标签:auth java return items date sage 更新 oct 指定
v-for<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.4.2/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="item in items" :key="item.id">
{{item.message}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
items: [
{id: 1, message: ‘Foo‘},
{id: 2, message: ‘Bar‘}
]
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
我们可以用v-for指令基于一个数组来渲染一个列表。item in items的items是源数据数组,item是被迭代的数组元素的别名。
注意:一般情况下,我们会给<li>指定key,这里的:key表示数据绑定。
v-for支持第二个参数,即当前项的索引。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.4.2/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in items" :key="index">
{{item.message}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
items: [
{id: 1, message: ‘Foo‘},
{id: 2, message: ‘Bar‘}
]
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
我们可以用v-for指令遍历一个对象的属性。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.4.2/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<!-- <li v-for="value in object"> -->
<!-- <li v-for="(value, name) in object"> -->
<li v-for="(value, name, index) in object" :key="index">
{{value}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
object: {
title: ‘How to do lists in Vue‘,
author: ‘Jane Doe‘,
publishedAt: ‘2016-04-10‘
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.4.2/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in items" :key="index">
{{item.message}}
<button @click="updateItem(index, {message: ‘Baz‘})">更新</button>
<button @click="deleteItem(index)">删除</button>
</li>
</ul>
<button @click="addItem({message: ‘Boo‘})">添加</button>
</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
items: [
{message: ‘Foo‘},
{message: ‘Bar‘}
]
},
methods: {
deleteItem: function(index){
this.items.splice(index, 1)
},
updateItem: function(index, newItem){
this.items.splice(index, 1, newItem)
},
addItem: function(newItem){
this.items.push(newItem)
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
注意:上面的splice和push方法不是数组原生的方法,而是Vue为了侦听数组内部数据而重写的方法。我们称这些方法为变异方法(mutation method)。
变异方法包括:
push()pop()shift()unshift()splice()sort()reverse()相比之下,非变异方法(non-mutating method)不会改变原始数组,而是返回一个新数组。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.4.2/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="searchName">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in filteritems" :key="index">
{{item.message}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
searchName: ‘‘,
items: [
{message: ‘Foo‘},
{message: ‘Bar‘},
{message: ‘Baz‘},
{message: ‘Boo‘}
]
},
computed: {
filteritems: function(){
const {searchName, items} = this
let arr = [...items]
if(searchName.trim()){
// filter()为非变异方法
arr = items.filter(item => item.message.toLocaleLowerCase().indexOf(searchName.toLocaleLowerCase())!==-1)
}
return arr;
}
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
① 利用索引直接设置一个数组项,比如vm.items[indexOfItem] = newValue。
② 修改数组的长度,比如vm.items.length = newLength。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
</style>
<!-- <script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.4.2/vue.min.js"></script> -->
