标签:cache environ exce wrap ssi sar abstract register 生命周期

“请你描述下 Spring Bean 的生命周期?”,这是面试官考察 Spring 的常用问题,可见是 Spring 中很重要的知识点。
我之前在准备面试时,去网上搜过答案,大多以下图给出的流程作为答案。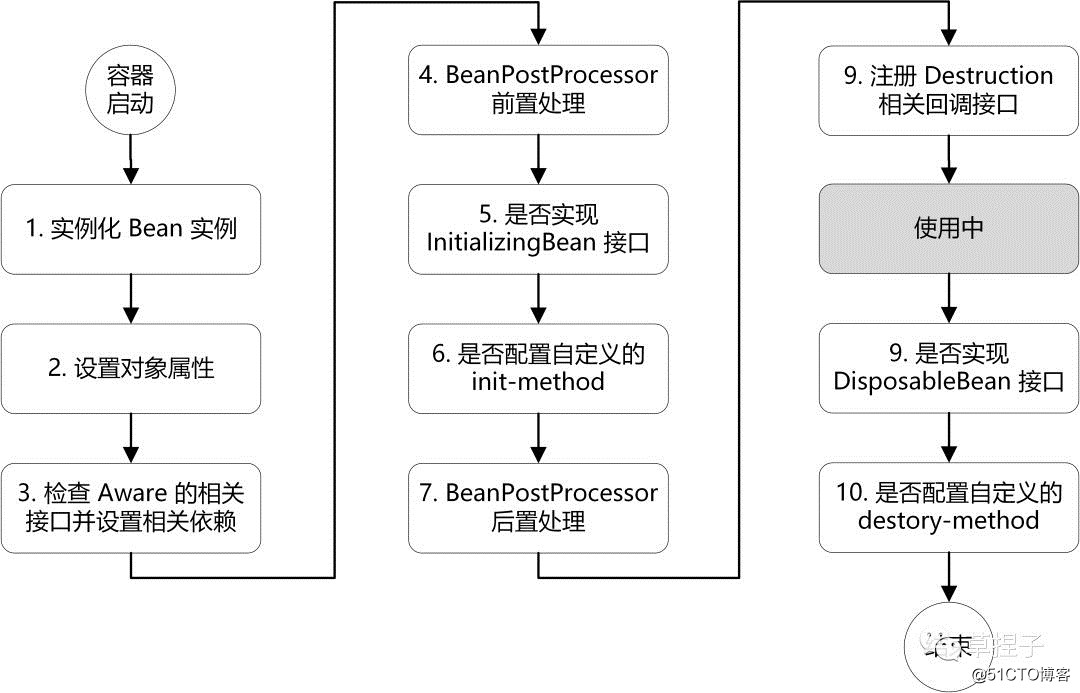
但是当我第一次看到该图时,就产生了很多困扰,“Aware,BeanPostProcessor......这些都是什么啊!而且这么多步骤,太多了,该怎么记啊!”。
其实要记忆该过程,还是需要我们先去理解,本文将从以下两方面去帮助理解 Bean 的生命周期:
扩展点的作用:详细介绍 Bean 生命周期中所涉及到的扩展点的作用。
Bean 的生命周期概括起来就是 4 个阶段:
销毁(Destruction)。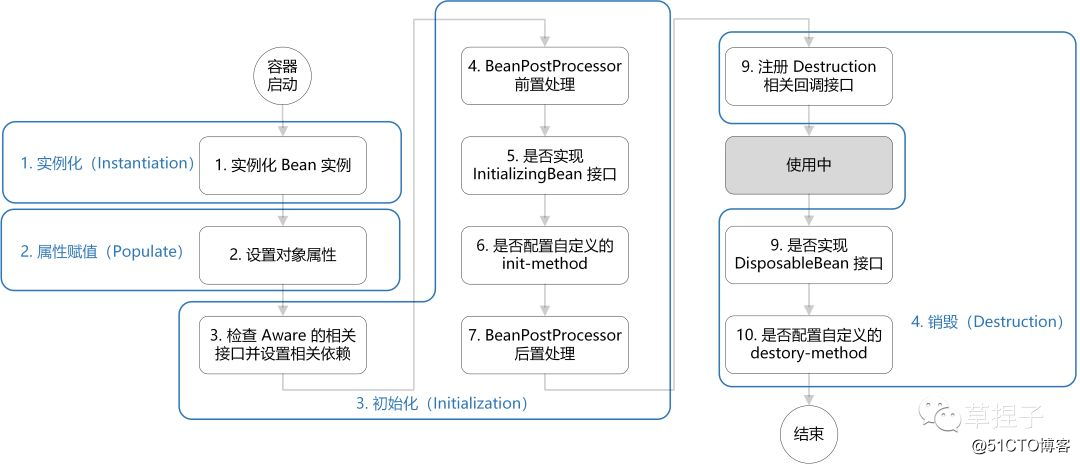
下面我们结合代码来直观的看下,在 doCreateBean() 方法中能看到依次执行了这 4 个阶段:
// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
protected
Object
doCreateBean
(
final
String
beanName
,
final
RootBeanDefinition
mbd
,
final
@Nullable
Object
[]
args
)
throws
BeanCreationException
{
// 1. 实例化
BeanWrapper
instanceWrapper
=
null
;
if
(
instanceWrapper
==
null
)
{
instanceWrapper
=
createBeanInstance
(
beanName
,
mbd
,
args
);
}
Object
exposedObject
=
bean
;
try
{
// 2. 属性赋值
populateBean
(
beanName
,
mbd
,
instanceWrapper
);
// 3. 初始化
exposedObject
=
initializeBean
(
beanName
,
exposedObject
,
mbd
);
}
// 4. 销毁-注册回调接口
try
{
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary
(
beanName
,
bean
,
mbd
);
}
return
exposedObject
;
}由于初始化包含了第 3~7步,较复杂,所以我们进到 initializeBean() 方法里具体看下其过程(注释的序号对应图中序号):
// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
protected
Object
initializeBean
(
final
String
beanName
,
final
Object
bean
,
@Nullable
RootBeanDefinition
mbd
)
{
// 3. 检查 Aware 相关接口并设置相关依赖
if
(
System
.
getSecurityManager
()
!=
null
)
{
AccessController
.
doPrivileged
((
PrivilegedAction
<
Object
>)
()
->
{
invokeAwareMethods
(
beanName
,
bean
);
return
null
;
},
getAccessControlContext
());
}
else
{
invokeAwareMethods
(
beanName
,
bean
);
}
// 4. BeanPostProcessor 前置处理
Object
wrappedBean
=
bean
;
if
(
mbd
==
null
||
!
mbd
.
isSynthetic
())
{
wrappedBean
=
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
(
wrappedBean
,
beanName
);
}
