标签:方案 元素 efi ++ names for ring put ref
先上题目,
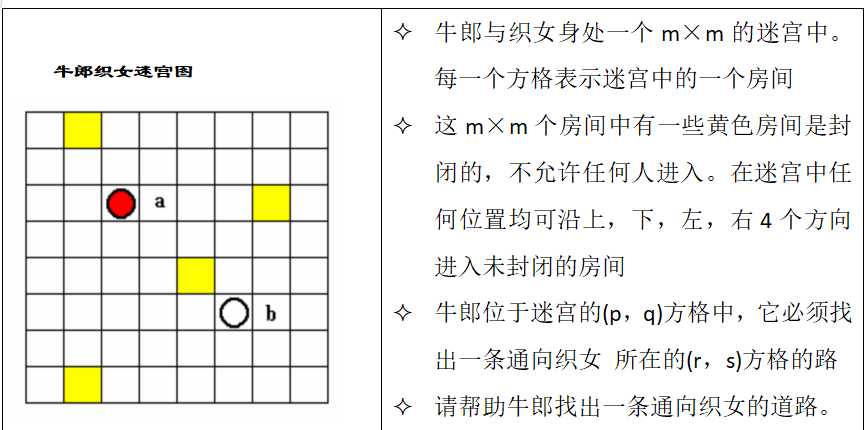

这个题...我用C++写了200+行的代码,不包括数据纠错(比如输入点超过了迷宫的限制,或者输入数据时输入的不是整数)
所以记录一下。
C++ vector自带的方法比较少,而且感觉不是很好用,几乎所有用到的方法都是重新写的。
我的思路是,已知牛郎的坐标(x1,y1) 然后织女的坐标(x2,y2)
那么无论牛郎怎么走,一定要走m=|x1-x2|个横坐标,n=|y1-y2|个纵坐标(先不考虑封闭房间)
并且路线一定是C(m+n,n)条(排列组合)。
我使用0 表示牛郎在x轴上走了一步,用1 表示牛郎在y轴上走了一步。
这样就能表示一条路径,比如牛郎在上图中的a点,织女在b点,那么 000111 就表示牛郎先向右走了3步,然后向下走了3步
当我们知道了两人的坐标后,也就知道了0的个数和1的个数,以上图为例,我们要求的路径就是 000111 这六个数字的无重复全排列。
这样我们就知道了所有牛郎走向织女的可能路径。接下来就要排除被封闭房间所挡住的路径。
以同样的方法,我们求出所有 牛郎通向封闭房间(在牛郎和织女之间的封闭房间)的路径,然后再删除 牛郎通向织女路径中 前部分与之重合的路径。
以上图为例,我们找到了一条通向封闭房间的路径,0011,接下来删除所有以 0011 开头的 牛郎通向织女的路径,然后重复这一过程,直至所有经过该封闭房间的路径都被删除,
再以同样的方法检索剩余的封闭房间。
最终剩下的,就是所有不经过封闭房间的 牛郎通向织女的路径。
另,在求全排列这个地方卡住了好久,最终找到一种巧妙的算法并改了改。
大概就是,先排出最小的路径,比如000111,然后从该数串的最后开始 ,选取两个数字进行比较,直到找到前一个数字比后一个数字小,在目前这个只有0 和1模型中就是找到“01”,
然后将左边这个0与最靠后的1进行交换,比如001110,然后把原来0位置后面的所有元素翻转,最终变成001011。这就是仅大于000111的排列,按照上述方法不断重复,最终就能按照从小到大的顺序找全所有的 排列。
我可能说的不太明白。我参考的是https://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/7370155中的非递归全排列方法。
贴上代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<vector> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 int min(int a, int b) { 7 if (a < b) 8 return a; 9 else 10 return b; 11 } 12 13 int max(int a, int b) { 14 if (a > b) 15 return a; 16 else 17 return b; 18 } 19 20 void Swap(int* a, int* b) { 21 int temp; 22 temp = *a; 23 *a = *b; 24 *b = temp; 25 } 26 27 void deleteVector(vector<vector<int>>& v, int i) { 28 //删除v中第i条路径 29 vector<int>* x, * y, temp; 30 x = &v[i]; 31 y = x + 1; 32 for (int n = 0; n < v.size() - i - 1; n++) { 33 temp = *x; 34 *x = *y; 35 *y = temp; 36 x++; y++; 37 } 38 v.pop_back(); 39 40 } 41 42 void showVector(vector<int>v) { 43 //打印一条路径 44 for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) { 45 cout << v[i] << ","; 46 } 47 cout << endl; 48 } 49 50 void showVector(vector<vector<int>> v) { 51 //打印所有路径 52 for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) { 53 cout << "第 " << i + 1 << "条路线:"; 54 for (int j = 0; j < v[0].size(); j++) { 55 cout << v[i][j] << ","; 56 } 57 cout << endl; 58 } 59 } 60 61 void TurnLanguage(vector<vector<int>> v,string x,string y) { 62 //转换成自然语言的路径 63 for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) { 64 cout << "第" << i + 1 << "条路线为: 从起始点开始-"; 65 for (int j = 0; j < v[0].size(); j++) { 66 if(v[i][j]==0) 67 cout << x << "-"; 68 else 69 cout << y << "-"; 70 } 71 cout << endl; 72 } 73 } 74 75 void reverseVector(int* a, int* b) { 76 //翻转 vector,vector自带的reverse老报错,没看出所以然来,所以重新写了个 77 while (a < b) { 78 Swap(a++, b--); 79 } 80 } 81 82 void all_path(vector<int> first_path, vector<vector<int>>& allthepath) { 83 //通过第一条路径 推算出所有路径 84 bool hasnext = true; 85 int* p, *q,*m,*the_end,counter=1; 86 the_end = &first_path[first_path.size() - 1]; 87 m = &first_path[first_path.size() - 1]; 88 p = &first_path[first_path.size() - 1]; 89 q = &first_path[first_path.size() - 2]; 90 91 allthepath.push_back(first_path); 92 93 while (hasnext) { 94 if (*q >= *p) { 95 //不触发 96 q--; p--; 97 if (p == &first_path[0]) { 98 hasnext = false; 99 break; 100 } 101 } 102 else { 103 //递增出现,触发,准备交换 104 counter++; 105 while (*m != 1) { 106 