标签:创建表 varchar over splay pac code 实现类 pos 保存
版本---maven 3.6.3
<properties>
<spring.version>5.2.5.RELEASE</spring.version> Spring的版本
<hibernate.version>5.4.10.Final</hibernate.version> hibernate的版本
<slf4j.version>1.7.30</slf4j.version>
<log4j.version>2.12.1</log4j.version>
<druid.version>1.1.21</druid.version>
<mysql.version>5.1.6</mysql.version>
</properties>
<dependencies> <!-- spring beg --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.5</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- spring对orm框架的支持包--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- hibernate beg --> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-entitymanager</artifactId> <version>${hibernate.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId> <version>${hibernate.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> <version>6.1.2.Final</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>classmate</artifactId> <groupId>com.fasterxml</groupId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <!-- hibernate end --> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>${mysql.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>${druid.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- spring data jpa 的坐标 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> <artifactId>spring-data-jpa</artifactId> <version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- el beg 使用spring data jpa 必须引入 --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.el</groupId> <artifactId>javax.el-api</artifactId> <version>3.0.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.glassfish</groupId> <artifactId>javax.el</artifactId> <version>3.0.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> <version>${slf4j.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j-api</artifactId> <version>${log4j.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:jpa="http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa" xmlns:task="http://www.springframework.org/schema/task" xmlns:contxt="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa http://www.springframework.org/schema/data/jpa/spring-jpa.xsd"> <!-- 配置实体类管理工厂 --> <bean id="entityManagerFactory" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean"> <!-- 配置数据源 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> <!-- 配置实体类包扫描 --> <property name="packagesToScan" value="com.ytfs.entity"/> <!-- 配置jpa提供方 --> <property name="persistenceProvider"> <bean class="org.hibernate.jpa.HibernatePersistenceProvider"/> </property> <!-- 配置JPA提供方的适配器 --> <property name="jpaVendorAdapter"> <bean class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.vendor.HibernateJpaVendorAdapter"> <!-- 是否显示sql语句 --> <property name="showSql" value="true"/> <!-- 数据库的类型 --> <property name="database" value="MYSQL"/> <!-- 数据库的方言 --> <property name="databasePlatform" value="org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect"/> <!-- 是否自动创建表 --> <property name="generateDdl" value="false"/> </bean> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置数据源 --> <contxt:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbcConfig.properties"/> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager"> <property name="entityManagerFactory" ref="entityManagerFactory"/> </bean> <!-- 整合jpa --> <jpa:repositories base-package="com.ytfs.dao" transaction-manager-ref="transactionManager" entity-manager-factory-ref="entityManagerFactory"/> <!-- 配置上spring包扫描器 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.ytfs"/>
