标签:集合 current private lan col img final overflow 容器
图片来源于:极客时间《数据结构与算法之美》 https://time.geekbang.org/column/intro/126
数组是最简单的数据结构,它的结构特点是:需要连续的内存空间,能够通过数组下标快速的访问数组内的元素,但是初始时需要指定大小,并且不能动态扩容,当容量不够时,需要通过Arrays.copy方法进行迁移
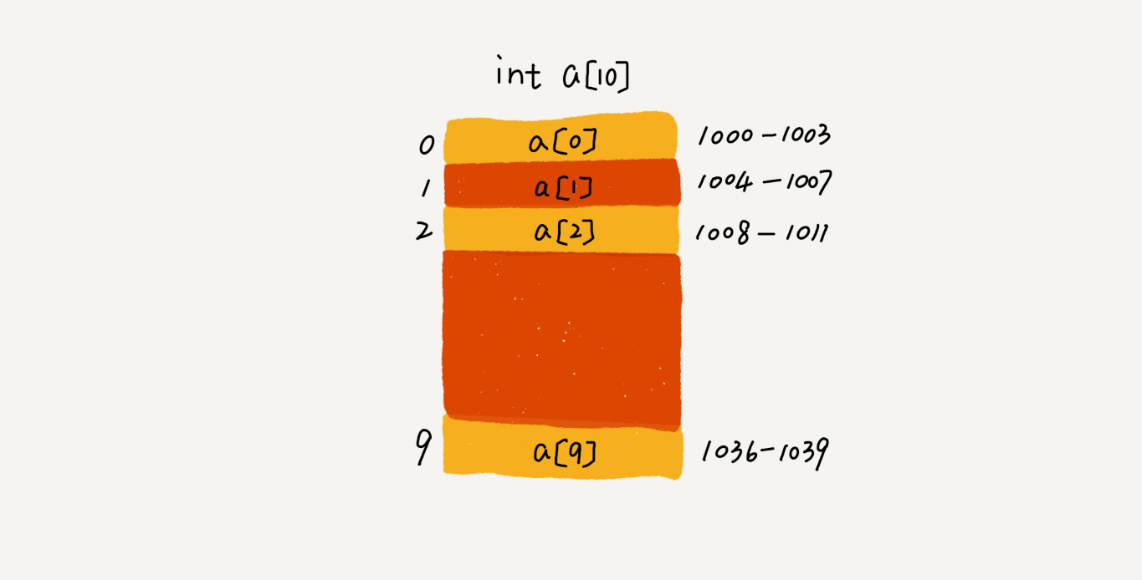
jdk 默认初始大小 为空 ,底层通过数组存储元素的值,能通过数组下标快速的访问元素,主要关注几个方法:
// 通过下标获取元素,会检查下标边界
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
// 替换元素,返回的是旧的元素的值 替换元素 modcount 没有增加
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
// 在增加 元素的时候,会增加modcount 并会判断是否需要扩容,在末尾增加
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
// 扩容为原来大小的 3/2 在通过将旧的数组复制过来
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
在进行大数据量进行分割处理时,使用subList 方法需要注意:
subList 使用有两个问题:
一个是 由于 subList 内部强依赖原来的 list 大量保存 会导致OOM 可以通过 new ArrayList()<row.subList()>;
另一个是 由于 sublist 中 modcount 是从源 modcount 相同,当源集合被修改的了之后,进行遍历时,会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 例子:
public class ArrayListOfSubListUsage {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> rawList = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 10).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList());
