 60 | 0001 | 240 |
| e | 30 | 00001 | 150 |
| f | 20 | 00000 | 100 |
如下图,将每个字符看作一个节点,将带有频率的字符全部放到优先队列中,每次从队列中取频率最小的两个节点 a 和 b(这里频率最小的 a 作为左子树),然后新建一个节点R,把节点设置为两个节点
的频率之和,然后把这个新节点R作为节点A和B的父亲节点。最后再把R放到优先队列中。重复这个过程,直到队列中只有一个元素,即为哈夫曼树的根节点。
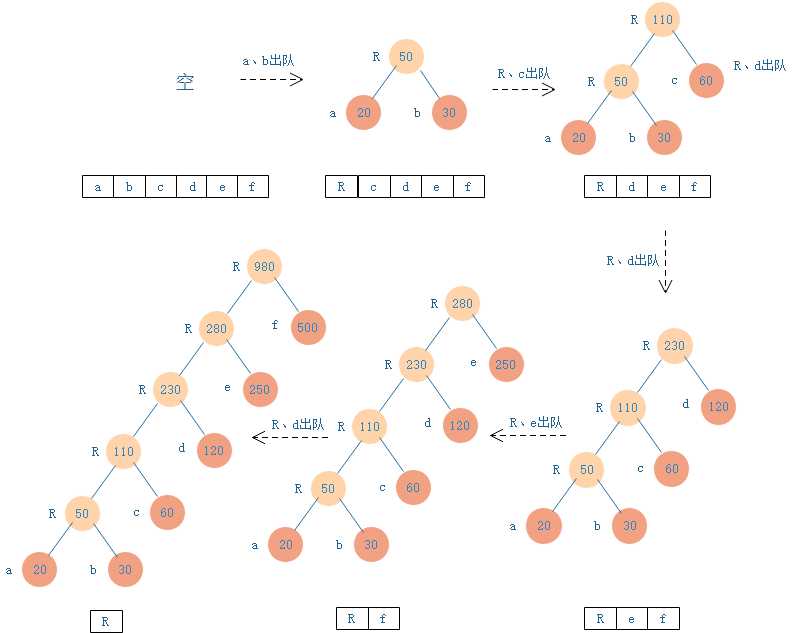
由上分析可得,哈夫曼编码的需要的总二进制位数为 500 + 500 + 360 + 240 + 150 + 100 = 1850。上面的例子如果用等长的编码对字符进行压缩,实现起来更简单,6 个字符必须要 3 位二进制位表示,
解压缩的时候每次从文本中读取 3 位二进制码就能翻译成对应的字符,如 000,001,010,011,100,101 分别表示 a,b,c,d,e,f。则需要总的二进制位数为 (500 + 250 + 120 + 60 + 30 + 20)*
3 = 2940。对比非常明显哈夫曼编码需要的总二进制位数比等长编码需要的要少很很多,这里的压缩率为 1850 / 2940 = 62%。哈夫曼编码的压缩率通常在 20% ~90% 之间。
下面代码是借助标准库的优先队列 std::priority_queque 实现哈夫曼树的代码简单实现,构造函数需要接受 afMap 入参,huffmanCode 函数是对象的唯一对外方法,哈夫曼编码的结果会写在 codeMap 里
面。这部分是创建哈夫曼树的核心代码,为方便调试,我还实现了打印二叉树树形结构的功能,这里就补贴代码,有兴趣的同学可以到文末给出的 github 仓库中下载。
1 using uchar = unsigned char;
2
3 struct Node {
4 uchar c;
5 int freq;
6 Node *left;
7 Node *right;
8 Node(uchar _c, int f, Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr)
9 : c(_c), freq(f), left(l), right(r) {}
10 bool operator<(const Node &node) const { //重载,优先队列的底层数据结构std::heap是最大堆
11 return freq > node.freq;
12 }
13 };
14
15 class huffTree {
16 public:
17 huffTree(const std::map<uchar, int>& afMap) {
18 for (auto i : afMap) {
19 Node n(i.first, i.second);
20 q.push(n);
21 }
22 _makehuffTree();
23 }
24 ~huffTree() {
25 Node node = q.top();
26 _deleteTree(node.left);
27 _deleteTree(node.right);
28 }
29 void huffmanCode(std::map<uchar, std::string>& codeMap) {
30 Node node = q.top();
31 std::string prefix;
32 _huffmanCode(&node, prefix, codeMap);
33 }
34 private:
35 static bool _isLeaf(Node* n) {
36 return n->left == nullptr && n->right == nullptr;
37 }
38 void _deleteTree(Node* n) {
39 if (!n) return ;
40 _deleteTree(n->left);
41 _deleteTree(n->right);
42 delete n;
43 }
44 void _makehuffTree() {
45 while (q.size() != 1) {
46 Node *left = new Node(q.top()); q.pop();
47 Node *right = new Node(q.top()); q.pop();
48 Node node(‘R‘, left->freq + right->freq, left, right);
49 q.push(node);
50 }
51 }
52 void _huffmanCode(Node *root, std::string& prefix,
53 std::map<uchar, std::string>& codeMap) {
54 std::string tmp = prefix;
55 if (root->left != nullptr) {
56 prefix += ‘0‘;
57 if (_isLeaf(root->left)) {
58 codeMap[root->left->c] = prefix;
59 } else {
60 _huffmanCode(root->left, prefix, codeMap);
61 }
62 }
63 if (root->right != nullptr) {
64 prefix = tmp;
65 prefix += ‘1‘;
