标签:process OLE intval 常用方法 player 学习 lag 方便 情况
包装类就是将基本数据类型封装在一个类之中,就好比如下的代码:
范例:定义一个包装类
class MyInt {
private int num ;
public MyInt(int num) {
this.num = num ;
}
public int intValue() {
return this.num ;
}
}
这时MyInt实际上就是一个int型数据的包装类,利用MyInt可以实现基本数据类型变为对象的需求。
范例:包装类的使用
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// 子类对象自动向Object转型,变为父类对象
Object obj = new MyInt(17) ; ;
MyInt temp = (MyInt)obj ; // 取出内容需要向下转型
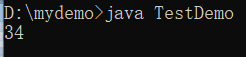
System.out.println(temp.intValue() * 2) ; // 取出里面的基本数据类型操作
}
}
将基本数据类型包装为一个类对象的本质在于方便的使用Object进行接收处理。但是Java中有8种基本数据类型,如果每种数据类型都按照上述方式编写,会存在如下问题:
为了解决这些问题,Java提供了包装类,而对于包装类提供有两种类型:
Boolean、Character;Byte、Double、Short、Long、Integer、Float。
说明:关于Number类
public abstract class Number extends Object implements Serializable,可以看出Number类是一个抽象类byteValue()、doubleValue()、floatValue()、intValue()、longValue()、shortValue()
在包装类与基本数据类型处理之中存在有两个概念:
xxxValue()方法。范例:观察int型
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Integer num = new Integer(17) ; // 装箱
int x = num.intValue() ; // 拆箱
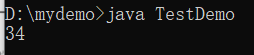
System.out.println(x * 2) ;
}
}
范例:观察double型
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Double num = new Double(17.1) ; // 装箱
double x = num.doubleValue() ; // 拆箱
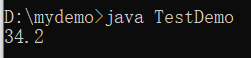
System.out.println(x * 2) ;
}
}
以上写法采用的是手工的装箱与拆箱处理操作形式,这种做法在JDK1.5之前使用。JDK1.5之后提供有自动装箱与拆箱的机制,最为重要的是,由于此类机制的存在,我们可以直接利用包装类的对象进行各种数学计算。
范例:观察自动装箱与拆箱
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Integer x = 17 ; // 自动装箱,变为包装类
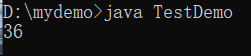
System.out.println(++x * 2) ;
// 可以看出,可以直接利用包装类对象操作
}
}
但是这是又出现了新问题:==和equals()问题。
范例:观察程序
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Integer num1 = 17 ; // 自动装箱,变为包装类
Integer num2 = 17 ; // 自动装箱,变为包装类
System.out.println(num1 == num2) ;
System.out.println(num1 == new Integer(17)) ;
System.out.println(num1.equals(new Integer(17))) ;
}
}
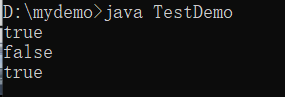
无需特别关注,以后绝大多数情况还是使用equals()方法。
经过包装类的学习,需要明确一个选择:使用int还是Integer()?
Integer();
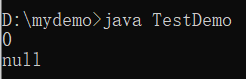
包装类取代基本数据类型,只有单纯描述一个数字时用int(如循环条件之类)。范例:观察默认值
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int num1 = 0 ;
Integer num2 = null ;
System.out.println(num1) ;
System.out.println(num2) ;
}
}
以后如果需要进行数据的输入,输入的类型一定是字符串。所以在开发中有这样的需求:如何将字符串转换为基本数据类型。这个操作需要包装类支持。
常用三种方法:
public static int parseInt(String s);public static double parseDouble(String s);public static boolean parseBoolean(String s);范例:观察字符串与int、double的转换
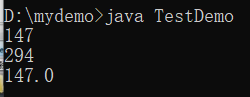
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "147" ;
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(str) ; // 字符串变为int型
double num2 = Double.parseDouble(str) ; // 字符串变为double型
System.out.println(str) ;
System.out.println(num1 * 2) ;
System.out.println(num2) ;
}
}
NumberFormatException)。范例:观察字符串与boolean的转换
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "true" ;
boolean flag = Boolean.parseBoolean(str) ;
System.out.println(str) ;
System.out.println(!flag) ;
}
}
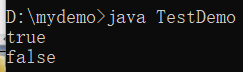
true时,其他任何内容转换为boolean类型输出都会是false。public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = "agbas" ;
boolean flag = Boolean.parseBoolean(str) ;
System.out.println(str) ;
System.out.println(flag) ; // false
}
}
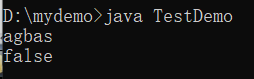
重点在于字符串转其他数据类型中的三种常用方法。
+连接上任意字符串(空白字符串也可以)就会变成字符串类型。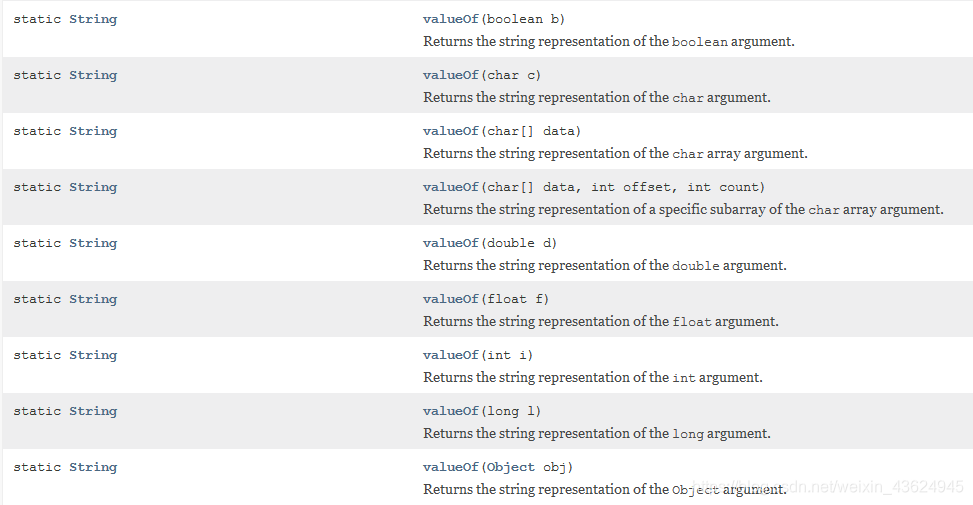
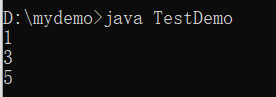
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str1 = String.valueOf(‘A‘) ; // 字符转换为字符串
String str2 = String.valueOf(147) ; // int型转换为字符串
String str3 = String.valueOf(147.0) ; // double型转换为字符串
System.out.println(str1.length()) ; // 如果可以调用length()方法说明是字符串
System.out.println(str2.length()) ;
System.out.println(str3.length()) ;
}
}
阿里云【名师课堂】Java面向对象开发79 ~ 81:包装类
标签:process OLE intval 常用方法 player 学习 lag 方便 情况
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/playerone/p/13168659.html