标签:扫描 停止 自己 eset sts encoding pat string image
1、基本概念
(1)数据分类
结构化数据:具有固定格式或有限长度的数据,如:数据库、元数据等
非结构化数据:不定长或无固定格式的数据,如:邮件、word文档等
(2)非结构化数据的查询方法
顺序扫描法:
所谓顺序扫描,比如要找内容包含某一个字符串的文件,就是一个文档一个文档的看,对于每一个文档,从头看到尾,如果此文档包含此字符串,则此文档为我们要找的文件,换着找下一个文件,直到扫描完所有的文件,如利用windows的搜索也可以搜索文件内容,但是速度太慢
全文检索:
先建立索引然后再对索引进行搜索的过程
索引的创建需要耗费资源,但是一旦创建了索引就可以使用多次
lucene可以实现全文检索,它提供了完整的查询引擎和索引引擎,部分文本分析引擎
数据量大、数据结构不固定的数据可以采用全文检索,如:百度、电商网站等搜索引擎
(3)solr与lucene
solr是基于lucene的
使用率高
(4)下载lucene
下载压缩包解压即可
2、索引与搜索流程
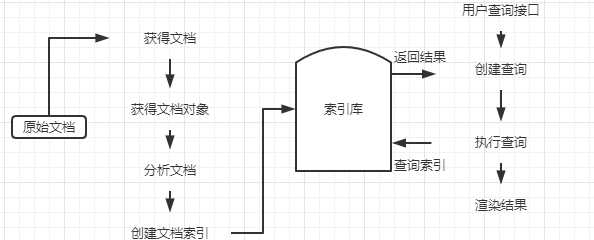
获取文档:将文档从磁盘读取到内存中
索引库包含原始文档和索引
原始文档:互联网的页面、数据库中的数据、磁盘上的文件等
lucene不提供信息采集的类库,需要通过爬虫程序来实现信息的采集
每一个文档对象都有一个唯一的ID,文档对象的属性再这里被称为域,例如:创建时间就是文档对象的一个域,而ID不是域
3、分析文档(英文文档)
将原始内容创建为包含域(Field)的文档(document),需要再对域中的内容进行分析,分析的过程是经过对原始文档提取单词、将字母转为小写、去除标点符号等过程生成最终的语汇单元,可以将语汇单元理解为一个一个的单词。每一个单词叫做一个term,不同的域中拆分出来的单词是不同的term。
4、lucene的使用
(1)导包
核心包:
lucene-analyzers-common:
lucene-queryparser:
其他:
(2)创建索引
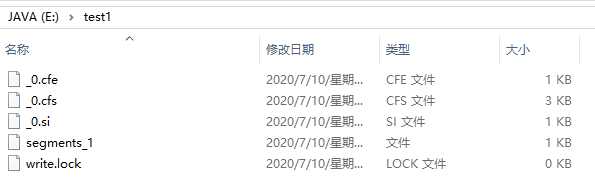
@Test public void testIndex() throws Exception { //指定一个分析器,对文档内容进行分析。 Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(); IndexWriterConfig config = new IndexWriterConfig(analyzer); //指定索引库的存放位置Directory对象,保存索引到内存中 (内存索引库) Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("E:\\test1").toPath()); //创建一个indexwriter对象 IndexWriter indexWriter = new IndexWriter(directory, config); //创建field对象,将field添加到document对象中。 File f = new File("E:\\test"); File[] listFiles = f.listFiles(); for (File file : listFiles) { //创建document对象 Document document = new Document(); // 文件名称 String file_name = file.getName(); //是否分析、是否索引、是否存储在索引中 Field fileNameField = new TextField("fileName", file_name, Field.Store.YES); // 文件大小 long fileSize = FileUtils.sizeOf(file); Field fieldSizeValue = new LongPoint("size",fileSize); Field fieldSizeStore = new StoredField("size",fileSize); // 文件路径 String file_path = file.getPath(); Field filePathField = new StoredField("filePath", file_path); // 文件内容 String file_content = FileUtils.readFileToString(file); Field fileContentField = new TextField("fileContent", file_content, Field.Store.NO); document.add(fileNameField); document.add(filePathField); document.add(fileContentField); document.add(fieldSizeValue); document.add(fieldSizeStore); //使用indexwriter对象将document对象写入索引库,此过程进行索引创建。并将索引和document对象写入索引库。 indexWriter.addDocument(document); } //关闭IndexWriter对象。 indexWriter.close(); }
运行结果:
(3)执行查询(搜索索引)
