标签:分词器 img swap follow file 全文检索 more multi gateway
本文已经收录至我的GitHub,欢迎大家踊跃star 和 issues。https://github.com/midou-tech/articles
题外话
这次本来是准备用filebeat写数据到es,然后下一篇写查询语法和一些查询操作。
就在我要写数据的时候,发现不对啊。mapping配置什么的都不知道,只是把数据塞进去了,完全不知道数据怎么结构化存储的,也不知道怎么查询。
一般去对接es业务,都需要告诉es的同学,有哪些字段,那些字段需要做查询,es的同学会根据你的业务去配置相应的mapping。
学习es请关注龙叔,带你走进es的世界。
正文
es配置这块作为es开发人员和维护人员属于基本知识,必须掌握的。作为es的业务方和使用者,了解es的配置有助于更好的在你的场景中去使用。
本篇文章主要讲下es的配置文件、mapping配置问题。
elasticsearch的目录结构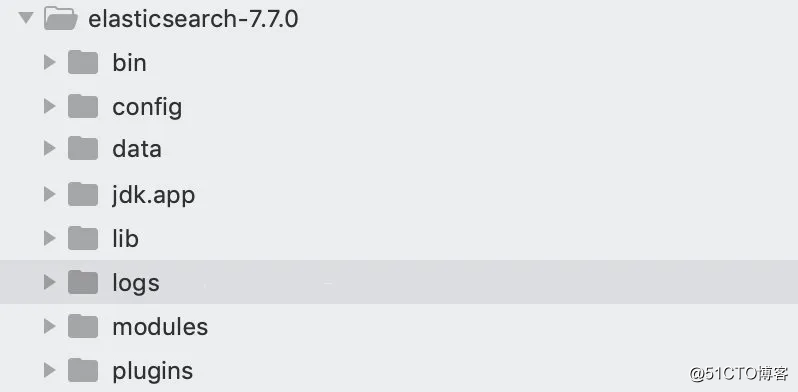
这是Elasticsearch 7.7.0版本的目录结构
bin目录存放一些必要的二进制文件或者启动脚本、config目录存放工程需要的配置文件、log目录就是日志文件、lib目录放一些工程必须的库、script目录放一些脚本。
elasticsearch.yml是elasticsearch的重要配置,下面说一下这个文件的一些配置项
# ---------------------------------- Cluster -----------------------------------
# Use a descriptive name for your cluster:
cluster.name: my-application
# ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------
# Use a descriptive name for the node:
node.name: node-1
# Add custom attributes to the node:
node.attr.rack: r1
# ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------
# Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma):
path.data: /path/to/data
# Path to log files:
path.logs: /path/to/logs
# ----------------------------------- Memory -----------------------------------
# Lock the memory on startup:
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
# Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available
# on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this limit.
# Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory.
# ---------------------------------- Network -----------------------------------
# Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6):
network.host: 192.168.0.1
# Set a custom port for HTTP:
http.port: 9200
# For more information, consult the network module documentation.
# --------------------------------- Discovery ----------------------------------
# Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started:
# The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"]
discovery.seed_hosts: ["host1", "host2"]
# Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes:
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2"]
