标签:-o bsp 作用 hashmap focus 方式 迭代器 不能 entry
简单来说,就是一个用来存储多个元素的容器,这一点与我们的数组类似。
元素类型 集合:引用类型(存储基本类型时自动装箱) 数组:基本类型
元素个数 集合:不固定 可任意扩容 数组:固定不能改变容量
通过对比知道集合有非常多的好处,实际开发中也用的很多‘
java集合分为两部分
单列集合(collection)
双列集合(map)
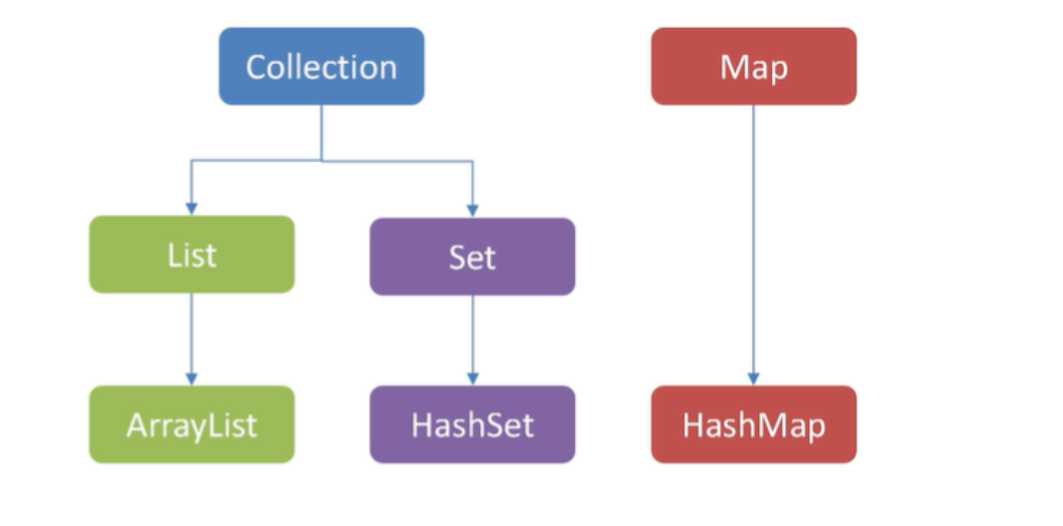
其中Collection List Set Map 都是接口,他们都有自己对应的实现类也就是ArrayList,HashSet,HashMap。
特点:可重复 有序(指 存取顺序)
基本使用:ArrrayList实例化 add()方法添加元素 size()方法获取元素个数 遍历方式for循环或增强for
写代码:
//学生类
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
/测试类
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
Student s1 = new Student("张三", 19);
Student s2 = new Student("李四", 21);
Student s3 = new Student("王五", 21);
list.add(s1);
list.add(s2);
list.add(s3);
//方式一 for循环遍历
int size = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Object stu = list.get(i);
System.out.println("索引为" + i + "的元素是" + stu);
?
}
//方式二 增强for
for (Object stu2 : list) {
System.out.println(stu2);
}
}
}
增强for(foreach循环)与迭代器都可用于遍历集合元素 增强for的底层就是迭代器,遍历时使用增强for更加便捷
简单演示:
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
//方式一 增强for
for (Object obj : list) {
System.out.println(obj);
}
//方式二 迭代器
//创建迭代器
Iterator it = list.iterator();
//判断迭代器中是否有元素有就迭代
while (it.hasNext()) {
String s = (String)it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
什么是泛型? 即泛指任意类型,对具体类型起到辅助作用,通俗来讲就是<>中的类型,起到具体的指定作用,
写了具体的数据类型,那么添加元素时就必须与其数据类型相符合。
好处:类型安全
避免了类型转换
public class MyTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("a");
list.add("b");
list.add("c");
list.add(2);//无泛型约束,报类型转换异常
?
//创建迭代器
Iterator it = list.iterator();
//判断迭代器中是否有元素有就迭代
while (it.hasNext()) {
String s = (String) it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
List<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();//jdk7开始 后面这个泛型可以不用写了
list2.add("a");
list2.add("b");
list2.add("c");
//list2.add(2); //泛型约束提示报红,只能传泛型指定的数据类型
?
for (String s2 : list2) {
System.out.println(s2);
?
}
?
}
}
5.1 简介 针对集合操作的工具类
5.2 常用成员方法
sort(List<T>) 根据列表指定顺序,将指定列表升序排序
max(Collection<T>)返回集合最大元素
reverse(List<T>)翻转集合元素
shuffle(List<T>)使用默认随机源随机置换指定的列表
特点:不可重复 无序
//测试类
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Student> set = new HashSet<>();
Student s1 = new Student("张三", 19);
Student s2 = new Student("李四", 21);
Student s3 = new Student("王五", 21);
set.add(s1);
set.add(s2);
set.add(s3);
?
//方式二 增强for
for (Object stu2 : set) {
System.out.println(stu2);
}
}
?
}
特点:双列集合 即由KY键值对组成
Key不可重复 Value可重复
基本使用:put()方法 添加元素
在 for 循环中使用 entries 实现 Map 的遍历(最常见和最常用的)
Map集合的遍历:
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Student> map = new HashMap<>();
Student s1 = new Student("张三", 19);
Student s2 = new Student("李四", 21);
Student s3 = new Student("王五", 21);
map.put("1",s1);
map.put("2",s2);
map.put("3",s3);
for (Map.Entry<String, Student> entry : map.entrySet()) {
String mapKey = entry.getKey();
Student mapValue = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(mapKey + ":" + mapValue);
}
}
}
使用 for-each 循环遍历 key 或者 values,一般适用于只需要 Map 中的 key 或者 value 时使用。性能上比 entrySet 较好。
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Student> map = new HashMap<>();
Student s1 = new Student("张三", 19);
Student s2 = new Student("李四", 21);
Student s3 = new Student("王五", 21);
map.put("1",s1);
map.put("2",s2);
map.put("3",s3);
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key);
}
// 打印值集合
for (Student value : map.values()) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}
到这里简单的集合框架就说到这里,搞定 收工!
标签:-o bsp 作用 hashmap focus 方式 迭代器 不能 entry
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/youx/p/12763108.html