标签:rap weixin put arrays task oss oid 注意 overflow
Java异常类是对于程序中可能出现的错误或者异常的一种处理方式。在设计程序的过程中,对于可能出现的异常错误,比如说用户输入错误,设备错误,磁盘满了或者代码错误等等,通常采用异常处理的方式来进行处理可能的错误。 JAVA的异常处理机制:如果某个方法不能按照正常的途径完成任务,就可以通过另一种路径退出该方法,并处理可能出现的错误。在这种情况下会抛出一个封装了错误信息的对象。 这个方法会立刻退出同时不返回任何值。另外,调用这个方法的其他代码也无法继续执行,异常处理机制会将代码执行交给异常处理器。
(一)Java异常
异常:导致程序中断运行的一种指令流。 在理想的情况下,程序完全按照我们设计的流程来执行,但是很多时候会出现这样或者那样的错误,如文件找不到,磁盘满了或者代码错误等,这些错误会影响程序的正常执行,对于这种情况,就有了异常处理情况,即使程序异常了,它也是按照某种逻辑在执行,只是没有按照我们给它安排的逻辑执行。异常在Java中定义为Throwable类,其结构层次图如下:
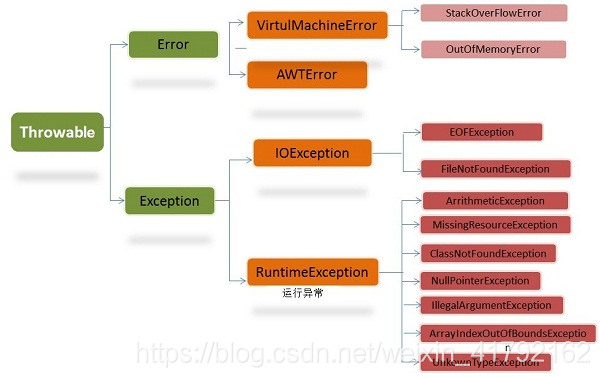
由上图可以看出,Thowable有两个重要的子类,一个是Error类,另一个是Expection类,每一个子类下面还有很多小的分类。
Error类指的是Java运行时系统的内部错误或者资源耗尽错误, 这是程序无法处理的错误,表示运行应用程序中较严重问题,对于这类问题,JVM告知用户,并尽力终止程序。
Expection类指的是 程序本身可以处理的异常。主要分为两类,RuntimeException类异常或者其他异常,由程序错误导致的异常称之为RuntimeExpection,比如说:错误的类型转化,数组访问过界,访问空指针等。而程序本身没有错误,像I/O错误这类问题所导致的异常称之为其他异常,比如说试图打开一个不存在的文件或类。
Java 异常类的另一种分类方式是:可查的异常(checked exceptions)和不可查的异常(unchecked exceptions)。
可查的异常(checked exceptions):正确的程序在运行时,出现情理可容的异常,除了RuntimeException及其子类以外,其他的Exception类及其子类都属于可查异常。对于此类异常,要么用try-catch语句捕获它,要么用throws子句声明抛出它,否则编译不会通过。
可不查的异常(unchecked exceptions): 包括RuntimeException及其子类和Error。 编译器不要求强制处理的异常。
(二) 异常处理
在 Java 应用程序中,异常处理机制为:抛出异常,捕捉异常。
抛出异常:在执行一个方法时,如果发生异常,则这个方法生成代表该异常的一个对象,并停止当前执行路径,并将此异常提交给系统。首先像创建普通的java对象一样,使用new在堆上创建一个异常对象;然后,当前的执行路径被终止,并且从当前环境中弹出对异常对象的引用。此时,异常处理机制接管程序,并开始寻找一个恰当的地方继续执行程序,这个恰当的地方就是异常处理程序或者异常处理器,它的任务是将程序从错误状态中恢复,以使程序要么换一种方式运行,要么继续运行下去。
捕捉异常:当系统捕捉到该异常后,寻求相应的代码来看处理该异常,在方法的调用栈中查找合适·的异常处理器,从生成异常的方法开始回溯,直到找到相应的异常处理代码,并在控制台上打印异常信息,包括异常的信息的堆栈的内容。
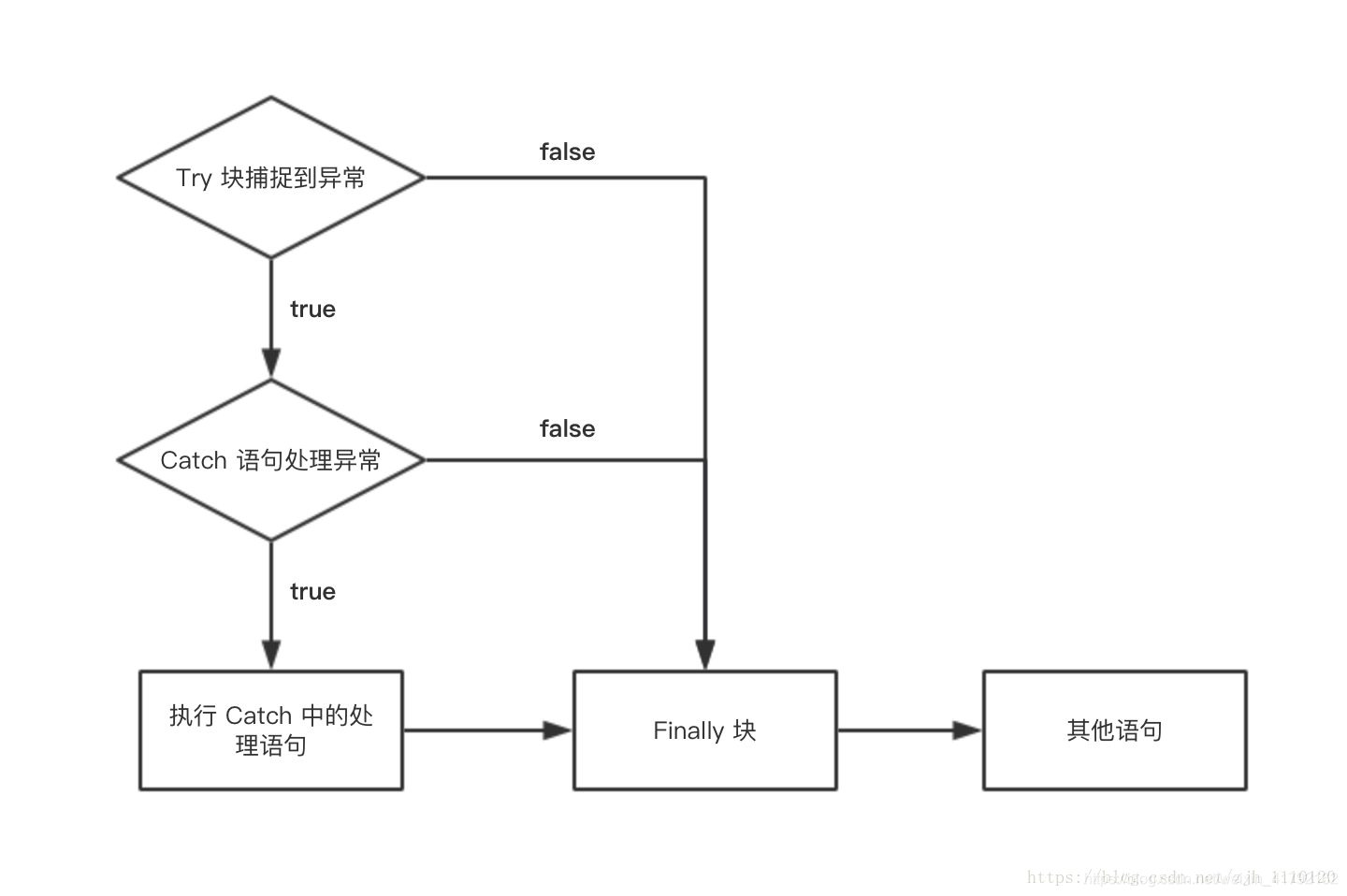
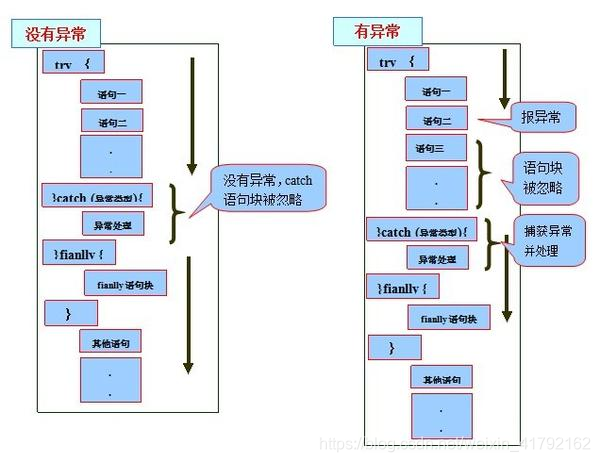
Java异常处理涉及到五个关键字,分别是:try、catch、finally、throw、throws。
try {
code1;
// 可能会发生异常的程序代码
} catch (Type1 id1) {
code2
// 捕获并处理try抛出的异常类型Type1
} catch (Type2 id2) {
code3
// 捕获并处理try抛出的异常类型Type2
} finally {
code4
// 无论是否发生异常,都将执行的语句块
}
其逻辑框图如下:
public class TestException
{
public static void main(String args[])
{ int i = 0;
String greetings[] = { " Hello world !", " Hello World !! ", " HELLO WORLD !!!" };
