标签:图标 readline pycha lazy its contains windows dog for
首先pycharm里面的代码格式化,也就是所说的美化快捷键【Ctrl+Alt+L】
1、IP地址由范围打印出每个ip地址,业务中有太多的ip需要整理,所以批量处理一下,已做到一步完成大规模的重复步骤
# -*-coding:utf-8-*- q = open(‘jieguo.txt‘, ‘w‘) f = open(‘addredd.txt‘) for line in f.readlines(): line = line.strip() line = line.split(‘-‘) val1 = line[0].split(‘.‘) val2 = line[1].split(‘.‘) title = ‘%s.%s.%s.‘ % (val1[0], val1[1], val1[2]) ip_start = val1[3] ip_end = val2[3] # print(title,ip_strat,ip_end) for i in range(int(ip_start), int(ip_end) + 1): # my_dict = [‘%s,%s‘%ip_strat,ip_end] # print("%s%s" %(title,i)) q.write(‘%s%s\n‘ % (title, i))
2、天气网北京昌平地区的天气情况
# 天气网昌平地区爬虫案例 import requests from lxml import etree class WeatherSpider: def __init__(self): # self.url = "http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101210404.shtml" self.url = "http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101010700.shtml" self.headers = { "User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/72.0.3626.119 Safari/537.36"} def get_url_content(self): return requests.get(self.url, headers=self.headers).content.decode() def get_weather_data(self, html): tmp_html = etree.HTML(html) tomorrow_doc = tmp_html.xpath("//div[contains(@class,‘con‘) and contains(@class,‘today‘)]//div[@class=‘c7d‘]/ul/li[2]")[0] weather_data = {} weather_data["日期"] = tomorrow_doc.xpath("./h1/text()")[0] weather_data["天气"] = tomorrow_doc.xpath("./p[@class=‘wea‘]/@title")[0] weather_data["最高气温"] = tomorrow_doc.xpath("./p[@class=‘tem‘]/span/text()")[0] weather_data["最低气温"] = tomorrow_doc.xpath("./p[@class=‘tem‘]/i/text()")[0] weather_data["空速"] = tomorrow_doc.xpath("./p[@class=‘win‘]/i/text()")[0] return weather_data def run(self): # 获取url请求内容 content_html = self.get_url_content() # 根据url内容获取天气数据 data = self.get_weather_data(content_html) # 打印爬取的天气数据 # data_dict = [] # for i in data: # data_dict.append() # print(data_dict) print(data) if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: spider = WeatherSpider() spider.run()
3、合并多个表格到一个sheet里面
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # 将多个Excel文件合并成一个 import xlrd import xlsxwriter # 打开一个excel文件 def open_xls(file): fh = xlrd.open_workbook(file) return fh # 获取excel中所有的sheet表 def getsheet(fh): return fh.sheets() # 获取sheet表的行数 def getnrows(fh, sheet): table = fh.sheets()[sheet] return table.nrows # 读取文件内容并返回行内容 def getFilect(file, shnum): fh = open_xls(file) table = fh.sheets()[shnum] num = table.nrows for row in range(num): rdata = table.row_values(row) datavalue.append(rdata) return datavalue # 获取sheet表的个数 def getshnum(fh): x = 0 sh = getsheet(fh) for sheet in sh: x += 1 return x if __name__ == ‘__main__‘: # 定义要合并的excel文件列表 allxls = [‘F:/test/excel1.xlsx‘, ‘F:/test/excel2.xlsx‘] # 存储所有读取的结果 datavalue = [] for fl in allxls: fh = open_xls(fl) x = getshnum(fh) for shnum in range(x): print("正在读取文件:" + str(fl) + "的第" + str(shnum) + "个sheet表的内容...") rvalue = getFilect(fl, shnum) # 定义最终合并后生成的新文件 endfile = ‘F:/test/excel3.xlsx‘ wb1 = xlsxwriter.Workbook(endfile) # 创建一个sheet工作对象 ws = wb1.add_worksheet() for a in range(len(rvalue)): for b in range(len(rvalue[a])): c = rvalue[a][b] ws.write(a, b, c) wb1.close() print("文件合并完成")
4、对比两个文本,查找不同的信息
# coding=utf-8 import re oldt = [] newt = [] f = open(‘new‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘) for a in f.readlines(): a = a.strip() newt.append(a) f.close() q = open(‘old‘, encoding=‘utf-8‘) for b in q.readlines(): b = b.strip() oldt.append(b) q.close() for i in newt: if i in oldt: pass else: print(‘%s‘ % i)
5、柱状图
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt np.random.seed(19680801) n_bins = 10 x = np.random.randn(1000, 3) fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2) ax0, ax1, ax2, ax3 = axes.flatten() colors = [‘red‘, ‘tan‘, ‘lime‘] ax0.hist(x, n_bins, density=True, histtype=‘bar‘, color=colors, label=colors) ax0.legend(prop={‘size‘: 10}) ax0.set_title(‘bars with legend‘) ax1.hist(x, n_bins, density=True, histtype=‘barstacked‘) ax1.set_title(‘stacked bar‘) ax2.hist(x, histtype=‘barstacked‘, rwidth=0.9) ax3.hist(x[:, 0], rwidth=0.9) ax3.set_title(‘different sample sizes‘) fig.tight_layout() plt.show()
6、饼图
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt labels = ‘Frogs‘, ‘Hogs‘, ‘Dogs‘, ‘Logs‘ sizes = [15, 30, 45, 10] explode = (0, 0.1, 0, 0) # only "explode" the 2nd slice (i.e. ‘Hogs‘) fig1, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2) ax1.pie(sizes, labels=labels, autopct=‘%1.1f%%‘, shadow=True) ax1.axis(‘equal‘) ax2.pie(sizes, autopct=‘%1.2f%%‘, shadow=True, startangle=90, explode=explode, pctdistance=1.12) ax2.axis(‘equal‘) ax2.legend(labels=labels, loc=‘upper right‘) plt.show()
7、柱状图
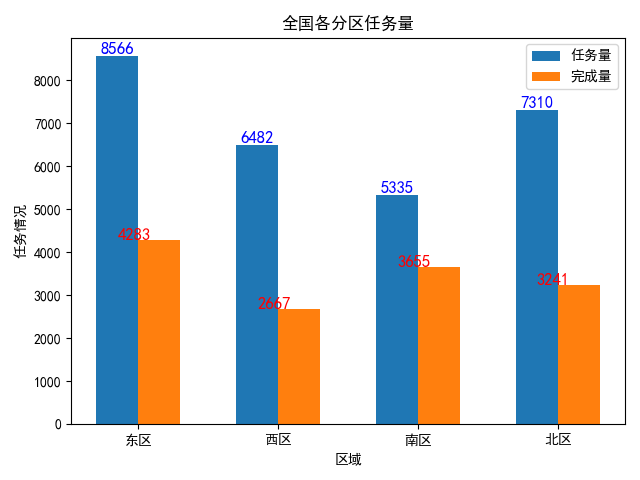
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.subplot(1, 1, 1) x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4]) y1 = np.array([8566, 6482, 5335, 7310]) y2 = np.array([4283, 2667, 3655, 3241]) plt.bar(x, y1, width=0.3, label="任务量") plt.bar(x + 0.3, y2, width=0.3, label="完成量") # x+0.3相当于完成量的每个柱子右移0.3 plt.title("全国各分区任务量", loc="center") # 添加数据标签 for a, b in zip(x, y1): plt.text(a, b, b, ha=‘center‘, va="bottom", fontsize=12, color="blue") for a, b in zip(x, y2): plt.text(a, b, b, ha=‘left‘, va="baseline", fontsize=12, color="r") plt.xlabel(‘区域‘) plt.ylabel(‘任务情况‘) # 设置x轴刻度值 plt.xticks(x + 0.15, ["东区", "西区", "南区", "北区"]) plt.rcParams[‘font.sans-serif‘]=[‘SimHei‘] #显示中文标签 plt.rcParams[‘axes.unicode_minus‘]=False #这两行需要手动设置 plt.grid(False) plt.legend() # 显示图例 plt.show()
