标签:log end ima stp std alt sort virt null
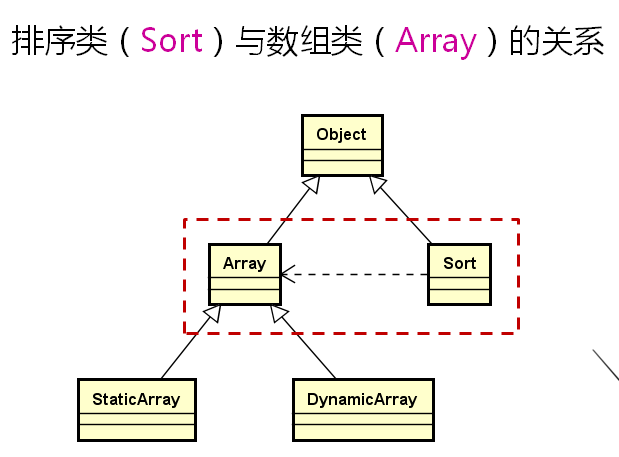
我们要使Srot能排序Array数组类。
Sort应该既能排序静态数组类又能排序动态数组类。
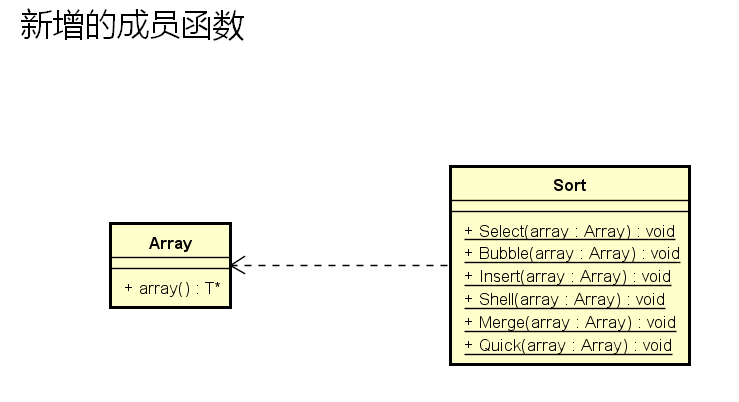
这个函数返回原生数组的首地址。
数组类需要新增成员函数array,排序类需要新增六个静态成员函数。
Array.h添加array函数:
#ifndef ARRAY_H
#define ARRAY_H
#include "Object.h"
#include "Exception.h"
namespace DTLib
{
template <typename T>
class Array : public Object
{
protected:
T* m_array;
public:
virtual bool set(int i, const T&e) //O(1)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < length()));
if( ret )
{
m_array[i] = e;
}
return ret;
}
virtual bool get(int i, T& e) const //O(1)
{
bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i < length()));
if( ret )
{
e = m_array[i];
}
return ret;
}
T& operator[] (int i) //O(1)
{
if((0 <= i) && (i < length()))
{
return m_array[i];
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ...");
}
}
T operator[] (int i) const //O(1)
{
return (const_cast<Array<T>>(*this))[i];
}
T* array()const
{
return m_array;
}
virtual int length() const = 0;
};
}
#endif // ARRAY_H
Sort.h改进如下:
#ifndef SORT_H
#define SORT_H
#include "Object.h"
#include <Array.h>
namespace DTLib
{
class Sort : public Object
{
private:
Sort();
Sort(const Sort&);
Sort& operator = (const Sort&);
template <typename T>
static void Swap(T& a, T& b)
{
T c(a);
a = b;
b = c;
}
template < typename T >
static void Merge(T src[], T helper[], int begin, int mid, int end, bool min2max=true)
{
int i = begin;
int j = mid + 1;
int k = begin; //代表辅助空间起始位置
while( (i <= mid) && (j <= end) )
{
if( min2max ? (src[i] < src[j]) : (src[i] > src[j]) )
{
helper[k++] = src[i++];
}
else
{
helper[k++] = src[j++];
}
}
while( i <= mid)
{
helper[k++] = src[i++];
}
while( j <= end )
{
helper[k++] = src[j++];
}
for(i = begin; i <= end; i++)
{
src[i] = helper[i];
}
}
template < typename T >
static void Merge(T src[], T helper[], int begin, int end, bool min2max)
{
if( begin < end )
{
int mid = (begin + end) / 2;
Merge(src, helper, begin, mid, min2max);
