标签:specific org ges alt ESS other tis 输出 get
上一节我们已经分析到AbsractApplicationContext类refresh方法中的postProcessBeanFactory方法,在分析registerBeanPostProcessors之前我们先介绍一下Spring 的钩子接口,后面我们会在Spring源代码中介绍到这些钩子接口的调用时机。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset ‘active‘ flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring‘s core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
Spring 提供了非常多的扩展接口,官方将这些接口称之为钩子,这些钩子会在特定的时间被回调,以此来增强 Spring 功能,众多优秀的框架也是通过扩展这些接口,来实现自身特定的功能,如 SpringBoot、mybatis 等。
Aware从字面的意思理解就是"知道"、“感知”的意思,是用来获取Spring内部对象的接口。Aware自身是一个顶级接口,它有一系列子接口,在一个 Bean 中实现这些子接口并重写里面的 set 方法后,Spring 容器启动时,就会回调该 set 方法,而相应的对象会通过方法参数传递进去。我们以其中的 ApplicationContextAware 接口为例。
大部分 Aware 系列接口都有一个规律,它们以对象名称为前缀,获取的就是该对象,所以 ApplicationContextAware 获取的对象是 ApplicationContext 。
public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware {
/**
* Set the ApplicationContext that this object runs in.
* Normally this call will be used to initialize the object.
* <p>Invoked after population of normal bean properties but before an init callback such
* as {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()}
* or a custom init-method. Invoked after {@link ResourceLoaderAware#setResourceLoader},
* {@link ApplicationEventPublisherAware#setApplicationEventPublisher} and
* {@link MessageSourceAware}, if applicable.
* @param applicationContext the ApplicationContext object to be used by this object
* @throws ApplicationContextException in case of context initialization errors
* @throws BeansException if thrown by application context methods
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanInitializationException
*/
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}
ApplicationContextAware 源码非常简单,其继承了 Aware 接口,并定义一个 set 方法,参数就是 ApplicationContext 对象,当然,其它系列的 Aware 接口也是类似的定义。其具体使用方式如下:
package com.goldwind.spring;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AwareTest implements ApplicationContextAware {
/*
* 保存应用上下文
*/
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
//输出所有BeanDefinition name
for(String name:applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
log.info(name);
}
}
}
在 Spring 启动过程中,会回调 setApplicationContext 方法,并传入 ApplicationContext 对象,之后就可对该对象进行操作。我们获取到ApplicationContext对象,并将所有BeanDefinition名称输出:
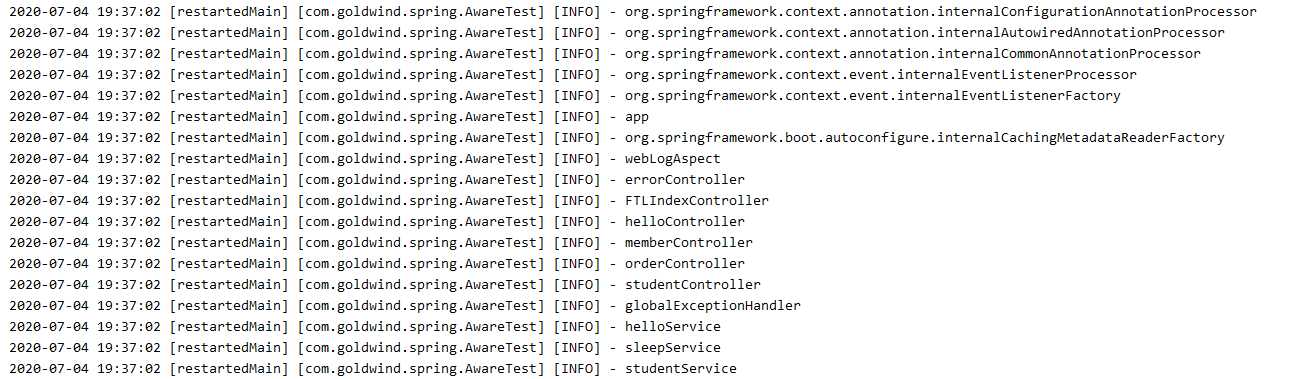
其它系列的 Aware 接口也是如此使用。具体的调用时机会在后面详细介绍。
以下是几种常用的 Aware 接口:
InitializingBean 是一个可以在 Bean 的生命周期执行自定义操作的接口,凡是实现该接口的 Bean,在初始化阶段都可以执行自定义的操作。
public interface InitializingBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} after it has set all bean properties
* and satisfied {@link BeanFactoryAware}, {@code ApplicationContextAware} etc.