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jpa
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root

package com.ytfs.entity; import javax.persistence.*; import java.io.Serializable; /** * @Classname Customer * @Description TODO(客户实体类) * @Date 2020/4/29 21:34 * @Created by ytfs */ @Entity @Table(name = "cst_customer") public class Customer implements Serializable { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) @Column(name = "cust_id") private Long custId; /** * cust_id` bigint(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT ‘客户编号(主键)‘, * `cust_name` varchar(32) NOT NULL COMMENT ‘客户名称(公司名称)‘, * `cust_source` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘客户信息来源‘, * `cust_industry` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘客户所属行业‘, * `cust_level` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘客户级别‘, * `cust_address` varchar(128) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘客户联系地址‘, * `cust_phone` v */ @Column(name = "cust_name") private String custName; @Column(name = "cust_source") private String custSource; @Column(name = "cust_industry") private String custIndustry; @Column(name = "cust_level") private String custLevel; @Column(name = "cust_address") private String custAddress; @Column(name = "cust_phone") private String custPhone; public Long getCustId() { return custId; } public void setCustId(Long custId) { this.custId = custId; } public String getCustName() { return custName; } public void setCustName(String custName) { this.custName = custName; } public String getCustSource() { return custSource; } public void setCustSource(String custSource) { this.custSource = custSource; } public String getCustIndustry() { return custIndustry; } public void setCustIndustry(String custIndustry) { this.custIndustry = custIndustry; } public String getCustLevel() { return custLevel; } public void setCustLevel(String custLevel) { this.custLevel = custLevel; } public String getCustAddress() { return custAddress; } public void setCustAddress(String custAddress) { this.custAddress = custAddress; } public String getCustPhone() { return custPhone; } public void setCustPhone(String custPhone) { this.custPhone = custPhone; } @Override public String toString() { return "Customer{" + "custId=" + custId + ", custName=‘" + custName + ‘\‘‘ + ", custSource=‘" + custSource + ‘\‘‘ + ", custIndustry=‘" + custIndustry + ‘\‘‘ + ", custLevel=‘" + custLevel + ‘\‘‘ + ", custAddress=‘" + custAddress + ‘\‘‘ + ", custPhone=‘" + custPhone + ‘\‘‘ + ‘}‘; } }
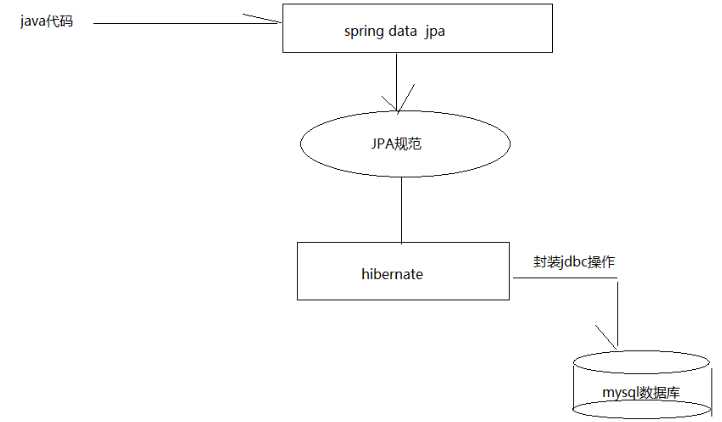
Spring Data JPA是spring提供的一款对于数据访问层(Dao层)的框架,使用Spring Data JPA,只需要按照框架的规范提供dao接口,不需要实现类就可以完成数据库的增删改查、分页查询等方法的定义,极大的简化了我们的开发过程。
在Spring Data JPA中,对于定义符合规范的Dao层接口,我们只需要遵循以下几点就可以了:
1.创建一个Dao层接口,并实现JpaRepository和JpaSpecificationExecutor
2.提供相应的泛型