List<Integer> subList = rawList.subList(0, 3);
rawList.add(11);
try {
subList.forEach(System.out::print);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
fail-fast: fail-fast,即快速失败机制,它是java集合中的一种错误检测机制,当多个线程(单个线程也是可以),在结构上对集合进行改变时,就有可能会产生fail-fast机制。结构改变其中不包括元素的替换。当Iterator这个迭代器被创建后,除了迭代器本身的方法(remove)可以改变集合的结构外,其他的因素如若改变了集合的结构,都被抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。一般来说,存在非同步的并发修改时,不可能做出任何坚决的保证的。但是快速失败迭代器会做出最大的努力来抛出ConcurrentModificationException。因此,编写依赖于此异常的程序的做法是不正确的。正确的做法应该是:迭代器的快速失败行为应该仅用于检测程序中的bug
fail-safe:是线程安全的在迭代过程中对元素的修改,这种机制基于原来元素复制形成一个快照,当对集合进行结构改变时,不影响迭代器中的快照,但是会有数据不一致情况 常见的的使用fail-safe方式遍历的容器有ConcerrentHashMap和CopyOnWriteArrayList等。
链表可以使用不连续的内存空间,通过后继指针保存下个元素的地址,在遍历时,需要从头指针从头往后进行遍历,虽然链表在增加元素与删除元素上只需要改变指针即可,但是也不要忽略定位到该元素的遍历所花费的时间
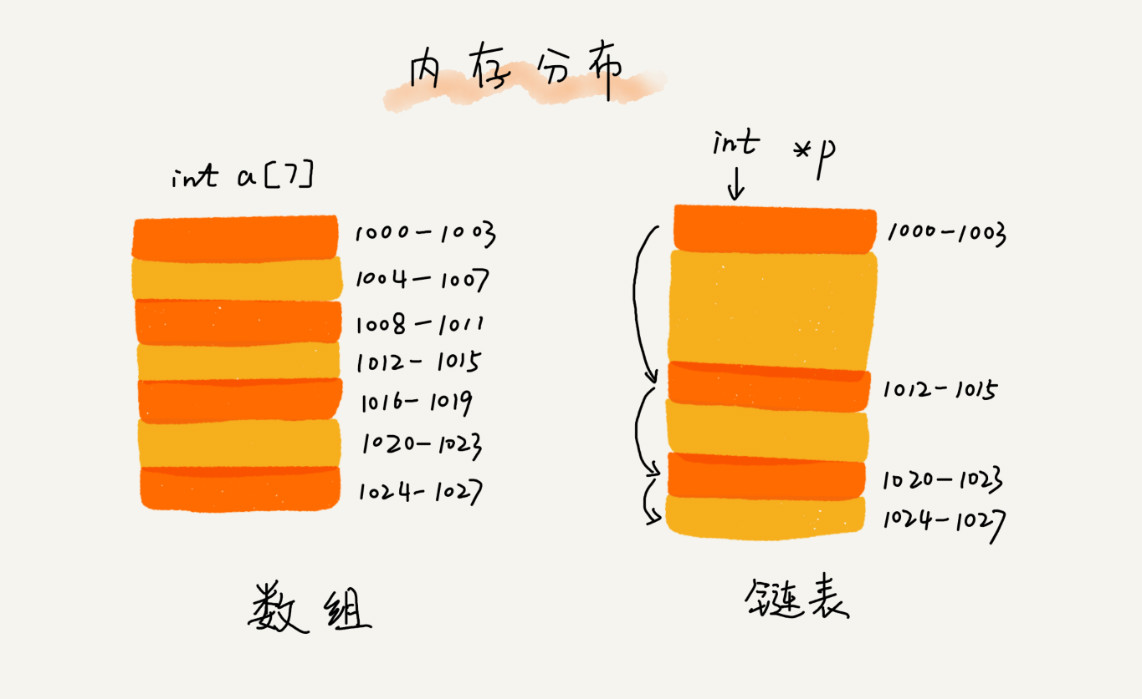
对于链表使用快慢指针能解决很多问题,回文数,判断单链表是否存在环等等
哨兵可以对边界问题进行简化但是不能降低复杂度
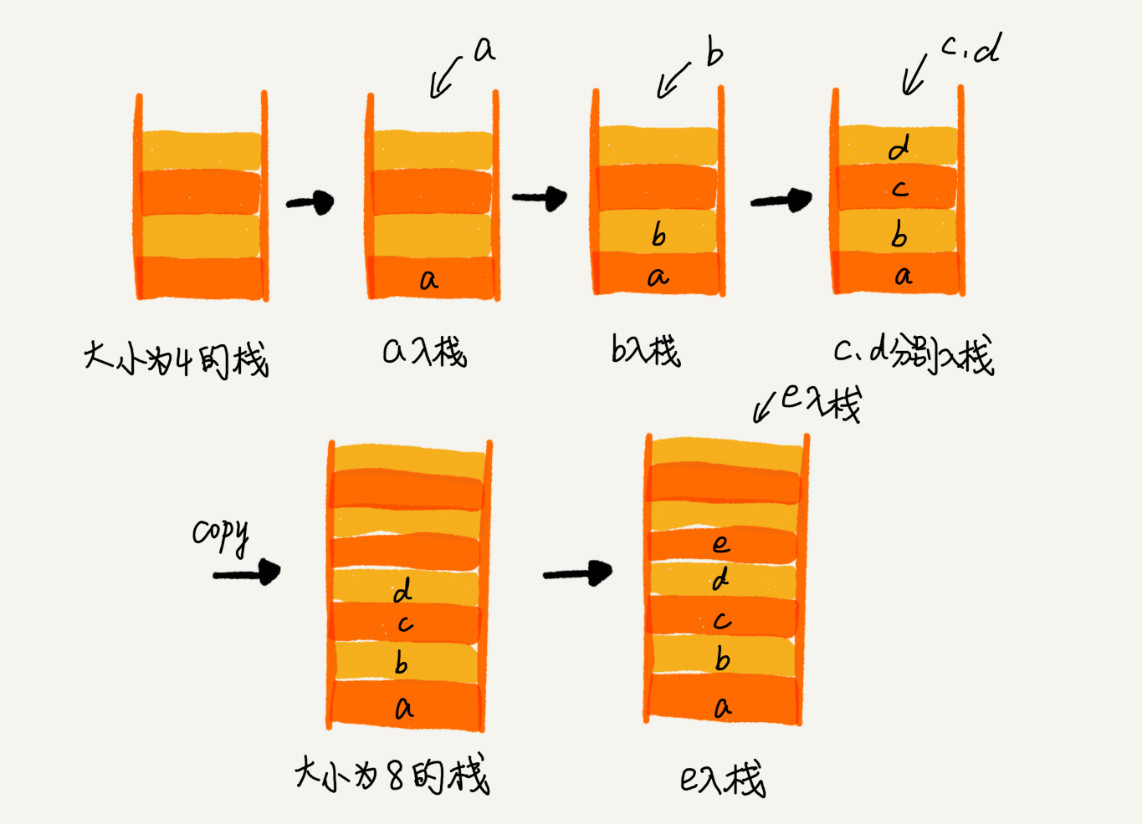
栈是一种先进后出的数据结构,只允许在一端进行插入与删除操作,底层可以通过数组实现也可以通过链表实现
为什么大多数语言在实现方法执行结构时,选择栈结构?
? 方法的作用域 问题,当进入方法时,进行压栈操作,当方法执行完成时,进行出栈操作,对于临时变量的生命周期也就在栈帧内可见
队列是先进先出的的结构
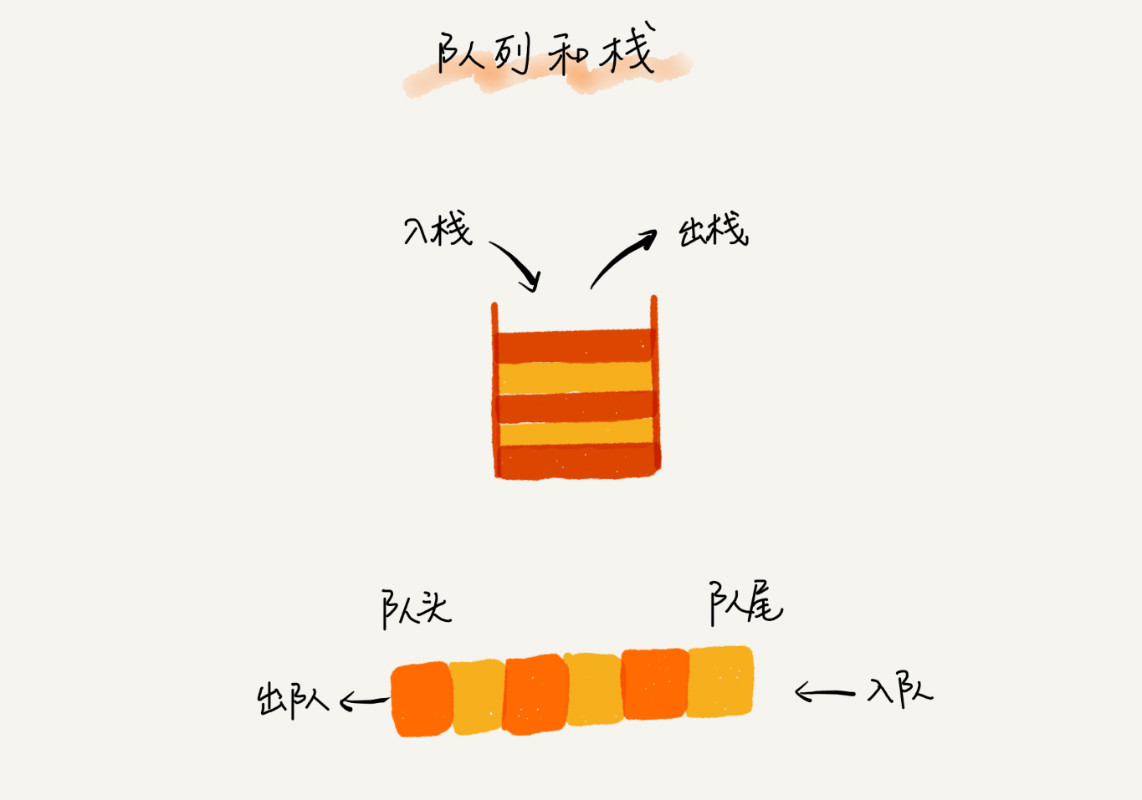