m--; 107 } 108 Swap(m, q); 109 reverseVector(p, the_end); 110 //cout << "find "<<counter<<" path!: " ; 111 //showVector(first_path); 112 the_end = &first_path[first_path.size() - 1]; 113 m = &first_path[first_path.size() - 1]; 114 p = &first_path[first_path.size() - 1]; 115 q = &first_path[first_path.size() - 2]; 116 int reverse_counter = first_path.size() - 1; 117 allthepath.push_back(first_path); 118 } 119 120 } 121 } 122 123 int main() { 124 int row, column; 125 int x_m, y_m, x_f, y_f; 126 int boxes; 127 int steps_x, steps_y; 128 vector<int> boxes_x,boxes_y; 129 130 cout << "Please input the row and column:" << endl; 131 cin >> row>>column; 132 cout << "Please input niulang‘x_ord and y_ord:" << endl; 133 cin >> x_m >> y_m; 134 cout << "Please input zhinv‘x_ord and y_ord:" << endl; 135 cin >> x_f >> y_f; 136 cout << "How many boxes do you want?"; 137 cin >> boxes; 138 for (int i = 0; i < boxes; i++) { 139 int temp_x, temp_y; 140 cout << "Please input the x_ord and y_ord of " << i +1<< " box" << endl; 141 cin >> temp_x >> temp_y; 142 boxes_x.push_back(temp_x); 143 boxes_y.push_back(temp_y); 144 } 145 steps_x = abs(x_m - x_f); 146 steps_y = abs(y_m - y_f); 147 //创建一个最小的数 作为第一条路径 148 vector<int> thefirst_path; 149 vector<vector<int>> solution; 150 for (int i = 0; i < steps_x; i++) { 151 thefirst_path.push_back(0); 152 } 153 for (int j = 0; j < steps_y; j++) { 154 thefirst_path.push_back(1); 155 } 156 all_path(thefirst_path,solution); 157 showVector(solution); 158 //删除路线中被盒子挡住的 159 for (int i = 0; i < boxes; i++) { 160 //筛除不在路径上的盒子 161 if (boxes_x[i]<=max(x_f,x_m)&&boxes_x[i]>=min(x_f,x_m)&&boxes_y[i]>=min(y_m,y_f)&&boxes_y[i]<=max(y_m,y_f)) { 162 //记录所有牛郎通向盒子的路径 163 int x_distance, y_distance; 164 vector<int> firstpath_NiuAndBox; 165 vector<vector<int>> paths_NiuAndBox; 166 x_distance = abs(x_m - boxes_x[i]); 167 y_distance = abs(y_m - boxes_y[i]); 168 for (int j = 0; j < x_distance;j++) { 169 firstpath_NiuAndBox.push_back(0); 170 } 171 for (int j = 0; j < y_distance; j++) { 172 firstpath_NiuAndBox.push_back(1); 173 } 174 all_path(firstpath_NiuAndBox,paths_NiuAndBox); 175 cout << "-----------"<<endl; 176 showVector(paths_NiuAndBox); 177 //删除牛郎通向织女的 且通过该盒子的路径 178 int same_counter=0; 179 for (int k = 0; k < paths_NiuAndBox.size(); k++) { 180 //先处理牛郎通向盒子的第k条路径 181 for (int u = 0; u < solution.size();u++) { 182 //与牛郎通向织女的第u条路径比较 183 same_counter = 0; 184 for (int v = 0; v < paths_NiuAndBox[0].size();v++) { 185 //通向盒子的 第k,v个元素与通向织女的第u,v个元素进行比较,如果全中,则删除该条牛郎通向织女的路径 186 if (paths_NiuAndBox[k][v] == solution[u][v]) { 187 same_counter++; 188 } 189 if (same_counter == paths_NiuAndBox[0].size()) { 190 //全中,删除且u-- 191 192 deleteVector(solution,u); 193 u--; 194 } 195 } 196 } 197 } 198 199 } 200 201 } 202 cout << "---------------------" << endl; 203 showVector(solution); 204 cout << "---------------------" << endl; 205 //转换成自然语言 206 cout << "所以,可行方案如下:" << endl; 207 string vector_x,vector_y; 208 if (x_m > x_f) 209 vector_x = "左"; 210 else 211 vector_x = "右"; 212 if (y_m > y_f) 213 vector_y = "下"; 214 else 215 vector_y = "上"; 216 217 TurnLanguage(solution, vector_x, vector_y); 218 }
同时 输入为 (5,5) 行列 (这个行列我都没用到...)