package com.ytfs.dao; import com.alibaba.druid.sql.visitor.functions.If; import com.ytfs.entity.Customer; import org.hibernate.mapping.Value; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaSpecificationExecutor; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Modifying; import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query; import java.lang.invoke.VarHandle; import java.security.spec.NamedParameterSpec; import java.util.List; /** * @Classname CustomerDao * @Description TODO(客户的数据库访问层) * @Date 2020/4/29 21:46 * @Created by ytfs * JpaRepository<实体类类型,主键类型>:用来完成基本CRUD操作 * JpaSpecificationExecutor<实体类类型>:用于复杂查询(分页等查询操作) */ public interface CustomerDao extends JpaRepository<Customer, Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Customer> { /** * JPQL的方式查询全部客户 * * @return */ @Query(value = "from Customer") List<Customer> findAllByJPQL(); /** * 根据客户名称和客户id查询客户 * jpql: from Customer where custName = ? and custId = ? * <p> * 对于多个占位符参数 * 赋值的时候,默认的情况下,占位符的位置需要和方法参数中的位置保持一致 * <p> * 可以指定占位符参数的位置 * ? 索引的方式,指定此占位的取值来源 */ @Query("from Customer where custName = ?2 and custId = ?1") Customer findCustomerById(Long custId, String custName); /** * 使用jpql完成更新操作 * 案例 : 根据id更新,客户的名称 * 更新4号客户的名称,将名称改为“黑马程序员” * * sql :update cst_customer set cust_name = ? where cust_id = ? * jpql : update Customer set custName = ? where custId = ? * * @Query : 代表的是进行查询 * * 声明此方法是用来进行更新操作 * @Modifying * * 当前执行的是一个更新操作 * */ @Query("update Customer set custName = ?1 where custId = ?2") @Modifying void updateCustomerById(String custName,Long Id); /** * 使用sql的形式查询: * 查询全部的客户 * sql : select * from cst_customer; * Query : 配置sql查询 * value : sql语句 * nativeQuery : 查询方式 * true : sql查询 * false:jpql查询 默认值 * */ @Query(value = "select * from cst_customer", nativeQuery = true) List<Customer> findAllBySql(); /** * 使用sql的形式查询: * 条件查询 * sql : select * from cst_customer where cust_name like ?; * Query : 配置sql查询 * value : sql语句 * nativeQuery : 查询方式 * true : sql查询 * false:jpql查询 默认值 * */ @Query(value = "select * from cst_customer where cust_name like ?1", nativeQuery = true) Customer FindCustomerByLikeCustName(String custName); /** * @author 雨听风说 * @param * @updateTime 2020/4/30 23:45 * 方法名的约定: * findBy : 查询 * 对象中的属性名(首字母大写) : 查询的条件 * CustName * * 默认情况 : 使用 等于的方式查询 * 特殊的查询方式 * * findByCustName -- 根据客户名称查询 * * 再springdataJpa的运行阶段 * 会根据方法名称进行解析 findBy from xxx(实体类) * 属性名称 where custName = * * 1.findBy + 属性名称 (根据属性名称进行完成匹配的查询=) * 2.findBy + 属性名称 + “查询方式(Like | isnull)” * findByCustNameLike * 3.多条件查询 * findBy + 属性名 + “查询方式” + “多条件的连接符(and|or)” + 属性名 + “查询方式” */ /** * 根据名称精准查询客户 * @param CustName * @return */ Customer findByCustName(String CustName); /** * 根据客户名称进行模糊查询 * @param CustName * @return */ List<Customer> findByCustNameLike(String CustName); /** * 根据客户名称模糊查询,并且通过id精确查询 * @param name * @param Id * @return */ List<Customer> findByCustNameLikeAndCustId(String name, Long Id); }
完成了Spring Data JPA的环境搭建,并且编写了符合Spring Data JPA 规范的Dao层接口之后,就可以使用定义好的Dao层接口进行客户的基本CRUD操作

