标签:原因 ack sed imu struct edm 最好 move 存储结构
容器主要包括 Collection 和 Map 两种:
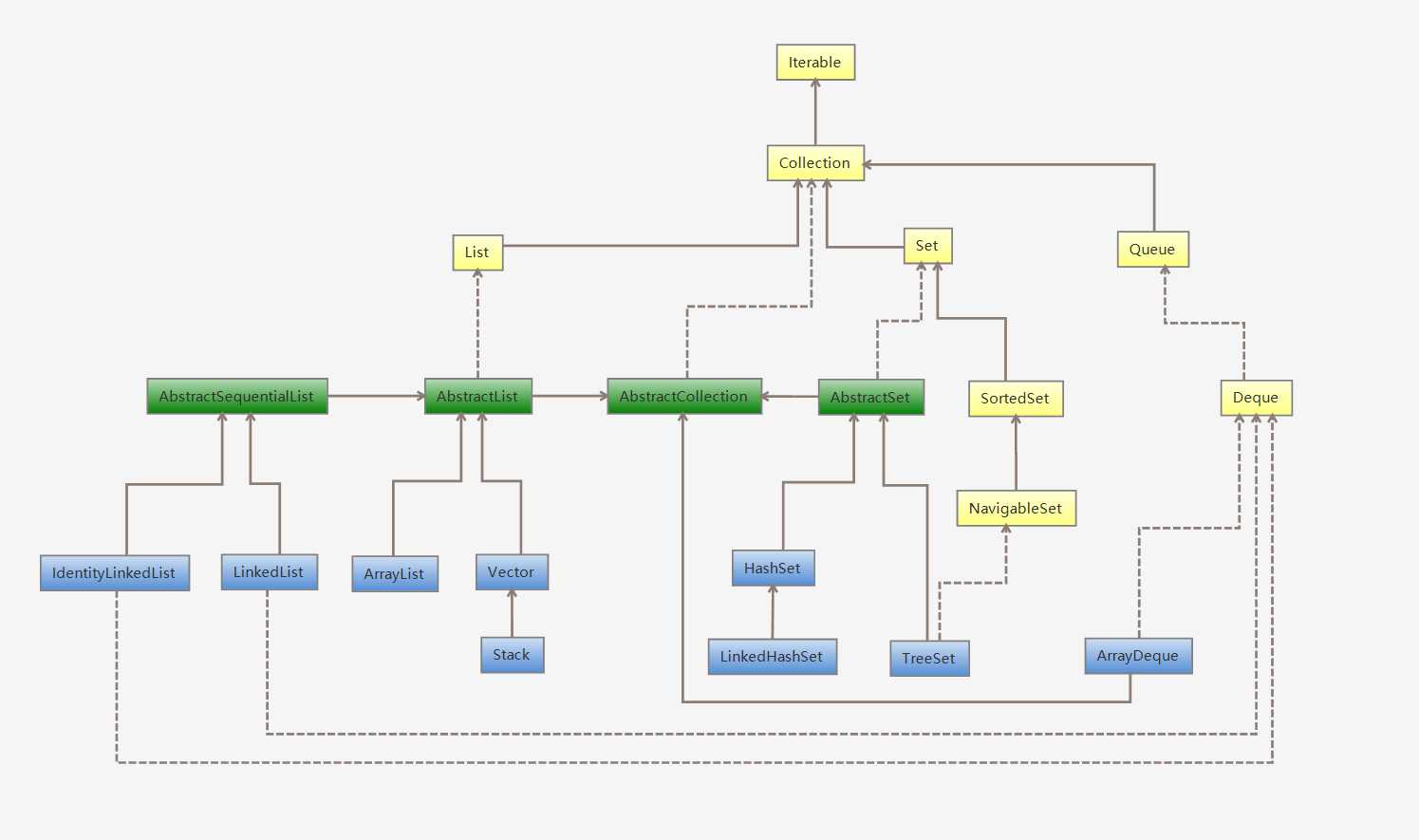
Collection:
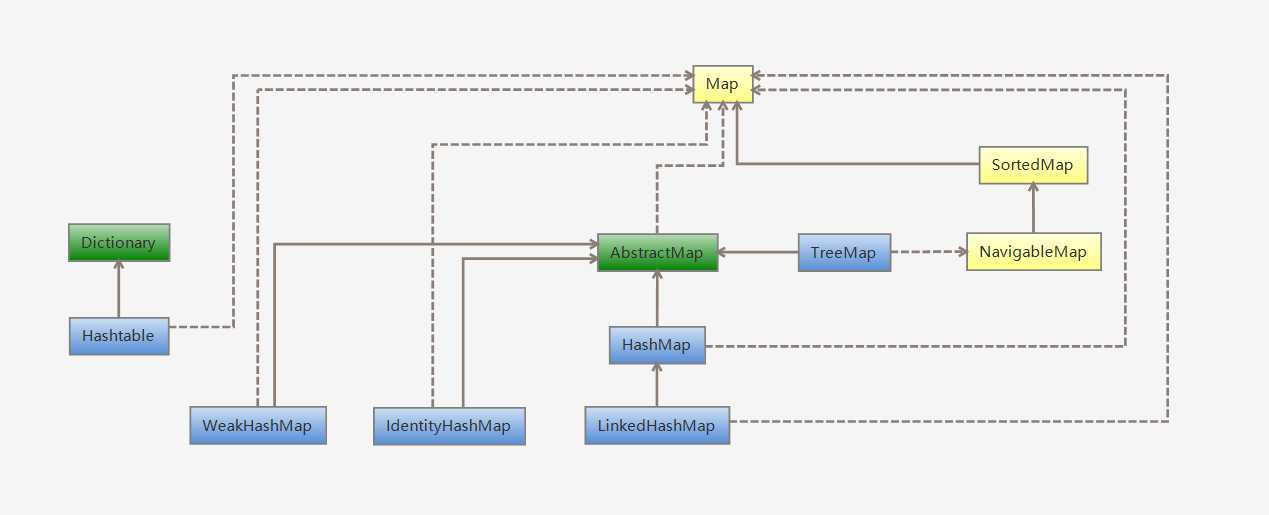
Map:
因为 ArrayList 是基于数组实现的,所以支持快速随机访问。RandomAccess 接口标识着该类支持快速随机访问。
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
可以看出,默认初始大小为10。
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
* 共享空数组实例,用于默认大小的空实例。
* 我们将其与EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA区分开来,以了解添加第一个元素时应该膨胀多少。
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
* 存储ArrayList元素的数组缓冲区。
* ArrayList的容量是这个数组缓冲区的长度。
* 任何带有elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA的空ArrayList
* 将在添加第一个元素时扩展为DEFAULT_CAPACITY。
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate (unless necessary).
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
可以看到构造函数分为3种:
DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection‘s
* iterator.
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// defend against c.toArray (incorrectly) not returning Object[]
// (see e.g. https://bugs.openjdk.java.net/browse/JDK-6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
添加元素的时候要检查当前数组是否存满,如果存满了,需要使用grow()方法进行扩容。
从源码中可以看出,新容量大小为oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1),也就是原来数组大小的1.5倍。
扩容需要调用Arrays.copyOf()方法将原数组复制到新数组中,代价较高,所以就像在讨论构造函数时所说,最好是在初始化时就指定好容量大小,减少扩容次数。
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length) // 检查是否需要扩容
elementData = grow();
elementData[s] = e;
size = s + 1;
}
public boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
add(e, elementData, size);
return true;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
modCount++;
final int s;
Object[] elementData;
if ((s = size) == (elementData = this.elementData).length)
elementData = grow();
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + 1,
s - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size = s + 1;
}
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData,
newCapacity(minCapacity));
}
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(size + 1);
}
private int newCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity <= 0) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA)
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return minCapacity;
}
