标签:back nio isp disco klist keep img cas 消费
Android中触摸事件类对应MotionEvent类,主要事件有三种:ACTION_DOWN、ACTION_MOVE、ACTION_UP。
屏幕上一次触摸事件,ACTION_DOWN、ACTION_UP事件是必须的,而ACTION_MOVE事件,依照实际操作确定,Move事件从Down事件点下开发,移动一定距离后触发一定阀值后才会触发ACTION_MOVE事件。
1. 事件分发(dispatch):事件分发对应dispatchTouchEvent()方法,在Android中触发的事件都是由dispatchTouchEvent()方法分发的,在Activity、ViewGroup、View都有此方法。
事件分发源码:
/** * Pass the touch screen motion event down to the target view, or this * view if it is the target. * * @param event The motion event to be dispatched. * @return True if the event was handled by the view, false otherwise. */ public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { ... }
方法返回值:true 当前事件被消费掉,事件不在继续分发。反之 false 或者 super.dispatchTouchEvent(event)方法为返回值,事件继续分发。如果当前视图是ViewGroup与其子类,则调用onInterceptTouchEvent()拦截事件方法,由此方法判断事件是否拦截。
2. 事件拦截(Intercept):事件拦截对应onInterceptTouchEvent()方法,onInterceptTouchEvent()方法只在ViewGroup中存在,而Activity、View中不存在此方法。
事件拦截源码:
/** * Implement this method to intercept all touch screen motion events. This * allows you to watch events as they are dispatched to your children, and * take ownership of the current gesture at any point. * * <p>Using this function takes some care, as it has a fairly complicated * interaction with {@link View#onTouchEvent(MotionEvent) * View.onTouchEvent(MotionEvent)}, and using it requires implementing * that method as well as this one in the correct way. Events will be * received in the following order: * * <ol> * <li> You will receive the down event here. * <li> The down event will be handled either by a child of this view * group, or given to your own onTouchEvent() method to handle; this means * you should implement onTouchEvent() to return true, so you will * continue to see the rest of the gesture (instead of looking for * a parent view to handle it). Also, by returning true from * onTouchEvent(), you will not receive any following * events in onInterceptTouchEvent() and all touch processing must * happen in onTouchEvent() like normal. * <li> For as long as you return false from this function, each following * event (up to and including the final up) will be delivered first here * and then to the target‘s onTouchEvent(). * <li> If you return true from here, you will not receive any * following events: the target view will receive the same event but * with the action {@link MotionEvent#ACTION_CANCEL}, and all further * events will be delivered to your onTouchEvent() method and no longer * appear here. * </ol> * * @param ev The motion event being dispatched down the hierarchy. * @return Return true to steal motion events from the children and have * them dispatched to this ViewGroup through onTouchEvent(). * The current target will receive an ACTION_CANCEL event, and no further * messages will be delivered here. */ public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { if (ev.isFromSource(InputDevice.SOURCE_MOUSE) && ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN && ev.isButtonPressed(MotionEvent.BUTTON_PRIMARY) && isOnScrollbarThumb(ev.getX(), ev.getY())) { return true; } return false; }
返回值:true 表示此事件被拦截,然后交由onTouchEvent()方法消费,反之 false 表示不拦截此事件,事件继续分发。
3. 事件消费(Consume):事件消费对应onTouchEvent()方法。Activity、ViewGroup、View都有此方法。
事件消费源码:
/** * Implement this method to handle touch screen motion events. * <p> * If this method is used to detect click actions, it is recommended that * the actions be performed by implementing and calling * {@link #performClick()}. This will ensure consistent system behavior, * including: * <ul> * <li>obeying click sound preferences * <li>dispatching OnClickListener calls * <li>handling {@link AccessibilityNodeInfo#ACTION_CLICK ACTION_CLICK} when * accessibility features are enabled * </ul> * * @param event The motion event. * @return True if the event was handled, false otherwise. */ public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { ... }
返回值:true 表示事件被消费,不再向父视图传递。反之 false 当前View不消费此事件,事件传递给父视图的onTouchEvent()方法。
PS:
Activity中有dispatchTouchEvent()和onTouchEvent()方法。
ViewGroup中有dispatchTouchEvent()、onInterceptTouchEvent()、onTouchEvent()方法。
View中有dispatchTouchEvent()和onTouchEvent()方法。
