标签:com protoc 技术 通过 read 修改 ams 必须 描述
统一资源定位符,缩写为URL,是对网络资源(网页、图像、文件)的引用。URL指定资源位置和检索资源的机制(http、ftp、mailto)。
举个例子,这里是这篇文章的 URL 地址:
https://dmitripavlutin.com/parse-url-JavaScript很多时候你需要获取到一段 URL 的某个组成部分。它们可能是 hostname(例如 dmitripavlutin.com),或者 pathname(例如 /parse-url-JavaScript)。
一个方便的用于获取 URL 组成部分的办法是通过 URL() 构造函数。
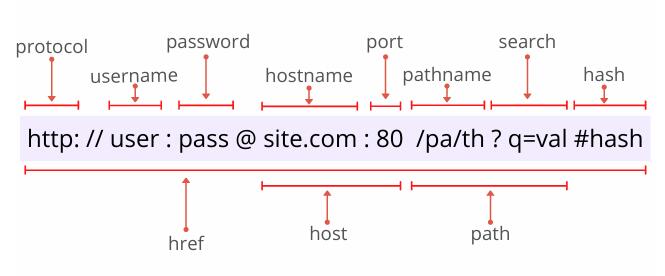
在这篇文章中,我将给大家展示一段 URL 的结构,以及它的主要组成部分。
接着,我会告诉你如何使用 URL() 构造函数来轻松获取 URL 的组成部分,比如 hostname,pathname,query 或者 hash。
一图胜千言。不需要过多的文字描述,通过下面的图片你就可以理解一段 URL 的各个组成部分:
URL() 构造函数允许我们用它来解析一段 URL:
const url = new URL(relativeOrAbsolute [, absoluteBase]);参数 relativeOrAbsolute 既可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径。如果第一个参数是相对路径的话,那么第二个参数 absoluteBase 则必传,且必须为第一个参数的绝对路径。
举个例子,让我们用一个绝对路径的 URL 来初始化 URL() 函数:
const url = new URL(‘http://example.com/path/index.html‘);
url.href; // => ‘http://example.com/path/index.html‘或者我们可以使用相对路径和绝对路径:
const url = new URL(‘/path/index.html‘, ‘http://example.com‘);
url.href; // => ‘http://example.com/path/index.html‘URL() 实例中的 href 属性返回了完整的 URL 字符串。
在新建了 URL() 的实例以后,你可以用它来访问前文图片中的任意 URL 组成部分。作为参考,下面是 URL() 实例的接口列表:
interface URL {
href: USVString;
protocol: USVString;
username: USVString;
password: USVString;
host: USVString;
hostname: USVString;
port: USVString;
pathname: USVString;
search: USVString;
hash: USVString;
readonly origin: USVString;
readonly searchParams: URLSearchParams;
tojsON(): USVString;
}上述的 USVString 参数在 JavaScript 中会映射成字符串。
url.search 可以获取到 URL 当中 ? 后面的 query 字符串:
const url = new URL(
‘http://example.com/path/index.html?message=hello&who=world‘
);
url.search; // => ‘?message=hello&who=world‘如果 query 参数不存在,url.search 默认会返回一个空字符串 ‘‘:
const url1 = new URL(‘http://example.com/path/index.html‘);
const url2 = new URL(‘http://example.com/path/index.html?‘);
url1.search; // => ‘‘
url2.search; // => ‘‘
相比于获得原生的 query 字符串,更实用的场景是获取到具体的 query 参数。
获取具体 query 参数的一个简单的方法是利用 url.searchParams 属性。这个属性是 URLSearchParams 的实例。
URLSearchParams 对象提供了许多用于获取 query 参数的方法,如get(param),has(param)等。
下面来看个例子:
const url = new URL(
‘http://example.com/path/index.html?message=hello&who=world‘
);
url.searchParams.get(‘message‘); // => ‘hello‘
url.searchParams.get(‘missing‘); // => nullurl.searchParams.get(‘message‘) 返回了 message 这个 query 参数的值——hello。
如果使用 url.searchParams.get(‘missing‘) 来获取一个不存在的参数,则得到一个 null。
url.hostname 属性返回一段 URL 的 hostname 部分:
const url = new URL(‘http://example.com/path/index.html‘);
url.hostname; // => ‘example.com‘
url. pathname 属性返回一段 URL 的 pathname 部分:
const url = new URL(‘http://example.com/path/index.html?param=value‘);
url.pathname; // => ‘/path/index.html‘如果这段 URL 不含 path,则该属性返回一个斜杠 /:
const url = new URL(‘http://example.com/‘);
url.pathname; // => ‘/‘
最后,我们可以通过 url.hash 属性来获取 URL 中的 hash 值:
const url = new URL(‘http://example.com/path/index.html#bottom‘);
url.hash; // => ‘#bottom‘当 URL 中的 hash 不存在时,url.hash 属性会返回一个空字符串 ‘‘:
const url = new URL(‘http://example.com/path/index.html‘);
url.hash; // => ‘‘
当使用 new URL() 构造函数来新建实例的时候,作为一种副作用,它同时也会对 URL 进行校验。如果 URL 不合法,则会抛出一个 TypeError。
举个例子,http ://example.com 是一段非法 URL,因为它在 http 后面多写了一个空格。
让我们用这个非法 URL 来初始化 URL() 构造函数:
try {
const url = new URL(‘http ://example.com‘);
} catch (error) {
error; // => TypeError, "Failed to construct URL: Invalid URL"
}因为 http ://example.com 是一段非法 URL,跟我们想的一样,new URL() 抛出了一个 TypeError。
除了获取 URL 的组成部分以外,像 search,hostname,pathname 和 hash 这些属性都是可写的——这也意味着你可以修改 URL。
举个例子,让我们把一段 URL 从 red.com 修改成 blue.io:
const url = new URL(‘http://red.com/path/index.html‘);
url.href; // => ‘http://red.com/path/index.html‘
url.hostname = ‘blue.io‘;
url.href; // => ‘http://blue.io/path/index.html‘注意,在 URL() 实例中只有 origin 和 searchParams 属性是只读的,其他所有的属性都是可写的,并且会修改原来的 URL。
广州vi设计公司 http://www.maiqicn.com 我的007办公资源网 https://www.wode007.com
URL() 构造函数是 JavaScript 中的一个能够很方便地用于解析(或者校验)URL 的工具。
new URL(relativeOrAbsolute [, absoluteBase]) 中的第一个参数接收 URL 的绝对路径或者相对路径。当第一个参数是相对路径时,第二个参数必传且必须为第一个参数的基路径。
在新建 URL() 的实例以后,你就能很轻易地获得 URL 当中的大部分组成部分了,比如:
标签:com protoc 技术 通过 read 修改 ams 必须 描述
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/cmqj/p/13640542.html