标签:traversal flag mic 连接 alt tin sof microsoft 顶点
图的遍历
有两种方法:深度优先,广度优先
深度优先遍历
邻接矩阵中实现思路:
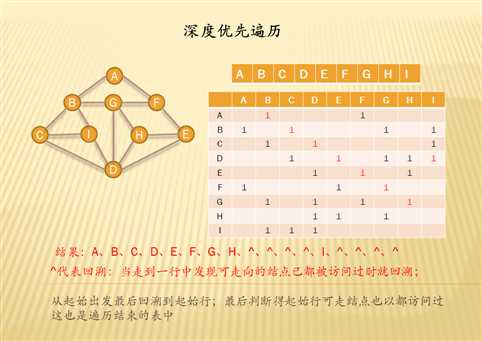
代码实现
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <malloc.h> 3 #define SIZE 9 4 5 void user(char *lin,int n){ 6 printf("%c ",lin[n]); 7 } 8 9 void depthTraversal(char *lin,int (*arr)[SIZE],int n){ 10 int i=0,j=n; 11 static int tab[]={0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}; 12 tab[j]=1; 13 user(lin,j); 14 for(i=0;i<SIZE;i++){ 15 if(i==j) 16 continue; 17 if(*(*(arr+j)+i)==1 && tab[i]==0) 18 depthTraversal(lin,arr,i); 19 } 20 } 21 22 void main(){ 23 char lin[]={‘A‘,‘B‘,‘C‘,‘D‘,‘E‘,‘F‘,‘G‘,‘H‘,‘I‘}; 24 int arr[9][9]={ 25 {0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0}, 26 {1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1}, 27 {0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1}, 28 {0,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,1}, 29 {0,0,0,1,0,1,0,1,0}, 30 {1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0}, 31 {0,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,0}, 32 {0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0}, 33 {0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0} 34 }; 35 depthTraversal(lin,arr,0); 36 printf("\n"); 37 }
马踏棋盘算法
问题概述:在国际棋盘(8*8)中将‘马’放在任意指定的方框中,按照‘马’走‘日’的规则将马进行移动。要求每个方格只能进入一次,最终使马走遍棋盘64个方格。
解决方法:利用深度遍历的方法(回溯);使马遇到死路时就回溯,直到走遍棋盘;
注:在(n*n)的棋盘上,当 n ≥ 5且为偶数时,以任一点都有解
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <malloc.h> 3 #define X 8 4 #define Y 8 5 6 int arr[X][Y]; 7 8 int nextxy(int *x,int*y,int count){ 9 switch(count){ 10 case 0: 11 if(*x+2<=X-1 && *y-1>=0 && arr[*x+2][*y-1]==0){ 12 *x+=2; 13 *y-=1; 14 return 1; 15 } 16 break; 17 case 1: 18 if(*x+2<=X-1 && *y+1<=Y-1 && arr[*x+2][*y+1]==0){ 19 *x+=2; 20 *y+=1; 21 return 1; 22 } 23 break; 24 case 2: 25 if(*x+1<=X-1 && *y-2>=0 && arr[*x+1][*y-2]==0){ 26 *x+=1; 27 *y-=2; 28 return 1; 29 } 30 break; 31 case 3: 32 if(*x+1<=X-1 && *y+2<=Y-1 && arr[*x+1][*y+2]==0){ 33 *x+=1; 34 *y+=2; 35 return 1; 36 } 37 break; 38 case 4: 39 if(*x-2>=0 && *y-1>=0 && arr[*x-2][*y-1]==0){ 40 *x-=2; 41 *y-=1; 42 return 1; 43 } 44 break; 45 case 5: 46 if(*x-2>=0 && *y+1<=Y-1 && arr[*x-2][*y+1]==0){ 47 *x-=2; 48 *y+=1; 49 return 1; 50 } 51 break; 52 case 6: 53 if(*x-1>=0 && *y-2>=0 && arr[*x-1][*y-2]==0){ 54 *x-=1; 55 *y-=2; 56 return 1; 57 } 58 break; 59 case 7: 60 if(*x-1>=0 && *y+2<=Y-1 && arr[*x-1][*y+2]==0){ 61 *x-=1; 62 *y+=2; 63 return 1; 64 } 65 break; 66 default: 67 break; 68 } 69 return 0; 70 } 71 72 void Print(){ 73 int i,j; 74 for(i=0;i<X;i++){ 75 for(j=0;j<Y;j++){ 76 printf("%d\t",arr[i][j]); 77 } 78 printf("\n"); 79 } 80 printf("\n"); 81 } 82 83 //(x,y)为位置坐标 84 //tag是标记变量,也用于记录步骤 85 int TravelBoard(int x,int y,int tag){ 86 int x1=x,y1=y; 87 int i=0; 88 int flag=0;//记录当前位置的选者是否会导致失败 89 arr[x][y]=tag; 90 if(X*Y==tag){ 91 Print();//打印 92 return 1; 93 } 94 //找到马下一个可走的坐标(x1,y1),如果找到flag=1,否者为0 95 flag=nextxy(&x1,&y1,i); 96 while(0==flag &&i<8){ 97 i++; 98 flag=nextxy(&x1,&y1,i); 99 } 100 101 while(flag){//这里的flag记录是否结束(失败) 102 if(TravelBoard(x1,y1,tag+1)){ 103 return 1; 104 } 105 106 //这个位置会导致后面碰壁失败,需要回溯到上个位置 107 x1=x; 108 y1=y; 109 i++; 110 flag=nextxy(&x1,&y1,i); 111 while(0==flag &&i<8){ 112 i++; 113 flag=nextxy(&x1,&y1,i); 114 } 115 } 116 if(flag==0){ 117 arr[x][y]=0; 118 } 119 return 0; 120 } 121 122 void main(){ 123 int i,j; 124 for(i=0;i<X;i++){ 125 for(j=0;j<Y;j++){ 126 arr[i][j]=0; 127 } 128 } 129 printf("请输入起始位置的行:"); 130 scanf("%d",&i); 131 printf("请输入起始位置的列:"); 132 scanf("%d",&j); 133 //建议用两行一列测试 134 135 if(!TravelBoard(i,j,1)){ 136 printf("马踏棋盘失败"); 137 } 138 }
广度优先遍历
其实广度优先遍历,类似与树的层序遍历
方法:
标签:traversal flag mic 连接 alt tin sof microsoft 顶点
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/TianLiang-2000/p/12853984.html