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(), View.OnClickListener, View.OnTouchListener { companion object { val TAG = MainActivity::class.java.simpleName } private val mCustomView: CustomTextView by lazy { findViewById<CustomTextView>(R.id.CustomView) } @SuppressLint("ClickableViewAccessibility") override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) mCustomView.setOnClickListener(this) mCustomView.setOnTouchListener(this) } override fun dispatchTouchEvent(event: MotionEvent): Boolean { when (event.action) { MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> Log.d(TAG, " dispatchTouchEvent down") MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> Log.d(TAG, " dispatchTouchEvent up") } return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event) } override fun onTouchEvent(event: MotionEvent): Boolean { when (event.action) { MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> Log.d(TAG, " onTouchEvent down") MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> Log.d(TAG, " onTouchEvent up") } return super.onTouchEvent(event) } override fun onClick(v: View) { if (R.id.CustomView == v.id) { Log.d(TAG, "onClick") } } override fun onTouch(v: View, event: MotionEvent): Boolean { when (event.action) { MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> Log.d(TAG, " ACTION_DOWN") MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> Log.d(TAG, " ACTION_UP") } return false } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#FFFFFFFF" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <com.example.learnandroidforkotlin.Views.CustomViewGroup android:layout_width="300dp" android:layout_height="200dp" android:background="#00BCD4" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"> <com.example.learnandroidforkotlin.Views.CustomTextView android:id="@+id/CustomView" android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:background="#FF9800" android:paddingStart="60dp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" /> </com.example.learnandroidforkotlin.Views.CustomViewGroup> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
@SuppressLint("AppCompatCustomView")
class CustomViewGroup @JvmOverloads constructor(
context: Context,
attr: AttributeSet?,
defStyleAttr: Int,
defStyleRes: Int
) : RelativeLayout(context, attr, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes) {
companion object {
val TAG = CustomViewGroup::class.java.simpleName
}
constructor(context: Context) : this(context, null)
constructor(context: Context, attr: AttributeSet?) : this(context, attr, 0)
constructor(context: Context, attr: AttributeSet?, defStyleAttr: Int) : this(
context,
attr,
defStyleAttr,
0
)
override fun dispatchTouchEvent(event: MotionEvent): Boolean {
when(event.action) {
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> Log.d(TAG + " dispatchTouchEvent: ", " down")
MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> Log.d(TAG + " dispatchTouchEvent: ", " up")
}
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event)
}
override fun onInterceptTouchEvent(event: MotionEvent): Boolean {
when(event.action) {
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> Log.d(TAG + " nInterceptTouchEvent: ", " down")
MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> Log.d(TAG + " onInterceptTouchEvent: ", " up")
}
return super.onInterceptTouchEvent(event)
}
override fun onTouchEvent(event: MotionEvent): Boolean {
when(event.action) {
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> Log.d(TAG + " onTouchEvent: ", " down")
MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> Log.d(TAG + " onTouchEvent: ", " up")
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event)
}
}
