标签:mode mic image tin for pac ati std 获取对象
github传送门为:https://nlohmann.github.io/json/
简介
首先这个库不是奔着性能去的,设计者考虑的是:直观的语法(Intuitive syntax)、微小的整合(Trivial integration)、认真的测试(Serious testing)
至于内存效率和速度,反倒不是优先考虑的。
先说说微小的整合。在项目中只需要包含一个json.hpp的单个头文件就可以了,为了便于编程,使用命名空间会更加方便:
#include <json.hpp> //... using json = nlohmann::json;
火线入门
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include "json.hpp"
using namespace std;
using json = nlohmann::json;
int main()
{
cout<<"Json test"<<endl;
json j;
j["name"]="castor";
j["sex"]="male";
j["age"]=12;
cout<<j<<endl;
string s="xdfile.json";
ofstream outFile(s);
outFile<<setw(4)<<j<<endl;
return 0;
}
可以看到,使用起来还是非常直观的,json类就像是一个cpp的原生类一样方便操作,还重载了<<。所写的文件打开如下:
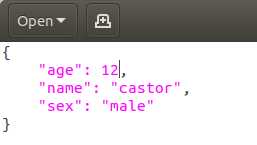
同时也会发现, json对键进行了排序,应该是使用了map的缘故。
从字符串到Json对象
通过字符串解析:
一种方式是使用_json:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include "json.hpp"
using namespace std;
using json = nlohmann::json;
int main()
{
cout<<"Json test"<<endl;
json j;
j="{ \"happy\": true, \"pi\": 3.141 }"_json;
cout<<setw(4)<<j<<endl;
return 0;
}
或者,直接使用原始字符串的方式:
j = R"(
{
"happy": true,
"pi": 3.141
}
)"_json;
或者使用json::parse:
j=json::parse("{ \"happy\": true, \"pi\": 3.141 }");
都将显示:
Json test
{
"happy": true,
"pi": 3.141
}
获取对象的字符串
需要提取其中的字符串时,使用j.dump()即可,如果提供一个整型参数,还可以缩进,例如一般我们用四个字符的话,就可以用j.dump(4),所以上面的例子中,不使用setw的话,可以这样写:
cout<<j.dump(4)<<endl;
另外一个方法是使用j..get<std::string>()方法,get获取的是原始字符串,而dump则是获取的序列化(serialized )的字符串值。
流操作
以文件流为例,读文件创建json对象:
ifstream i("xdfile.json");
i >> j;
至于写文件,和写标准输出流没什么差别,前面的火线入门已经展示过。
简单好用的C++ json库——JSON for Modern C++
标签:mode mic image tin for pac ati std 获取对象
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/castor-xu/p/12786531.html