标签:pie 定时任务 绑定 启动服务 来源 initial 客户 步骤 异步执行
1.工作原理示意图:
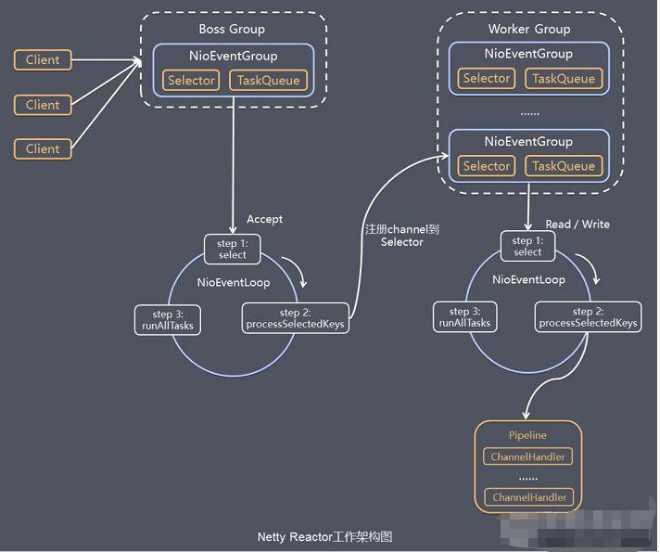
说明:
1. Netty抽象出两组线程池 BossGroup 专门负责接收客户端的连接, WorkerGroup 专门负责网络的读写
2. BossGroup 和 WorkerGroup 类型都是 NioEventLoopGroup
3. NioEventLoopGroup 相当于一个事件循环组, 这个组中含有多个事件循环 ,每一个事件循环是 NioEventLoop
4. NioEventLoop 表示一个不断循环的执行处理任务的线程, 每个NioEventLoop 都有一个selector , 用于监听绑定在其上的socket的网络通讯
5. NioEventLoopGroup 可以有多个线程, 即可以含有多个NioEventLoop
6. 每个Boss中NioEventLoop 循环执行的步骤有3步
a. 轮询accept 事件
b. 处理accept 事件 , 与client建立连接 , 生成NioScocketChannel , 并将其注册到某个worker中NIOEventLoop上的selector
c. 处理任务队列的任务 ,即 runAllTasks
7. 每个 Worker中NIOEventLoop 循环执行的步骤
a. 轮询read, write 事件
b. 处理i/o事件, 即read , write 事件,在对应NioScocketChannel 处理
c. 处理任务队列的任务 , 即 runAllTasks
8. 每个Worker NIOEventLoop 处理业务时,会使用pipeline(管道), pipeline 中包含了 channel , 即通过pipeline 可以获取到对应通道, 管道中维护了很多的 处理器
2. Netty快速入门实例-TCP服务
2.1. 客户端
public class NettyClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //客户端需要一个事件循环组 EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { //创建客户端启动对象 //注意客户端使用的不是 ServerBootstrap 而是 Bootstrap Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); //设置相关参数 bootstrap.group(group) //设置线程组 .channel(NioSocketChannel.class) // 设置客户端通道的实现类(反射) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { System.out.println("客户socketchannel=" + ch.hashCode()); ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyClientHandler()); //加入自己的处理器 } }); System.out.println("客户端 ok.."); //启动客户端去连接服务器端 //关于 ChannelFuture 要分析,涉及到netty的异步模型 ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 6668).sync(); //给关闭通道进行监听 channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { group.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
2.2. 客户端-自定义处理类
/** * 自定义Handler类 */ public class NettyClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { //当通道就绪就会触发该方法 @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("client " + ctx); //Unpooled是Netty提供的用来操作缓冲区的工具类。 ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello, 服务端!!!!我是客户端......", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } //当通道有读取事件时,会触发 @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println("服务器回复的消息:" + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); System.out.println("服务器的地址: "+ ctx.channel().remoteAddress()); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
2.3. 服务端
public class NettyServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { //创建BossGroup 和 WorkerGroup //说明 //1. 创建两个线程组 bossGroup 和 workerGroup //2. bossGroup 只是处理连接请求 , 真正的和客户端业务处理,会交给 workerGroup完成 //3. 两个都是无限循环 //4. bossGroup 和 workerGroup 含有的子线程(NioEventLoop)的个数 // 默认实际 cpu核数 * 2 /** * 模拟1个bossGroup子线程+8个workerGroup工作 * 1.设置参数 * 2.启动服务器 * 3.打开多个客户端 * 4.控制台查看线程名 */ EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); //默认线程数:cpu核数*2=8 try { //创建服务器端的启动对象,配置参数 ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); //使用链式编程来进行设置 bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) //设置两个线程组 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) //使用NioServerSocketChannel 作为服务器的通道实现 .option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) // 设置线程队列得到连接个数 .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true) //设置保持活动连接状态 // .handler(null) // 该 handler对应 bossGroup , childHandler 对应 workerGroup .