class CustomTextView @JvmOverloads constructor( context: Context, attr: AttributeSet?, defStyleAttr: Int, defStyleRes: Int ) : RelativeLayout(context, attr, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes) { companion object { val TAG = CustomTextView::class.java.simpleName } constructor(context: Context) : this(context, null) constructor(context: Context, attr: AttributeSet?) : this(context, attr, 0) constructor(context: Context, attr: AttributeSet?, defStyleAttr: Int) : this( context, attr, defStyleAttr, 0 ) override fun dispatchTouchEvent(event: MotionEvent): Boolean { when(event.action) { MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> Log.d(TAG + " dispatchTouchEvent: ", " down") MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> Log.d(TAG + " dispatchTouchEvent: ", " up") } return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event) } override fun onInterceptTouchEvent(event: MotionEvent): Boolean { when(event.action) { MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> Log.d(TAG + " onInterceptTouchEvent: ", " down") MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> Log.d(TAG + " onInterceptTouchEvent: ", " up") } return super.onInterceptTouchEvent(event) } override fun onTouchEvent(event: MotionEvent): Boolean { when(event.action) { MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN -> Log.d(TAG + " onTouchEvent: ", " down") MotionEvent.ACTION_UP -> Log.d(TAG + " onTouchEvent: ", " up") } return super.onTouchEvent(event) } }
结果1,View事件未被消费:
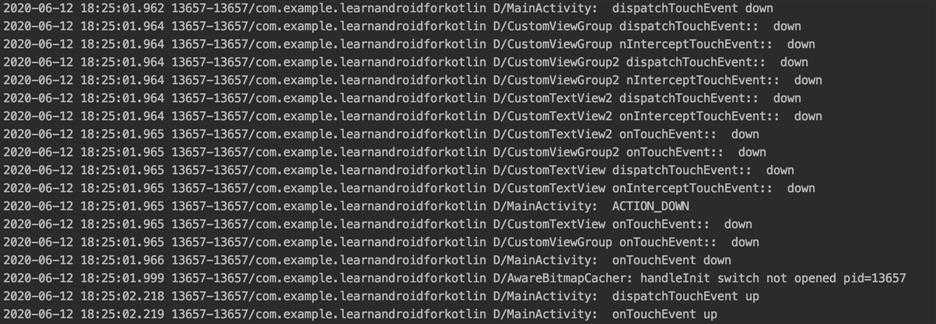
结果2,View事件被消费:
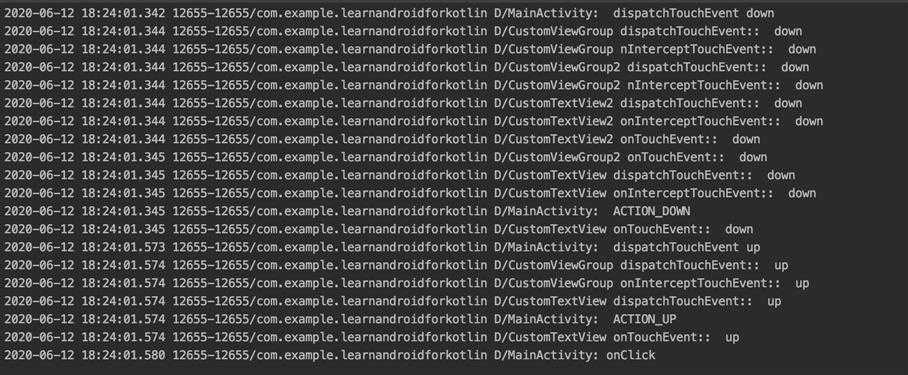
PS:Android中一次完整的事件执行,分三个阶段:1. 事件分发;2. 事件拦截;3. 事件消费(事件消费后不再向父视图传递,未被消费则继续向父视图传递);每个阶段都有不同分支执行,效果不同。重点是事件是否继续分发,是否拦截,是否被消费。
举例说明:
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="#FFFFFFFF" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <com.example.learnandroidforkotlin.Views.CustomViewGroup android:id="@+id/CustomViewGroup1" android:layout_width="300dp" android:layout_height="200dp" android:background="#00BCD4" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"> <com.example.learnandroidforkotlin.Views.CustomViewGroup2 android:id="@+id/CustomViewGroup2" android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:background="#FF5722" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"> <com.example.learnandroidforkotlin.Views.CustomTextView android:id="@+id/CustomView" android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="50dp" android:background="#009688" android:paddingStart="60dp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" /> <com.example.learnandroidforkotlin.Views.CustomTextView2 android:id="@+id/CustomView2" android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="50dp" android:background="#FF9800" android:paddingStart="60dp" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" /> </com.example.learnandroidforkotlin.Views.CustomViewGroup2> </com.example.learnandroidforkotlin.Views.CustomViewGroup> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
事件通过ClickListener进行事件绑定,下面以setOnClickListener()方法绑定事件为例说明流程,事件绑定setOnClickListener()方法源码:
@UiThread public class View implements Drawable.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback, AccessibilityEventSource { /** * Register a callback to be invoked when this view is clicked. If this view is not * clickable, it becomes clickable. * * @param l The callback that will run * * @see #setClickable(boolean) */ public void setOnClickListener(@Nullable OnClickListener l) { if (!isClickable()) { setClickable(true); } getListenerInfo().mOnClickListener = l; } /** * Enables or disables click events for this view. When a view * is clickable it will change its state to "pressed" on every click. * Subclasses should set the view clickable to visually react to * user‘s clicks. * * @param clickable true to make the view clickable, false otherwise * * @see #isClickable() * @attr ref android.R.styleable#View_clickable */ public void setClickable(boolean clickable) { setFlags(clickable ? CLICKABLE : 0, CLICKABLE); } /** * Set flags controlling behavior of this view. * * @param flags Constant indicating the value which should be set * @param mask Constant indicating the bit range that should be changed */ @UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = Build.VERSION_CODES.P, trackingBug = 115609023) void setFlags(int flags, int mask) { final boolean accessibilityEnabled = AccessibilityManager.getInstance(mContext).isEnabled(); final boolean oldIncludeForAccessibility = accessibilityEnabled && includeForAccessibility(); int old = mViewFlags; mViewFlags = (mViewFlags & ~mask) | (flags & mask); int changed = mViewFlags ^ old; if (changed == 0) { return; } int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags; boolean shouldNotifyFocusableAvailable = false; // If focusable is auto, update the FOCUSABLE bit. int focusableChangedByAuto = 0; if (((mViewFlags & FOCUSABLE_AUTO) != 0) && (changed & (FOCUSABLE_MASK | CLICKABLE)) != 0) { // Heuristic only takes into account whether view is clickable. final int newFocus; if ((mViewFlags & CLICKABLE) != 0) { newFocus = FOCUSABLE; } else { newFocus = NOT_FOCUSABLE; } mViewFlags = (mViewFlags & ~FOCUSABLE) | newFocus; focusableChangedByAuto = (old & FOCUSABLE) ^ (newFocus & FOCUSABLE); changed = (changed & ~FOCUSABLE) | focusableChangedByAuto; } /* Check if the FOCUSABLE bit has changed */ if (((changed & FOCUSABLE) != 0) && ((privateFlags & PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS) != 0)) { if (((old & FOCUSABLE) == FOCUSABLE) && ((privateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) != 0)) { /* Give up focus if we are no longer focusable */ clearFocus(); if (mParent instanceof ViewGroup) { ((ViewGroup) mParent).clearFocusedInCluster(); } } else if (((old & FOCUSABLE) == NOT_FOCUSABLE) && ((privateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) == 0)) { /* * Tell the view system that we are now available to take focus * if no one else already has it. */ if (mParent != null) { ViewRootImpl viewRootImpl = getViewRootImpl(); if (!sAutoFocusableOffUIThreadWontNotifyParents || focusableChangedByAuto == 0 || viewRootImpl == null || viewRootImpl.mThread == Thread.currentThread()) { shouldNotifyFocusableAvailable = canTakeFocus(); } } } } final int newVisibility = flags & VISIBILITY_MASK; if (newVisibility == VISIBLE) { if ((changed & VISIBILITY_MASK) != 0) { /* * If this view is becoming visible, invalidate it in case it changed while * it was not visible. Marking it drawn ensures that the invalidation will * go through. */ mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN; invalidate(true); needGlobalAttributesUpdate(true); // a view becoming visible is worth notifying the parent about in case nothing has // focus. Even if this specific view isn‘t focusable, it may contain something that // is, so let the root view try to give this focus if nothing else does. shouldNotifyFocusableAvailable = hasSize(); } } if ((changed & ENABLED_MASK) != 0) { if ((mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED) { // a view becoming enabled should notify the parent as long as the view is also // visible and the parent wasn‘t already notified by becoming visible during this // setFlags invocation. shouldNotifyFocusableAvailable = canTakeFocus(); } else { if (isFocused()) clearFocus(); } } if (shouldNotifyFocusableAvailable && mParent != null) { mParent.focusableViewAvailable(this); } /* Check if the GONE bit has changed */ if ((changed & GONE) != 0) { needGlobalAttributesUpdate(false); requestLayout(); if (((mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == GONE)) { if (hasFocus()) { clearFocus(); if (mParent instanceof ViewGroup) { ((ViewGroup) mParent).clearFocusedInCluster(); } } clearAccessibilityFocus(); destroyDrawingCache(); if (mParent instanceof View) { // GONE views noop invalidation, so invalidate the parent ((View) mParent).invalidate(true); } // Mark the view drawn to ensure that it gets invalidated properly the next // time it is visible and gets invalidated mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN; } if (mAttachInfo != null) { mAttachInfo.mViewVisibilityChanged = true; } } /* Check if the VISIBLE bit has changed */ if ((changed & INVISIBLE) != 0) { needGlobalAttributesUpdate(false); /* * If this view is becoming invisible, set the DRAWN flag so that * the next invalidate() will not be skipped. */ mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN; if (((mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == INVISIBLE)) { // root view becoming invisible shouldn‘t clear focus and accessibility focus if (getRootView() != this) { if (hasFocus()) { clearFocus(); if (mParent instanceof