@Test public void testSearch() throws Exception { //创建一个Directory对象,也就是索引库存放的位置 Directory directory = FSDirectory.open(new File("E:\\test1").toPath());// 磁盘 //创建一个indexReader对象,需要指定Directory对象 IndexReader indexReader = DirectoryReader.open(directory); //创建一个indexsearcher对象,需要指定IndexReader对象 IndexSearcher indexSearcher = new IndexSearcher(indexReader); //创建一个TermQuery对象,指定查询的域和查询的关键词 Query query = new TermQuery(new Term("fileName", "1")); //执行查询 TopDocs topDocs = indexSearcher.search(query, 10); //返回查询结果,遍历查询结果并输出 ScoreDoc[] scoreDocs = topDocs.scoreDocs; for (ScoreDoc scoreDoc : scoreDocs) { int doc = scoreDoc.doc; Document document = indexSearcher.doc(doc); // 文件名称 String fileName = document.get("fileName"); System.out.println(fileName); // 文件内容 String fileContent = document.get("fileContent"); System.out.println(fileContent); // 文件大小 String fileSize = document.get("fileSize"); System.out.println(fileSize); // 文件路径 String filePath = document.get("filePath"); System.out.println(filePath); } // 第七步:关闭IndexReader对象 indexReader.close(); }
执行结果:
1.txt null null E:\test\1.txt
因为在创建文件索引的时候没有添加文件的内容和文件的大小的域,因此,这里的查询为空
5、分析器
搜索使用的分析器和索引使用的分析器要一致
(1)英文分析器
分析的过程是经过对原始文档提取单词、将字母转为小写、去除标点符号等过程生成最终的语汇单元,可以将语汇单元理解为一个一个的单词。每一个单词叫做一个term,不同的域中拆分出来的单词是不同的term。
@Test public void testTokenStream() throws Exception { // 创建一个标准分析器对象 Analyzer analyzer = new StandardAnalyzer(); // 获得tokenStream对象,第一个参数:域名,可以随便给一个,第二个参数:要分析的文本内容 TokenStream tokenStream = analyzer.tokenStream("test", "Binzhou Medical University is a common medical university at provincial level in Shandong" + " Province,and its predecessor was the Public Medical School of Shandong University " + "originally established in 1946."); // 添加一个引用,可以获得每个关键词 CharTermAttribute charTermAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(CharTermAttribute.class); // 添加一个偏移量的引用,记录了关键词的开始位置以及结束位置 OffsetAttribute offsetAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(OffsetAttribute.class); // 将指针调整到列表的头部 tokenStream.reset(); // 遍历关键词列表,通过incrementToken方法判断列表是否结束 while (tokenStream.incrementToken()) { // 关键词的起始位置 System.out.println("start->" + offsetAttribute.startOffset()); // 取关键词 System.out.println(charTermAttribute); // 结束位置 System.out.println("end->" + offsetAttribute.endOffset()); } tokenStream.close(); }
分词效果:
start->0 binzhou end->7 start->8 medical end->15 start->16 university end->26 start->32 common end->38 start->39 medical end->46 start->47 university end->57 start->61 provincial end->71 start->72 level end->77 start->81 shandong end->89 start->90 province end->98 start->103 its end->106 start->107 predecessor end->118 start->127 public end->133 start->134 medical end->141 start->142 school end->148 start->152 shandong end->160 start->161 university end->171 start->172 originally end->182 start->183 established end->194 start->198 1946 end->202
(2)中文分析器
导包:
