标签:factory 管理 效率 over 记录 参数调用 除了 test 工厂
Spring IOC 注入手动实例化与外部引入
图一: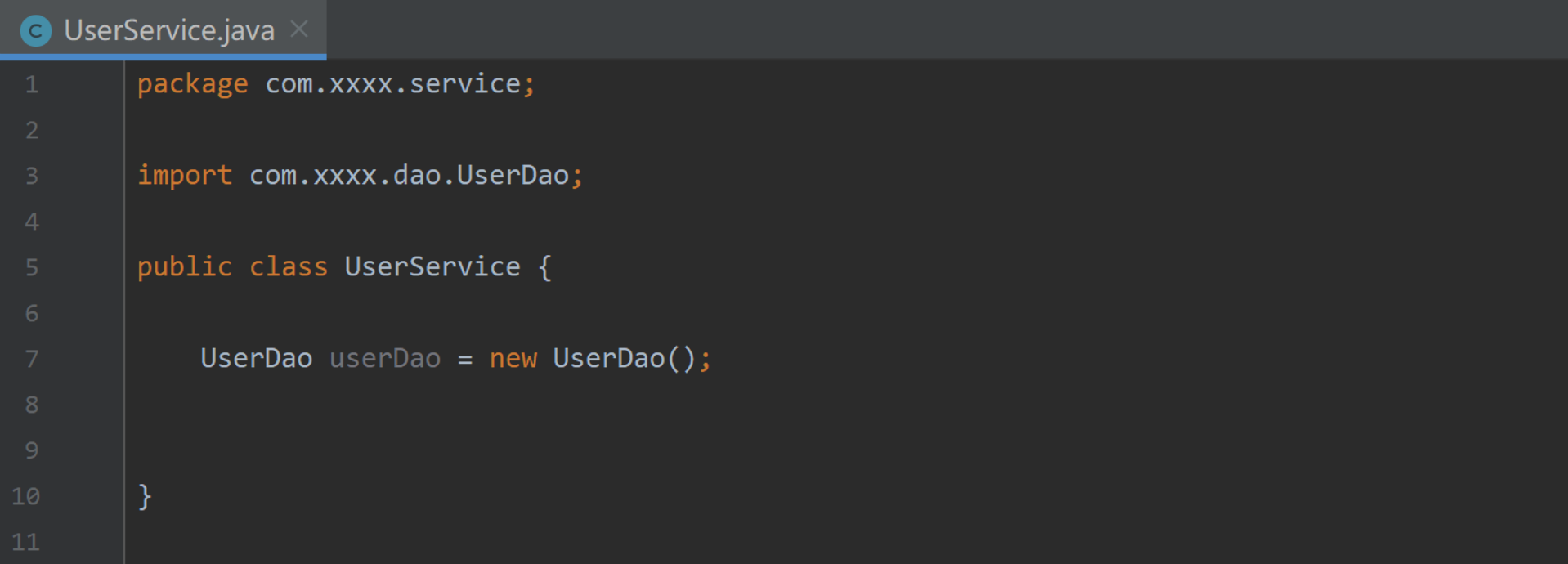
图二: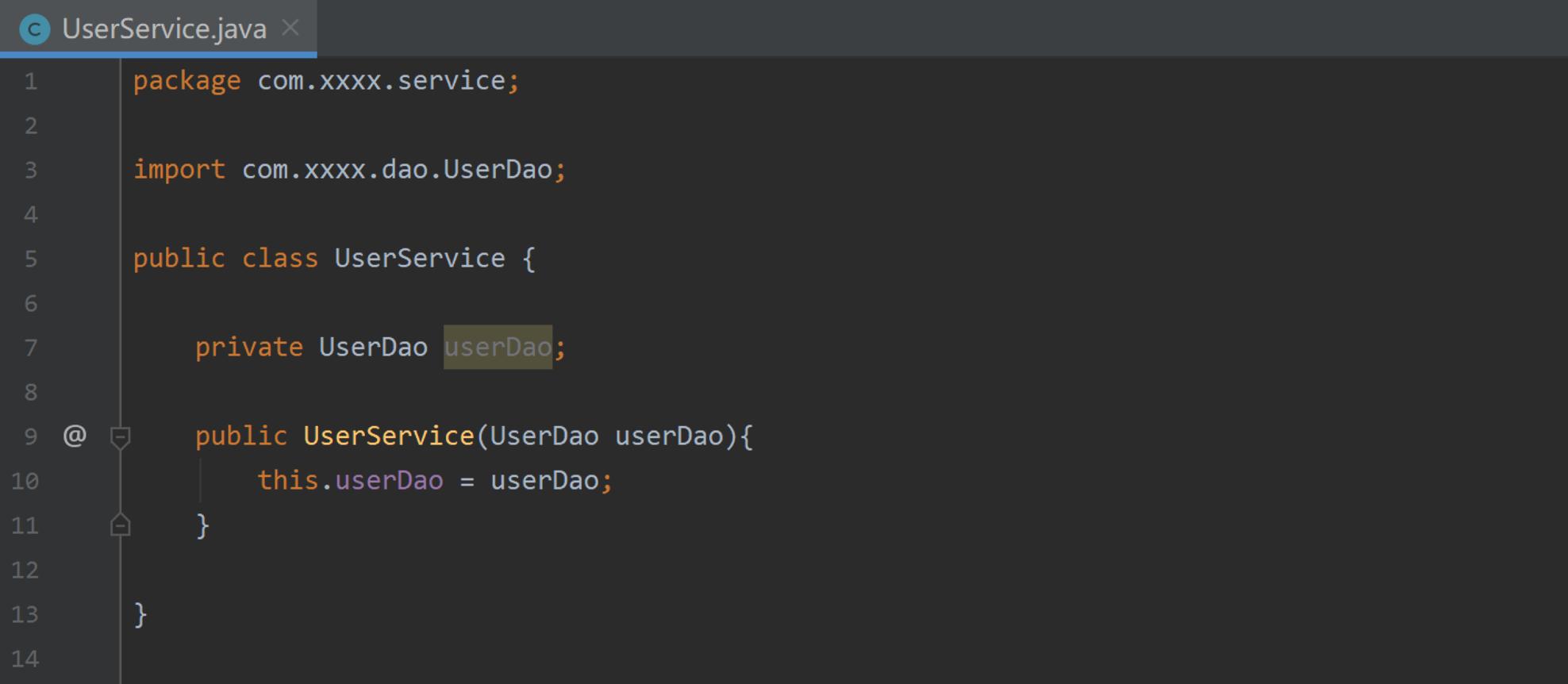
? 对比发现:图二中对于 UserDao 对象的创建并没有像图一那样主动的去实例化,而是通过带参方法形式将UserDao 传入过来,从而实现 UserService 对UserDao类 的依赖。
? 而实际创建对象的幕后对象即是交给了外部来创建。
? Spring 支持的注入方式共有四种:set 注入、构造器注入、静态工厂注入、实例化工厂注入。
注:
属性字段提供set方法
public class UserService {
// 业务对象UserDao set注入(提供set方法)
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
}配置文件的bean标签设置property标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
IOC通过property标签手动装配(注入):
Set方法注入
name:bean对象中属性字段的名称
ref:指定bean标签的id属性值
-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService">
<!--业务对象 注入-->
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
</beans>属性字段提供set方法
public class UserService {
// 常用对象String set注入(提供set方法)
private String host;
public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
}
// 基本类型Integer set注入(提供set方法)
private Integer port;
public void setPort(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
}
配置文件的bean标签设置property标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
IOC通过property标签手动装配(注入):
Set方法注入
name:bean对象中属性字段的名称
value:具体的值(基本类型 常用对象|日期 集合)
-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService">
<!--常用对象String 注入-->
<property name="host" value="127.0.0.1"/>
<!--基本类型注入-->
<property name="port" value="8080"/>
</bean>
</beans>属性字段提供set方法
public class UserService {
// List集合 set注入(提供set方法)
public List<String> list;
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
// Set集合 set注入(提供set方法)
private Set<String> set;
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
this.set = set;
}
// Map set注入(提供set方法)
private Map<String,Object> map;
public void setMap(Map<String, Object> map) {
this.map = map;
}
// Properties set注入(提供set方法)
private Properties properties;
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
}配置文件的bean标签设置property标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
IOC通过property标签手动装配(注入):
Set方法注入
name:bean对象中属性字段的名称
value:具体的值(基本类型 常用对象|日期 集合)
-->
<!--List集合 注入-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>上海</value>
<value>北京</value>
<value>杭州</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--Set集合注入-->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>上海SH</value>
<value>北京BJ</value>
<value>杭州HZ</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--Map注入-->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry>
<key><value>周杰伦</value></key>
<value>我是如此相信</value>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>林俊杰</value></key>
<value>可惜没如果</value>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>陈奕迅</value></key>
<value>十年</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--Properties注入-->
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="上海">东方明珠</prop>
<prop key="北京">天安门</prop>
<prop key="杭州">西湖</prop>
</props>
</property>
</beans>UserService.java
public class UserService {
// 业务对象UserDao set注入(提供set方法)
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
// 常用对象String set注入(提供set方法)