java中队列的实现 PriorityQueue 优先队列,使用堆结构排序,保证队顶的元素最大或者最小,这样通过,出队获取队顶的元素,就实现了优先级的概念
说优先队列之前,先说下堆的数据结构,堆是一种特殊的二叉树结构,需要满足两个条件:
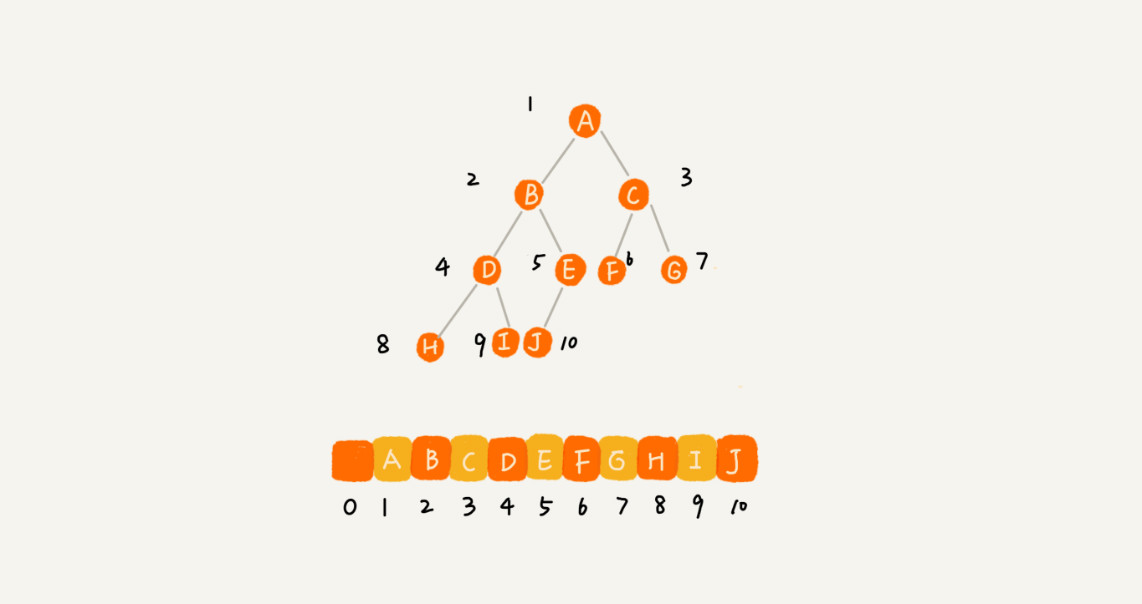
完全二叉树通过数组存储:如果节点 X 存储在数组中下标为 i 的位置,下标为 2 * i 的位置存储的就是左子节点,下标为 2 * i + 1 的位置存储的就是右子节点。反过来,下标为 i/2 的位置存储就是它的父节点
了解以上之后在来看看java 中优先队列的实现
public class PriorityQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements java.io.Serializable {
// 默认大小 11
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;
// 底层通过数组存储
transient Object[] queue; // non-private to simplify nested class access
// 比较器,可以使用基本类型的包装类型的比较器,对于其他对象需要实现 comparable接口,或者通过外部的 compator比较器进行比较,才能实现比较
private final Comparator<? super E> comparator;
// 队列中入队的元素个数
private int size = 0;
//保存结构被修改的次数
transient int modCount = 0; // non-private to simplify nested class access
//构造方法 可以看到队列中的对象需要提供比较器
public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity,
Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
// Note: This restriction of at least one is not actually needed,
// but continues for 1.5 compatibility
if (initialCapacity < 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.comparator = comparator;
}
// 入队操作
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
// 扩容
grow(i + 1);
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0)
queue[0] = e;
else
//树比较,将元素放到数组的最后,也就是堆的最底层节点,通过与父节点比较,确定位置
siftUp(i, e);
return true;
}
// 扩容
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Double size if small; else grow by 50%
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((oldCapacity < 64) ?
(oldCapacity + 2) :
(oldCapacity >> 1));
// overflow-conscious code
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x;
while (k > 0) {
// 与父节点比较 注意 父节点在数组中的下标为 ( k - 1 )/ 2 处
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = queue[parent];
if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
// 出队操作
public E poll() {
if (size == 0)
return null;
int s = --size;
modCount++;
// 取出队顶元素
E result = (E) queue[0];
// 取出末尾元素
E x = (E) queue[s];
// 将末尾元素设置为 null
queue[s] = null;
if (s != 0)
// 将 末尾元素设置为队顶,然后从上往下比较
siftDown(0, x);
return result;
}
}
标签:集合 current private lan col img final overflow 容器
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/sunyangblog/p/14495463.html