while (i < 4) {
try { // 特别注意循环控制变量i的设计,避免造成无限循环
System.out.println(greetings[i++]);
}
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("数组下标越界异常");
} finally
{
System.out.println("--------------------------");
}
}
}
}
public void test() throws FileNotFoundException {
method();
}
public void method() throws FileNotFoundException {
//一个会抛出异常的方法
method2();
}
//这里 方法后是throws
public void method2() throws FileNotFoundException {
//这里是throw
throw new FileNotFoundException();
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
throw new TestException20180809("自定义异常:天王盖地虎");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
import java.lang.Exception;
public class TestException {
static void pop() throws NegativeArraySizeException {
// 定义方法并抛出NegativeArraySizeException异常
int[] arr = new int[-3]; // 创建数组
}
public static void main(String[] args) { // 主方法
try { // try语句处理异常信息
pop(); // 调用pop()方法
} catch (NegativeArraySizeException e) {
System.out.println("pop()方法抛出的异常");// 输出异常信息
}
}
import java.lang.Exception;
public class TestException {
static int quotient(int x, int y) throws MyException { // 定义方法抛出异常
if (y < 0) { // 判断参数是否小于0
throw new MyException("除数不能是负数"); // 异常信息
}
return x/y; // 返回值
}
public static void main(String args[]) { // 主方法
int a =3;
int b =0;
try { // try语句包含可能发生异常的语句
int result = quotient(a, b); // 调用方法quotient()
} catch (MyException e) { // 处理自定义异常
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // 输出异常信息
} catch (ArithmeticException e) { // 处理ArithmeticException异常
System.out.println("除数不能为0"); // 输出提示信息
} catch (Exception e) { // 处理其他异常
System.out.println("程序发生了其他的异常"); // 输出提示信息
}
}
}
class MyException extends Exception { // **创建自定义异常类**
String message; // 定义String类型变量
public MyException(String ErrorMessagr) { // 父类方法
message = ErrorMessagr;
}
public String getMessage() { // 覆盖getMessage()方法
return message;
}
}
(三)Java常见异常
五种常见的运行时异常:
ClassCastException(类转换异常)
IndexOutOfBoundsException(数组越界)