8、折线图
import numpy as np import random import xlrd import xlwt import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D x=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] y=[3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12] plt.grid(True,linestyle = "-.") plt.plot(x,y,marker=‘*‘,color=‘green‘) # 设置数字标签 for a, b in zip(x, y): plt.text(a, b+2, b, ha=‘center‘, va=‘bottom‘, fontsize=10) plt.ylim(0,30) plt.xlabel(‘the value of k‘) plt.ylabel(‘number‘) plt.title(‘red vs green‘) plt.show()
9、数据生成Excel
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import xlsxwriter # 创建一个excel workbook = xlsxwriter.Workbook("../z周联系/chart_line.xlsx") # 创建一个sheet worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet() # worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet("bug_analysis") # 自定义样式,加粗 bold = workbook.add_format({‘bold‘: 1}) # --------1、准备数据并写入excel--------------- # 向excel中写入数据,建立图标时要用到 headings = [‘Number‘, ‘testA‘, ‘testB‘] data = [ [‘2017-9-1‘, ‘2017-9-2‘, ‘2017-9-3‘, ‘2017-9-4‘, ‘2017-9-5‘, ‘2017-9-6‘], [10, 40, 50, 20, 10, 50], [30, 60, 70, 50, 40, 30], ] # 写入表头 worksheet.write_row(‘A1‘, headings, bold) # 写入数据 worksheet.write_column(‘A2‘, data[0]) worksheet.write_column(‘B2‘, data[1]) worksheet.write_column(‘C2‘, data[2]) # --------2、生成图表并插入到excel--------------- # 创建一个柱状图(line chart) chart_col = workbook.add_chart({‘type‘: ‘line‘}) # 配置第一个系列数据 chart_col.add_series({ # 这里的sheet1是默认的值,因为我们在新建sheet时没有指定sheet名 # 如果我们新建sheet时设置了sheet名,这里就要设置成相应的值 ‘name‘: ‘=Sheet1!$B$1‘, ‘categories‘: ‘=Sheet1!$A$2:$A$7‘, ‘values‘: ‘=Sheet1!$B$2:$B$7‘, ‘line‘: {‘color‘: ‘red‘}, }) # 配置第二个系列数据 chart_col.add_series({ ‘name‘: ‘=Sheet1!$C$1‘, ‘categories‘: ‘=Sheet1!$A$2:$A$7‘, ‘values‘: ‘=Sheet1!$C$2:$C$7‘, ‘line‘: {‘color‘: ‘yellow‘}, }) # 配置第二个系列数据(用了另一种语法) # chart_col.add_series({ # ‘name‘: [‘Sheet1‘, 0, 2], # ‘categories‘: [‘Sheet1‘, 1, 0, 6, 0], # ‘values‘: [‘Sheet1‘, 1, 2, 6, 2], # ‘line‘: {‘color‘: ‘yellow‘}, # }) # 设置图表的title 和 x,y轴信息 chart_col.set_title({‘name‘: ‘The xxx site Bug Analysis‘}) chart_col.set_x_axis({‘name‘: ‘Test number‘}) chart_col.set_y_axis({‘name‘: ‘Sample length (mm)‘}) # 设置图表的风格 chart_col.set_style(1) # 把图表插入到worksheet并设置偏移 worksheet.insert_chart(‘A10‘, chart_col, {‘x_offset‘: 25, ‘y_offset‘: 10}) workbook.close()
标签:图标 readline pycha lazy its contains windows dog for
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/security-guard/p/14168155.html