return (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE <= 0)
? newCapacity
: hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
}
删除元素需要调用System.arraycopy()将index + 1后面的元素都复制到前一个位置上,时间复杂度是O(N),代价较高
public E remove(int index) {
Objects.checkIndex(index, size);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
}
快速失败(fail—fast):在用迭代器遍历一个集合对象时,如果遍历过程中对集合对象的内容进行了修改(增加、删除、修改),则会抛出Concurrent Modification Exception。
modCount 用来记录 ArrayList 结构发生变化的次数。
结构发生变化是指添加或者删除至少一个元素的所有操作,或者是调整内部数组的大小,仅仅只是设置元素的值不算结构发生变化。
在进行序列化或者迭代等操作时,需要比较操作前后 modCount 是否改变,如果改变了需要抛出 ConcurrentModificationException。
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out element count, and any hidden stuff
int expectedModCount = modCount;
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone()
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
s.writeObject(elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
下面是迭代器部分的源码,可以看到,在对其进行操作前,要比较前后modCount是否改变。
注意:单线程环境下,remove()方法最后会让expectModCount和modCount相等,所以不会抛出异常。
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such
int expectedModCount = modCount;
// prevent creating a synthetic constructor
Itr() {}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
int i = cursor;
if (i >= size)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;
if (i >= elementData.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
cursor = i + 1;
return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);
cursor = lastRet;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int size = ArrayList.this.size;
int i = cursor;
if (i < size) {
final Object[] es = elementData;
if (i >= es.length)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
for (; i < size && modCount == expectedModCount; i++)
action.accept(elementAt(es, i));
// update once at end to reduce heap write traffic
cursor = i;
lastRet = i - 1;
checkForComodification();
}
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
它的实现与ArrayList类似,但是它是线程安全的,方法使用了synchronized进行同步。
RandomAccess 接口标识着该类支持快速随机访问。
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
/**
* The array buffer into which the components of the vector are
* stored. The capacity of the vector is the length of this array buffer,
* and is at least large enough to contain all the vector‘s elements.
