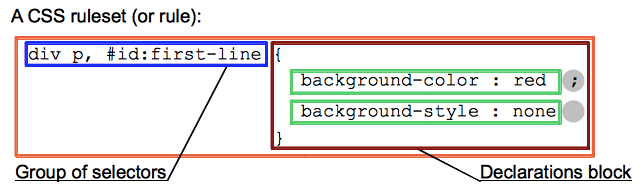
CSS选择器和规则:
在css声明块前添加一个选择器,用来指明将css声明应用在哪些元素上。
如图所示:
标签选择器
标签选择器又叫元素选择器,换句话说,文档的元素就是最基本的选择器,使用元素名称直接选中元素即可。
演示代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>标签选择器</title>
<style>
div{
border:1px solid #ccc;
}
p{
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bolder;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>你好,标签选择器!</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>类选择器
类选择以点"."开头,后面紧跟一个类名。类名不允许有空格,与元素中class属性的值保持一致。一个元素可以有多个class的值,每个值通过空格分割开。类名相同的元素属于一类元素。
演示代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>类选择器</title>
<style>
.first{font-weight: bold;}
.third{font-size: 2em;}
.done {color: orange;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li class="first done">Create an HTML document</li>
<li class="second done">Create a CSS style sheet</li>
<li class="third done">Link them all together</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>ID选择器
ID选择器以"#"开头,后面紧跟一个ID名,在一个文档中,ID值不能重复,因此在选择文档中唯一元素的时候该选择器比较有用。
演示代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>ID选择器</title>
<style>
#polite {font-family: cursive;}
#rude {
font-family: monospace;
text-transform: uppercase;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p id="polite"> — "Good morning."</p>
<p id="rude"> — "Go away!"</p>
</body>
</html>普遍选择器
使用"*”来表示普遍选择器,表示选择所有元素,通常用在组合选择器中。
演示代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>普遍选择器</title>
<style>
.left-nav > * {
width:200px;
background-color:#fafafa;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<article class="left-nav">
<dl>
<dt>推荐</dt>
<dd>发现音乐</dd>
</dl>
<dl>
<dt>我的音乐</dt>
<dd>下载的音</dd>
</dl>
</article>
</body>
</html>层次选择器
后代选择器( descendant selector )
使用 “ ” 隔开两个选择器。
例如 :“ul li”表示选择ul的后代元素li,li可以为ul的直接子元素,也可以为ul的孙子元素。
子代选择器(child selector)
使用 “>” 隔开两个选择器。
例如:"ul>li"表示选择ul的直接子代元素li,ul的孙子元素li无法被选择到。
相邻同胞选择器(adjacent sibling selector)
使用 “+” 隔开两个选择器。
例如:".one+*"表示选择class为"one"元素的下一个兄弟元素。
一般同胞选择器( general sibling selector)
使用 “~” 隔开两个选择器。
例如:".one~*"表示选择class为"one"元素的所有兄弟元素。
演示代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>层次选择器</title>