# For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation.
# ---------------------------------- Gateway -----------------------------------
# Block initial recovery after a full cluster restart until N nodes are started:
gateway.recover_after_nodes: 3
# For more information, consult the gateway module documentation.
# ---------------------------------- Various -----------------------------------
# Require explicit names when deleting indices:
action.destructive_requires_name: true本来还想注释解释一下的,结果看了下这里面的英文解释,很so easy,就不在这里赘述了。
Es的Mapping
Mapping类似于数据库中的表结构定义,我们创建一个表需要定义一个表结构。
在es里面每个索引都会有一个mapping配置。
主要作用如下:
定义倒排索引的相关配置,比如是否索引、记录postion等
Mapping完整的内容可以分为四部分内容:
上一篇Es文章中简单的写入数据到es中,写的时候没有配置任何mapping结构的,不知道是否还记得之前写的数据。
别管原理,先run起来(戳我查看),贴了链接,里面有插入数据的语法。
太长了,这里就不截插入数据的图了,有兴趣的戳链接查看。
GET /user/_mapping 使用这个接口可以获取user索引的mapping结构如下:
{
"user" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"desc" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"title" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}可以看到,默认情况下,插入数据是会自动创建mapping结构的。
三个字段name、titile、desc都自动识别为text类型,同时分别增加了keyword字段,类型为keyword。
GET /user/_mapping/field/title 可以获取字段name的mapping结构。
{
"user" : {
"mappings" : {
"title" : {
"full_name" : "title",
"mapping" : {
"title" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}上面展示了如何获取mapping,可以通过获取整个index的mapping,也可以获取某个字段的mapping。
数据类型
主要的数据类型
string :text and keyword 两种
long, integer, short, byte, double, float, half_float, scaled_float
Date
date 日期类型
Date nanoseconds
date_nanos
Boolean
boolean
Binary
binary
Range
integer_range, float_range, long_range, double_range, date_range, ip_range
复杂数据类型
Object:单个json对象
Nested :嵌套json对象
地理位置数据类型
Geo-point :地理经纬度
Geo-shape :多边形等复杂形状
专用数据类型
IP
支持IPv4 and IPv6 地址,这个用的蛮多的,日志查询经常用到。
Completion datatype
范围类型,为了优化在查找时输入自动补全而设计的类型,输入自动补全会在查询部分专题详解。
Token count
令牌计数类型,接收一个字符串经过分析后将返回词根的个数
mapper-murmur3
需要安装 map-per-murmur3插件,提供了在索引时索引和记录该字段的散列值,对于聚合有性能提升
Join
join类型允许在同一个索引中(同一个类型type)中定义多个不同类型的文档(例如学生文档、班级文档-)这些类型是个一对多关联关系(父子级联关系)。
Alias
指定字段别名
Arrays
数组类型
range datatype
数据范围类型,一个字段表示一个范围,例如
Meta-Fields(元字段)
身份元字段
_index , _type , _id
_index:文档所属索引 , 自动被索引,可被查询,聚合,排序使用,或者脚本里访问
type:文档所属类型,自动被索引,可被查询,聚合,排序使用,或者脚本里访问
_id:文档的唯一标识,建索引时候传入 ,不被索引, 可通过_uid被查询,脚本里使用,不能参与聚合或排序
数据源元字段
_source , _size
_source : 一个doc的原生的json数据,不会被索引,用于获取提取字段值 ,启动此字段,索引体积会变大,如果既想使用此字段又想兼顾索引体积,可以开启索引压缩。
_size : 整个_source字段的字节数大小
索引元字段
_field_names , _ignored
_field_names:索引了每个字段的名字,可以包含null值,可以通过exists查询或missing查询方法来校验特定的字段
_ignored: 默认情况下,尝试将错误的数据类型索引到字段中会引发异常,并拒绝整个文档。ignore_malformed如果将参数设置为true,则可以忽略异常。格式错误的字段未编制索引,但文档中的其他字段已正常处理。
路由元字段
_routing
其他元字段
_meta
Mapping parameters(mapping参数)
analyzer
指定分词器。elasticsearch是一款支持全文检索的分布式存储系统,对于text类型的字段,首先会使用分词器进行分词,然后将分词后的词根一个一个存储在倒排索引中,后续查询主要是针对词根的搜索。
analyzer参数可以在每个查询、每个字段、每个索引中使用,其优先级如下(越靠前越优先):1、字段上定义的分词器 2、索引配置中定义的分词器 3、默认分词器(standard)