*
* <p>Any array elements following the last element in the Vector are null.
*
* @serial
*/
protected Object[] elementData;
/**
* The number of valid components in this {@code Vector} object.
* Components {@code elementData[0]} through
* {@code elementData[elementCount-1]} are the actual items.
*
* @serial
*/
protected int elementCount; // size()方法
/**
* The amount by which the capacity of the vector is automatically
* incremented when its size becomes greater than its capacity. If
* the capacity increment is less than or equal to zero, the capacity
* of the vector is doubled each time it needs to grow.
*
* @serial
*/
protected int capacityIncrement; // 用于扩容
构造函数有4种:
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
elementCount = elementData.length;
// defend against c.toArray (incorrectly) not returning Object[]
// (see e.g. https://bugs.openjdk.java.net/browse/JDK-6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
添加时会判断是否还有容量添加,如果不够,那么使用grow()函数进行扩容。
如何扩容根据成员变量capacityIncrement决定
capacityIncrement <= 0,那么新容量 = 老容量 * 2,即:newCapacity = oldCapacity + oldCapacity;capacityIncrement > 0,那么新容量 = 老容量 + capacityIncrement,即:newCapacity = oldCapacity + capacityIncrement;根据上述构造函数可以发现:如果没有指定capacityIncrement,那么默认为0,也就是说,默认情况下,Vector每次扩容容量都会翻倍。
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow();
elementData[s] = e;
elementCount = s + 1;
}
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
add(e, elementData, elementCount);
return true;
}
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData,
newCapacity(minCapacity));
}
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(elementCount + 1);
}
private int newCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity <= 0) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return minCapacity;
}
return (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE <= 0)
? newCapacity
: hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
}
可以使用 Collections.synchronizedList(); 得到一个线程安全的 ArrayList。
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> synList = Collections.synchronizedList(list);
原理如下:
调用Collections.synchronizedList(list),会调用new SynchronizedRandomAccessList<>(list)
public static <T> List<T> synchronizedList(List<T> list) {
return (list instanceof RandomAccess ?
new SynchronizedRandomAccessList<>(list) :
new SynchronizedList<>(list));
}
SynchronizedRandomAccessList是类Collections的一个内部类,继承自SynchronizedList,所以会调用父类的构造方法
static class SynchronizedRandomAccessList<E>
extends SynchronizedList<E>
implements RandomAccess {
SynchronizedRandomAccessList(List<E> list) {
super(list);
}
// ...
}
SynchronizedList是类Collections的另一个内部类,继承自SynchronizedCollection,继续调用父类的构造方法,内部有许多List特有的方法,用synchronized修饰了一下,使其线程安全
static class SynchronizedList<E>
extends SynchronizedCollection<E>
implements List<E> {
final List<E> list;
SynchronizedList(List<E> list) {
super(list);
this.list = list;
}
// 内部定义了许多使用synchronized修饰的方法,主要是List特有的方法
public void add(int index, E element) {
synchronized (mutex) {list.add(index, element);}
}
public E remove(int index) {
synchronized (mutex) {return list.remove(index);}
}
// ...