Merge(src, helper, mid+1, end, min2max);
Merge(src, helper, begin, mid, end, min2max); //真正的归并操作
}
}
template < typename T >
static int Partition(T array[], int begin, int end, bool min2max)
{
T pv = array[begin];
while( begin < end )
{
while( (begin < end) && (min2max ? (array[end] > pv) : (array[end] < pv)) )
{
end--;
}
Swap(array[begin], array[end]);
while( (begin < end) && (min2max ? (array[begin] <= pv) : (array[begin] >= pv)) )
{
begin++;
}
Swap(array[begin], array[end]);
}
array[begin] = pv; //基准就位
return begin;
}
template < typename T >
static void Quick(T array[], int begin, int end, bool min2max)
{
if( begin < end )
{
int pivot = Partition(array, begin, end, min2max);
Quick(array, begin, pivot - 1, min2max);
Quick(array, pivot + 1, end, min2max);
}
}
public:
template < typename T >
static void Select(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true)
{
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
int min = i;
for(int j = i + 1; j < len; j++)
{
if( min2max ? (array[min] > array[j]) : (array[min] < array[j]) )
{
min = j;
}
}
if( min != i)
{
Swap(array[i], array[min]);
}
}
}
template < typename T >
static void Insert(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true)
{
for(int i=1; i < len; i++) //从1开始,第0个元素没有必要插入操作
{
int k = i;
T e = array[i];
for(int j=i-1; (j>=0) && (min2max ? (array[j] > e) : (array[j] < e)); j--)
{
array[j+1] = array[j];
k = j;
}
if( k != i ) //赋值比“比较操作耗时”
{
array[k] = e;
}
}
}
template < typename T >
static void Bubble(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true)
{
bool exchange = true;
for(int i=0; (i<len) && exchange; i++)
{
exchange = false;
for(int j=len-1; j>i; j--)
{
if(min2max ? (array[j] < array[j-1]) : (array[j] > array[j-1]))
{
Swap(array[j], array[j-1]);
exchange = true;
}
}
}
}
template < typename T >
static void Shell(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true)
{
int d = len;
do
{
d = d / 3 + 1; //d的减小方式(实践证明这样做效果比较好)
for(int i = d; i < len; i+=d)
{
int k = i;