NullPointerException(空指针)
ArrayStoreException(数据存储异常,操作数组时类型不一致)
IO操作的BufferOverflowException异常
非运行时异常必须得捕获,否则编译不过去,java编译器要求程序员必须对这种异常进行catch,Java认为Checked异常都是可以被处理(修复)的异常,所以Java程序必须显式处理Checked异常。常见的非运行异常有io异常和sql异常。
IOException、FileNotFoundExcetion 和SQLException
(四)当异常遇到return
在一个方法中,无论 Try 块中有没有异常、Return,只要 Finally 块中有 Return,那么函数的返回值都由 Finally 块提供。
Java异常总结:(1)一个图:异常类型图。(2)五个关键字,try, catch finally throws throw
(3)继承关系:先大后小,(4)异常和重写:子类重写异常范围不能超出父类。
实例说明:
public class TestException {
public TestException() {
}
boolean testEx() throws Exception {
boolean ret = true;
try {
ret = testEx1();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("testEx, catch exception");
ret = false;
throw e;
} finally {
System.out.println("testEx, finally; return value=" + ret);
return ret;
}
}
boolean testEx1() throws Exception {
boolean ret = true;
try {
ret = testEx2();
if (!ret) {
return false;
}
System.out.println("testEx1, at the end of try");
return ret;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("testEx1, catch exception");
ret = false;
throw e;
} finally {
System.out.println("testEx1, finally; return value=" + ret);
return ret;
}
}
boolean testEx2() throws Exception {
boolean ret = true;
try {
int b = 12;
int c;
for (int i = 2; i >= -2; i--) {
c = b / i;
System.out.println("i=" + i);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("testEx2, catch exception");
ret = false;
throw e;
} finally {
System.out.println("testEx2, finally; return value=" + ret);
return ret;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestException testException1 = new TestException();
try {
testException1.testEx();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果:
i=2
i=1
testEx2, catch exception
testEx2, finally; return value=false
testEx1, finally; return value=false
testEx, finally; return value=false
常见的异常·:


JAVA异常知识结构

标签:rap weixin put arrays task oss oid 注意 overflow
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/ShangZhuo/p/13693713.html