标签:varchar mod 约束 表名 否则 查询 sel key inno
create table t1(
id int,
name char(16) not null,
gender enum(‘male‘,‘female‘) default ‘male‘
);
# 插入数据时可以指定字段,且values后面的数据与字段名是一一对应的
insert into t1(name, id) values(‘yumi‘,1);
insert into t1(name, gender, id) values(‘rem‘, ‘female‘, 2);
# 单列唯一
create table t2(
id int unique,
name char(16) not null
);
insert into t2 values(1, ‘yumi‘),(1,‘rem‘); # Duplicate entry...
insert into t2 values(2,‘rem‘);
# 联合唯一
create table t3(
id int unique,
ip varchar(30),
port varchar(10),
unique(ip,port)
);
insert into t3 values(1, ‘127.0.0.1‘,8080);
insert into t3 values(2, ‘127.0.0.1‘,8081);
insert into t3 values(3, ‘127.0.0.2‘,8080);
insert into t3 values(4, ‘127.0.0.1‘,8080); # 报错 Duplicate entry...
# primary key = unique + not null 的效果 非空且唯一
create table t4(
id int primary key
);
insert into t4 values(null); # 报错 Column ‘id‘ cannot be null
insert into t4 values(1),(1); # 报错 Duplicate entry ‘1‘ for key ‘PRIMARY‘
"""
2.它除了有约束效果之外 它还是Innodb存储引擎组织数据的依据
Innodb存储引擎在创建表的时候必须要有primary key
因为它类似于书的目录 能够帮助提示查询效率并且也是建表的依据
"""
# 注意:
‘‘‘
1、一张表有且只有一个主键,如果没有设置就会默认从上往下搜错直到遇到一个非空且唯一的字段并将它升级为主键
2、如果表中没有任何非空唯一字段,Innodb会采用自己内部一个隐藏字段作为主键,无法提升查询速度
3、一个表中通常都应该有一个主键字段,通常我们会将表的id(数据的唯一标识)字段作为主键
create table t4(
id int primary key
);
4、可以多个字段联合作为一个主键
create table t4(
ip char(16),
port int,
primary key(ip,port)
);
‘‘‘
# 只能跟键搭配使用,且通常都是加在主键上,不能用在普通字段上(否则会报错)
create table t5(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name char(16)
# cid int auto_increment
);
# 报错 Incorrect table definition; there can be only one auto column and it must be defined as a key
insert into t5(name) values(‘yumi‘),(‘rem‘),(‘megumi‘);
# 补充知识点
delete from t1; # 删除表中数据后 主键的自增不会停止
truncate t1; # 清空表数据并且重置主键 就相当于是新建一张表
‘‘‘
foreign key 用来帮助我们建立表与表之间的关系的
foreign key(字段名) references 表名(字段名)
‘‘‘
‘‘‘
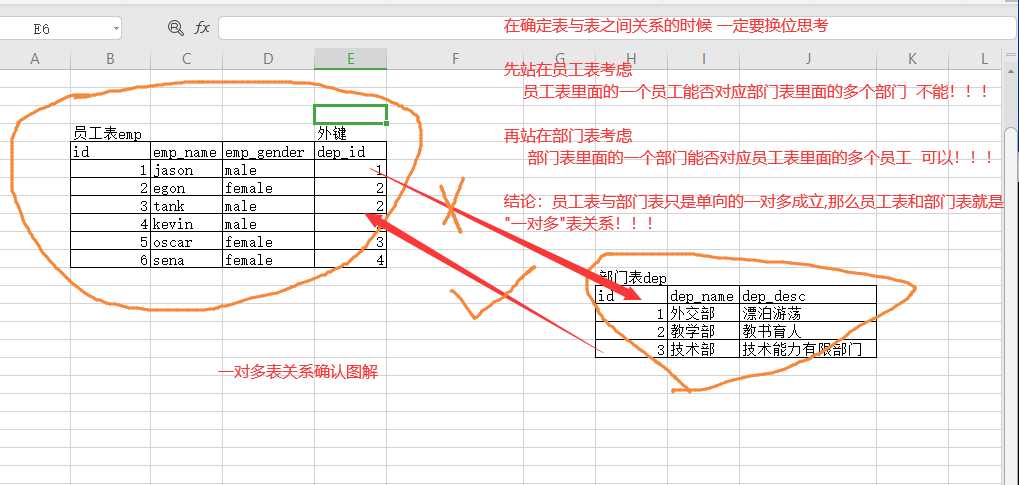
员工表与部门表为例
先站在员工表
思考一个员工能否对应多个部门(一条员工数据能否对应多条部门数据)
再站在部门表
思考一个部门能否对应多个员工(一个部门数据能否对应多条员工数据)
得出结论
员工表与部门表示单向的一对多
所以表关系就是一对多
foreign key
1 一对多表关系 外键字段建在多的一方
2 在创建表的时候 一定要先建被关联表
3 在录入数据的时候 也必须先录入被关联表
‘‘‘
# sql语句建立表间关系
create table dep(
id int primary key auto_increment,
dep_name varchar(30)
);
create table emp(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(16),
dep_id int,
foreign key(dep_id) references dep(id)
on update cascade # 级联更新
on delete cascade # 级联删除
);