}
SynchronizedCollection是类Collections的另一个内部类,内部定义了许多集合共有的方法,用synchronized修饰,使其线程安全
static class SynchronizedCollection<E> implements Collection<E>, Serializable {
final Collection<E> c; // Backing Collection
final Object mutex; // Object on which to synchronize
SynchronizedCollection(Collection<E> c) {
this.c = Objects.requireNonNull(c);
mutex = this;
}
// 内部定义了许多使用synchronized修饰的方法,集合共有的方法
public boolean add(E e) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.add(e);}
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
synchronized (mutex) {return c.remove(o);}
}
// ...
}
也可以使用 concurrent 并发包下的 CopyOnWriteArrayList 类。
List<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
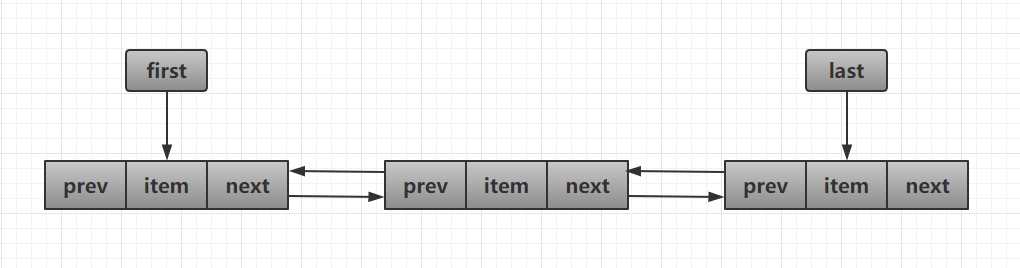
基于双向链表实现,使用Node存储链表节点信息。
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
每个链表有first和last指针,指向首尾节点。
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last;
HashMap可以分为两个版本解读,JDK7和JDK8,两个版本有着很大的不同,可以说JDK7 的设计存在一些缺陷,而JDK8对其进行了相当大的改进。
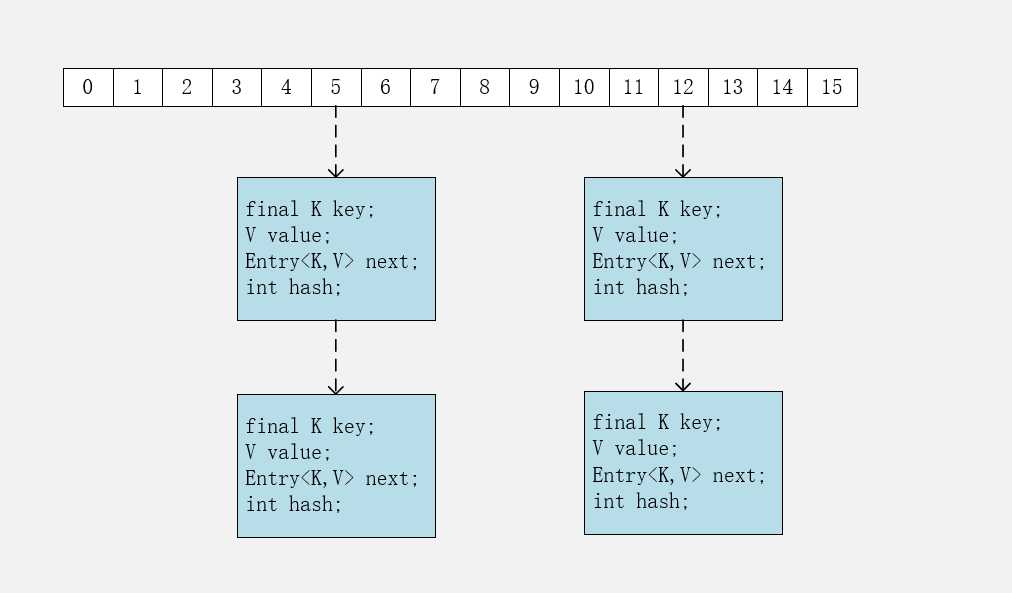
经典的哈希表实现:数组 + 链表,并且使用拉链法解决冲突问题。
包含了一个Entry类型的数组table
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
int hash;
// ...