在查询上下文,分词器的查找优先为:1、full-text query中定义的分词器 2、定义类型映射时,字段中search_analyzer 定义的分词器 3、定义字段映射时analyzer定义的分词器 4、索引中default_search中定义的分词器 5、索引中默认定义的分词器 6、标准分词器(standard)
coerce
是否进行类型“隐式转换”。例如
"fans":{
"type":"integer"
}声明粉丝数是整形,如果coerce:true "10000" 也可以写进fans字段,coerce:false 则必须使用 1000 赋值给fans字段。
boost
权重值,可以提升在查询时的权重,对查询相关性有直接的影响,其默认值为1.0。其影响范围为词根查询(team query),对前缀、范围查询、全文索引(match query)不生效。
copy_to
copy_to参数允许您创建自定义的_all字段。换句话说,多个字段的值可以复制到一个字段中。
{
"user" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"desc" : {
"type" : "text",
"analyzer" : "standard",
"copy_to" : "content"
},
"fans" : {
"type" : "integer",
"copy_to" : "content"
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text",
"analyzer" : "standard",
"copy_to" : "content"
},
"content" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
}
}
}content的值为 desc、fans、name字段值拼接的结果。
copy_to注意事项:? ?1、字段的复制是原始值,而不是分词后的词根。? ?2、复制字段不会包含在_souce字段中,但可以使用复制字段进行查询。? ?3、同一个字段可以复制到多个字段,写法如下:“copy_to”: [ “field_1”, “field_2” ]
doc_values
当需要对一个字段进行排序时,es需要提取匹配结果集中的排序字段值集合,然后进行排序。倒排索引的数据结构对检索来说相当高效,但对排序就不那么擅长。
dynamic
是否允许动态的隐式增加字段。
normalizer
规划化,主要针对keyword类型,在索引该字段或查询字段之前,可以先对原始数据进行一些简单的处理,然后再将处理后的结果当成一个词根存入倒排索引中
enabled
是否建立索引,默认情况下es会尝试为你索引所有的字段,但有时候某些类型的字段,无需建立索引,只是用来存储数据即可。
eager_global_ordinals
全局序列号,它以字典顺序为每个唯一的术语保持递增的编号。
fielddata
为了解决排序与聚合,elasticsearch提供了doc_values属性来支持列式存储,但doc_values不支持text字段类型。
因为text字段是需要先分析(分词),会影响doc_values列式存储的性能。es为了支持text字段高效排序与聚合,引入了一种新的数据结构(fielddata),使用内存进行存储。
format
在JSON文档中,日期表示为字符串。
{
"user": {
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"desc": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "standard",
"copy_to": "content"
},
"fans": {
"type": "integer",
"copy_to": "content"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "standard",
"copy_to": "content"
},
"content": {
"type": "text"
},
"date": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"
}
}
}
}
}fields
fields允许对同一索引中同名的字段进行不同的设置
index
定义字段是否索引,true:代表索引,false表示不索引(则无法通过该字段进行查询),默认值为true。
index_options
控制文档添加到反向索引的额外内容,可以选择的参数如下:
docs:文档编号添加到倒排索引。freqs:文档编号与访问频率。positions:文档编号、访问频率、词位置(顺序性),proximity 和phrase queries 需要用到该模式。offsets:文档编号,词频率,词偏移量(开始和结束位置)和词位置(序号),高亮显示,需要设置为该模式。
norms
字段的评分规范,存储该规范信息,会提高查询时的评分计算效率
null_value
将显示的null值替换为新定义的额外值
search_analyzer
通常,在索引时和搜索时应用相同的分析器,以确保查询中的术语与反向索引中的术语具有相同的格式,如果想要在搜索时使用与存储时不同的分词器,则使用search_analyzer属性指定,通常用于ES实现即时搜索(edge_ngram)。
similarity
指定相似度算法,其可选值:
默认情况下,字段值被索引以使其可搜索,但它们不存储
term_vector
term_vector包含分析过程产生的术语的信息
Dynamic Mapping(动态mapping)
动态字段映射
管理动态field检测的规则
动态模板
用于配置动态添加字段的映射的自定义规则
上一篇文章我们只是把数据写进来,并没有配置mapping结构。写进来的数据也是具有mapping结构的,可以进行搜索。
这些mapping结构就是es的动态mapping在起作用。
总结
mapping配置是很重要的一部分,对于elasticsearch学习者来说必须要掌握。
本部分内容在官方文档都有详细的说明和示例,如果在看龙叔的文章有什么问题可以用官网文档示例校正。
独自旅行 分割线
我是龙叔,一个分享互联网技术和心路历程的star。
标签:分词器 img swap follow file 全文检索 more multi gateway
原文地址:https://blog.51cto.com/13449864/2560622