标签:重复 dal boolean func 顺序 void min character 排序
(o1, o2) -> Integer.compare(o1, o2);
@Test
public void test2(){
Comparator<Integer> com1 = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return Integer.compare(o1,o2);
}
};
int compare1 = com1.compare(12,21);
System.out.println(compare1);
System.out.println("***********************");
//Lambda表达式的写法
Comparator<Integer> com2 = (o1,o2) -> Integer.compare(o1,o2);
int compare2 = com2.compare(32,21);
System.out.println(compare2);
System.out.println("***********************");
//方法引用
Comparator<Integer> com3 = Integer :: compare;
int compare3 = com3.compare(32,21);
System.out.println(compare3);
}
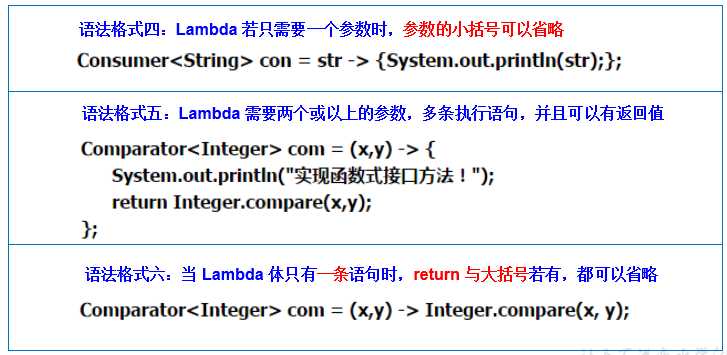
如果一个接口中,只声明了一个抽象方法,则此接口就称为函数式接口。
我们可以在一个接口上使用@FunctionalInterface注解,这样做可以检查是否是一个函数式接口。
Lambda表达式的本质:作为函数式接口的实例。
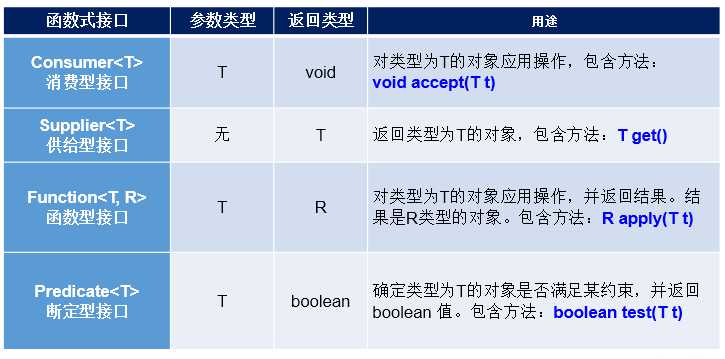
方法引用可以看做是Lambda表达式深层次的表达。换句话说,方法引用就是Lambda表达式,也就是函数式接口的一个实例,通过方法的名字来指向一个方法。
类(或对象) :: 方法名要求接口中的抽象方法的形参列表和返回值类型与方法引用的方法的形参列表和返回值类型相同!(针对于情况1和情况2)
当函数式接口方法的第一个参数是需要引用方法的调用者,并且第二个参数是需要引用方法的参数(或无参数)时:ClassName::methodName(针对于情况3)
//Consumer中的void accept(T t)
//PrintStream中的void println(T t)
@Test
public void test1() {
Consumer<String> con1 = str -> System.out.println(str);
con1.accept("北京");
System.out.println("*******************");
PrintStream ps = System.out;
Consumer<String> con2 = ps::println;
con2.accept("beijing");
}
//Supplier中的T get()
//Employee中的String getName()
@Test
public void test2() {
Employee emp = new Employee(1001,"Tom",23,5600);
Supplier<String> sup1 = () -> emp.getName();
System.out.println(sup1.get());
System.out.println("*******************");
Supplier<String> sup2 = emp::getName;
System.out.println(sup2.get());
}
//Comparator中的int compare(T t1,T t2)
//Integer中的int compare(T t1,T t2)
@Test
public void test3() {
Comparator<Integer> com1 = (t1,t2) -> Integer.compare(t1,t2);
System.out.println(com1.compare(12,21));
System.out.println("*******************");
Comparator<Integer> com2 = Integer::compare;
System.out.println(com2.compare(12,3));
}
//Function中的R apply(T t)
//Math中的Long round(Double d)
@Test
public void test4() {
Function<Double,Long> func = new Function<Double, Long>() {
@Override
public Long apply(Double d) {
return Math.round(d);
}
};
System.out.println("*******************");
Function<Double,Long> func1 = d -> Math.round(d);
System.out.println(func1.apply(12.3));
System.out.println("*******************");
Function<Double,Long> func2 = Math::round;
System.out.println(func2.apply(12.6));
}
// Comparator中的int comapre(T t1,T t2)
// String中的int t1.compareTo(t2)
@Test
public void test5() {
Comparator<String> com1 = (s1,s2) -> s1.compareTo(s2);
System.out.println(com1.compare("abc","abd"));
System.out.println("*******************");
Comparator<String> com2 = String :: compareTo;
System.out.println(com2.compare("abd","abm"));
}
// Function中的R apply(T t)
// Employee中的String getName();
@Test
public void test7() {
Employee employee = new Employee(1001, "Jerry", 23, 6000);
Function<Employee,String> func1 = e -> e.getName();
System.out.println(func1.apply(employee));
System.out.println("*******************");
Function<Employee,String> func2 = Employee::getName;
System.out.println(func2.apply(employee));
}
/*