private String host;
public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
}
// 基本类型Integer set注入(提供set方法)
private Integer port;
public void setPort(Integer port) {
this.port = port;
}
// List集合 set注入(提供set方法)
public List<String> list;
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
// List集合输出
public void printList() {
list.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
}
// Set集合 set注入(提供set方法)
private Set<String> set;
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
this.set = set;
}
// Set集合输出
public void printSet() {
set.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
}
// Map set注入(提供set方法)
private Map<String,Object> map;
public void setMap(Map<String, Object> map) {
this.map = map;
}
// Map输出
public void printMap() {
map.forEach((k,v) -> System.out.println(k + "," + v));
}
// Properties set注入(提供set方法)
private Properties properties;
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
// Properties输出
public void printProperties(){
properties.forEach((k,v) -> System.out.println(k + ","+ v ));
}
public void test(){
System.out.println("UserService Test...");
userDao.test();
studentDao.test();
System.out.println("Host:" + host + ",port:" + port);
// List集合
printList();
// Set集合
printSet();
// Map
printMap();
// Properties
printProperties();
}
}spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
IOC通过property标签手动装配(注入):
Set方法注入
name:bean对象中属性字段的名称
ref:指定bean标签的id属性值
value:具体的值(基本类型 常用对象|日期 集合)
-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService">
<!--业务对象 注入-->
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"/>
<!--常用对象String 注入-->
<property name="host" value="192.168.1.109"/>
<!--基本类型注入-->
<property name="port" value="8080"/>
<!--List集合 注入-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>上海</value>
<value>北京</value>
<value>杭州</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--Set集合注入-->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>上海SH</value>
<value>北京BJ</value>
<value>杭州HZ</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--Map注入-->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry>
<key><value>周杰伦</value></key>
<value>我是如此相信</value>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>林俊杰</value></key>
<value>可惜没如果</value>
</entry>
<entry>
<key><value>陈奕迅</value></key>
<value>十年</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<!--Properties注入-->
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="上海">东方明珠</prop>
<prop key="北京">天安门</prop>
<prop key="杭州">西湖</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>注:
Java 代码
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao; // JavaBean 对象
public UserService(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void test(){
System.out.println("UserService Test...");
userDao.test();
}
}XML配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
IOC通过构造器注入:
通过constructor-arg标签进行注入
name:属性名称
ref:指定bean标签的id属性值
-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao" ></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService">