}
从代码中可以看到,Entry存储了键值对。包含了4个字段,从next字段可以看出,Entry是一个链表。
数组中的每个位置被当成一个桶,一个桶存放一个链表。
使用拉链法解决冲突,同一个链表中存放哈希值和散列桶取模运算结果相同的Entry。
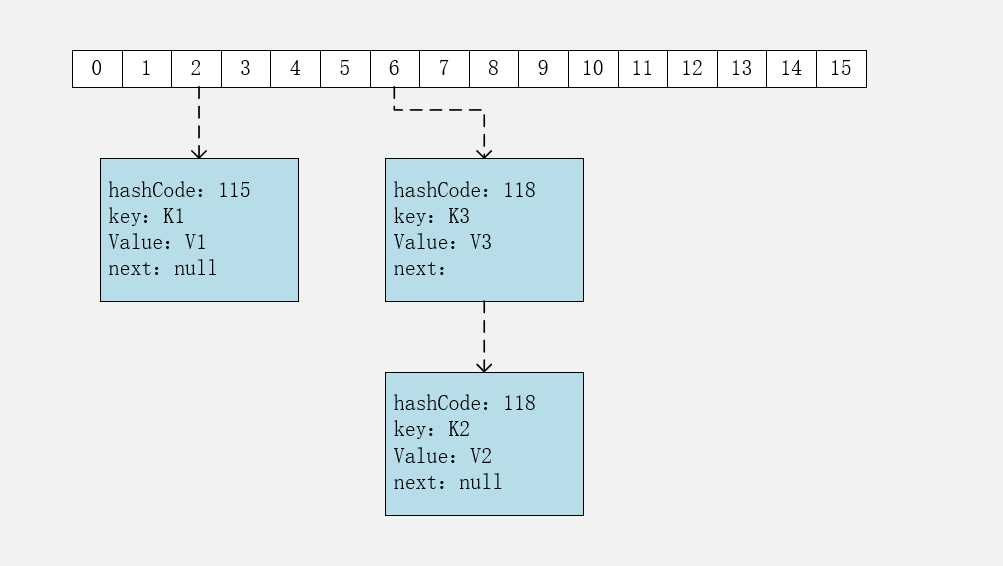
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("K1", "V1");
map.put("K2", "V2");
map.put("K3", "V3");
应该注意到链表的插入是以头插法方式进行的,例如上面的 <K3,V3> 不是插在 <K2,V2> 后面,而是插入在链表头部。
查找需要分成两步进行:
public V put(K key, V value) {
// hashmap一开始不申请内存,直到使用时才初始化
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
// 对null键单独操作
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
// 确认桶下标
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
// 如果存在该键,那么更新value
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
// 不存在该键,存入键值对
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
HashMap 允许插入键为 null 的键值对。但是因为无法调用 null 的 hashCode() 方法,也就无法确定该键值对的桶下标,只能通过强制指定一个桶下标来存放。HashMap 使用第 0 个桶存放键为 null 的键值对。
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
// 存在null键,那么更新value
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
// 不存在null键,添加null键值对
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}
使用链表的头插法,也就是新的键值对插在链表的头部,而不是链表的尾部。
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
// 头插法,链表头部指向新的键值对
// 新节点的next指向e中保存的原来的头
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
从注释中可以看出,写了这么复杂的hash函数的主要原因就是,防止一些质量低的哈希函数造成在低比特位上的碰撞太多
/**
* Retrieve object hash code and applies a supplemental hash function to the
* result hash, which defends against poor quality hash functions. This is
* critical because HashMap uses power-of-two length hash tables, that
* otherwise encounter collisions for hashCodes that do not differ
* in lower bits. Note: Null keys always map to hash 0, thus index 0.
*/
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
令 x = 1<<4,即 x 为 2 的 4 次方,它具有以下性质:
x : 0001 0000
x-1 : 0000 1111
令一个数 y 与 x-1 做与运算,可以去除 y 位级表示的第 4 位以上数:
y : 1011 0010
x-1 : 0000 1111
y&(x-1) : 0000 0010
这个性质和 y 对 x 取模效果是一样的:
y : 1011 0010
x : 0001 0000
y%x : 0000 0010
我们知道,位运算的代价比求模运算小的多,因此在进行这种计算时用位运算的话能带来更高的性能。
确定桶下标的最后一步是将 key 的 hash 值对桶个数取模:hash % capacity,如果能保证 capacity 为 2 的 n 次方,那么就可以将这个操作转换为位运算。
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
由此,可以得出一个面试题的答案。
Q:为什么hashmap的容量要是2的n次幂?