package com.ytfs.test; import com.ytfs.dao.CustomerDao; import com.ytfs.entity.Customer; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import java.util.List; /** * @Classname SpringDataJpaTest * @Description TODO(springDataJpa的测试案例) * @Date 2020/4/29 21:58 * @Created by ytfs */ @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml") public class SpringDataJpaTest { @Autowired private CustomerDao customerDao; /** * @description 查询全部 * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/29 22:44 */ @Test public void testFindALl() { List<Customer> list = this.customerDao.findAll(); list.forEach(System.out::println); } /** * @description 根据id查询客户 * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/29 22:49 */ @Test public void testFindById() { System.out.println(this.customerDao.findById(1L)); } /** * @description 根据Id删除 * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/29 22:53 */ @Test public void testDelete() { this.customerDao.deleteById(4l); } /** * @description 保存客户, save, 保存并且返回保存的对象 * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/29 23:03 */ @Test public void testSave() { Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setCustName("雨听风说"); this.customerDao.save(customer); } /** * @description 当保存方法执行的时候, 如果需要保存的对象有id, 那么将自动更新这个id的对象 * 并且将该对象为设置的参数置为null * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/29 23:07 */ @Test public void testUpdate() { Customer customer = new Customer(); customer.setCustId(5l); customer.setCustName("雨听风说修改"); this.customerDao.save(customer); } }
顾名思义,方法命名规则查询就是根据方法的名字,就能创建查询。只需要按照Spring Data JPA提供的方法命名规则定义方法的名称,就可以完成查询工作。Spring Data JPA在程序执行的时候会根据方法名称进行解析,并自动生成查询语句进行查询
按照Spring Data JPA 定义的规则,查询方法以findBy开头,涉及条件查询时,条件的属性用条件关键字连接,要注意的是:条件属性首字母需大写。框架在进行方法名解析时,会先把方法名多余的前缀截取掉,然后对剩下部分进行解析。
|
//方法命名方式查询(根据客户名称查询客户) public Customer findByCustName(String custName); |
具体的关键字,使用方法和生产成SQL如下表所示
|
Keyword |
Sample |
JPQL |
||
|
And |
findByLastnameAndFirstname |
… where x.lastname = ?1 and x.firstname = ?2 |
||
|
Or |
findByLastnameOrFirstname |
… where x.lastname = ?1 or x.firstname = ?2 |
||
|
Is,Equals |
findByFirstnameIs, findByFirstnameEquals |
… where x.firstname = ?1 |
||
|
Between |
findByStartDateBetween |
… where x.startDate between ?1 and ?2 |
||
|
LessThan |
findByAgeLessThan |
… where x.age < ?1 |
||
|
LessThanEqual |
findByAgeLessThanEqual |
… where x.age ⇐ ?1 |
||
|
GreaterThan |
findByAgeGreaterThan |
… where x.age > ?1 |
||
|
GreaterThanEqual |
findByAgeGreaterThanEqual |
… where x.age >= ?1 |
||
|
After |
findByStartDateAfter |
… where x.startDate > ?1 |
||
|
Before |
findByStartDateBefore |
… where x.startDate < ?1 |
||
|
IsNull |
findByAgeIsNull |
… where x.age is null |
||
|
IsNotNull,NotNull |
findByAge(Is)NotNull |
… where x.age not null |
||
|
Like |
findByFirstnameLike |
… where x.firstname like ?1 |
||
|
NotLike |
findByFirstnameNotLike |
… where x.firstname not like ?1 |
||
|
StartingWith |
findByFirstnameStartingWith |
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with appended %) |
||
|
EndingWith |
findByFirstnameEndingWith |
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound with prepended %) |
||
|
Containing |
findByFirstnameContaining |
… where x.firstname like ?1 (parameter bound wrapped in %) |
||
|
OrderBy |
findByAgeOrderByLastnameDesc |
… where x.age = ?1 order by x.lastname desc |
||
|
Not |
findByLastnameNot |
… where x.lastname <> ?1 |
||
|
In |
findByAgeIn(Collection ages) |
… where x.age in ?1 |
||
|
NotIn |
findByAgeNotIn(Collection age) |
… where x.age not in ?1 |
||
|
TRUE |
findByActiveTrue() |
… where x.active = true |
||
|
FALSE |
findByActiveFalse() |
… where x.active = false |
||
|
IgnoreCase |
findByFirstnameIgnoreCase |
