标签:管程 flag tran 对象 强制 timeout watch public 机制
进程:正在执行的程序。
线程:可以理解成进程中独立运行的子任务,一个进程至少有一个线程。
多线程:一个进程中有多个线程。
继承Thread类。
public class TestThread extends Thread{
@Override
//重写run方法
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("我在学习"+(i+1));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread testThread = new TestThread();
testThread.start();//调用start()方法实现多线程
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("我在睡觉"+(i+1));
}
}
}
实现Runnable接口。
public class TestRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
System.out.println("我在学习"+(i+1));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestRunnable testRunnable = new TestRunnable();
new Thread(testRunnable).start();//代理
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("我在睡觉"+(i+1));
}
}
}
通过Callable和Future创建线程。
public class TestCallable implements Callable<Boolean> {//自定义返回值,还可以抛出异常
@Override
public Boolean call() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("我在学习"+(i+1));
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
TestCallable testCallable = new TestCallable();
//创建执行服务
ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
//提交执行
Future<Boolean> result = ser.submit(testCallable);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("我在睡觉"+(i+1));
}
//获取结果
boolean r1 = result.get();
//关闭服务
ser.shutdownNow();
}
}
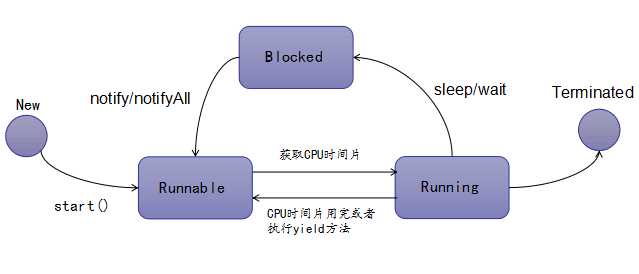
Thread.sleep(1000):线程休眠1s。Thread.yield():礼让看CPU心情。Thread.join():等到此线程执行完,再执行其他线程。Thread.State
NEW
尚未启动的线程处于此状态。
RUNNABEL
在Java虚拟机中执行的线程处于此状态
BLOCKED
被阻塞等待监视器锁定的线程处于此状态。
WAITTING
正在等待另一个线程执行特定动作的线程处于此状态。
TIMED_WAITTING
正在等待另一个线程执行动作达到指定等待时间的线程处于此状态。
TERMINATED
已退出的线程处于此状态。
线程的优先级用数字表示,范围从1~10。
使用getPriority()、setPriority()获取或者改变优先级。
优先级低只是意味着获得CPU调度的概率低。
线程分为用户线程和守护线程。
虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕。
虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕。
thread.setDaemon(true):设置为守护线程。
不安全的买票:
public class UnsafeBuyTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuyTicket station = new BuyTicket();
new Thread(station,"小猪").start();
new Thread(station,"小鸡").start();
new Thread(station,"小狗").start();
}
}
class BuyTicket implements Runnable{
private int ticketNums = 10;
boolean flag = true;//外部停止方式
@Override
public void run() {
while(flag){
try {
buy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public void buy() throws InterruptedException {
if(ticketNums <= 0){
flag = false;
return;
}
Thread.sleep(100);//模拟延时,放大问题的发生性
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"抢到第"+ticketNums--+"张票。");
}
}
不安全的取钱:
public class UnsafeBank {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = new Account(100, "结婚基金");
Drawing me = new Drawing(account,50,"我");
Drawing anotherMe = new Drawing(account,100,"平行空间里的我");
me.start();
anotherMe.start();
}
}
//账户
class Account{
int money;
String name;
public Account(int money, String name){
this.name = name;
this.money = money;
}
}
//银行
class Drawing extends Thread{
int nowMoney;
Account account;
int drawingMoney;
String name;
public Drawing(Account account, int drawingMoney, String name){
super(name);
this.account = account;
this.drawingMoney =drawingMoney;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if(account.money-drawingMoney < 0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"钱不够,取不了!");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
account.money = account.money-drawingMoney;
nowMoney = nowMoney+drawingMoney;
System.out.println(account.name+"余额为:"+account.money);
System.out.println(this.getName()+"手里的钱:"+nowMoney);
}
}
不安全的集合:
public class UnsafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
安全的买票:将买票方法设置为同步方法public synchronized void buy(){}。
public class SafeBuyTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BuyTicket station = new BuyTicket();
new Thread(station,"小猪").start();
new Thread(station,"小鸡").start();
new Thread(station,"小狗").start();
}
}
class BuyTicket implements Runnable{
private int ticketNums = 10;
boolean flag = true;//外部停止方式
@Override
public void run() {
while(flag){
try {
buy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public synchronized void buy() throws InterruptedException {
if(ticketNums <= 0){
flag = false;
return;
}
Thread.sleep(100);//模拟延时,放大问题的发生性
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"抢到第"+ticketNums--+"张票。");
}
}
安全的取钱:用同步代码块锁住Account对象。
public class SafeBank {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = new Account(100, "结婚基金");
Drawing me = new Drawing(account,50,"我");