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="userDao"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>Java 代码
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao; // JavaBean 对象
private AccountDao accountDao // JavaBean 对象
public UserService(UserDao userDao, AccountDao accountDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public void test(){
System.out.println("UserService Test...");
userDao.test();
accountDao.test();
}
}XML配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
IOC通过构造器注入:
通过constructor-arg标签进行注入
name:属性名称
ref:指定bean标签的id属性值
-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao" ></bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.AccountDao" ></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService">
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="userDao"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>Java 代码
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao; // JavaBean 对象
private AccountDao accountDao; // JavaBean 对象
private String uname; // 字符串类型
public UserService(UserDao userDao, AccountDao accountDao, String uname) {
this.userDao = userDao;
this.accountDao = accountDao;
this.uname = uname;
}
public void test(){
System.out.println("UserService Test...");
userDao.test();
accountDao.test();
System.out.println("uname:" + uname);
}
}XML配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
IOC通过构造器注入:
通过constructor-arg标签进行注入
name:属性名称
ref:指定bean标签的id属性值
value:基本类型 常用对象的值
index:构造器中参数的下标,从0开始
-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao" ></bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.AccountDao" ></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService">
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="userDao"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="uname" value="admin"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>循环问题产生的原因:
? Bean通过构造器注入,之间彼此相互依赖对方导致bean无法实例化。
问题展示:
Java 代码
public class AccountService {
private RoleService roleService;
public AccountService(RoleService roleService) {
this.roleService = roleService;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("AccountService Test...");
}
}
public class RoleService {
private AccountService accountService;
public RoleService(AccountService accountService) {
this.accountService = accountService;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("RoleService Test...");
}
}XML配置
<!--
如果多个bean对象中互相注入,则会出现循环依赖的问题
可以通过set方法注入解决
-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.xxxx.service.AccountService">
<constructor-arg name="roleService" ref="roleService"/>
</bean>
<bean id="roleService" class="com.xxxx.service.RoleService">
<constructor-arg name="accountService" ref="accountService"/>
</bean>如有疑问,可加入群:10803-55292,输入暗号13,即可有大佬传授十年经验
如何解决:将构造器注入改为set方法注入
Java代码
public class AccountService {
private RoleService roleService;
/* public AccountService(RoleService roleService) {
this.roleService = roleService;
}*/
public void setRoleService(RoleService roleService) {