和方法引用类似,函数式接口的抽象方法的形参列表和构造器的形参列表一致。抽象方法的返回值类型即为构造器所属
的类的类型
*/
//Supplier中的T get()
//Employee的空参构造器:Employee()
@Test
public void test1(){
Supplier<Employee> sup = new Supplier<Employee>() {
@Override
public Employee get() {
return new Employee();
}
};
System.out.println("*******************");
Supplier<Employee> sup1 = () -> new Employee();
System.out.println(sup1.get());
System.out.println("*******************");
Supplier<Employee> sup2 = Employee :: new;
System.out.println(sup2.get());
}
//Function中的R apply(T t)
@Test
public void test2(){
Function<Integer,Employee> func1 = id -> new Employee(id);
Employee employee = func1.apply(1001);
System.out.println(employee);
System.out.println("*******************");
Function<Integer,Employee> func2 = Employee :: new;
Employee employee1 = func2.apply(1002);
System.out.println(employee1);
}
//BiFunction中的R apply(T t,U u)
@Test
public void test3(){
BiFunction<Integer,String,Employee> func1 = (id,name) -> new Employee(id,name);
System.out.println(func1.apply(1001,"Tom"));
System.out.println("*******************");
BiFunction<Integer,String,Employee> func2 = Employee :: new;
System.out.println(func2.apply(1002,"Tom"));
}
// 格式:数组类型[] :: new
//Function中的R apply(T t)
@Test
public void test4(){
Function<Integer,String[]> func1 = length -> new String[length];
String[] arr1 = func1.apply(5);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
System.out.println("*******************");
Function<Integer,String[]> func2 = String[] :: new;
String[] arr2 = func2.apply(10);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
}
@Test
public void test1(){
List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
// default Stream<E> stream() : 返回一个顺序流
Stream<Employee> stream = employees.stream();
// default Stream<E> parallelStream() : 返回一个并行流
Stream<Employee> parallelStream = employees.parallelStream();
}
@Test
public void test2(){
int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6};
//调用Arrays类的static <T> Stream<T> stream(T[] array): 返回一个流
IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(arr);
Employee e1 = new Employee(1001,"Tom");
Employee e2 = new Employee(1002,"Jerry");
Employee[] arr1 = new Employee[]{e1,e2};
Stream<Employee> stream1 = Arrays.stream(arr1);
}
@Test
public void test3(){
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
}
@Test
public void test4(){
// 迭代
// public static<T> Stream<T> iterate(final T seed, final UnaryOperator<T> f)
//遍历前10个偶数
Stream.iterate(0, t -> t + 2).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
// 生成
// public static<T> Stream<T> generate(Supplier<T> s)
Stream.generate(Math::random).limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);
}

package com.atguigu.java3;
import com.atguigu.java2.Employee;
import com.atguigu.java2.EmployeeData;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* 测试Stream的中间操作
*
* @author shkstart
* @create 2019 下午 4:42
*/
public class StreamAPITest1 {
//1-筛选与切片
@Test
public void test1(){
List<Employee> list = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
// filter(Predicate p)——接收 Lambda , 从流中排除某些元素。
Stream<Employee> stream = list.stream();
//练习:查询员工表中薪资大于7000的员工信息
stream.filter(e -> e.getSalary() > 7000).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// limit(n)——截断流,使其元素不超过给定数量。