// 5. 若实现 InitializingBean 接口,调用 afterPropertiesSet() 方法
// 6. 若配置自定义的 init-method方法,则执行
try
{
invokeInitMethods
(
beanName
,
wrappedBean
,
mbd
);
}
catch
(
Throwable
ex
)
{
throw
new
BeanCreationException
(
(
mbd
!=
null
?
mbd
.
getResourceDescription
()
:
null
),
beanName
,
"Invocation of init method failed"
,
ex
);
}
// 7. BeanPostProceesor 后置处理
if
(
mbd
==
null
||
!
mbd
.
isSynthetic
())
{
wrappedBean
=
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
(
wrappedBean
,
beanName
);
}
return
wrappedBean
;
}在 invokInitMethods() 方法中会检查 InitializingBean 接口和 init-method 方法,销毁的过程也与其类似:
// DisposableBeanAdapter.java
public
void
destroy
()
{
// 9. 若实现 DisposableBean 接口,则执行 destory()方法
if
(
this
.
invokeDisposableBean
)
{
try
{
if
(
System
.
getSecurityManager
()
!=
null
)
{
AccessController
.
doPrivileged
((
PrivilegedExceptionAction
<
Object
>)
()
->
{
((
DisposableBean
)
this
.
bean
).
destroy
();
return
null
;
},
this
.
acc
);
}
else
{
((
DisposableBean
)
this
.
bean
).
destroy
();
}
}
}
// 10. 若配置自定义的 detory-method 方法,则执行
if
(
this
.
destroyMethod
!=
null
)
{
invokeCustomDestroyMethod
(
this
.
destroyMethod
);
}
else
if
(
this
.
destroyMethodName
!=
null
)
{
Method
methodToInvoke
=
determineDestroyMethod
(
this
.
destroyMethodName
);
if
(
methodToInvoke
!=
null
)
{
invokeCustomDestroyMethod
(
ClassUtils
.
getInterfaceMethodIfPossible
(
methodToInvoke
));
}
}
}从 Spring 的源码我们可以直观的看到其执行过程,而我们记忆其过程便可以从这 4 个阶段出发,实例化、属性赋值、初始化、销毁。其中细节较多的便是初始化,涉及了 Aware、BeanPostProcessor、InitializingBean、init-method 的概念。这些都是 Spring 提供的扩展点,其具体作用将在下一节讲述。
3.1 Aware 接口
若 Spring 检测到 bean 实现了 Aware 接口,则会为其注入相应的依赖。所以通过让bean 实现 Aware 接口,则能在 bean 中获得相应的 Spring 容器资源。
Spring 中提供的 Aware 接口有:
// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
private
void
invokeAwareMethods
(
final
String
beanName
,
final
Object
bean
)
{
if
(
bean
instanceof
Aware
)
{
if
(
bean
instanceof
BeanNameAware
)
{
((
BeanNameAware
)
bean
).