66 if (_isLeaf(root->right)) {
67 codeMap[root->right->c] = prefix;
68 } else {
69 _huffmanCode(root->right, prefix, codeMap);
70 }
71 }
72 }
73 private:
74 std::priority_queue<Node> q;
75 };
首先需要给出文件压缩和下面将要提到的文件解压缩的公共头文件,如下:
1 //得到index位的值,若index位为0,则GET_BYTE值为假,否则为真
2 #define GET_BYTE(vbyte, index) (((vbyte) & (1 << ((index) ^ 7))) != 0)
3 //index位置1
4 #define SET_BYTE(vbyte, index) ((vbyte) |= (1 << ((index) ^ 7)))
5 //index位置0
6 #define CLR_BYTE(vbyte, index) ((vbyte) &= (~(1 << ((index) ^ 7))))
7
8 using uchar = unsigned char;
9
10 struct fileHead {
11 char flag[4]; //压缩二进制文件头部标志 ycy
12 uchar alphaVariety; //字符种类
13 uchar lastValidBit; //最后一个字节的有效位数
14 char unused[10]; //待用空间
15 }; //这个结构体总共占用16个字节的空间
16
17 struct alphaFreq {
18 uchar alpha; //字符,考虑到文件中有汉字,所以定义成uchar
19 int freq; //字符出现的频度
20 alphaFreq() {}
21 alphaFreq(const std::pair<char, int>& x)
22 : alpha(x.first), freq(x.second) {}
23 };
下面是文件压缩的代码具体实现。过程其实相对简单,理解起来不难。首先需要读取文件信息,统计每一个字符出现的次数,这里实现是从 std::map 容器以字符为 key 累加统计字符出现的次数。然后,
用统计的结果 _afMap 创建哈夫曼树,得到相应的每个字符的哈夫曼编码 _codeMap。最后,就是将数据写入压缩文件,该过程需要先写入文件头部信息, 即结构体 fileHead 的内容,这部分解压缩的时
候进行格式校验等需要用到。接着将 _afMap 的字符及频率数据依次写入文件中,这部分是解压缩时重新创建哈夫曼树用来译码。到这一步就依次读取源文件的每一个字符,将其对应的哈夫曼编码写进
文件中去。至此压缩文件的过程结束。下面的代码不是很难,我就不加注释了。
1 class huffEncode {
2 public:
3 bool encode(const char* srcFilename, const char* destFilename) {
4 if (!_getAlphaFreq(srcFilename)) return false;
5 huffTree htree(_afMap);
6 htree.huffmanCode(_codeMap);
7 return _encode(srcFilename, destFilename);
8 }
9 private:
10 int _getLastValidBit() {
11 int sum = 0;
12 for (auto it : _codeMap) {
13 sum += it.second.size() * _afMap.at(it.first);
14 sum &= 0xFF;
15 }
16 sum &= 0x7;
17 return sum == 0 ? 8 : sum;
18 }
19 bool _getAlphaFreq(const char* filename) {
20 uchar ch;
21 std::ifstream is(filename, std::ios::binary);
22 if (!is.is_open()) {
23 printf("read file failed! filename: %s", filename);
24 return false;
25 }
26 is.read((char*)&ch, sizeof(uchar));
27 while (!is.eof()) {
28 _afMap[ch]++;
29 is.read((char*)&ch, sizeof(uchar));
30 }
31 is.close();
32 return true;
33 }
34 bool _encode(const char* srcFilename, const char* destFilename) {
35 uchar ch;
36 uchar value;
37 int bitIndex = 0;
38 fileHead filehead = {‘e‘, ‘v‘, ‘e‘, ‘n‘};
39 filehead.alphaVariety = (uchar) _afMap.size();
40 filehead.lastValidBit = _getLastValidBit();
41
42 std::ifstream is(srcFilename, std::ios::binary);
43 if (!is.is_open()) {