list.stream().limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// skip(n) —— 跳过元素,返回一个扔掉了前 n 个元素的流。若流中元素不足 n 个,则返回一个空流。与 limit(n) 互补
list.stream().skip(3).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// distinct()——筛选,通过流所生成元素的 hashCode() 和 equals() 去除重复元素
list.add(new Employee(1010,"刘强东",40,8000));
list.add(new Employee(1010,"刘强东",41,8000));
list.add(new Employee(1010,"刘强东",40,8000));
list.add(new Employee(1010,"刘强东",40,8000));
list.add(new Employee(1010,"刘强东",40,8000));
// System.out.println(list);
list.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
}
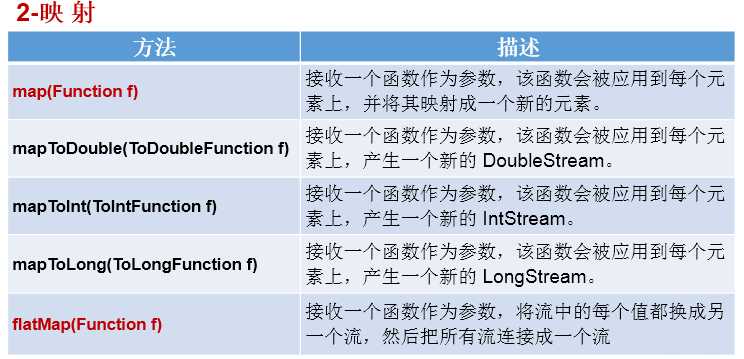
//映射
@Test
public void test2(){
// map(Function f)——接收一个函数作为参数,将元素转换成其他形式或提取信息,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素。
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa", "bb", "cc", "dd");
list.stream().map(str -> str.toUpperCase()).forEach(System.out::println);
// 练习1:获取员工姓名长度大于3的员工的姓名。
List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
Stream<String> namesStream = employees.stream().map(Employee::getName);
namesStream.filter(name -> name.length() > 3).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
//练习2:
Stream<Stream<Character>> streamStream = list.stream().map(StreamAPITest1::fromStringToStream);
streamStream.forEach(s ->{
s.forEach(System.out::println);
});
System.out.println();
// flatMap(Function f)——接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流。
Stream<Character> characterStream = list.stream().flatMap(StreamAPITest1::fromStringToStream);
characterStream.forEach(System.out::println);
}
//将字符串中的多个字符构成的集合转换为对应的Stream的实例
public static Stream<Character> fromStringToStream(String str){//aa
ArrayList<Character> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(Character c : str.toCharArray()){
list.add(c);
}
return list.stream();
}
@Test
public void test3(){
ArrayList list1 = new ArrayList();
list1.add(1);
list1.add(2);
list1.add(3);
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList();
list2.add(4);
list2.add(5);
list2.add(6);
// list1.add(list2);
list1.addAll(list2);
System.out.println(list1);
}
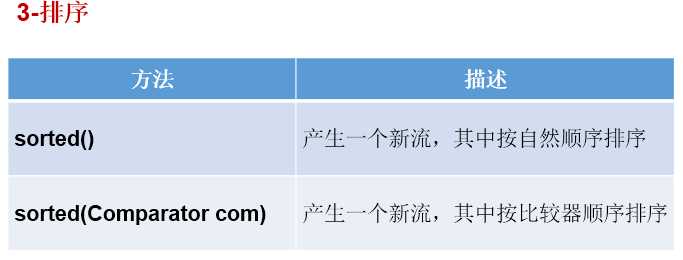
//3-排序
@Test
public void test4(){
// sorted()——自然排序
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(12, 43, 65, 34, 87, 0, -98, 7);
list.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
//抛异常,原因:Employee没有实现Comparable接口
// List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
// employees.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println);
// sorted(Comparator com)——定制排序
List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
employees.stream().sorted( (e1,e2) -> {
int ageValue = Integer.compare(e1.getAge(),e2.getAge());
if(ageValue != 0){
return ageValue;
}else{
return -Double.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary());
}
}).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}

Collector需要使用Collectors提供实例。

package com.atguigu.java3;
import com.atguigu.java2.Employee;
import com.atguigu.java2.EmployeeData;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
/**
* 测试Stream的终止操作
*
* @author shkstart
* @create 2019 下午 6:37
*/
public class StreamAPITest2 {