ViewGroup) { ((ViewGroup) mParent).clearFocusedInCluster(); } } clearAccessibilityFocus(); } } if (mAttachInfo != null) { mAttachInfo.mViewVisibilityChanged = true; } } if ((changed & VISIBILITY_MASK) != 0) { // If the view is invisible, cleanup its display list to free up resources if (newVisibility != VISIBLE && mAttachInfo != null) { cleanupDraw(); } if (mParent instanceof ViewGroup) { ViewGroup parent = (ViewGroup) mParent; parent.onChildVisibilityChanged(this, (changed & VISIBILITY_MASK), newVisibility); parent.invalidate(true); } else if (mParent != null) { mParent.invalidateChild(this, null); } if (mAttachInfo != null) { dispatchVisibilityChanged(this, newVisibility); // Aggregated visibility changes are dispatched to attached views // in visible windows where the parent is currently shown/drawn // or the parent is not a ViewGroup (and therefore assumed to be a ViewRoot), // discounting clipping or overlapping. This makes it a good place // to change animation states. if (mParent != null && getWindowVisibility() == VISIBLE && ((!(mParent instanceof ViewGroup)) || ((ViewGroup) mParent).isShown())) { dispatchVisibilityAggregated(newVisibility == VISIBLE); } notifySubtreeAccessibilityStateChangedIfNeeded(); } } if ((changed & WILL_NOT_CACHE_DRAWING) != 0) { destroyDrawingCache(); } if ((changed & DRAWING_CACHE_ENABLED) != 0) { destroyDrawingCache(); mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID; invalidateParentCaches(); } if ((changed & DRAWING_CACHE_QUALITY_MASK) != 0) { destroyDrawingCache(); mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID; } if ((changed & DRAW_MASK) != 0) { if ((mViewFlags & WILL_NOT_DRAW) != 0) { if (mBackground != null || mDefaultFocusHighlight != null || (mForegroundInfo != null && mForegroundInfo.mDrawable != null)) { mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW; } else { mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW; } } else { mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW; } requestLayout(); invalidate(true); } if ((changed & KEEP_SCREEN_ON) != 0) { if (mParent != null && mAttachInfo != null && !mAttachInfo.mRecomputeGlobalAttributes) { mParent.recomputeViewAttributes(this); } } if (accessibilityEnabled) { // If we‘re an accessibility pane and the visibility changed, we already have sent // a state change, so we really don‘t need to report other changes. if (isAccessibilityPane()) { changed &= ~VISIBILITY_MASK; } if ((changed & FOCUSABLE) != 0 || (changed & VISIBILITY_MASK) != 0 || (changed & CLICKABLE) != 0 || (changed & LONG_CLICKABLE) != 0 || (changed & CONTEXT_CLICKABLE) != 0) { if (oldIncludeForAccessibility != includeForAccessibility()) { notifySubtreeAccessibilityStateChangedIfNeeded(); } else { notifyViewAccessibilityStateChangedIfNeeded( AccessibilityEvent.CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_UNDEFINED); } } else if ((changed & ENABLED_MASK) != 0) { notifyViewAccessibilityStateChangedIfNeeded( AccessibilityEvent.CONTENT_CHANGE_TYPE_UNDEFINED); } } } }
通过上面代码可以看出事件与View间绑定,通过View.mViewFlags成员变量进行状态保存。通过状态判断View与事件是否绑定。
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { final float x = event.getX(); final float y = event.getY(); final int viewFlags = mViewFlags; final int action = event.getAction(); final boolean clickable = ((viewFlags & CLICKABLE) == CLICKABLE || (viewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE) || (viewFlags & CONTEXT_CLICKABLE) == CONTEXT_CLICKABLE; ... }
View.mViewFlags 定义:
@UiThread public class View implements Drawable.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback, AccessibilityEventSource { /** * The view flags hold various views states. * * Use {@link #setTransitionVisibility(int)} to change the visibility of this view without * triggering updates. * {@hide} */ @ViewDebug.ExportedProperty(formatToHexString = true) @UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = Build.VERSION_CODES.P) int mViewFlags; ... }
PS:在View类上面使用了注解@UIThread表示View在UI线程执行。
onTouch()方法优于onClick()方法执行。
标签:back nio isp disco klist keep img cas 消费
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/naray/p/13099030.html