<style>
.container li {color: orange;}
.header {overflow: hidden;}
.header > div {
float: left;
line-height: 3em;
height: 3em;
}
.header > .loginInfo > .list {display: none;}
.aa li:nth-child(2) + li{color: lightblue;}
.bb li:nth-child(2) ~ *{color: pink;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<!-- 头部 -->
<div class="header">
<div class="logo">LOGO</div>
<div class="loginInfo">
欢迎您,张三
<div class="list">
<a href="#">注销</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 体部 -->
<div class="content">
<p>这是一个网页</p>
<hr>
<div class="aa">
<ul>
<li>one</li>
<li>two</li>
<li>three</li>
<li>four</li>
<li>five</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 尾部 -->
<div class="footer">
<p>版权信息</p>
</div>
<div class="bb">
<ul>
<li>one</li>
<li>two</li>
<li>three</li>
<li>four</li>
<li>five</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>属性选择器
[attr] 选择具有attr属性的元素、无论该属性的值为什么。
[attr=val] 选择具有attr属性的、并且attr的值为val元素。
[attr~=val] 选择具有attr属性的、并且attr的值之一为val的元素。
[attr^=val] 选择具有attr属性的、并且attr的值以val开头的元素。
[attr$=val] 选择具有attr属性的、并且attr的值以val结尾的元素。
[attr*=val] 选择具有attr属性的、并且attr的值包含val的元素。
演示代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>属性选择器</title>
<style>
button[name=del]{border:2px solid red;}
button[name~=btn]{border:2px dotted orange;}
button[name*=d]{color: blue;}
#studentForm input[name=password] { border:1px solid lightblue; }
input[name$=e] {border:1px solid green;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container row">
<button class="addBtn" name="add btn">添加</button>
<button class="delBtn" name="del">删除</button>
<button class="updBtn" name="upd">修改</button>
<button name="search btn">搜索</button>
</div>
<br>
<form action="" id="studentForm">
姓名: <input type="text" name="username"> <br><br>
密码:<input type="text" name="password"> <br><br>
性别:
<label>
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="male"> 男
</label>
<label>
<input type="radio" name="gender" value="female"> 女
</label> <br>
</form>
</body>
</html>伪类选择器
伪类以":"开头,用在选择器后,用于指明元素在某种特殊的状态下才能被选中。
表示子元素的
:only-child
:first-child
:last-child
:nth-child(n) 、: nth-last-child(n)