this.roleService = roleService;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("AccountService Test...");
}
}
public class RoleService {
private AccountService accountService;
/* public RoleService(AccountService accountService) {
this.accountService = accountService;
}*/
public void setAccountService(AccountService accountService) {
this.accountService = accountService;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("RoleService Test...");
}
}XML配置
<!--
<bean id="accountService" class="com.xxxx.service.AccountService">
<constructor-arg name="roleService" ref="roleService"/>
</bean>
<bean id="roleService" class="com.xxxx.service.RoleService">
<constructor-arg name="accountService" ref="accountService"/>
</bean>
-->
<!--修改为set方法注入-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.xxxx.service.AccountService">
<property name="roleService" ref="roleService"/>
</bean>
<bean id="roleService" class="com.xxxx.service.RoleService">
<property name="accountService" ref="accountService"/>
</bean>定义静态工厂类
public class StaticFactory {
// 定义静态方法
public static TypeDao createTypeDao() {
return new TypeDao();
}
}Java代码
public class TypeService {
private TypeDao typeDao;
public void setTypeDao(TypeDao typeDao) {
this.typeDao = typeDao;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("TypeService Test...");
}
}XML配置
在配置文件中设置bean标签,指定工厂对象并设置对应的方法
<bean id="typeService" class="com.xxxx.service.TypeService">
<property name="typeDao" ref="typeDao"/>
</bean>
<!--
静态工厂注入:
静态工厂注入也是借助set方法注入,只是被注入的bean对象的实例化是通过静态工厂实例化的
-->
<bean id="typeDao" class="com.xxxx.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="createTypeDao"></bean>定义工厂类
public class InstanceFactory {
public TypeDao createTypeDao() {
return new TypeDao();
}
}Java代码
public class TypeService {
private TypeDao typeDao;
public void setTypeDao(TypeDao typeDao) {
this.typeDao = typeDao;
}
public void test() {
System.out.println("TypeService Test...");
}
}XML配置
声明工厂bean标签,声明bean对象,指明工厂对象和工厂方法
<bean id="typeService" class="com.xxxx.service.TypeService">
<property name="typeDao" ref="typeDao"/>
</bean>
<!--
实例化工厂注入:
实例化工厂注入也是借助set方法注入,只是被注入的bean对象的实例化是通过实例化工厂实例化的
-->
<bean id="instanceFactory" class="com.xxxx.factory.InstanceFactory"></bean>
<bean id="typeDao" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="createTypeDao"></bean>重点掌握set注入和构造器注入,工厂方式了解即可。实际开发中基本使用set方式注入bean。
? 开发项目中set方式注入首选
? 使用构造注入可以在构建对象的同时一并完成依赖关系的建立,对象一建立则所有的一切也就准备好了,但如果要建立的对象关系很多,使用构造器注入会在构建函数上留下一长串的参数,且不易记忆,这时使用Set注入会是个不错的选择。
使用Set注入可以有明确的名称,可以了解注入的对象会是什么,像setXXX()这样的名称会比记忆Constructor上某个参数的位置代表某个对象更好。
p名称空间的使用
? spring2.5以后,为了简化setter方法属性注入,引用p名称空间的概念,可以将<property> 子元素,简化为<bean>元素属性配置。
属性字段提供 set 方法
public class UserService {
// 业务对象UserDao set注入(提供set方法)
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
// 常用对象String set注入(提供set方法)
private String host;
public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
}
}在配置文件 spring.xml 引入 p 名称空间
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao"></bean>
<!--
p:属性名:="xxx" 引入常量值