… where UPPER(x.firstame) = UPPER(?1) |

package com.ytfs.test; import com.ytfs.dao.CustomerDao; import com.ytfs.entity.Customer; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.test.annotation.Rollback; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import javax.transaction.Transactional; import java.util.List; /** * @Classname SpringDataJPAJpqlTest * @Description TODO(SpringDataJpaJpql测试) * @Date 2020/4/30 21:15 * @Created by ytfs */ /** * jpql的查询方式 * jpql : jpa query language (jpq查询语言) * 特点:语法或关键字和sql语句类似 * 查询的是类和类中的属性 * 需要将JPQL语句配置到接口方法上 * 1.特有的查询:需要在dao接口上配置方法 * 2.在新添加的方法上,使用注解的形式配置jpql查询语句 * 3.注解 : @Query */ @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml") public class SpringDataJPAJpqlTest { @Autowired private CustomerDao customerDao; /** * @description 通过JPQL的方式查询所有的客户 * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/30 21:48 */ @Test public void testFindAll() { List<Customer> list = this.customerDao.findAllByJPQL(); list.forEach(System.out::println); } /** * @description 通过客户姓名和客户的Id查询一个客户 * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/30 21:48 */ @Test public void testFindCustomerByIdAndName() { Customer customer = this.customerDao.findCustomerById(5L, "雨听风说"); System.out.println("customer = " + customer); } /** * @description 通过Id修改客户的姓名 * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/30 21:59 * <p> * 测试jpql的更新操作 * springDataJpa中使用jpql完成 更新/删除操作 * 需要手动添加事务的支持 * 默认会执行结束之后,回滚事务 * @Rollback :设置是否自动回滚 * false|true */ @Test @Transactional @Rollback(value = false) public void testUpdateCustomerById() { this.customerDao.updateCustomerById("雨听风说", 5L); } /** * @description 通过sql语句的形式查询全部的客户 * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/30 22:08 */ @Test public void testFindAllBySql() { List<Customer> customers = this.customerDao.findAllBySql(); customers.forEach(System.out::println); } /** * @description 通过sql语句的形式模糊条件查询 * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/30 22:08 */ @Test public void testFindCustomerByLikeCustName() { Customer customer = this.customerDao.FindCustomerByLikeCustName("雨听风说"); System.out.println(customer); } /** * @description 根据名称精准查客户 * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/30 23:47 */ @Test public void testByName() { Customer customer = this.customerDao.findByCustName("雨听风说"); System.out.println("customer = " + customer); } /** * @description 根据客户的名称模糊查询 * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/30 23:51 */ @Test public void testFindByNameLike() { List<Customer> byCustNameLike = this.customerDao.findByCustNameLike("%风说%"); byCustNameLike.forEach(System.out::println); } /** * @description 根据客户名称模糊查询,并且根据id精准查询 * @author 雨听风说 * @updateTime 2020/4/30 23:56 */ @Test public void testFindCustomerByNameLikeAndId() { List<Customer> byCustNameLikeAndCustId = this.customerDao.findByCustNameLikeAndCustId("%风说%", 5L); byCustNameLikeAndCustId.forEach(System.out::println); } }
在客户的案例中,我们发现在自定义的CustomerDao中,并没有提供任何方法就可以使用其中的很多方法,那么这些方法究竟是怎么来的呢?答案很简单,对于我们自定义的Dao接口,由于继承了JpaRepository和JpaSpecificationExecutor,所以我们可以使用这两个接口的所有方法。
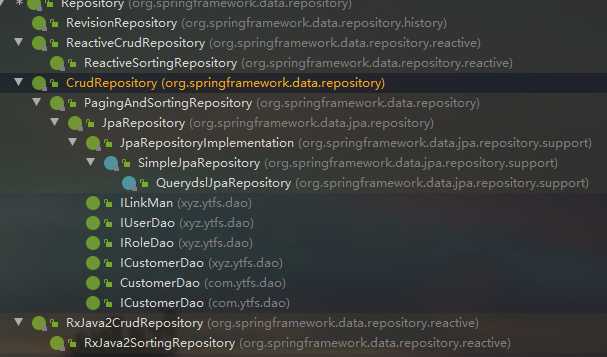
在使用Spring Data JPA时,一般实现JpaRepository和JpaSpecificationExecutor接口,这样就可以使用这些接口中定义的方法,但是这些方法都只是一些声明,没有具体的实现方式,那么在 Spring Data JPA中它又是怎么实现的呢?