44 printf("read file failed! filename: %s", srcFilename);
45 return false;
46 }
47 std::ofstream io(destFilename, std::ios::binary);
48 if (!io.is_open()) {
49 printf("read file failed! filename: %s", destFilename);
50 return false;
51 }
52
53 io.write((char*)&filehead, sizeof(fileHead));
54 for (auto i : _afMap) {
55 alphaFreq af(i);
56 io.write((char*)&af, sizeof(alphaFreq));
57 }
58
59 is.read((char*)&ch, sizeof(uchar));
60 while (!is.eof()) {
61 std::string code = _codeMap.at(ch);
62 for (auto c : code) {
63 if (‘0‘ == c) {
64 CLR_BYTE(value, bitIndex);
65 } else {
66 SET_BYTE(value, bitIndex);
67 }
68 ++bitIndex;
69 if (bitIndex >= 8) {
70 bitIndex = 0;
71 io.write((char*)&value, sizeof(uchar));
72 }
73 }
74 is.read((char*)&ch, sizeof(uchar));
75 }
76
77 if (bitIndex) {
78 io.write((char*)&value, sizeof(uchar));
79 }
80 is.close();
81 io.close();
82 return true;
83 }
84 private:
85 std::map<uchar, int> _afMap;
86 std::map<uchar, std::string> _codeMap;
87 };
文件解压缩其实就是哈夫曼编码的译码过程,处理过程相对于压缩过程来说相对复杂一点,但其实就是将文件编码按照哈夫曼编码的既定规则翻译出原来对应的字符,并将字符写到文件中的过程。较为
详细的过程是先读取文件头部信息,校验文件格式是否是上面压缩文件的格式(这里是flag的四个字符为even),不是则返回错误。然后根据头部信息字符种类 alphaVariety(即字符的个数)依次读取字
符及其频率,并将读取的内容放到 _afMap 中,然后创建哈夫曼树,得到相应的每个字符的哈夫曼编码 _codeMap,并遍历 _codeMap 创建以字符编码为 key 的译码器 _decodeMap,主要方便是后面译码
的时候根据编码获取其对应的字符。然后读取压缩文件剩余的内容,每次读取一个字节即 8 个二进制位,获取哈夫曼树根节点,用一个树节点指针pNode指向根节点,然后逐个读取二进制,每次根据二
进制位的值,当值为 0 指针走左子树,当值为 1 指针走右子树,并将值添加到 std::string 类型的字符串 code 后面,直到走到叶子结点位置为止。用 code 作为 key 可在译码器 _decodeMap 中取得对应
的字符,将字符写到新文件中去。然后清空 code,pNode重新指向根节点,继续走上面的流程,直到读完文件内容。文件最后一个字节的处理和描述有点不一样,需根据文件头信息的最后一位有效
位 lastValidBit 进行特殊处理,这里特别提醒一下。
1 class huffDecode {
2 public:
3 huffDecode() : _fileHead(nullptr), _htree(nullptr) {
4 _fileHead = new fileHead();
5 }
6 ~huffDecode() {
7 if (!_fileHead) delete _fileHead;
8 if (!_htree) delete _htree;
9 }
10 private:
11 static bool _isLeaf(Node* n) {
12 return n->left == nullptr && n->right == nullptr;
13 }
14 long _getFileSize(const char* strFileName) {
15 std::ifstream in(strFileName);
16 if (!in.is_open()) return 0;
17
18 in.seekg(0, std::ios_base::end);
19 std::streampos sp = in.tellg();
20 in.close();
21 return sp;
22 }
23 bool _getAlphaFreq(const char* filename) {
24 std::ifstream is(filename, std::ios::binary);
25 if (!is) {
26 printf("read file failed! filename: %s", filename);
27 return false;
28 }
29
30 is.read((char*)_fileHead, sizeof(fileHead));
31 if (!(_fileHead->flag[0] == ‘e‘ &&
