标签:class 冒泡排序 == flag 实现 static 更新 mic 说明
它重复地走访过要排序的元素列,依次比较两个相邻的元素,如果顺序(如从大到小、首字母从Z到A)错误就把他们交换过来。走访元素的工作是重复地进行直到没有相邻元素需要交换,也就是说该元素列已经排序完成。
因为排序的过程中,各元素不断接近自己的位置,如果一趟比较下来没有进行过交换,就说明序列有序,因此要在排序过程中设置一个标志flag判断元素是否进行过交换。从而减少不必要的比较。
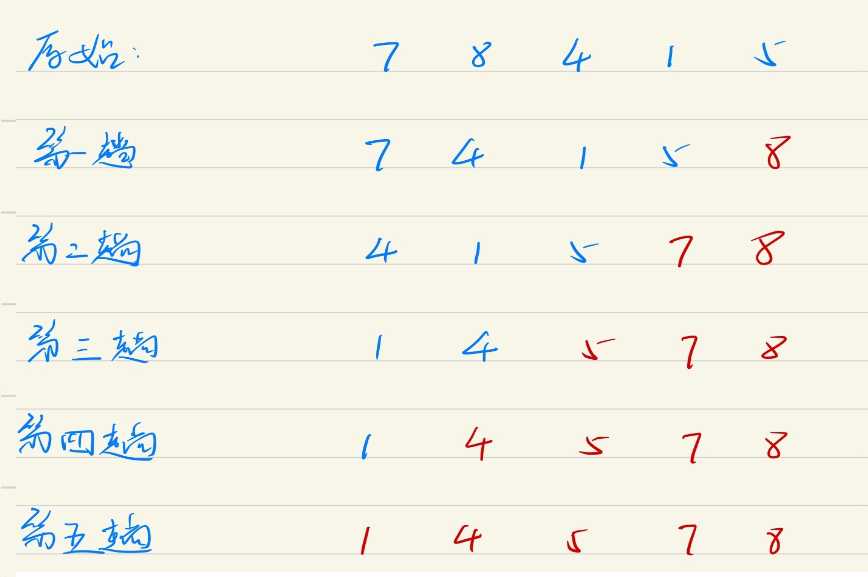
冒泡排序规则
public class Sort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构建测试数组
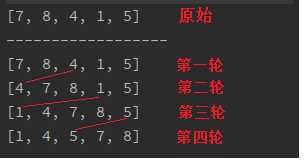
int[] array = {7,8,4,1,5};
int[] arr = bubbleSort(array);
System.out.println("------------------");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
// 算法的具体实现
public static int[] bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
boolean flag = false; // 用于判断是否发生数字交换
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length-1-i; j++) {
int temp = 0; // 构建中间变量
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]) {
flag = true;
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
if (flag) { // 发生交换,则继续循环
flag = false;
}else { // 未发生交换,跳出循环
break;
}
}
return arr;
}
}

public static int[] selectSort(int[] nums) {
int minIndex = 0;
int min = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length-1; i++) {
min = nums[i];
minIndex = i;
for (int j = i+1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (min > nums[j]) {
min = nums[j];
minIndex = j;
}
}
if (minIndex != i) {
nums[minIndex] = nums[i];
nums[i] = min;
}
}
return nums;
}
public static int[] insertSort(int[] nums) {
int insertNum = 0;
int insertIndex = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
insertNum = nums[i]; // 定义待插入的数
insertIndex = i-1; // 定义搜索的开始索引
// 判断越界情况,以及寻找插入位置
while (insertIndex >= 0 && insertNum < nums[insertIndex]) {
nums[insertIndex+1] = nums[insertIndex]; // 将大于待插入数的数后移一位
insertIndex-- ; // 更新判断的位置
}
// 已找到比他小的数,则插入位置为这个数的后一个位置
// 判断条件:insertIndex+1 == 1;实际上与循环一开始定义的第一个搜索位置一致,则判断没有发生插入情况
if(insertIndex+1 != i]){
nums[insertIndex+1] = insertNum;
}
}
return nums;
}
标签:class 冒泡排序 == flag 实现 static 更新 mic 说明
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/njuptzheng/p/13264074.html