T e = array[i];
for(int j=i-d; (j>=0) && (min2max ? (array[j] > e) : (array[j] < e)); j-=d)
{
array[j+d] = array[j];
k = j;
}
if( k != i ) //赋值比“比较操作耗时”
{
array[k] = e;
}
}
}while( d > 1 );
}
template < typename T >
static void Merge(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true)
{
T* helper = new T[len];
if( helper != NULL )
{
Merge(array, helper, 0, len - 1, min2max);
}
delete[] helper;
}
template < typename T >
static void Quick(T array[], int len, bool min2max=true)
{
Quick(array, 0, len - 1, min2max);
}
template < typename T >
static void Select(Array<T>& array, bool min2max=true)
{
Select(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template < typename T >
static void Insert(Array<T>& array, bool min2max=true)
{
Insert(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template < typename T >
static void Bubbble(Array<T>& array, bool min2max=true)
{
Bubble(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template < typename T >
static void Shell(Array<T>& array, bool min2max=true)
{
Shell(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template < typename T >
static void Merge(Array<T>& array, bool min2max=true)
{
Merge(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
template < typename T >
static void Quick(Array<T>& array, bool min2max=true)
{
Quick(array.array(), array.length(), min2max);
}
};
}
#endif // SORT_H

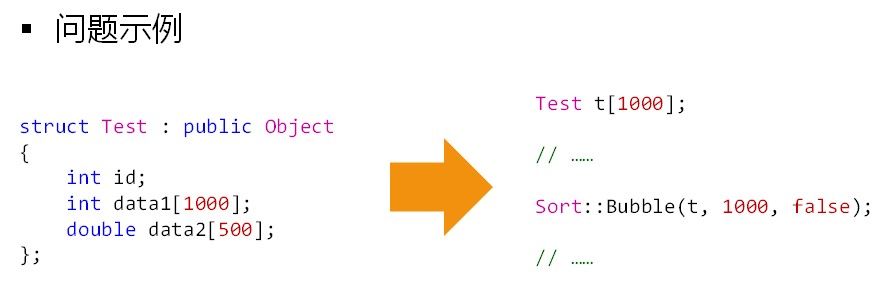

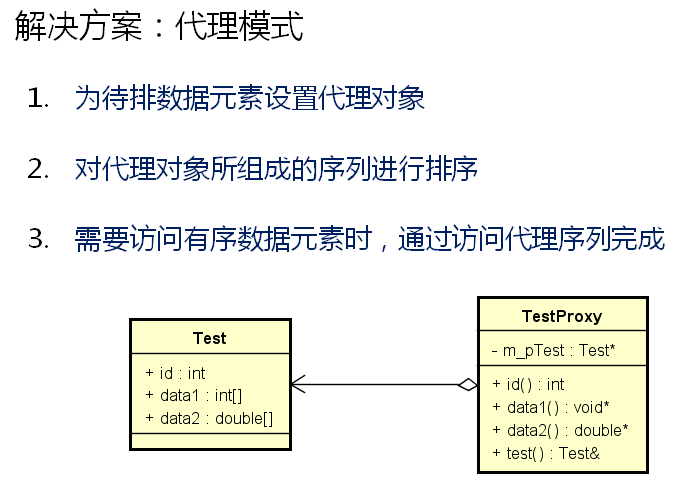
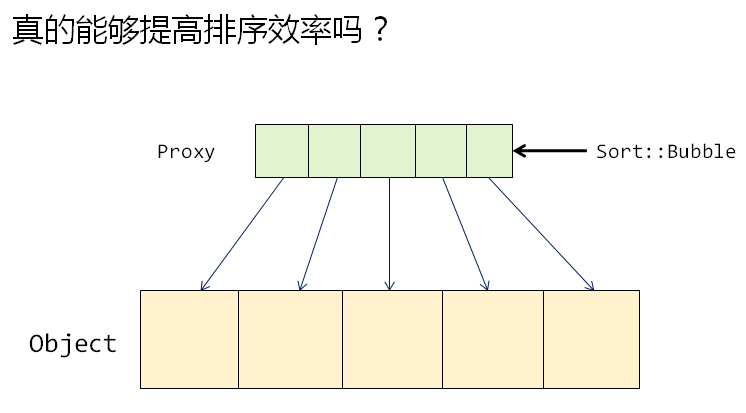
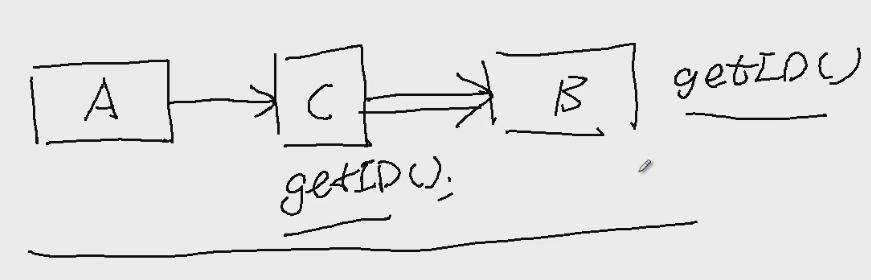
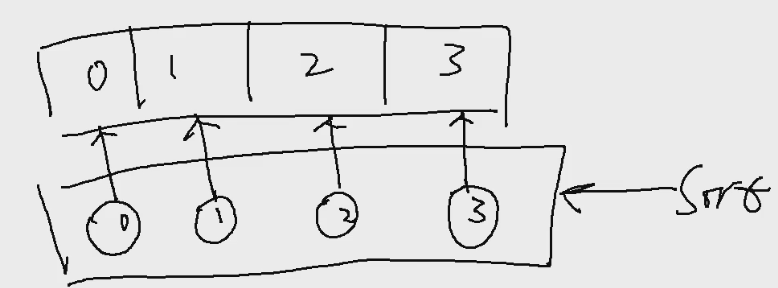
无代理时的测试程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include "Sort.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
struct Test : public Object
{
int id;
int data1[1000];
double data2[500];
bool operator < (const Test& obj)
{
return id < obj.id;
}
bool operator >= (const Test& obj)
{
return id >= obj.id;
}
bool operator > (const Test& obj)
{
return id > obj.id;
}
bool operator <= (const Test& obj)
