标签:ntp 事件 tac embed ret 国际化 port rar public
在Spring中有许多的Aware接口,提供给应用开发者使用,通过Aware接口,我们可以通过set的方式拿到我们需要的bean对象(包括容器中提供的一些对象,ApplicationContext等),根据需要可以将其注入到本地对象的属性中。
先来看一个Spring两个基础的接口
bean的后置处理器接口,在依赖注入的初始化方法前后进行调用
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 初始化方法调用前要进行的处理逻辑
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
/**
* 在初始化方法指定后要进行的处理逻辑
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
所有Aware接口本身是一种修改bean信息的功能接口,但它自身并不会被触发,既然是修改bean属性的功能接口,所以它应该被一个BeanPostProcessor调用———— *AwareProcessor(例如ApplicationContextAwarePostProcessor)
Bean在创建过程,会在实例化后,如果实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,会在实例化后统一调用BeanPostProcessor接口
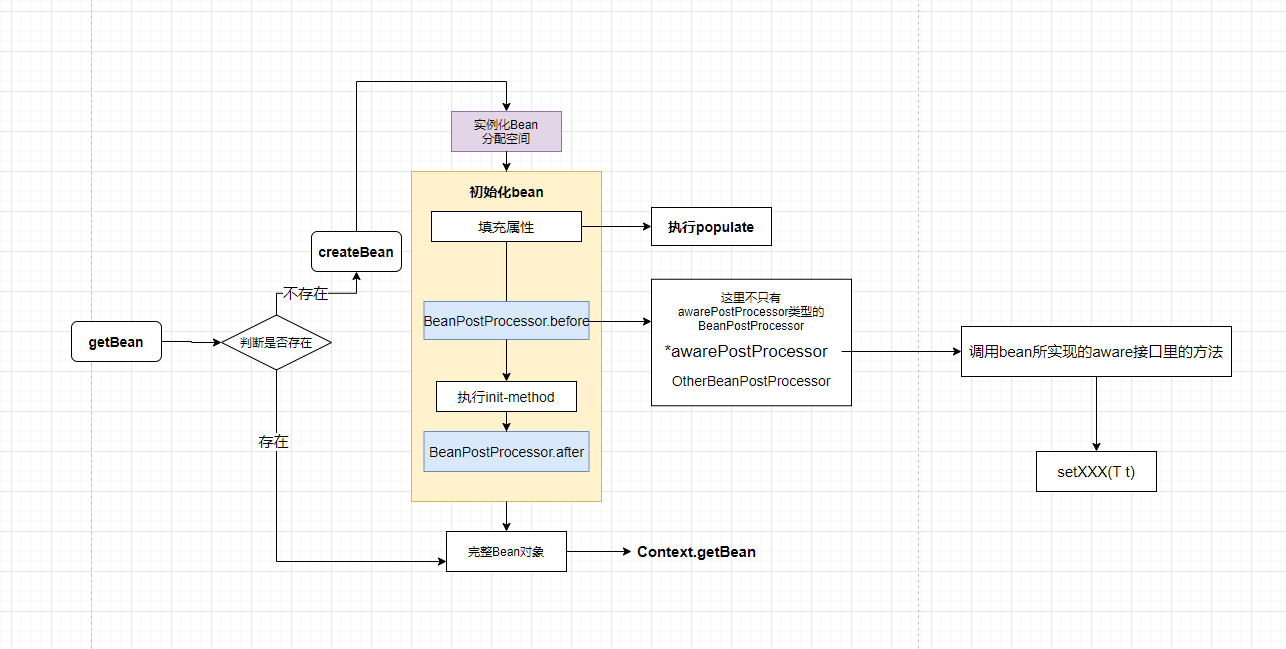
在我们日常开发中,可以通过在bean中实现ApplicationContextAware的方式将ApplicationContext注入到我们的bean对象中去
在Spring中其实是有一个BeanPostProcessor类——ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,用来处理实现了ApplicationContextAware等接口的bean。
ApplicationContextAware类源码
public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware {
/**
* Set the ApplicationContext that this object runs in.
* Normally this call will be used to initialize the object.