通过对客户案例,以debug断点调试的方式,通过分析Spring Data JPA的原来来分析程序的执行过程
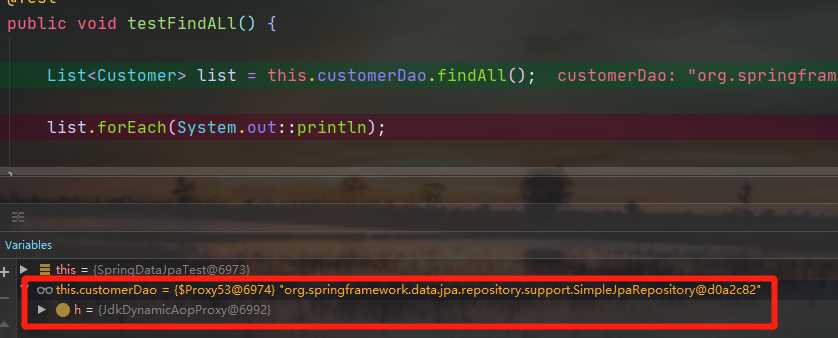
当程序执行的时候,会通过JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke方法,对customerDao对象生成动态代理对象。根据对Spring Data JPA介绍而知,要想进行findAll查询方法,最终还是会出现JPA规范的API完成操作,那么这些底层代码存在于何处呢?答案很简单,都隐藏在通过JdkDynamicAopProxy生成的动态代理对象当中,而这个动态代理对象就是SimpleJpaRepository
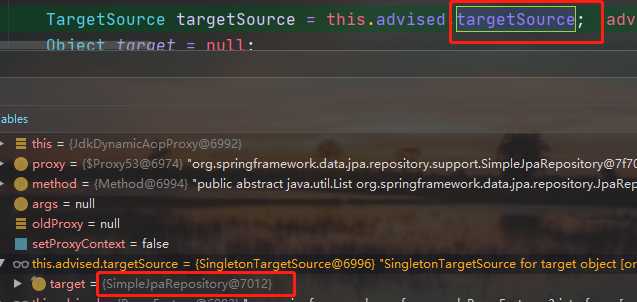
通过SimpleJpaRepository的源码分析,定位到了getOne方法,在此方法中,返回em.find()的返回结果,那么em又是什么呢?
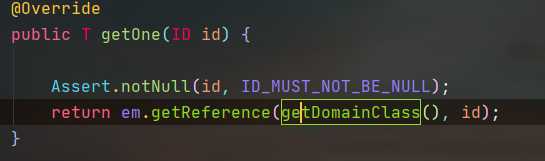
带着问题继续查找em对象,我们发现em就是EntityManager对象,而他是JPA原生的实现方式,所以我们得到结论Spring Data JPA只是对标准JPA操作进行了进一步封装,简化了Dao层代码的开发

说明了是sring data jpa 的执行方式
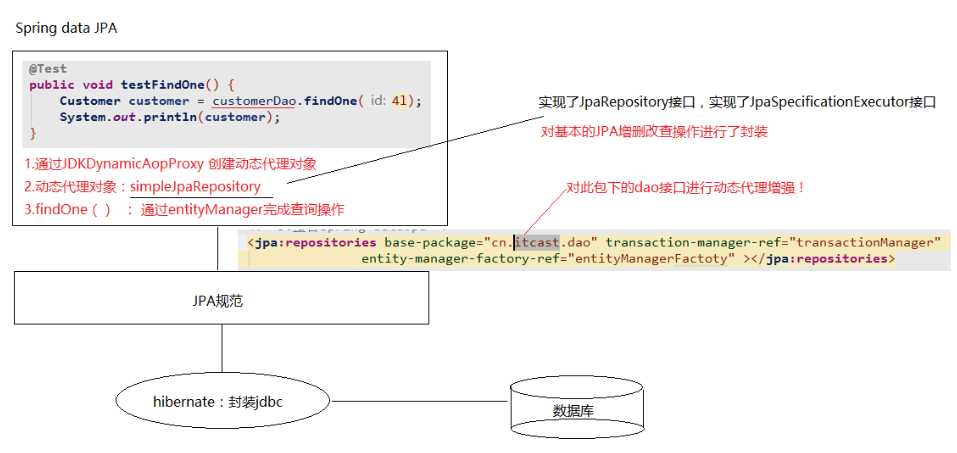
private ICustomerDao cusstomerDao; //接口 真正发挥作用: 接口的是接口的实现类 在程序运行的过程中,自动的使用JdkDynamicProxy代理了接口,动态的生成了接口的实现类对象
JPA---Spring-data-JPA---Hibernate
标签:创建表 varchar over splay pac code 实现类 pos 保存
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/TJ21/p/12863358.html