{
return id <= obj.id;
}
};
Test t[1000];
int main()
{
clock_t begin = 0;
clock_t end = 0;
for(int i=0; i < 1000; i++)
{
t[i].id = i;
}
begin = clock();
Sort::Bubble(t, 1000, false);
end = clock();
cout << "Time : " << (end - begin) << endl;
for(int i=0; i < 1000; i++)
{
//cout << t[i]. << endl;
}
return 0;
}
结果如下:
使用代理类:
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include "Sort.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace DTLib;
struct Test : public Object
{
int id;
int data1[1000];
double data2[500];
bool operator < (const Test& obj)
{
return id < obj.id;
}
bool operator >= (const Test& obj)
{
return id >= obj.id;
}
bool operator > (const Test& obj)
{
return id > obj.id;
}
bool operator <= (const Test& obj)
{
return id <= obj.id;
}
};
class TestProxy : public Object
{
protected:
Test* m_pTest;
public:
//原始对象能干的事代理对象必须也要能干,因此要实现以下函数
int id()
{
return m_pTest->id;
}
int* data1()
{
return m_pTest->data1;
}
double* data2()
{
return m_pTest->data2;
}
Test& test() const //请出委托者的函数
{
return *m_pTest;
}
bool operator < (const TestProxy& obj)
{
return test() < obj.test(); //代理类对象的比较就是原始对象的比较
}
bool operator >= (const TestProxy& obj)
{
return test() >= obj.test(); //代理类对象的比较就是原始对象的比较
}
bool operator > (const TestProxy& obj)
{
return test() > obj.test(); //代理类对象的比较就是原始对象的比较
}
bool operator <= (const TestProxy& obj)
{
return test() <= obj.test(); //代理类对象的比较就是原始对象的比较
}
Test& operator = (Test& test)
{
m_pTest = &test;
return test;
}
};
Test t[1000];
TestProxy pt[1000];
int main()
{
clock_t begin = 0;
clock_t end = 0;
for(int i=0; i < 1000; i++)
{
t[i].id = i;
pt[i] = t[i]; //一一映射
}
begin = clock();
Sort::Bubble(pt, 1000, false);
end = clock();
cout << "Time : " << (end - begin) << endl;
for(int i=0; i < 1000; i++)
{
//cout << t[i]. << endl;
}
return 0;
}
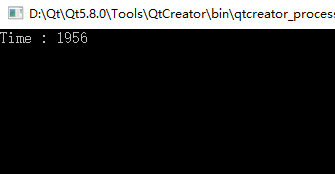
结果如下:
小结:

标签:log end ima stp std alt sort virt null
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/lh03061238/p/13958174.html