setBeanName
(
beanName
);
}
if
(
bean
instanceof
BeanClassLoaderAware
)
{
((
BeanClassLoaderAware
)
bean
).
setBeanClassLoader
(
bcl
);
}
if
(
bean
instanceof
BeanFactoryAware
)
{
((
BeanFactoryAware
)
bean
).
setBeanFactory
(
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
.
this
);
}
}
}以上是针对 BeanFactory 类型的容器,而对于 ApplicationContext 类型的容器,也提供了 Aware 接口,只不过这些 Aware 接口的注入实现,是通过 BeanPostProcessor 的方式注入的,但其作用仍是注入依赖。
// ApplicationContextAwareProcessor.java
private
void
invokeAwareInterfaces
(
Object
bean
)
{
if
(
bean
instanceof
EnvironmentAware
)
{
((
EnvironmentAware
)
bean
).
setEnvironment
(
this
.
applicationContext
.
getEnvironment
());
}
if
(
bean
instanceof
EmbeddedValueResolverAware
)
{
((
EmbeddedValueResolverAware
)
bean
).
setEmbeddedValueResolver
(
this
.
embeddedValueResolver
);
}
if
(
bean
instanceof
ResourceLoaderAware
)
{
((
ResourceLoaderAware
)
bean
).
setResourceLoader
(
this
.
applicationContext
);
}
if
(
bean
instanceof
ApplicationEventPublisherAware
)
{
((
ApplicationEventPublisherAware
)
bean
).
setApplicationEventPublisher
(
this
.
applicationContext
);
}
if
(
bean
instanceof
MessageSourceAware
)
{
((
MessageSourceAware
)
bean
).
setMessageSource
(
this
.
applicationContext
);
}
if
(
bean
instanceof
ApplicationContextAware
)
{
((
ApplicationContextAware
)
bean
).
setApplicationContext
(
this
.
applicationContext
);
}
}3.2 BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor 是 Spring 为修改 bean 提供的强大扩展点,其可作用于容器中所有 bean,其定义如下:
public
interface
BeanPostProcessor
{
// 初始化前置处理
default
Object
postProcessBeforeInitialization
(
Object
bean
,
String
beanName
)
throws
BeansException
{
return
bean
;
}
// 初始化后置处理
default
Object
postProcessAfterInitialization
(
Object
bean
,
String
beanName
)
throws
BeansException
{
return
bean
;
}
}常用场景有:
// AbstractAutoProxyCreator.java
public
Object
postProcessBeforeInstantiation
(
Class
<?>
beanClass
,
String
beanName
)
{
TargetSource
targetSource
=
getCustomTargetSource
(
beanClass
,
beanName
);
if
(
targetSource
!=
null
)
{
if
(
StringUtils
.
hasLength
(
beanName
))
{
this
.
targetSourcedBeans
.
add
(
beanName
);
}
Object
[]
specificInterceptors
=
getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
(
beanClass
,
beanName
,
targetSource
);
Object
proxy
=
createProxy
(
beanClass
,
beanName
,
specificInterceptors
,
targetSource
);
this
.
proxyTypes
.
put
(
cacheKey
,
proxy
.
getClass
());
// 返回代理类
return
proxy
;
}
return
null
;
}3.3 InitializingBean 和 init-method
InitializingBean 和 init-method 是 Spring 为 bean 初始化提供的扩展点。
InitializingBean接口 的定义如下:
public
interface
InitializingBean
{
void
afterPropertiesSet
()
throws
Exception
;
}在 afterPropertiesSet() 方法写初始化逻辑。
指定 init-method 方法,指定初始化方法:
<?
xml version
=
"1.0"
encoding
=
"UTF-8"
?>
<beans
xmlns
=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi
=
"http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation
=
"http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
>
<bean
id
=
"demo"
class
=
"com.chaycao.Demo"
init-method
=
"init()"
/>
</beans>DisposableBean 和 destory-method 与上述类似,就不描述了。
最后总结下如何记忆 Spring Bean 的生命周期:
大家可以长按二维码,关注下~
你的订阅,是我写作路上最大的支持!

标签:cache environ exce wrap ssi sar abstract register 生命周期
原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/9167833/2544296