:first-of-type、:last-of-type 、
:nth-of-type(n)、:nth-last-of-type(n)
——n可以为元素的序号,也可以为特殊的字符,比如“odd”,“even
元素状态相关
:hover、 :active、 :focus
:enabled、 :disabled;:checked、 :default
:invalid、 :valid、 :required、 :optional、 :in-range 、:out-of-range
演示代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伪类选择器</title>
<style>
ul.top_nav > li:nth-child(2n+1){
background-color: orange;
}
dl > *:nth-of-type(2){background-color: #ccc;}
li {cursor: pointer;}
li:hover {
background-color: yellow;
color: #fff;
}
a:active {color: green; }
input[name=username]:focus {border:1px solid pink;}
body ,ul,ol,dl {
margin: 0 ;
padding: 0;
}
ul,ol,dl {list-style: none;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul class="top_nav">
<li>国内新闻</li>
<li>国际新闻</li>
<li>明星八卦</li>
<li>NBA赛事</li>
<li>时事热点</li>
<li>娱乐周刊</li>
<li>国内外交</li>
<li>文化输出</li>
<li>综合国力</li>
<li>科技发展</li>
</ul>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">百度一下</a>
<input type="text" name="username"><br><br>
<dl>
<dt>小学一年级</dt>
<dd>1班</dd>
<dd>2班</dd>
<dt>小学二年级</dt>
<dd>1班</dd>
<dd>2班</dd>
<dt>小学三年级</dt>
<dd>1班</dd>
<dd>2班</dd>
</dl>
</body>
</html>伪元素选择器
伪元素以"::"开头,用在选择器后,用于选择指定的元素。
如:
::after
::before
::first-letter
::first-line
::selection
演示代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伪元素选择器</title>
<style>
ul.top_nav > li:nth-child(2n+1){background-color: #ccc;}
li {cursor: pointer;}
li:hover {
background-color:orange;
color: #fff;
}
body,ul,ol{margin: 0;padding: 0;}
ul,ol {list-style: none;}
.top_nav {background-color: #ededed;}
.top_nav::after{
content: ‘‘;
display: block;
clear: both;
}
.top_nav > li {
float: left;
line-height: 3em;
height: 3em;
padding: 0 1em;
}
p::first-letter {color: red;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul class="top_nav">
<li>国内新闻</li>
<li>国际新闻</li>
<li>明星八卦</li>
<li>NBA赛事</li>
<li>时事热点</li>
<li>娱乐周刊</li>
<li>国内外交</li>
<li>文化输出</li>
<li>综合国力</li>
<li>科技发展</li>
</ul>
<p>hello world</p>
<p>good morming</p>
</body>
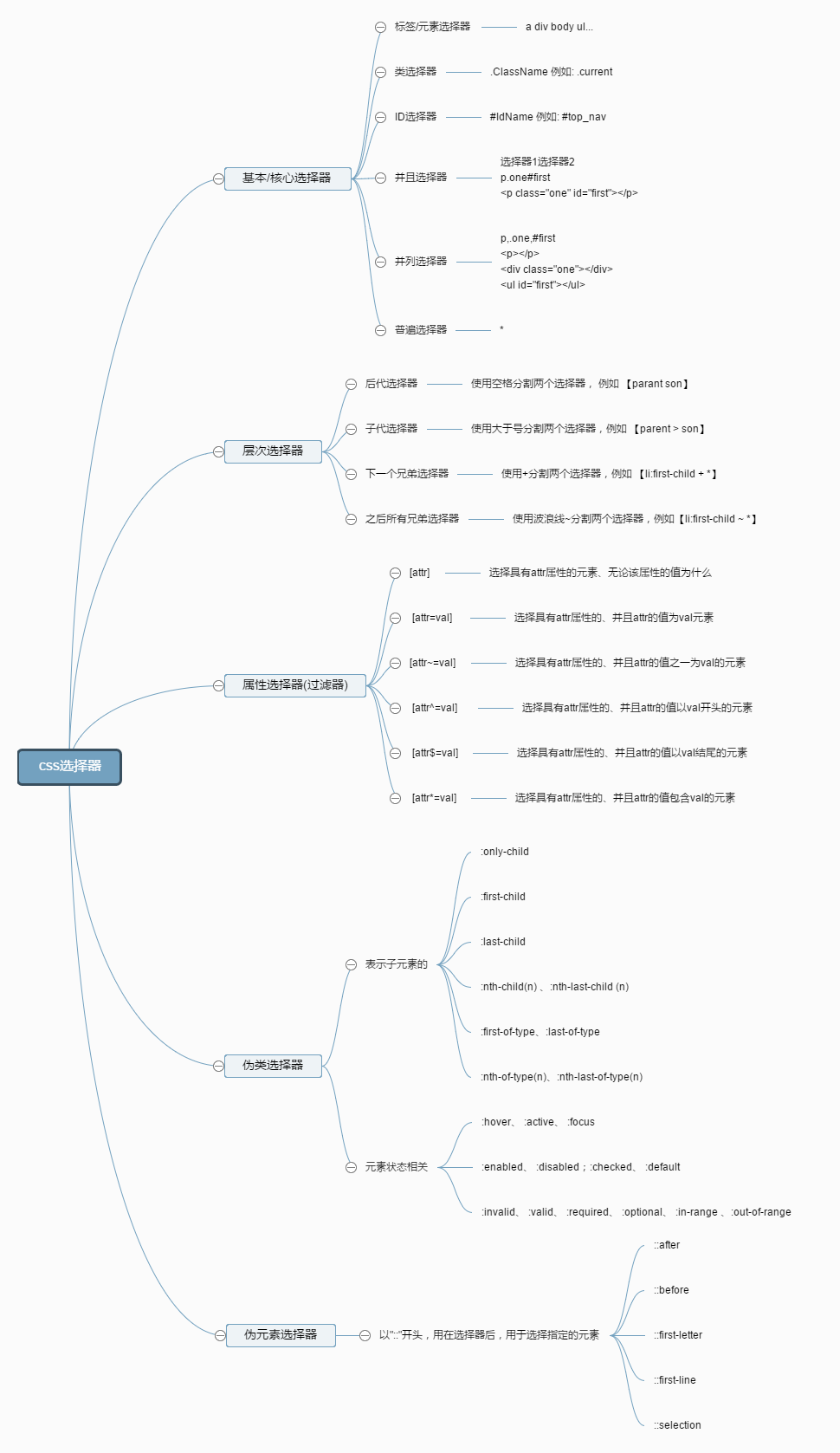
</html>以上就是在CSS中常见的选择器,下面用两张图来总结和归纳。
CSS选择器的分类
CSS选择器元素/属性简介
以上就是我关于CSS选择器的理解与运用,后续有任何补充或修改均会在此基础上添加,有任何问题欢迎指出,谢谢!