p:属性名-ref:="xxx" 引入其他Bean对象的id属性值
-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService"
p:userDao-ref="userDao"
p:host="127.0.0.1" />
</beans>注解方式注入 Bean
? 对于 bean 的注入,除了使用 xml 配置以外,可以使用注解配置。注解的配置,可以简化配置文件,提高开发的速度,使程序看上去更简洁。对于注解的解释,Spring对于注解有专门的解释器,对定义的注解进行解析,实现对应bean对象的注入。通过反射技术实现。
修改配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">开启自动化注入
<!--开启自动化装配(注入)-->
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao"></bean>
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService"></bean> @Resource注解实现自动注入(反射)
代码示例
默认根据属性字段名称查找对应的bean对象 (属性字段的名称与bean标签的id属性值相等)
/**
* @Resource注解实现自动注入(反射)
* 默认根据属性字段名称查找对应的bean对象 (属性字段的名称与bean标签的id属性值相等)
*/
public class UserService {
@Resource
private UserDao userDao; // 属性字段的名称与bean标签的id属性值相等
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void test() {
// 调用UserDao的方法
userDao.test();
}
}如果属性字段名称未找到,则会通过类型(Class类型)查找
/**
* @Resource注解实现自动注入(反射)
* 如果属性字段名称未找到,则会通过类型(Class类型)查找
*/
public class UserService {
@Resource
private UserDao ud; // 当在配置文件中属性字段名(ud)未找到,则会查找对应的class(UserDao类型)
public void setUd(UserDao ud) {
this.ud = ud;
}
public void test() {
// 调用UserDao的方法
ud.test();
}
}属性可以提供set方法,也可以不提供set方法
/**
* @Resource注解实现自动注入(反射)
* 属性可以提供set方法,也可以不提供set方法
*/
public class UserService {
@Resource
private UserDao userDao; // 不提供set方法
public void test() {
// 调用UserDao的方法
userDao.test();
}
}注解可以声明在属性级别 或 set方法级别
/**
* @Resource注解实现自动注入(反射)
* 注解可以声明在属性级别 或 set方法级别
*/
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Resource // 注解也可设置在set方法上
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void test() {
// 调用UserDao的方法
userDao.test();
}
}可以设置name属性,name属性值必须与bean标签的id属性值一致;如果设置了name属性值,就只会按照name属性值查找bean对象
/**
* @Resource注解实现自动注入(反射)
* 可以设置name属性,name属性值必须与bean的id属性值一致;
* 如果设置了name属性值,就只会按照name属性值查找bean对象
*/
public class UserService {
@Resource(name = "userDao") // name属性值与配置文件中bean标签的id属性值一致
private UserDao ud;
public void test() {
// 调用UserDao的方法
ud.test();
}
}当注入接口时,如果接口只有一个实现则正常实例化;如果接口存在多个实现,则需要使用name属性指定需要被实例化的bean对象
定义接口类 IUserDao.java
package com.xxxx.dao;
/**
* 定义接口类
*/
public interface IUserDao {
public void test();
}定义接口实现类 UserDao01.java
package com.xxxx.dao;
/**
* 接口实现类
*/
public class UserDao01 implements IUserDao {
@Override
public void test(){
System.out.println("UserDao01...");
}
}定义接口实现类 UserDao02.java
package com.xxxx.dao;
/**
* 接口实现类
*/
public class UserDao02 implements IUserDao {
@Override
public void test(){
System.out.println("UserDao02...");
}
}XML配置文件
<!--开启自动化装配(注入)-->
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="userService" class="com.xxxx.service.UserService"></bean>
<bean id="userDao01" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao01"></bean>
<bean id="userDao02" class="com.xxxx.dao.UserDao01"></bean>使用注解 UserService.java
/**
* @Resource注解实现自动注入(反射)
* 当注入接口时,如果接口只有一个实现则正常实例化;如果接口存在多个实现,则需要使用name属性指定需要被实例化的bean对象
*/
public class UserService {
@Resource(name = "userDao01") // name属性值与其中一个实现类的bean标签的id属性值一致
private IUserDao iUserDao; // 注入接口(接口存在多个实现)
