标签:foreach iter info nal cto lazy 数组 array 生成
1.Stream API的理解:
1.1 Stream关注的是对数据的运算,与CPU打交道
集合关注的是数据的存储,与内存打交道
1.2 java8提供了一套api,使用这套api可以对内存中的数据进行过滤、排序、映射、归约等操作。类似于sql对数据库中表的相关操作。
2.注意点:
* ①Stream 自己不会存储元素。
* ②Stream 不会改变源对象。相反,他们会返回一个持有结果的新Stream。
* ③Stream 操作是延迟执行的。这意味着他们会等到需要结果的时候才执行。
3.Stream的使用流程:
* ① Stream的实例化
* ② 一系列的中间操作(过滤、映射、...)
* ③ 终止操作
4.使用流程的注意点:
* 4.1 一个中间操作链,对数据源的数据进行处理
* 4.2 一旦执行终止操作,就执行中间操作链,并产生结果。之后,不会再被使用
5.步骤一:Stream实例化
//创建 Stream方式一:通过集合 @Test public void test1(){ List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); // default Stream<E> stream() : 返回一个顺序流 Stream<Employee> stream = employees.stream(); // default Stream<E> parallelStream() : 返回一个并行流 Stream<Employee> parallelStream = employees.parallelStream(); } //创建 Stream方式二:通过数组 @Test public void test2(){ int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6}; //调用Arrays类的static <T> Stream<T> stream(T[] array): 返回一个流 IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(arr); Employee e1 = new Employee(1001,"Tom"); Employee e2 = new Employee(1002,"Jerry"); Employee[] arr1 = new Employee[]{e1,e2}; Stream<Employee> stream1 = Arrays.stream(arr1); } //创建 Stream方式三:通过Stream的of() @Test public void test3(){ Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6); } //创建 Stream方式四:创建无限流 @Test public void test4(){ // 迭代 // public static<T> Stream<T> iterate(final T seed, final UnaryOperator<T> f) //遍历前10个偶数 Stream.iterate(0, t -> t + 2).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); // 生成 // public static<T> Stream<T> generate(Supplier<T> s) Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println); }
6.步骤二:中间操作

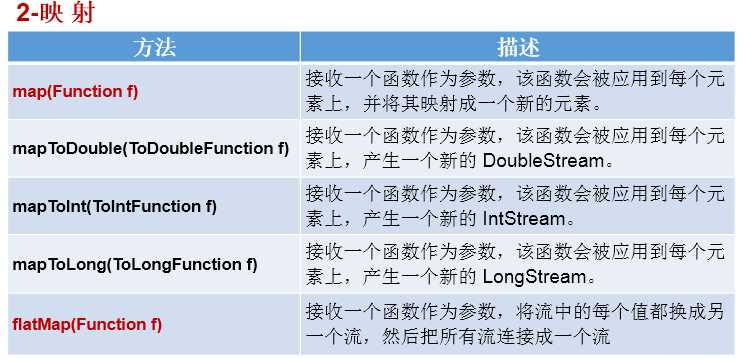
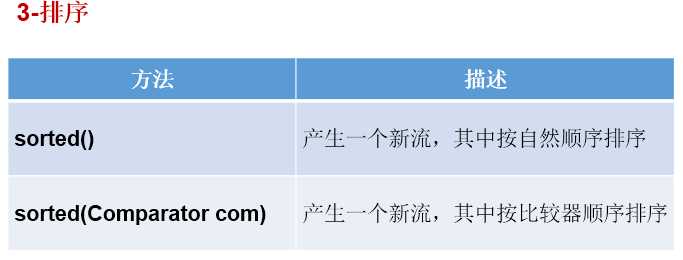
7.步骤三:终止操作
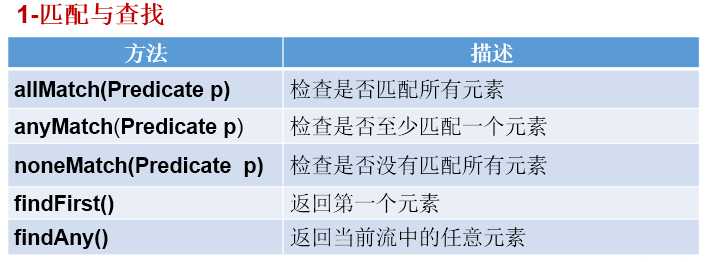
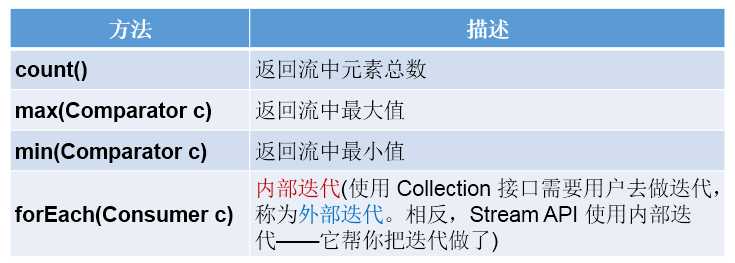

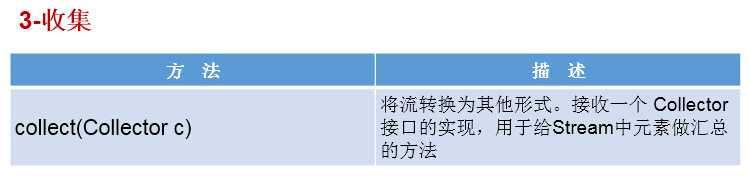
Collector需要使用Collectors提供实例。

java 基本语法(十八)Lambda (五)Stream API
标签:foreach iter info nal cto lazy 数组 array 生成
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/qiu-hua/p/13196667.html