@Test public void testTokenStream() throws Exception { // 创建一个标准分析器对象 Analyzer analyzer = new SmartChineseAnalyzer(); // 获得tokenStream对象,第一个参数:域名,可以随便给一个,第二个参数:要分析的文本内容 TokenStream tokenStream = analyzer.tokenStream("test", "我爱你中国,我爱你春天蓬勃的秧苗,我爱你秋日金黄的硕果"); // 添加一个引用,可以获得每个关键词 CharTermAttribute charTermAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(CharTermAttribute.class); // 添加一个偏移量的引用,记录了关键词的开始位置以及结束位置 OffsetAttribute offsetAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(OffsetAttribute.class); // 将指针调整到列表的头部 tokenStream.reset(); // 遍历关键词列表,通过incrementToken方法判断列表是否结束 while (tokenStream.incrementToken()) { // 关键词的起始位置 System.out.println("start->" + offsetAttribute.startOffset()); // 取关键词 System.out.println(charTermAttribute); // 结束位置 System.out.println("end->" + offsetAttribute.endOffset()); } tokenStream.close(); }
分词效果:
start->0 我 end->1 start->1 爱 end->2 start->2 你 end->3 start->3 中国 end->5 start->6 我 end->7 start->7 爱 end->8 start->8 你 end->9 start->9 春天 end->11 start->11 蓬勃 end->13 start->13 的 end->14 start->14 秧苗 end->16 start->17 我 end->18 start->18 爱 end->19 start->19 你 end->20 start->20 秋日 end->22 start->22 金黄 end->24 start->24 的 end->25 start->25 硕果 end->27
但是该分词器扩展性差:
TokenStream tokenStream = analyzer.tokenStream("test",
"硬核,柠檬精、“我酸了”,奥利给");
分词结果:
start->0 硬 end->1 start->1 核 end->2 start->3 柠檬精 end->6 start->8 我 end->9 start->9 酸 end->10 start->10 了 end->11 start->13 奥 end->14 start->14 利 end->15 start->15 给 end->16
IK分词器:
导包、创建配置文件
ext是自己导入的词语,stopword是忽略的词语
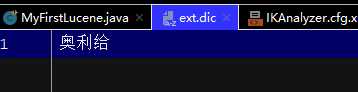
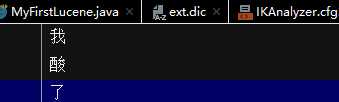
配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd">
<properties>
<comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置</comment>
<!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展字典 -->
<entry key="ext_dict">ext.dic;</entry>
<!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展停止词字典-->
<entry key="ext_stopwords">stopword.dic;</entry>
</properties>
测试代码:
@Test public void testTokenStream() throws Exception { // 创建一个标准分析器对象 Analyzer analyzer = new IKAnalyzer(); // 获得tokenStream对象,第一个参数:域名,可以随便给一个,第二个参数:要分析的文本内容 TokenStream tokenStream = analyzer.tokenStream("test", "硬核,柠檬精,我酸了,奥利给"); // 添加一个引用,可以获得每个关键词 CharTermAttribute charTermAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(CharTermAttribute.class); // 添加一个偏移量的引用,记录了关键词的开始位置以及结束位置 OffsetAttribute offsetAttribute = tokenStream.addAttribute(OffsetAttribute.class); // 将指针调整到列表的头部 tokenStream.reset(); // 遍历关键词列表,通过incrementToken方法判断列表是否结束 while (tokenStream.incrementToken()) { // 关键词的起始位置 System.out.println("start->" + offsetAttribute.startOffset()); // 取关键词 System.out.println(charTermAttribute); // 结束位置 System.out.println("end->" + offsetAttribute.endOffset()); } tokenStream.close(); }
测试结果:
加载扩展词典:ext.dic 加载扩展停止词典:stopword.dic start->0 硬核 end->2 start->3 柠檬精 end->6 start->3 柠檬 end->5 start->5 精 end->6 start->11 奥利给 end->14
标签:扫描 停止 自己 eset sts encoding pat string image
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhai1997/p/13276105.html