* <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform validation of its overall
* configuration and final initialization when all bean properties have been set.
* @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such as failure to set an
* essential property) or if initialization fails for any other reason
*/
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
从 InitializingBean 源码中可以看出它有一个 afterPropertiesSet 方法,当一个 Bean 实现该接口时,在 Bean 的初始化阶段,会回调 afterPropertiesSet 方法,其初始化阶段具体指 Bean 设置完属性之后。
同理,DisposableBean在Bean销毁时执行自定义的操作,必须资源的释放。
public interface DisposableBean {
/**
* Invoked by the containing {@code BeanFactory} on destruction of a bean.
* @throws Exception in case of shutdown errors. Exceptions will get logged
* but not rethrown to allow other beans to release their resources as well.
*/
void destroy() throws Exception;
}
比如:
package com.goldwind.spring;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Data
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class BeanTest implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
/*
* 构造函数
*/
public BeanTest(){
log.info("New object...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
log.info("Destroying ...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
log.info("Initializing ....");
}
}
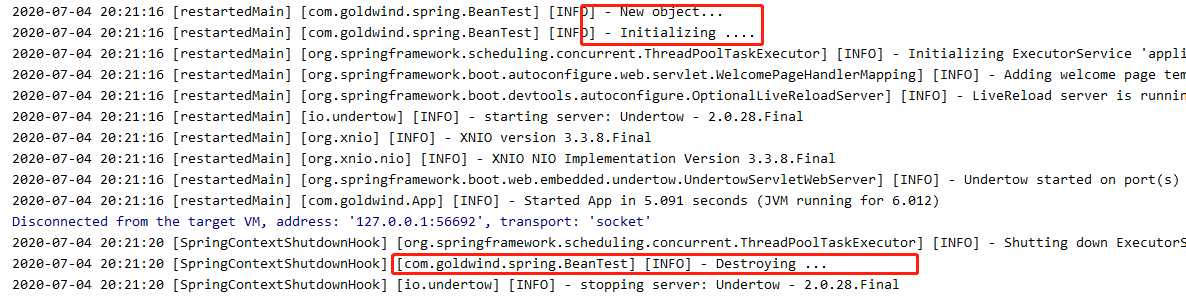
BeanPostProcessor 和 InitializingBean 有点类似,也是可以在 Bean 的生命周期执行自定义操作,一般称之为 Bean 的后置处理器,不同的是, BeanPostProcessor 可以在 Bean 初始化前、后执行自定义操作,且针对的目标也不同,InitializingBean 针对的是实现 InitializingBean 接口的 Bean,而 BeanPostProcessor 针对的是所有的 Bean。并且postProcessBeforeInitialization在对象创建之后,afterPropertiesSet之前执行,而postProcessAfterInitialization在afterPropertiesSet之后执行:
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
// Bean 初始化前调用
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
// Bean 初始化后调用
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
所有的 Bean 在初始化前、后都会回调接口中的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 和 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法,入参是当前正在初始化的 Bean 对象和 BeanName。值得注意的是 Spring 内置了非常多的 BeanPostProcessor ,以此来完善自身功能,这部分会在后面文章深入讨论。
我们扩充我们的测试类AwareTest :
package com.goldwind.spring;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AwareTest implements ApplicationContextAware, BeanPostProcessor {
/*
* 保存应用上下文
*/
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
//输出所有BeanDefinition name
for(String name:applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
log.info(name);
}
}
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if(beanName.equals("beanTest")) {
log.info("postProcessBeforeInitialization:" + beanName);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if(beanName.equals("beanTest")) {