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {//创建一个通道初始化对象(匿名对象) //给pipeline 设置处理器 @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { /* 可以使用一个集合管理 SocketChannel, 再推送消息时, 可以将业务加入到各个channel 对应的 NIOEventLoop 的 taskQueue 或者 scheduleTaskQueue */ System.out.println("客户端socketchannel=" + ch.hashCode()); ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyServerHandler()); } }); // 给我们的workerGroup 的 EventLoop 对应的管道设置处理器 System.out.println(".....服务器 is ready..."); //绑定一个端口并且同步, 生成了一个 ChannelFuture 对象 //启动服务器(并绑定端口) ChannelFuture cf = bootstrap.bind(6668).sync(); //给cf 注册监听器,监控我们关心的事件 cf.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { if (cf.isSuccess()) { System.out.println("监听端口 6668 成功"); } else { System.out.println("监听端口 6668 失败"); } } }); //对关闭通道进行监听 cf.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } }
2.4. 服务端处理类
/** * 自定义Handler类,给workerGroup的eventLoop对应管道设置处理器 */ public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { //读取数据实际(这里我们可以读取客户端发送的消息) /* 1. ChannelHandlerContext ctx:上下文对象, 含有 管道pipeline , 通道channel, 地址 2. Object msg: 就是客户端发送的数据 默认Object */ @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { /** * 模拟同步超时 */ /*Thread.sleep(50 * 1000); ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("模拟超时.....", CharsetUtil.UTF_8));*/ /** *模拟异步任务-> 异步执行 -> 提交该channel 对应的 *NIOEventLoop 的 taskQueue中 */ // 解决方案1 用户程序自定义的普通任务 /*ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(50 * 1000); ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("服务端模拟异步超时,线程1....", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); System.out.println("channel code=" + ctx.channel().hashCode()); } catch (Exception ex) { System.out.println("发生异常" + ex.getMessage()); } } }); ctx.channel().eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(50 * 1000); ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("服务端模拟异步超时,线程2....", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); System.out.println("channel code=" + ctx.channel().hashCode()); } catch (Exception ex) { System.out.println("发生异常" + ex.getMessage()); } } });*/ //解决方案2 : 用户自定义定时任务 -》 该任务是提交到 scheduleTaskQueue中 ctx.channel().eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(5 * 1000); ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("服务器模拟定时任务.....", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } catch (Exception ex) { System.out.println("发生异常" + ex.getMessage()); } } }, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); System.out.println("go on ..."); /** * 控制台查看workerGroup线程名 */ System.out.println("服务器读取线程 :" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ,channle =" + ctx.channel()); Channel channel = ctx.channel(); ChannelPipeline pipeline = ctx.pipeline(); //本质是一个双向链接, 出站入站 /** * 将 msg 转成一个 ByteBuf ByteBuf 是 Netty 提供的,不是 NIO 的 ByteBuffer. */ ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg; System.out.println("收到客户端消息:" + buf.toString(CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); System.out.println("客户端地址:" + channel.remoteAddress()); } //数据读取完毕 @Override public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //writeAndFlush 是 write + flush //将数据写入到缓存,并刷新 //一般讲,我们对这个发送的数据进行编码 //发送给客户端消息 ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello, 客户端!!!!我是服务端.......", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); } //处理异常, 一般是需要关闭通道 @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { ctx.close(); } }
备注:本文资源来源于B站韩顺平讲师,表示感谢!
标签:pie 定时任务 绑定 启动服务 来源 initial 客户 步骤 异步执行
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/hyy9527/p/13064616.html