标签:adc pos trace collect argument tar connect rename ++
Netty中的内存分配是基于ByteBufAllocator这个接口实现的,通过对它的具体实现,可以用来分配我们之前描述过的任意类型的BytebBuf实例;我们先看一下ByteBufAllocator接口中的定义的关键方法
public interface ByteBufAllocator { ByteBufAllocator DEFAULT = ByteBufUtil.DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR; //根据具体实现返回基于直接内存或堆内内存的ByteBuf ByteBuf buffer(); //根据具体实现返回一个给定初始容量的基于直接内存或堆内内存的ByteBuf ByteBuf buffer(int initialCapacity); //根据具体实现返回一个给定初始容量与最大量的基于直接内存或堆内内存的ByteBuf ByteBuf buffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity); //返回一个用于套接字操作的ByteBuf ByteBuf ioBuffer(); //返回一个用于套接字操作的给定初始量ByteBuf ByteBuf ioBuffer(int initialCapacity); //返回一个用于套接字操作的给定初始量与最大量的ByteBuf ByteBuf ioBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity); //返回一个基于堆内内存的ByteBuf ByteBuf heapBuffer(); //返回一个给定初始量基于堆内内存的ByteBuf ByteBuf heapBuffer(int initialCapacity); //返回一个给定初始量与最大量的基于堆内内存的ByteBuf ByteBuf heapBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity); //返回一个基于直接内存的ByteBuf ByteBuf directBuffer(); //返回一个给定初始量基于直接内存的ByteBuf ByteBuf directBuffer(int initialCapacity); //返回一个给定初始量与最大量的基于直接内存的ByteBuf ByteBuf directBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity); //返回一个基于复合缓冲区的ByteBuf,基于堆还是直接内存看具体实现 CompositeByteBuf compositeBuffer(); //返回一个给定最大量的基于复合缓冲区的ByteBuf,基于堆还是直接内存看具体实现 CompositeByteBuf compositeBuffer(int maxNumComponents); //返回一个基于堆内存的CompositeByteBuf CompositeByteBuf compositeHeapBuffer(); //返回一个给定最大量基于堆内存的CompositeByteBuf CompositeByteBuf compositeHeapBuffer(int maxNumComponents); //返回一个基于直接内存的CompositeByteBuf CompositeByteBuf compositeDirectBuffer(); //返回一个给定最大量的基于直接内存的CompositeByteBuf CompositeByteBuf compositeDirectBuffer(int maxNumComponents); //直接内存是否池化管理 boolean isDirectBufferPooled(); //计算bytebuf需要扩展时的新容量 int calculateNewCapacity(int minNewCapacity, int maxCapacity); }
可以看到接口中定义的方法基本都是用于分配不同类型的内存,接下来我们看下基于ByteBufAllocator 接口的具体实现类。
看下实现ByteBufAllocator 接口的类结构图
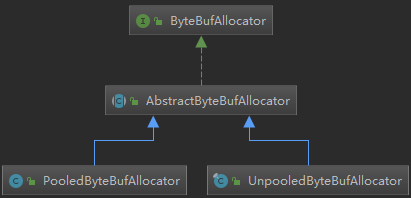
顶层抽象类AbstractByteBufAllocator下有两大子类PooledByteBufAllocator与UnpooledByteBufAllocator,分别用于池化与非池化内存的构造;
首先我们需要注意下ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR这个配置项,如果不进行特殊配置, 默认为PooledByteBufAllocator,默认ByteBuf类型为PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf,这里演示需要改为UnpooledByteBufAllocator
b.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, UnpooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
在数据入站Handler中,我们通过使用不同的BufAllocator实现类来分配ByteBuf进行对比,主要关注下分配的ByteBuf的类型与是否池化
public class BuffHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{ PooledByteBufAllocator pdallocator = new PooledByteBufAllocator(true);//池化直接内存 PooledByteBufAllocator pallocator = new PooledByteBufAllocator(false);//池化堆内存 UnpooledByteBufAllocator adllocator = new UnpooledByteBufAllocator(true);//非池化直接内存 UnpooledByteBufAllocator allocator = new UnpooledByteBufAllocator(false);//非池化堆内存 @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { ByteBuf outBuffer = (ByteBuf) msg; System.err.println("outBuffer is :"+outBuffer.getClass()); System.err.println("outBuffer‘s model is :"+outBuffer.isDirect()); outBuffer = ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer();//ByteBufAllocator默认内存类型 System.err.println("ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer() is :"+outBuffer.getClass()); System.err.println("ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer()‘s model is :"+outBuffer.isDirect()); outBuffer = pdallocator.buffer();////池化直接内存 System.err.println("PooledByteBufAllocator(true) is :"+outBuffer.getClass()); System.err.println("PooledByteBufAllocator(true)‘s model is :"+outBuffer.isDirect()); outBuffer = pallocator.buffer();//池化队堆内存 System.err.println("PooledByteBufAllocator(false) is :"+outBuffer.getClass()); System.err.println("PooledByteBufAllocator(false)‘s model is :"+outBuffer.isDirect()); outBuffer = adllocator.buffer();////非池化直接内存 System.err.println("UnpooledByteBufAllocator(true) is :"+outBuffer.getClass()); System.err.println("UnpooledByteBufAllocator(true)‘s model is :"+outBuffer.isDirect()); outBuffer = allocator.buffer();//非池化堆内存 System.err.println("UnpooledByteBufAllocator(false) is :"+outBuffer.getClass()); System.err.println("UnpooledByteBufAllocator(false)‘s model is :"+outBuffer.isDirect()); byte[] sendBytes = new byte[] {0x7E,0x01,0x02,0x7e}; outBuffer.writeBytes(sendBytes); ctx.writeAndFlush(outBuffer); } @Override public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { ctx.flush(); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) { // Close the connection when an exception is raised. cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
