标签:str string error 设定 设置 current 结果 range inf
已剪辑自: https://www.jianshu.com/p/bb5105303d85
JAVA并发包中有三个类用于同步一批线程的行为,分别是CountDownLatch、Semaphore和CyclicBarrier。
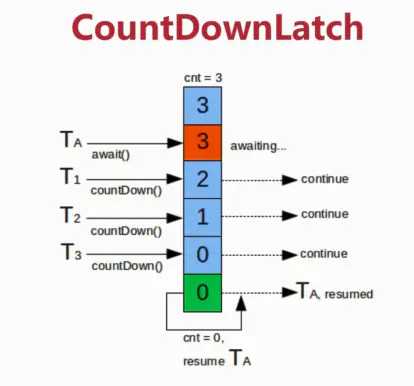
CountDownLatch是一个计数器闭锁,通过它可以完成类似于阻塞当前线程的功能,即:一个线程或多个线程一直等待,直到其他线程执行的操作完成。CountDownLatch用一个给定的计数器来初始化,该计数器的操作是原子操作,即同时只能有一个线程去操作该计数器。调用该类await方法的线程会一直处于阻塞状态,直到其他线程调用countDown方法使当前计数器的值变为零,每次调用countDown计数器的值减1。当计数器值减至零时,所有因调用await()方法而处于等待状态的线程就会继续往下执行。这种现象只会出现一次,因为计数器不能被重置,如果业务上需要一个可以重置计数次数的版本,可以考虑使用CycliBarrier。
在某些业务场景中,程序执行需要等待某个条件完成后才能继续执行后续的操作;典型的应用如并行计算,当某个处理的运算量很大时,可以将该运算任务拆分成多个子任务,等待所有的子任务都完成之后,父任务再拿到所有子任务的运算结果进行汇总。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@Slf4j
public class CountDownLatchExample1 {
private final static int threadCount = 200;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
final int threadNum = i;
exec.execute(() -> {
try {
test(threadNum);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("exception", e);
} finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
log.info("finish");
exec.shutdown();
}
private static void test(int threadNum) throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(100);
log.info("{}", threadNum);
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
结果:
20:18:32.917 [pool-1-thread-7] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample1 - 6
20:18:32.917 [pool-1-thread-6] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample1 - 5
20:18:32.919 [pool-1-thread-5] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample1 - 4
20:18:32.918 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample1 - 0
20:18:32.918 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample1 - 2
20:18:32.916 [pool-1-thread-9] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample1 - 8
20:18:32.918 [pool-1-thread-4] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample1 - 3
20:18:32.916 [pool-1-thread-10] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample1 - 9
20:18:32.916 [pool-1-thread-8] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample1 - 7
20:18:32.917 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample1 - 1
20:18:33.032 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample1 - finish
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j
public class CountDownLatchExample2 {
private final static int threadCount = 200;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(threadCount);
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
final int threadNum = i;
exec.execute(() -> {
try {
test(threadNum);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("exception", e);
} finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
});
}
countDownLatch.await(10, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
log.info("finish");
exec.shutdown();
}
private static void test(int threadNum) throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(100);
log.info("{}", threadNum);
}
}
结果: 超过指定时间跳过等待
20:19:34.878 [main] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample2 - finish
20:19:34.964 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample2 - 2
20:19:34.965 [pool-1-thread-10] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample2 - 9
20:19:34.964 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample2 - 0
20:19:34.965 [pool-1-thread-8] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample2 - 7
20:19:34.964 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample2 - 1
20:19:34.965 [pool-1-thread-5] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample2 - 4
20:19:34.965 [pool-1-thread-7] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample2 - 6
20:19:34.964 [pool-1-thread-4] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample2 - 3
20:19:34.965 [pool-1-thread-9] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample2 - 8
20:19:34.965 [pool-1-thread-6] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CountDownLatchExample2 - 5
Semaphore与CountDownLatch相似,不同的地方在于Semaphore的值被获取到后是可以释放的,并不像CountDownLatch那样一直减到底。它也被更多地用来限制流量,类似阀门的 功能。如果限定某些资源最多有N个线程可以访问,那么超过N个主不允许再有线程来访问,同时当现有线程结束后,就会释放,然后允许新的线程进来。有点类似于锁的lock与 unlock过程。相对来说他也有两个主要的方法:
用于获取权限的acquire(),其底层实现与CountDownLatch.countdown()类似;
用于释放权限的release(),其底层实现与acquire()是一个互逆的过程。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
@Slf4j
public class SemaphoreExample1 {
private final static int threadCount = 20;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 每次最多三个线程获取许可
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
final int threadNum = i;
exec.execute(() -> {
try {
semaphore.acquire(); // 获取一个许可
test(threadNum);
semaphore.release(); // 释放一个许可
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("exception", e);
}
});
}
exec.shutdown();
}
private static void test(int threadNum) throws Exception {
log.info("{}", threadNum);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
@Slf4j
public class SemaphoreExample2 {
private final static int threadCount = 20;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
final int threadNum = i;
exec.execute(() -> {
try {
semaphore.acquire(3); // 获取多个许可
test(threadNum);
semaphore.release(3); // 释放多个许可
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("exception", e);
}
});
}
exec.shutdown();
}
private static void test(int threadNum) throws Exception {
log.info("{}", threadNum);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j
public class SemaphoreExample3 {
private final static int threadCount = 20;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
final int threadNum = i;
exec.execute(() -> {
try {
if (semaphore.tryAcquire()) { // 尝试获取一个许可
test(threadNum);
semaphore.release(); // 释放一个许可
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("exception", e);
}
});
}
exec.shutdown();
}
private static void test(int threadNum) throws Exception {
log.info("{}", threadNum);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j
public class SemaphoreExample4 {
private final static int threadCount = 20;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) {
final int threadNum = i;
exec.execute(() -> {
try {
if (semaphore.tryAcquire(5000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) { // 尝试获取一个许可
test(threadNum);
semaphore.release(); // 释放一个许可
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("exception", e);
}
});
}
exec.shutdown();
}
private static void test(int threadNum) throws Exception {