public void test() {
iUserDao.test();
}
}@Autowired注解实现自动化注入:
默认通过类型(Class类型)查找bean对象 与属性字段的名称无关
/**
* @Autowired注解实现自动化注入
* 默认通过类型(Class类型)查找bean对象 与属性字段的名称无关
*/
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao; // 默认通过类型(Class类型)查找bean对象 与属性字段的名称无关
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void test() {
// 调用UserDao的方法
userDao.test();
}
}属性可以提供set方法,也可以不提供set方法
/**
* @Autowired注解实现自动化注入
* 属性可以提供set方法,也可以不提供set方法
*/
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao; // 不提供set方法
public void test() {
// 调用UserDao的方法
userDao.test();
}
}注解可以声明在属性级别 或 set方法级别
/**
* @Autowired注解实现自动化注入
* 注解可以声明在属性级别 或 set方法级别
*/
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Autowired// 注解可以声明在set方法级别
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void test() {
// 调用UserDao的方法
userDao.test();
}
}可以添加@Qualifier结合使用,通过value属性值查找bean对象(value属性值必须要设置,且值要与bean标签的id属性值对应)
/**
* @Autowired注解实现自动化注入
* 可以添加@Qualifier结合使用,通过value属性值查找bean对象
value属性值必须要设置,且值要与bean标签的id属性值对应
*/
public class UserService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value="userDao") // value属性值必须要设置,且值要与bean标签的id属性值对应
private UserDao userDao;
public void test() {
userDao.test();
}
}推荐使用@Resource 注解是属于J2EE的,减少了与Spring的耦合。
? 实际的开发中,bean的数量非常多,采用手动配置bean的方式已无法满足生产需要,Spring这时候同样提供了扫描的方式,对扫描到的bean对象统一进行管理,简化开发配置,提高开发效率。
Spring IOC 扫描器
作用:bean对象统一进行管理,简化开发配置,提高开发效率
1、设置自动化扫描的范围
如果bean对象未在指定包范围,即使声明了注解,也无法实例化
2、使用指定的注解(声明在类级别) bean对象的id属性默认是 类的首字母小写
Dao层:
@Repository
Service层:
@Service
Controller层:
@Controller
任意类:
@Component
注:开发过程中建议按照指定规则声明注解设置自动化扫描范围
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 设置自动化扫描的范围 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.xxxx"/>
</beans>使用特定的注解
@Repository (Dao层)
@Repository
public class ResourceDao {
public void test() {
System.out.println("ResourceDao...");
}
}@Service(Service层 )
@Service
public class ResourceService {
@Resource
private ResourceDao resourceDao; // service层注入dao层的bean对象
public void test() {
System.out.println("ResourceService...");
resourceDao.test();
}
}@Controller (Controller 层 )
@Controller
public class ResourceController {
@Autowired
private ResourceService resourceService; // Controller层注入service层的bean对象
public void test() {
System.out.println("ResourceController...");
resourceService.test();
}
}@Component (任意层)
@Component
public class PropertyUtils {
public void test(){
System.out.println("PropertyUtils...");
}
}定义JavaBean User.java
package com.xxxx.po;
/**
* User 用户实体类
*/
public class User {
private String userName; // 用户名称
private String userPwd; // 用户密码
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getUserPwd() {
return userPwd;
}
public void setUserPwd(String userPwd) {
this.userPwd = userPwd;
}
}编写Dao层 UserDao.java
package com.xxxx.dao;
import com.xxxx.po.User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class UserDao {
private final String USERNAME = "admin";
private final String USERPWD = "admin";
/**
* 通过用户名称查询用户对象
* @param userName
* @return
*/
public User queryUserByUserName(String userName){