log.info("postProcessAfterInitialization:" + beanName);
}
return bean;
}
}
BeanTest :
package com.goldwind.spring;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Data
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class BeanTest implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean, BeanNameAware {
/*
* 保存当前bean name
*/
private String beanName;
/*
* 构造函数
*/
public BeanTest(){
log.info("New object...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
log.info("Destroying ...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
log.info("Initializing ....");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
this.beanName = name;
log.info("Current bean name:" + name);
}
}
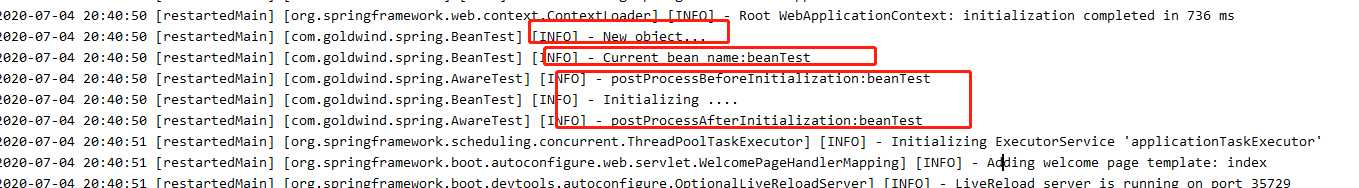
可以看到beanTest对象先是被实例化出来,然后执行BeanPostProcessor的postProcessBeforeInitialization,再执行InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet,最后执行BeanPostProcessor的postProcessAfterInitialization方法。而ApplicationContextAware的setApplicationContext方法执行时所有BeanDefinition都已加载,但还未实例化Bean
BeanPostProcessor 使用场景其实非常多,因为它可以获取正在初始化的 Bean 对象,然后可以对Bean 对象做一些定制化的操作,如:判断该 Bean 是否为某个特定对象、获取 Bean 的注解元数据等。事实上,Spring 内部也正是这样使用的,之前我们介绍的Spring Boot -- Spring AOP原理及简单实现手写AOP时也是利用了BeanPostProcessor的特性,我们对@Pointcut注解指定的Bean都进行了代理处理。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 是 Bean 工厂的后置处理器,一般用来修改上下文中的 BeanDefinition,修改 Bean 的属性值。
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
// 入参是一个 Bean 工厂:ConfigurableListableBeanFactory。该方法执行时,所有 BeanDefinition 都已被加载,但还未实例化 Bean。
// 可以对其进行覆盖或添加属性,甚至可以用于初始化 Bean。
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 源码非常简单,其提供了一个 postProcessBeanFactory 方法,当所有的 BeanDefinition 被加载时,该方法会被回调。值得注意的是,Spring 内置了许多 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的实现,以此来完善自身功能。 这里,我们来实现一个自定义的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor:
package com.goldwind.spring;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Data
@Slf4j
@Component
public class AwareTest implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
log.info("------------------------------------------postProcessBeanFactory-------------------------");
String beanNames[] = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
log.info(beanDefinition.toString());
}
}
}
主要是通过 Bean 工厂获取所有的 BeanDefinition 。
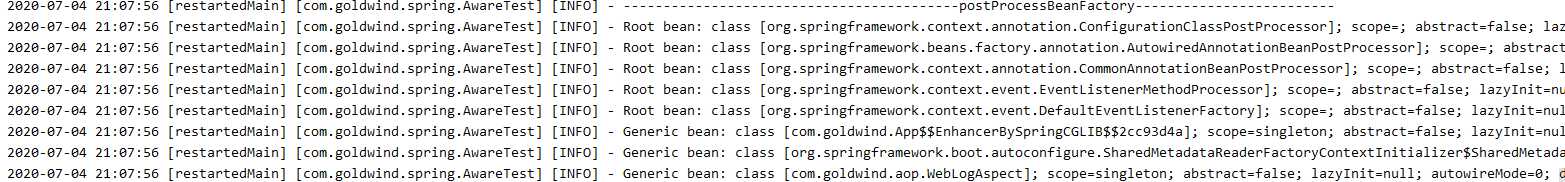
可以看到,BeanDefinition 正确输出,里面是一些 Bean 的相关定义,如:是否懒加载、Bean 的 Class 以及 Bean 的属性等。
参考文章:
[1]Spring(七)核心容器 - 钩子接口(转载)
Spring Boot -- 启动流程分析之ApplicationContext 中
标签:specific org ges alt ESS other tis 输出 get
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zyly/p/13236679.html