Drawing anotherMe = new Drawing(account,100,"平行空间里的我");
me.start();
anotherMe.start();
}
}
//账户
class Account{
int money;
String name;
public Account(int money, String name){
this.name = name;
this.money = money;
}
}
//银行
class Drawing extends Thread{
int nowMoney;
Account account;
int drawingMoney;
String name;
public Drawing(Account account, int drawingMoney, String name){
super(name);
this.account = account;
this.drawingMoney =drawingMoney;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (account){
if(account.money-drawingMoney < 0){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"钱不够,取不了!");
return;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
account.money = account.money-drawingMoney;
nowMoney = nowMoney+drawingMoney;
System.out.println(account.name+"余额为:"+account.money);
System.out.println(this.getName()+"手里的钱:"+nowMoney);
}
}
}
安全的集合:用同步代码块锁住List对象,这里也可以用线程安全的CopyOnWriteArrayList集合。
public class SafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
synchronized(list){
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
产生死锁的四个必要条件:
从JDK 5.0 开始,Java提供了更强大的线程同步机制,通过显示定义同步锁对象来实现同步。同步锁使用Lock对象。
锁提供了对共享资源的独占访问,每次只能有一个线程对Lock对象加锁,线程开始访问共享资源之前应先获得Lock对象。
ReentrantLock(可重入锁)类实现了Lock,它拥有了与synchronized相同的并发性和内存语义,在实现线程安全的控制中,比较常用的是ReentrantLock,可以显式加锁、释放锁。
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
lock.lock();
//业务逻辑...
lock.unlock();//如果同步代码有异常,可以将解锁操作放到try...catch的finally里
synchronized和Lock的区别:
Java提供了几个方法来解决线程之间的通信问题。
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| wait() | 表示线程一直等待,直到其他线程通知,与sleep不同,会释放锁。 |
| wait(long timeout) | 指定等待的毫秒数。 |
| notify() | 唤醒一个处于等待状态的线程。 |
| notifyAll() | 唤醒同一个对象上所有调用wait()方法的线程,优先级高的线程优先调度。 |
生产者消费者模式:
管程法(利用缓冲区)
public class PAC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Container container = new Container();
new Producer(container).start();
new Customer(container).start();
}
}
class Producer extends Thread{
Container container;
public Producer(Container container){
this.container = container;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
container.push(new Chicken(i));
System.out.println("生产了"+i+"只鸡");
}
}
}
class Customer extends Thread{
Container container;
public Customer(Container container){
this.container = container;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("消费了"+container.pop().id+"只鸡");
}
}
}
class Chicken{
int id;
public Chicken(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
class Container{
Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10];
int cnt = 0;
public synchronized void push(Chicken chicken){
//如果容器满了,等待消费者消费
if(cnt == chickens.length){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
chickens[cnt] = chicken;
cnt++;
this.notifyAll();
}
public synchronized Chicken pop(){
//判断能否消费
if(cnt == 0){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
cnt--;
Chicken chicken = chickens[cnt];
this.notifyAll();
return chicken;
}
}
信号灯法(利用标志位)
public class PAC2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV tv = new TV();
new Performer(tv).start();
new Viewer(tv).start();
}
}
class Performer extends Thread{
private TV tv;
public Performer(TV tv){
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
if(i%2 == 0){
this.tv.perform("小猪佩奇");
}else{
this.tv.perform("哆啦A梦");
}
}
}
}
class Viewer extends Thread{
private TV tv;
public Viewer(TV tv){
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
tv.watch();
}
}
}
class TV{
private String program;
boolean flag = true;
public synchronized void perform(String program){
if(!flag){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("演员表演了"+program);
this.notifyAll();
this.program = program;
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
public synchronized void watch(){
if(flag){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("观众观看了"+program);
this.notifyAll();
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
}
提前创建好多个线程,放入线程池,使用时直接获取,使用完放回池中。
使用线程池的好处:
JDK 5.0起提供了线程池相关的API:ExecutorService和Executors。
public class ThreadPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);//创建容量为10的线程池
service.execute(new Thread(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());}));//开启线程
service.execute(new Thread(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());}));
service.execute(new Thread(()->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());}));
service.shutdown();
}
}
标签:管程 flag tran 对象 强制 timeout watch public 机制
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/baihan/p/12994181.html