User user = null;
// 判断用户名称是否正确
if(!USERNAME.equals(userName)){
// 如果不正确,返回null
return null;
}
// 如果正确,将用户名称和密码设置到user对象中
user = new User();
user.setUserName(USERNAME);
user.setUserPwd(USERPWD);
return user;
}
}定义业务处理返回消息模型 MessageModel.java
package com.xxxx.po.vo;
/**
* 定义业务处理返回消息模型
* 封装返回结果
*/
public class MessageModel {
private Integer resultCode = 1; // 结果状态码 1=成功,0=失败
private String resultMsg = "操作成功!"; // 结果提示信息
public Integer getResultCode() {
return resultCode;
}
public void setResultCode(Integer resultCode) {
this.resultCode = resultCode;
}
public String getResultMsg() {
return resultMsg;
}
public void setResultMsg(String resultMsg) {
this.resultMsg = resultMsg;
}
}编写Service层 UserService.java
package com.xxxx.service;
import com.xxxx.dao.UserDao1;
import com.xxxx.po.User;
import com.xxxx.po.vo.MessageModel;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Resource
private UserDao userDao;
/**
* 验证用户登录
* @param userName
* @param userPwd
* @return
*/
public MessageModel userLoginCheck(String userName, String userPwd){
// 定义业务处理返回消息模型
MessageModel messageModel = new MessageModel();
// 判断用户名称是否非空
if(null == userName || "".equals(userName.trim())){
messageModel.setResultCode(0);
messageModel.setResultMsg("用户名不能为空!");
return messageModel;
}
// 判断用户密码是否为空
if(null == userPwd || "".equals(userPwd.trim())){
messageModel.setResultCode(0);
messageModel.setResultMsg("密码不能为空!");
return messageModel;
}
// 通过用户名称查询用户对象
User user = userDao.queryUserByUserName(userName);
// 判断用户对象是否为空
if(null == user){
messageModel.setResultCode(0);
messageModel.setResultMsg("该用户不存在!");
return messageModel;
}
// 如果用户对象不为空,判断密码是否正确
if(!user.getUserPwd().equals(userPwd)){
messageModel.setResultCode(0);
messageModel.setResultMsg("用户密码不正确!");
return messageModel;
}
// 登录成功
messageModel.setResultMsg("登录成功!");
return messageModel;
}
}编写Controller层 UserController.java
package com.xxxx.controller;
import com.xxxx.po.vo.MessageModel;
import com.xxxx.service.UserService1;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Resource
private UserService userService;
/**
* 用户登录
* @param userName
* @param userPwd
* @return
*/
public MessageModel login(String userName, String userPwd){
// 调用Dao层判断用户登录操作,返回结果
MessageModel messageModel = userService.userLoginCheck(userName, userPwd);
return messageModel;
}
}package com.xxxx;
import com.xxxx.controller.UserController;
import com.xxxx.po.vo.MessageModel;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestLogin {
@Test
public void test() {
// 得到Spring容器上下文环境
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
// 得到UserController实例化对象
UserController userController = (UserController) ac.getBean("userController");
// 传入参数调用UserController的方法,返回封装类
MessageModel messageModel= userController.login("admin", "admin");
System.out.println("状态码:" + messageModel.getResultCode() + ",提示信息:" + messageModel.getResultMsg());
}
}再学一遍Spring IOC 注入会有新的认识--乐字节微服务
标签:factory 管理 效率 over 记录 参数调用 除了 test 工厂
原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/14819669/2509995