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in items" :key="index">
{{item}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
items: [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘]
}
});
vm.items[1] = ‘x‘
</script>
</body>
</html>
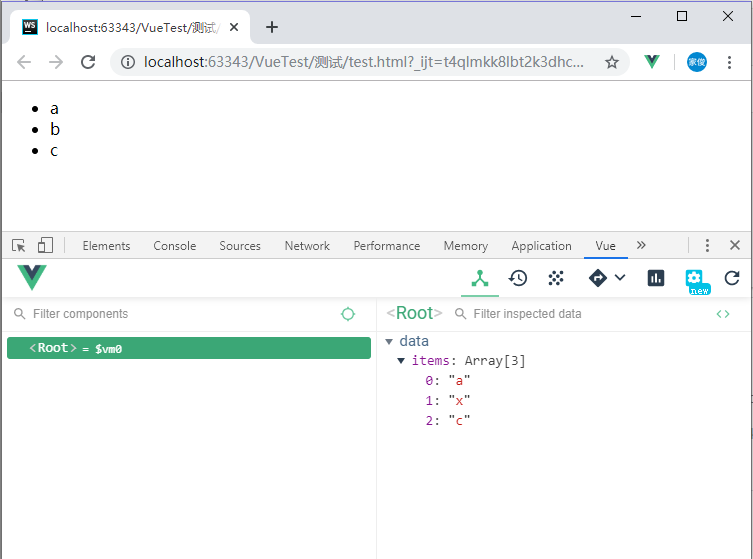
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
</style>
<!-- <script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.4.2/vue.min.js"></script> -->
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) in items" :key="index">
{{item}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
items: [‘a‘, ‘b‘, ‘c‘]
}
});
Vue.set(vm.items, 1, ‘x‘)
</script>
</body>
</html>
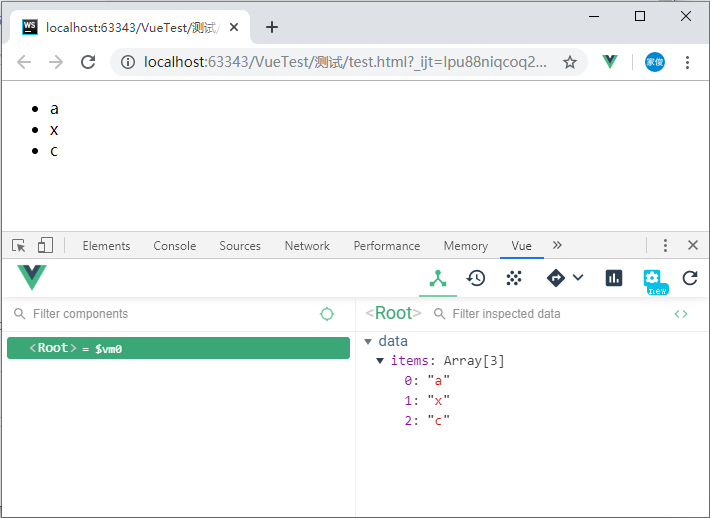
我们可以使用Vue.set(target, propertyName/index, value)来实现响应式数据。
注意:对象变更检测注意事项
<template>上使用v-for<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.4.2/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<template v-for="(item, index) in items" :key="index">
<li>{{item.name}}</li>
<li>----------</li>
</template>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
items: [
{name:‘张飞‘},
{name:‘李四‘},
]
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
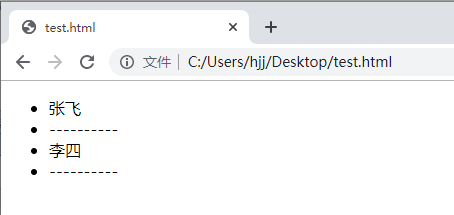
我们可以使用带有v-for的<template>来循环渲染一段包含多个元素的内容。
注意:我们不推荐在同一元素上使用v-if和v-for。当它们处于同一节点,v-for的优先级比v-if更高。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.4.2/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<ul v-if="todos.length">
<li v-for="todo in todos">
{{ todo }}
</li>
</ul>
<p v-else>No todos left!</p>
</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: ‘#app‘,
data: {
todos: []
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
v-for<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
</style>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/vue/2.4.2/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="todo-list-example">
<form v-on:submit.prevent="addNewTodo">
<label for="new-todo">Add a todo</label>
<input
v-model="newTodoText"
id="new-todo"
placeholder="E.g. Feed the cat"
>
<button>Add</button>
</form>
<ul>
<li
is="todo-item"
v-for="(todo, index) in todos"
v-bind:key="todo.id"
v-bind:title="todo.title"
v-on:remove="todos.splice(index, 1)"
></li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
Vue.component(‘todo-item‘, {
template: ‘ <li> {{ title }} <button v-on:click="$emit(\‘remove\‘)">Remove</button> </li> ‘,
props: [‘title‘]
})
new Vue({
el: ‘#todo-list-example‘,
data: {
newTodoText: ‘‘,
todos: [
{id: 1, title: ‘Do the dishes‘},
{id: 2, title: ‘Take out the trash‘},
{id: 3, title: ‘Mow the lawn‘}
],
nextTodoId: 4
},
methods: {
addNewTodo: function () {
this.todos.push({
id: this.nextTodoId++,
title: this.newTodoText
})
this.newTodoText = ‘‘
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
任何数据都不会被自动传递到组件里,因为组件有自己独立的作用域。
为了把迭代数据传递到组件里,我们要使用prop。
注意:这里is="todo-item"实现的效果和<todo-item>相同,但是可以避免一些潜在的浏览器解析错误。
参考:
标签:auth java return items date sage 更新 oct 指定
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/gzhjj/p/11763951.html