标签:tps 方式 static col 字符串的操作 监听 hash算法 次数 ash
Java的字符串拼接问题已经是老生常谈的问题了,目前遇到一个业务场景是,在游戏底层新使用了一套事件监听的组件,字符串作为事件的条件值,所以需要较为频繁的拼接和将数字转换为字符串,去匹配事件监听的条件。在条件值已知有限的情况下,可不可以通过空间换时间的方式,用HashMap缓存条件对应字符串的关系,去优化频繁字符串拼接与转换的执行效率?测试如下:
public class TestString { public static long startMs; public static void main(String[] args) { testStringBuilder(); testCache(); } public static void testStringBuilder() { TestString testString = new TestString(); String className = testString.getClass().getSimpleName(); int max = 10000000; // 开始计时 startMs = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int b = 0; b <= max / 10000; b++) { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { String s = className + i; doSomething(s); } } System.out.println("testStringBuilder结束,循环次数:" + max + ",耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMs) + "ms"); } public static void testCache() { Map<Class<?>, Map<Integer, String>> cache = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, String> temp = new HashMap<>(); Class<?> testClass = TestString.class; int max = 10000000; for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { String s = testClass.getSimpleName() + i; temp.put(i, s); } cache.put(testClass, temp); // 开始计时 startMs = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int b = 0; b <= max / 10000; b++) { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { String s = cache.get(testClass).get(i); doSomething(s); } } System.out.println("testCache结束,循环次数:" + max + ",耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMs) + "ms"); } public static void doSomething(String result) { // System.out.println(result); } }
假定条件样本为1万份不重复,循环1千万次字符串拼接/Map获取操作。JDK8中,通过+号的方式动态的拼接字符串,会被编译器优化为StringBuilder.append()方法,是效率较高的字符串拼接方式。 多次运行,平均结果如下:
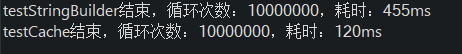
通过HashMap缓存映射关系比每次都去拼接字符串执行速度快了差不读4倍,还是比较明显的
public class TestString2 { public static long startMs; public static void main(String[] args) { testIntegerToString(); testCacheMap(); } public static void testIntegerToString() { int max = 10000000; startMs = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int b = 0; b <= max / 10000; b++) { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { String s = Integer.toString(i); // String s = String.valueOf(i); 方法内部也是调用Integer.toString方法 doSomething(s); } } System.out.println("testToString结束,循环次数:" + max + ",耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMs) + "ms"); } public static void testCacheMap() { Map<Integer, String> temp = new HashMap<>(); int max = 10000000; for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { String s = Integer.toString(i); temp.put(i, s); } // ========== 开始计时 ========== startMs = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int b = 0; b <= max / 10000; b++) { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { String s = temp.get(i); doSomething(s); } } System.out.println("testCache结束,循环次数:" + max + ",耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMs) + "ms"); } public static void doSomething(String result) { // System.out.println(result); } }
假定条件样本为1万份不重复,循环1千万次对1到10000的数字转换为字符串的操作/Map获取操作。Integer.toString(i)的方式与String.valueOf(i)的方式相同,String.valueOf方法内部也是调用的Integer.toString方法。多次运行,平均结果如下:
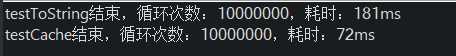
可以看出执行效率相差也是比较多的,执行速度大约相差了2.5倍。
Hash算法确实是很快,如果业务场景需要拼接或转换为字符串的操作特别频繁,要拼接字符串的基本字符串有一定规则、可以穷举,并且内存大小在可承受的范围内时,可以采用多级Hash提前缓存映射关系,可以大程度提升执行速度,是典型的空间换时间。
标签:tps 方式 static col 字符串的操作 监听 hash算法 次数 ash
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/feng-gamer/p/12965499.html