* <p>Invoked after population of normal bean properties but before an init callback such
* as {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()}
* or a custom init-method. Invoked after {@link ResourceLoaderAware#setResourceLoader},
* {@link ApplicationEventPublisherAware#setApplicationEventPublisher} and
* {@link MessageSourceAware}, if applicable.
* @param applicationContext the ApplicationContext object to be used by this object
* @throws ApplicationContextException in case of context initialization errors
* @throws BeansException if thrown by application context methods
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanInitializationException
*/
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}
可以看到此aware接口主要是为了在实现类中注入applicationContext,提供这么一个回调方法
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor类源码
class ApplicationContextAwareProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
private final ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver;
/**
* 将Context注入进来
*/
public ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.embeddedValueResolver = new EmbeddedValueResolver(applicationContext.getBeanFactory());
}
/**
* 接口beanPostProcessor规定的方法,会在bean创建时,实例化后,初始化前,对bean对象应用
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (!(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||
bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||
bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware)){
return bean;
}
AccessControlContext acc = null;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext();
}
if (acc != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
// 检测bean上是否实现了某个aware接口,有的话进行相关的调用
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
return null;
}, acc);
}
else {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
}
return bean;
}
/**
* 如果某个bean实现了某个aware接口,给指定的bean设置相应的属性值
*
* @param bean
*/
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}
}
在ApplicationContextAwareProcessor中我们可以看到,其实它处理了好几个aware接口,所以当我们的Bean只要实现了以下任意的接口,都会在invokeAwareInterfaces方法中被处理
当然看到这个地方,肯定有人会疑惑,这个ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,我们并没有在代码中将其实例化为一个Bean。为什么只要实现了ApplicationContextAware接口的Bean对象,就可以注入进来ApplicationContext对象。
其实在Spring源码中在准备beanFactory的时候就已经将ApplicationContextAwareProcessor添加到beanPostProcessor List列表中了
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context‘s class loader etc.
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
// 添加beanPostProcessor,ApplicationContextAwareProcessor此类用来完成某些Aware对象的注入
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
我们希望在自定义的SpringUtils中注入一个ApplicationContext对象,能够在代码里通过getBean的形式来获取IOC容器的中Bean对象
再次感谢spring的开发团队,因为spring的易扩展性,它为我们提供了超级简单的方法来获取applicationContext对象
不多说,看代码
@Component
public class SpringUtils implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
/**
* 注入 applicationContext
*
* @param applicationContext
* @throws BeansException
*/
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
SpringUtils.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
/**
* 获取指定类的bean对象
*
* @param clazz 类类型
* @return
*/
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return applicationContext.getBean(clazz);
}
/**
* 获取指定类的指定名称的bean对象
*
* @param name bean名称
* @param clazz 类类型
* @return
*/
public static <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> clazz) {
return applicationContext.getBean(name, clazz);
}
}
一个静态的SpringUtils就这样写好了,是不是So Easy???
第1步 实现aware接口,定义好需要注入的对象及其相应方法
public interface GlobalSessionAware extends Aware {
/**
* 注入全局的session
*
* @param session
*/
public void setGlobalSession(GlobalSession session);
}
第2步 实现BeanPostProcessor,并回调aware接口中的set方法,将BeanPostProcessor作为一个bean对象,加入到spring容器中
@Component
public class GlobalSessionAwarePostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor, ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Object session = this.applicationContext.getBean("globalSession");
if (session == null) {
return bean;
}
if (session instanceof GlobalSession && bean instanceof GlobalSessionAware) {
((GlobalSessionAware) bean).setGlobalSession((GlobalSession) session);
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
第3步 使用GlobalSession,在需要注入GlobalSession的bean中实现GlobalSessionAware接口
@Component
public class WebTT implements GlobalSessionAware {
private GlobalSession session;
/**
* GlobalSession
*
* @param session
*/
@Override
public void setGlobalSession(GlobalSession session) {
this.session = session;
}
}
到此已经实现了aware接口的自定义,这个地方我们需要知道的是,Awarer接口本身属于修改bean信息的一种功能性接口,但它需要在创建bean时能够被调用到,所以这个地方BeanPostProcessor就能够实现这个功能
标签:ntp 事件 tac embed ret 国际化 port rar public
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/yanchuanbin/p/14582813.html