(4,1) 牛郎坐标
(1,4) 织女坐标
1 封闭房间个数
(2,3) 封闭房间坐标
的结果:
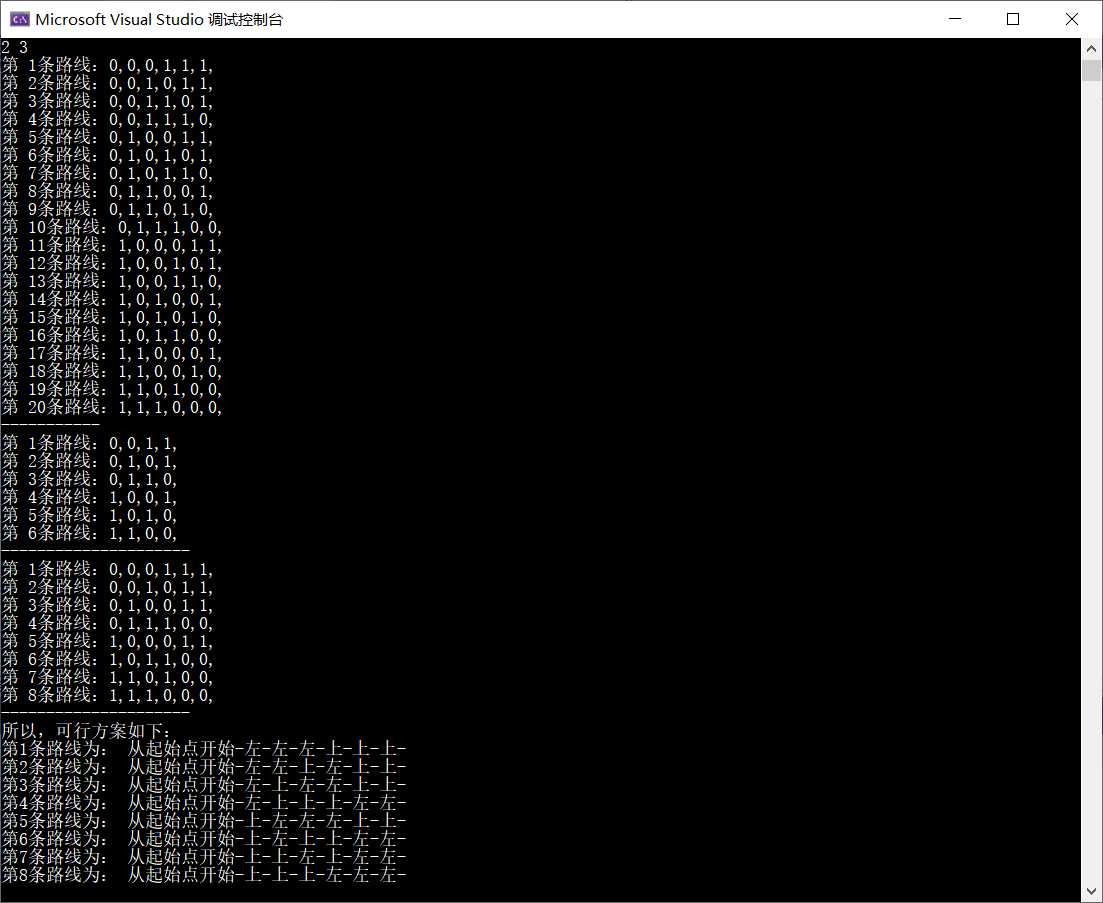
第一块表示所有不考虑封闭房间的牛郎织女路径
第二块表示牛郎到封闭房间的路径
第三块表示 第一块去掉所有第二块开头的,也就是不经过该封闭房间的路径。
最终转换为自然语言。
感觉应该有更巧妙的方法,希望有大佬指正,我这代码也太多了。
标签:方案 元素 efi ++ names for ring put ref
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/reluctante1/p/12723751.html