A: 由于将取模操作转化为位运算,需要capacity为2的幂数。
设 HashMap 的 table 长度为 $M$,需要存储的键值对数量为 $N$,如果哈希函数满足均匀性的要求,那么每条链表的长度大约为 $N/M$,因此平均查找次数的复杂度为 $O(N/M)$。
为了让查找的成本降低,应该尽可能使得$ N/M$ 尽可能小,因此需要保证 M 尽可能大,也就是说 table 要尽可能大。HashMap 采用动态扩容来根据当前的 N 值来调整 M 值,使得空间效率和时间效率都能得到保证。
和扩容相关的参数主要有:capacity、size、threshold 和 load_factor。
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| capacity | table 的容量大小,默认为 16。需要注意的是 capacity 必须保证为 2 的 n 次方。 |
| size | 键值对数量。 |
| threshold | size 的临界值,当 size 大于等于 threshold 就必须进行扩容操作。 |
| loadFactor | 装载因子,table 能够使用的比例,threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor)。 |
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
transient Entry[] table;
transient int size;
int threshold;
final float loadFactor;
transient int modCount;
从下面的添加元素的代码可以看出,当需要扩容时,capacity为原来的2倍。
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
扩容使用resize()实现,扩容操作需要调用transfer()函数,把所有的oldTable中的键值对重新插入到newTable中,这一步是非常耗时的,所以,建议在声明HashMap时指定容量,以空间换时间。
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
/**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}
在进行扩容时,需要把键值对重新计算桶下标,从而放到对应的桶上。在前面提到,HashMap 使用 hash % capacity ?来确定桶下标。
HashMap capacity 为 2 的 n 次方这一特点能够极大降低重新计算桶下标操作的复杂度。
假设原数组长度 capacity 为 16,扩容之后 new capacity 为 32:
capacity : 0001 0000
new capacity : 0010 0000
对于一个 Key,它的哈希值 hash 在第 5 位:
JDK8的改进:
下面的注释,说出了为什么树化阈值为8
/*
* Because TreeNodes are about twice the size of regular nodes, we
* use them only when bins contain enough nodes to warrant use
* (see TREEIFY_THRESHOLD). And when they become too small (due to
* removal or resizing) they are converted back to plain bins. In
* usages with well-distributed user hashCodes, tree bins are
* rarely used. Ideally, under random hashCodes, the frequency of
* nodes in bins follows a Poisson distribution
* (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poisson_distribution) with a
* parameter of about 0.5 on average for the default resizing
* threshold of 0.75, although with a large variance because of
* resizing granularity. Ignoring variance, the expected
* occurrences of list size k are (exp(-0.5) * pow(0.5, k) /
* factorial(k)). The first values are:
*
* 0: 0.60653066
* 1: 0.30326533
* 2: 0.07581633
* 3: 0.01263606
* 4: 0.00157952
* 5: 0.00015795
* 6: 0.00001316
* 7: 0.00000094
* 8: 0.00000006
* more: less than 1 in ten million
*/
根据注释可以看出,只有当桶中的元素足够多的时候(TREEIFY_THRESHOLD),才会树化,变成红黑树结构。当扩容或者删除节点,桶中元素变少时,又会从树结构变回链表结构。
当使用分布非常好得hashCode的时候,红黑树很少被用到。
理想情况下,在完全随机的hashCode中,桶中节点数符合泊松分布,当桶中节点数为8时的概率已经足够小了,所以选择8作为阈值。
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
HashMap 构造函数允许用户传入的容量不是 2 的 n 次方,因为它可以自动地将传入的容量转换为 2 的 n 次方。
先考虑如何求一个数的掩码,对于 1001 0000,它的掩码为 1111 1111,可以使用以下方法得到:
mask |= mask >> 1 1101 1000
mask |= mask >> 2 1111 1110
mask |= mask >> 4 1111 1111
mask+1 是大于原始数字的最小的 2 的 n 次方。
num 1001 0000
mask + 1 1000 0000
以下是 HashMap 中计算数组容量的代码:
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 没初始化,进行初始化
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 桶中无节点,直接添加
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
// 存在相同键值,保存到e中,后续覆盖
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 节点是红黑树,使用红黑树的插入操作
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else { // 节点是链表
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
// 链表中没找到,插入一个新节点
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 如果超过了变树阈值,进行树化
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 存在相同键值,已经存到了e中,后续覆盖
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 上面找到了键相同的节点,那么覆盖掉对应的value
if (e != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
标签:原因 ack sed imu struct edm 最好 move 存储结构
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/mytlx/p/12923067.html