log.info("{}", threadNum);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
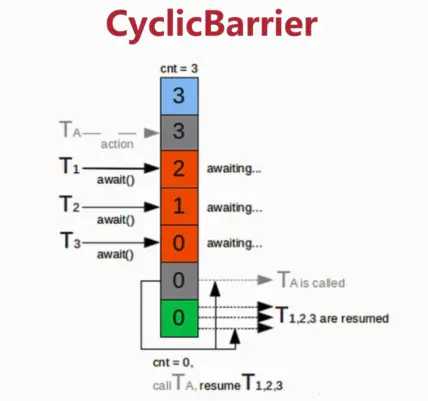
CyclicBarrier也是一个同步辅助类,它允许一组线程相互等待,直到到达某个公共屏障点(common barrier point)。通过它可以完成多个线程之间相互等待,只有当每个线程都准备就绪后,才能各自继续往下执行后面的操作。类似于CountDownLatch,它也是通过计数器来实现的。当某个线程调用await方法时,该线程进入等待状态,且计数器加1,当计数器的值达到设置的初始值时,所有因调用await进入等待状态的线程被唤醒,继续执行后续操作。因为CycliBarrier在释放等待线程后可以重用,所以称为循环barrier。CycliBarrier支持一个可选的Runnable,在计数器的值到达设定值后(但在释放所有线程之前),该Runnable运行一次,注,Runnable在每个屏障点只运行一个。
使用场景类似于CountDownLatch与CyclicBarrier的区别
@Slf4j
public class CyclicBarrierExample1 {
private static CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(5);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int threadNum = i;
Thread.sleep(1000);
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
race(threadNum);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("exception", e);
}
});
}
executor.shutdown();
}
private static void race(int threadNum) throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info("{} is ready", threadNum);
barrier.await();
log.info("{} continue", threadNum);
}
}
结果: ready ready .. go
20:24:34.616 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 0 is ready
20:24:35.610 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 1 is ready
20:24:36.610 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 2 is ready
20:24:37.611 [pool-1-thread-4] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 3 is ready
20:24:38.612 [pool-1-thread-5] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 4 is ready
20:24:38.612 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 0 continue
20:24:38.612 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 1 continue
20:24:38.612 [pool-1-thread-5] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 4 continue
20:24:38.612 [pool-1-thread-4] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 3 continue
20:24:38.612 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 2 continue
20:24:39.614 [pool-1-thread-6] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 5 is ready
20:24:40.613 [pool-1-thread-5] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 6 is ready
20:24:41.614 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 7 is ready
20:24:42.615 [pool-1-thread-4] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 8 is ready
20:24:43.615 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 9 is ready
20:24:43.615 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 9 continue
20:24:43.615 [pool-1-thread-6] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 5 continue
20:24:43.615 [pool-1-thread-5] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 6 continue
20:24:43.615 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 7 continue
20:24:43.615 [pool-1-thread-4] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample1 - 8 continue
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j
public class CyclicBarrierExample2 {
private static CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(5);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int threadNum = i;
Thread.sleep(1000);
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
race(threadNum);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("exception", e);
}
});
}
executor.shutdown();
}
private static void race(int threadNum) throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info("{} is ready", threadNum);
try {
barrier.await(2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("BarrierException", e);
}
log.info("{} continue", threadNum);
}
}
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@Slf4j
public class CyclicBarrierExample3 {
private static CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(5, () -> {
log.info("callback is running");
});
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
final int threadNum = i;
Thread.sleep(1000);
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
race(threadNum);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("exception", e);
}
});
}
executor.shutdown();
}
private static void race(int threadNum) throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.info("{} is ready", threadNum);
barrier.await();
log.info("{} continue", threadNum);
}
}
结果:
20:28:32.790 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 0 is ready
20:28:33.785 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 1 is ready
20:28:34.786 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 2 is ready
20:28:35.787 [pool-1-thread-4] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 3 is ready
20:28:36.787 [pool-1-thread-5] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 4 is ready
20:28:36.787 [pool-1-thread-5] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - callback is running
20:28:36.787 [pool-1-thread-5] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 4 continue
20:28:36.788 [pool-1-thread-1] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 0 continue
20:28:36.788 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 1 continue
20:28:36.788 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 2 continue
20:28:36.788 [pool-1-thread-4] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 3 continue
20:28:37.788 [pool-1-thread-6] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 5 is ready
20:28:38.789 [pool-1-thread-4] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 6 is ready
20:28:39.789 [pool-1-thread-5] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 7 is ready
20:28:40.790 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 8 is ready
20:28:41.791 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 9 is ready
20:28:41.791 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - callback is running
20:28:41.791 [pool-1-thread-3] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 9 continue
20:28:41.791 [pool-1-thread-6] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 5 continue
20:28:41.791 [pool-1-thread-4] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 6 continue
20:28:41.818 [pool-1-thread-2] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 8 continue
20:28:41.818 [pool-1-thread-5] INFO com.mmall.concurrency.example.aqs.CyclicBarrierExample3 - 7 continue
Java并发之CountDownLatch、Semaphore和CyclicBarrier
标签:str string error 设定 设置 current 结果 range inf
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/sweetorangezzz/p/13186587.html