标签:spn logs class 传递 sde develop tab 自定义 env
原文:.NET CORE 中间件
对于中间件我们其实并不陌生,在.NET CORE出现之前中间件的概念在OWIN应用程序中就已经普遍使用了。
中间件官方定义: 中间件是一种集成到应用管道中间来处理请求和响应的模块,每个中间件可以:
ASP.NETCORE中的中间件本质上是一个请求委托 Func< RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware。
RequestDelegate本身也是一个委托,定义为 public delegate Task RequestDelegate(HttpContext Context)。
在ASP.NETCORE请求管道中,形成一条委托链。
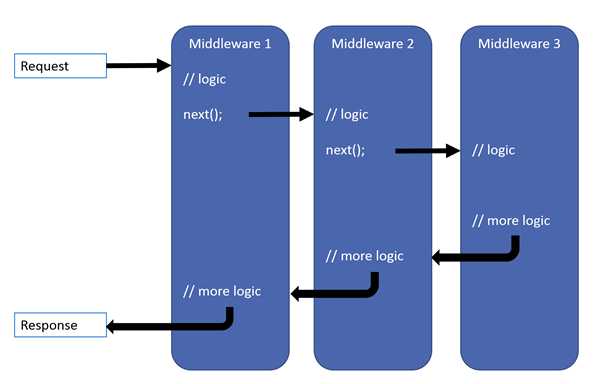
请求管道短路:当委托不选择将请求传递到下一个委托时,称之为“短路”。
在ASP.NETCORE中,使用 IApplicationBuilder 来创建/插入中间件管道。提供了 Run和Use 两类方式。依赖组件包 Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Abstractions
Run是一种 约定 的终端管道,即短路,不再执行下一个委托
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.Run(async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello world 1"); });
//这里不会执行到!!
app.Run(async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello world 2"); });
}
Use通常以扩展方法提供中间件,很适合处理一些AOP的事务。
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
//可以在invoke之前做一些事
await next.Invoke();
//可以在invoke之后做一些事
});
app.Run(async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello world"); });
}
实际开发中我们通常需要自己定义中间件,有两种方式可以实现。
public class RequestIdInRequestMiddleware
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public RequestIdInRequestMiddleware(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public Task Invoke(HttpContext httpContext,IService service)
{
service.SayHello();
//request head 加入requestid
var requestId = Guid.NewGuid().ToString("n");
httpContext.Request.Headers.Add("REQUESTID", requestId);
return _next(httpContext);
}
}
如上有以下约定:
RequestDelegate 的参数公共构造函数Invoke 或 InvokeAsync 的公共方法,且此方法必须:
TaskHttpContext目前官方是推荐使用约定方式, 注意:该方式加入管道中的生命周期为单例。也因此如果依赖一些Service,建议从Invoke 或 InvokeAsync的方法参数注入,而不是从构造函数注入。(可以想想为什么?单例构造函数注入对Service的生命周期有要求~~)。
官方也提供了IMiddleware接口,用于扩展创建中间件。这种方式有两个优点:
可以按需(生命周期)注入
中间件强类型话,更易理解
public class RequestIdInResponseMiddleware:IMiddleware
{
private readonly IService _service;
public RequestIdInResponseMiddleware(IService service)
{
_service = service;
}
public Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context, RequestDelegate next)
{
var requestId = Guid.NewGuid().ToString("n");
context.Response.Headers.Add("REQUESTID", requestId);
return next(context);
}
}
中间件一般都是基于IApplicationBuilder扩展方法加入管道。
public static class RequestIdMiddlewareExtensions
{
public static IApplicationBuilder UseRequestIdInResponseMiddleware(this IApplicationBuilder builder)
{
return builder.UseMiddleware<RequestIdInResponseMiddleware>();
}
}
可以在 Configure 方法中调用加入 app.UseRequestIdInResponseMiddleware();
如果是 强类型 方式创建的Middleware,还需要在 ConfigureServices 中注册 services.AddSingleton<RequestIdInResponseMiddleware>();
中间件显著受加入的顺序影响,官方提供的默认中间件顺序图
Map 扩展用来约定创建管道分支,和管道短路类似,不过它是基于给定的请求路径匹配项来创建请求管道分支。官方提供的例子,
public class Startup
{
private static void HandleMapTest1(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Map Test 1");
});
}
private static void HandleMapTest2(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Map Test 2");
});
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
app.Map("/map1", HandleMapTest1);
app.Map("/map2", HandleMapTest2);
app.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello from non-Map delegate. <p>");
});
}
}
根据请求会响应不同结果
| 请求 | 响应 |
|---|---|
| localhost:1234 | Hello from non-Map delegate. |
| localhost:1234/map1 | Map Test 1 |
| localhost:1234/map2 | Map Test 2 |
| localhost:1234/map3 | Hello from non-Map delegate. |
另外还可以使用 UseWhen 创建管道分支,只有匹配一定条件才会短路管道。
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app)
{
//只有请求url包含查询字符串变量 branch,才会短路管道
app.UseWhen(context => context.Request.Query.ContainsKey("branch"),
builder => builder.Use(async (context, next) =>
{
var branchVer = context.Request.Query["branch"];
// Do work that doesn‘t write to the Response.
await next();
// Do other work that doesn‘t write to the Response.
}));
app.Run(async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello from main pipeline.");
});
}
针对中间件的单元测试,可以使用 TestServer 来进行。它有以下几个优点:
HttpContexthttp请求发送模拟可以使用 HttpClient 和 HttpContext ,分别可以验证Response和Request Context相关功能。下面分别测试RequestIdInRequestMiddleware,RequestIdInResponseMiddleware。
新建xunit单元测试项目,加入依赖包: Microsoft.AspNetCore.TestHost , Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting 。
测试代码如下:
public class MiddlewareTest
{
/// <summary>
/// HttpContext模拟,验证request header是否成功加入requestId
/// </summary>
[Fact]
public void MiddlewareTest_RequestHeaderExistRequestId()
{
var hostBuilder = new HostBuilder()
.ConfigureWebHost(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder
.UseTestServer()
.ConfigureServices((context, services) =>
{
services.AddTransient<IService, MyService>();
})
.Configure(app =>
{
app.UseRequestIdInRequestMiddleware();
});
});
using (var host = hostBuilder.Start())
{
var context = host.GetTestServer().SendAsync(c =>
{
c.Request.Path = "/map";
c.Request.Method = HttpMethods.Get;
}).Result;
Assert.True(context.Request.Headers.ContainsKey("REQUESTID"));
}
}
/// <summary>
/// HttpClient模拟,验证response header是否成功加入requestId
/// </summary>
[Fact]
public void MiddlewareTest_ResponseHeaderExistRequestId()
{
var hostBuilder = new HostBuilder()
.ConfigureWebHost(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder
.UseTestServer()
.ConfigureServices((context, services) =>
{
services.AddSingleton<RequestIdInResponseMiddleware>();
services.AddTransient<IService, MyService>();
})
.Configure(app =>
{
app.UseRequestIdInResponseMiddleware();
});
});
using (var host = hostBuilder.Start())
{
host.GetTestServer().CreateRequest("/map").GetAsync()
.ContinueWith(task =>
{
var response = task.Result;
Assert.True(response.Headers.Contains("REQUESTID"));
}).Wait();
}
}
}标签:spn logs class 传递 sde develop tab 自定义 env
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lonelyxmas/p/13046540.html