insert into dep(dep_name) values(‘教学部‘),(‘外交部‘),(‘技术部‘);
insert into emp(name,dep_id) values(‘yumi‘,3),(‘rem‘,1),(‘ram‘,2);
# 课程表
create table course(
id int primary key auto_increment,
course_name varchar(16) not null
);
# 学生表
create table student(
id int primary key auto_increment,
stu_name varchar(16) not null
);
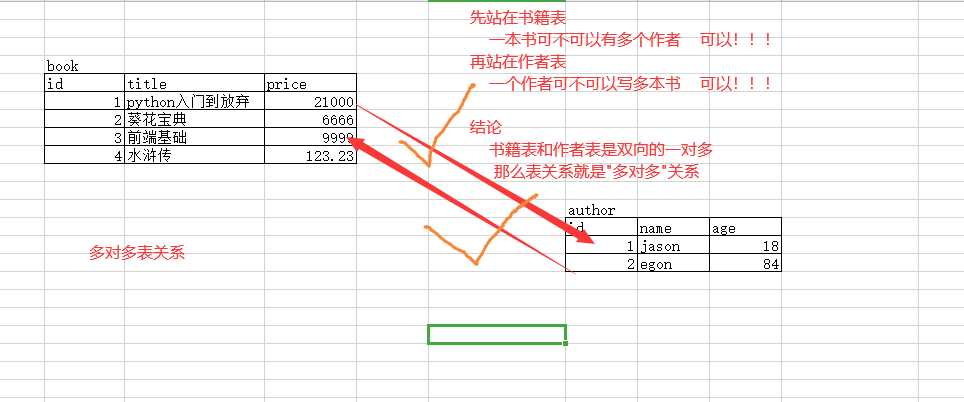
# 多对多关系表
create table stu_course(
id int primary key auto_increment,
stu_id int,
course_id int,
foreign key(stu_id) references student(id)
on update cascade
on delete cascade,
foreign key(course_id) references course(id)
on update cascade
on delete cascade
);
insert into course(course_name) values(‘python‘),(‘go‘),(‘mysql‘),(‘linux‘);
insert into student(stu_name) values(‘yumi‘),(‘rem‘),(‘ram‘),(‘megumi‘),(‘rushia‘);
insert into stu_course(stu_id,course_id) values(1,1),(2,1),(3,2),(4,3),(5,4);
"""
id name age addr phone hobby email........
如果一个表的字段特别多 每次查询又不是所有的字段都能用得到
将表一分为二
用户表
用户表
id name age
用户详情表
id addr phone hobby email........
站在用户表
一个用户能否对应多个用户详情
站在详情表
一个详情能否属于多个用户
结论:单向的一对多都不成立 那么这个时候两者之间的表关系
就是一对一
或者没有关系(好判断)
"""
# 一对一关系,外键字段建在任意一方都可以,推荐建在查询频率较高的表中
create table user_info(
id int primary key auto_increment,
age int,
address varchar(60)
);
create table user(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(16),
user_info_id int unique,
foreign key(user_info_id) references user_info(id)
on update cascade
on delete cascade
);
insert into user_info(age,address) values(18,‘x市‘),(18,‘x市‘);
insert into user(name, user_info_id) values(‘yumi‘,1);
insert into user(name, user_info_id) values(‘rem‘,2);
insert into user(name, user_info_id) values(‘rem‘,);# 报错 Duplicate entry...
‘‘‘
表间关系的建立需要使用foreign key
一对多:外键字段建在多的一方
多对多:另外开设第三章表进行存储
一对一:建在任意一方都可以,推荐建在查询频率较高的表中
‘‘‘
# MySQL对大小写是不敏感的
"""
1 修改表名
alter table 表名 rename 新表名;
2 增加字段
alter table 表名 add 字段名 字段类型(宽度) 约束条件;
alter table 表名 add 字段名 字段类型(宽度) 约束条件 first;
alter table 表名 add 字段名 字段类型(宽度) 约束条件 after 字段名;
3 删除字段
alter table 表名 drop 字段名;
4 修改字段
alter table 表名 modify 字段名 字段类型(宽度) 约束条件;
alter table 表名 change 旧字段名 新字段名 字段类型(宽度) 约束条件;
"""
"""
我们sql语句查询的结果其实也是一张虚拟表
"""
# 只复制旧表的表结构跟表数据,不能够复制主键以及外键等
create table 表名 select * from 旧表;
# 假如旧表中的数据id小于3则会产生一个空表
create table new_dep2 select * from dep where id>3;
标签:varchar mod 约束 表名 否则 查询 sel key inno
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/guanxiying/p/12831483.html