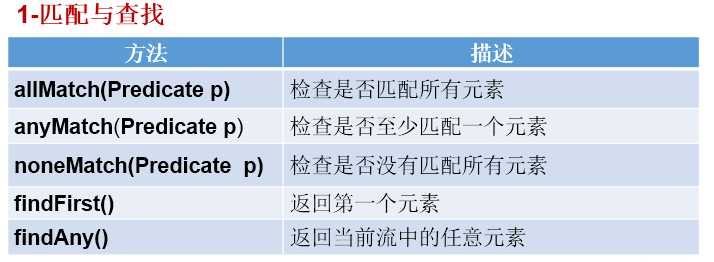
//1-匹配与查找
@Test
public void test1(){
List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
// allMatch(Predicate p)——检查是否匹配所有元素。
// 练习:是否所有的员工的年龄都大于18
boolean allMatch = employees.stream().allMatch(e -> e.getAge() > 18);
System.out.println(allMatch);
// anyMatch(Predicate p)——检查是否至少匹配一个元素。
// 练习:是否存在员工的工资大于 10000
boolean anyMatch = employees.stream().anyMatch(e -> e.getSalary() > 10000);
System.out.println(anyMatch);
// noneMatch(Predicate p)——检查是否没有匹配的元素。
// 练习:是否存在员工姓“雷”
boolean noneMatch = employees.stream().noneMatch(e -> e.getName().startsWith("雷"));
System.out.println(noneMatch);
// findFirst——返回第一个元素
Optional<Employee> employee = employees.stream().findFirst();
System.out.println(employee);
// findAny——返回当前流中的任意元素
Optional<Employee> employee1 = employees.parallelStream().findAny();
System.out.println(employee1);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
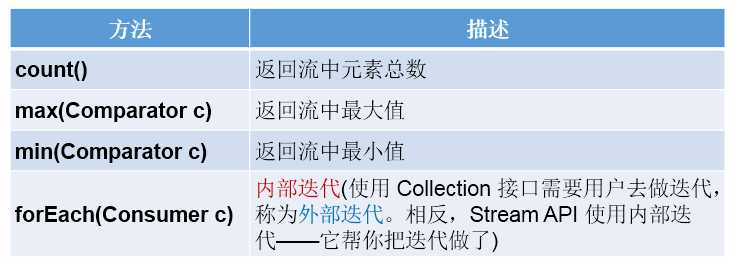
// count——返回流中元素的总个数
long count = employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getSalary() > 5000).count();
System.out.println(count);
// max(Comparator c)——返回流中最大值
// 练习:返回最高的工资:
Stream<Double> salaryStream = employees.stream().map(e -> e.getSalary());
Optional<Double> maxSalary = salaryStream.max(Double::compare);
System.out.println(maxSalary);
// min(Comparator c)——返回流中最小值
// 练习:返回最低工资的员工
Optional<Employee> employee = employees.stream().min((e1, e2) -> Double.compare(e1.getSalary(), e2.getSalary()));
System.out.println(employee);
System.out.println();
// forEach(Consumer c)——内部迭代
employees.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
//使用集合的遍历操作
employees.forEach(System.out::println);
}
//2-归约
@Test
public void test3(){
// reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator)——可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值。返回 T
// 练习1:计算1-10的自然数的和
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10);
Integer sum = list.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);
System.out.println(sum);
// reduce(BinaryOperator) ——可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值。返回 Optional<T>
// 练习2:计算公司所有员工工资的总和
List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
Stream<Double> salaryStream = employees.stream().map(Employee::getSalary);
// Optional<Double> sumMoney = salaryStream.reduce(Double::sum);
Optional<Double> sumMoney = salaryStream.reduce((d1,d2) -> d1 + d2);
System.out.println(sumMoney.get());
}
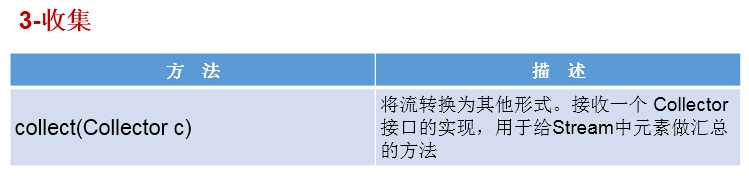
//3-收集
@Test
public void test4(){
// collect(Collector c)——将流转换为其他形式。接收一个 Collector接口的实现,用于给Stream中元素做汇总的方法
// 练习1:查找工资大于6000的员工,结果返回为一个List或Set
List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees();
List<Employee> employeeList = employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getSalary() > 6000).collect(Collectors.toList());
employeeList.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
Set<Employee> employeeSet = employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getSalary() > 6000).collect(Collectors.toSet());
employeeSet.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
标签:重复 dal boolean func 顺序 void min character 排序
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/mango-peel527/p/13206075.html