32 _fileHead->flag[1] == ‘v‘ &&
33 _fileHead->flag[2] == ‘e‘ &&
34 _fileHead->flag[3] == ‘n‘)) {
35 printf("not support this file format! filename: %s\n", filename);
36 return false;
37 }
38 for (int i = 0; i < static_cast<int>(_fileHead->alphaVariety); ++i) {
39 alphaFreq af;
40 is.read((char*)&af, sizeof(af));
41 _afMap.insert(std::pair<char, int>(af.alpha, af.freq));
42 }
43 is.close();
44 return true;
45 }
46 bool _decode(const char* srcFilename,
47 const char* destFilename) {
48 long fileSize = _getFileSize(srcFilename);
49
50 std::ifstream is(srcFilename, std::ios::binary);
51 if (!is) {
52 printf("read file failed! filename: %s", srcFilename);
53 return false;
54 }
55 is.seekg(sizeof(fileHead) + sizeof(alphaFreq) * _fileHead->alphaVariety);
56
57 Node node = _htree->getHuffTree();
58 Node* pNode = &node;
59
60 std::ofstream io(destFilename, std::ios::binary);
61 if (!io) {
62 printf("create file failed! filename: %s", destFilename);
63 return false;
64 }
65
66 uchar value;
67 std::string code;
68 int index = 0;
69 long curLocation = is.tellg();
70 is.read((char*)&value, sizeof(uchar));
71 while (1) {
72 if (_isLeaf(pNode)) {
73 uchar alpha = _decodeMap[code];
74 io.write((char*)&alpha, sizeof(uchar));
75 if (curLocation >= fileSize && index >= _fileHead->lastValidBit) {
76 break;
77 }
78 code.clear();
79 pNode = &node;
80 }
81
82 if (GET_BYTE(value, index)) {
83 code += ‘1‘;
84 pNode = pNode->right;
85 } else {
86 pNode = pNode->left;
87 code += ‘0‘;
88 }
89 if (++index >= 8) {
90 index = 0;
91 is.read((char*)&value, sizeof(uchar));
92 curLocation = is.tellg();
93 }
94 }
95
96 is.close();
97 io.close();
98 return true;
99 }
100 public:
101 bool decode(const char* srcFilename, const char* destFilename) {
102 if (!_getAlphaFreq(srcFilename)) return false;
103 long fileSize = _getFileSize(srcFilename);
104 _htree = new huffTree(_afMap);
105 _htree->watch();
106 _htree->huffmanCode(_codeMap);
107
108 for (auto it : _codeMap) {
109 _decodeMap.insert(std::pair<std::string, uchar>(it.second, it.first));
110 }
111
112 return _decode(srcFilename, destFilename);
113 }
114 private:
115 fileHead *_fileHead;
116 huffTree *_htree;
117 std::map<uchar, int> _afMap;
118 std::map<uchar, std::string> _codeMap;
119 std::map<std::string, uchar> _decodeMap;
120 };
标签:ons 位置 方法 规则 很多 new 分析 opera 最小
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ybqjymy/p/12720035.html