根据BufAllocator具体实现类与preferDirect参数会分配不同类型的ByteBuf,输出结果如下:
outBuffer is :class io.netty.buffer.UnpooledByteBufAllocator$InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeNoCleanerDirectByteBuf outBuffer‘s model is :true ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer() is :class io.netty.buffer.PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer()‘s model is :true PooledByteBufAllocator(true) is :class io.netty.buffer.PooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf PooledByteBufAllocator(true)‘s model is :true PooledByteBufAllocator(false) is :class io.netty.buffer.PooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf PooledByteBufAllocator(false)‘s model is :false UnpooledByteBufAllocator(true) is :class io.netty.buffer.UnpooledByteBufAllocator$InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeNoCleanerDirectByteBuf UnpooledByteBufAllocator(true)‘s model is :true UnpooledByteBufAllocator(false) is :class io.netty.buffer.UnpooledByteBufAllocator$InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf UnpooledByteBufAllocator(false)‘s model is :false
上面示例中,BufAllocator具体实现基本可以分为以下四种,下面我们对四种分配模式的具体实现进行下追踪与分析
new PooledByteBufAllocator(true);//池化直接内存 new PooledByteBufAllocator(false);//池化堆内存 new UnpooledByteBufAllocator(true);//非池化直接内存 new UnpooledByteBufAllocator(false);//非池化堆内存
ByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.buffer()
这里使用了 ByteBufUtil DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR,我们进入ByteBufUtil类内部看下具体实现
static final ByteBufAllocator DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR; static { String allocType = SystemPropertyUtil.get( "io.netty.allocator.type", PlatformDependent.isAndroid() ? "unpooled" : "pooled"); allocType = allocType.toLowerCase(Locale.US).trim();//读取io.netty.allocator.type配置 //根据配置类型实例化不同类型的BufAllocator实现类 ByteBufAllocator alloc; if ("unpooled".equals(allocType)) { // DEFAULT = new UnpooledByteBufAllocator(PlatformDependent.directBufferPreferred()); alloc = UnpooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT; logger.debug("-Dio.netty.allocator.type: {}", allocType); } else if ("pooled".equals(allocType)) { // DEFAULT = new PooledByteBufAllocator(PlatformDependent.directBufferPreferred()); alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT; logger.debug("-Dio.netty.allocator.type: {}", allocType); } else { alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT; logger.debug("-Dio.netty.allocator.type: pooled (unknown: {})", allocType); } DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR = alloc; THREAD_LOCAL_BUFFER_SIZE = SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.threadLocalDirectBufferSize", 0); logger.debug("-Dio.netty.threadLocalDirectBufferSize: {}", THREAD_LOCAL_BUFFER_SIZE); MAX_CHAR_BUFFER_SIZE = SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.maxThreadLocalCharBufferSize", 16 * 1024); logger.debug("-Dio.netty.maxThreadLocalCharBufferSize: {}", MAX_CHAR_BUFFER_SIZE); }
ByteBufUtil 的静态构造中会根据io.netty.allocator.type配置的不同实例化不同类型的BufAllocator实现类,下面我们看下BufAllocator的两个具体实现类PooledByteBufAllocator与UnpooledByteBufAllocator
在PooledByteBufAllocator构造函数中,首先会进行内存池的详细配置
public PooledByteBufAllocator(boolean preferDirect, int nHeapArena, int nDirectArena, int pageSize, int maxOrder, int tinyCacheSize, int smallCacheSize, int normalCacheSize, boolean useCacheForAllThreads, int directMemoryCacheAlignment) { super(preferDirect); //声明一个PoolThreadLocalCache用于内存申请 threadCache = new PoolThreadLocalCache(useCacheForAllThreads); this.tinyCacheSize = tinyCacheSize; this.smallCacheSize = smallCacheSize; this.normalCacheSize = normalCacheSize; chunkSize = validateAndCalculateChunkSize(pageSize, maxOrder); checkPositiveOrZero(nHeapArena, "nHeapArena"); checkPositiveOrZero(nDirectArena, "nDirectArena"); checkPositiveOrZero(directMemoryCacheAlignment, "directMemoryCacheAlignment"); if (directMemoryCacheAlignment > 0 && !isDirectMemoryCacheAlignmentSupported()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("directMemoryCacheAlignment is not supported"); } if ((directMemoryCacheAlignment & -directMemoryCacheAlignment) != directMemoryCacheAlignment) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("directMemoryCacheAlignment: " + directMemoryCacheAlignment + " (expected: power of two)"); } int pageShifts = validateAndCalculatePageShifts(pageSize); if (nHeapArena > 0) { heapArenas = newArenaArray(nHeapArena); List<PoolArenaMetric> metrics = new ArrayList<PoolArenaMetric>(heapArenas.length); for (int i = 0; i < heapArenas.length; i ++) { PoolArena.HeapArena arena = new PoolArena.HeapArena(this, pageSize, maxOrder, pageShifts, chunkSize, directMemoryCacheAlignment); heapArenas[i] = arena; metrics.add(arena); } heapArenaMetrics = Collections.unmodifiableList(metrics); } else { heapArenas = null; heapArenaMetrics = Collections.emptyList(); } if (nDirectArena > 0) { directArenas = newArenaArray(nDirectArena); List<PoolArenaMetric> metrics = new ArrayList<PoolArenaMetric>(directArenas.length); for (int i = 0; i < directArenas.length; i ++) { PoolArena.DirectArena arena = new PoolArena.DirectArena( this, pageSize, maxOrder, pageShifts, chunkSize, directMemoryCacheAlignment); directArenas[i] = arena; metrics.add(arena); } directArenaMetrics = Collections.unmodifiableList(metrics); } else { directArenas = null; directArenaMetrics = Collections.emptyList(); } metric = new PooledByteBufAllocatorMetric(this); }
紧接着看下PooledByteBufAllocator具体的内存分配方法
newDirectBuffer 分配直接内存
@Override protected ByteBuf newDirectBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) { PoolThreadCache cache = threadCache.get(); PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena = cache.directArena;//具体的内存分配类PoolArena final ByteBuf buf; if (directArena != null) {//PoolArena就是Netty的内存池实现类。实现具体内存分配 buf = directArena.allocate(cache, initialCapacity, maxCapacity); } else { buf = PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe() ? UnsafeByteBufUtil.newUnsafeDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) : new UnpooledDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity); } return toLeakAwareBuffer(buf); }
heapBuffer 分配堆内内存
protected ByteBuf newHeapBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) { PoolThreadCache cache = threadCache.get(); PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena = cache.heapArena; final ByteBuf buf; if (heapArena != null) { //通过PoolArena分配堆内内存 buf = heapArena.allocate(cache, initialCapacity, maxCapacity); } else { buf = PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe() ? new UnpooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) : new UnpooledHeapByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity); } return toLeakAwareBuffer(buf); }
由于采用非池化管理,UnpooledByteBufAllocator构造函数中需要指定内存清理策略
public UnpooledByteBufAllocator(boolean preferDirect, boolean disableLeakDetector, boolean tryNoCleaner) { super(preferDirect); this.disableLeakDetector = disableLeakDetector; //内存清理策略,默认noCleaner需要使用 unSafe 的 freeMemory 方法释放内存 //noCleaner 使用 unSafe.freeMemory(address); //hasCleaner 使用 DirectByteBuffer 的 Cleaner 的 clean 方法。 noCleaner = tryNoCleaner && PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe() && PlatformDependent.hasDirectBufferNoCleanerConstructor(); }
紧接着看下UnpooledByteBufAllocator具体的内存分配方法
newDirectBuffer 分配直接内存
@Override protected ByteBuf newDirectBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) { final ByteBuf buf; if (PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe()) {//判断是否适用Unsafe操作 buf = noCleaner ? new InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeNoCleanerDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) : new InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity); } else { buf = new InstrumentedUnpooledDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity); } return disableLeakDetector ? buf : toLeakAwareBuffer(buf);//是否进行堆外内存泄露监控 }
newHeapBuffer 分配堆内内存
@Override protected ByteBuf newHeapBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) { return PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe() ? new InstrumentedUnpooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) : new InstrumentedUnpooledHeapByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity); }
通过以上内容我们梳理了Netty中BufAllocator的具体实现及分配内存的类型,从内存管理模式上分为池化与非池化,从内存分配类型上分为直接内存与堆内内存,本文我们只是初步对其进行了总结,Netty分配内存的具体实现及精巧设计都还未涉及,后续我们会继续对其进行进一步的探究,希望本文对大家能有所帮助,其中如有不足与不正确的地方还望指出与海涵。
关注微信公众号,查看更多技术文章。

Netty源码分析之ByteBuf(二)—内存分配器ByteBufAllocator
标签:adc pos trace collect argument tar connect rename ++
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/dafanjoy/p/13687834.html