标签:lips convert ase 文本 argument 阶段 读取文本 选择 load
(这部分比较抽象且写的不是很好,可能还要再编辑)
【概述】
流:流是一系列数据,包括输入流和输出流。你可以想象成黑客帝国的“代码雨”,只要我们输入指令,这些数据就像水一样流进流出了
IO:Input和OutPut,输入和输出文件
通过IO流,我们可以利用Java去读取来自文件的数据(目前阶段大多是记事本里面的数据)
下面列举了常见的流
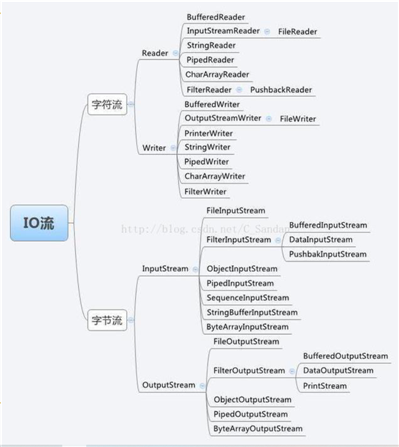
因为我们只是初步了解使用IO流,并不需要全部了解这些流,下面会逐步写出现阶段用到的流
在使用之前,别忘了打上你的import java.io;
【BufferedReader】
BufferedReader类从字符输入流中读取文本并缓冲字符,以便有效地读取字符,数组和行
由Reader构成的每个读取请求都会导致相应的读取请求由基础字符或字节流构成,建议通过BufferedReader包装Reader的实例类以提高效率
可以暂时把BufferedReader理解为一个存储数据的,“缓冲流”
import java.io.*;
public class BRReadLines{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException{
BufferedReaderbr= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str;System.out.println("Enter lines of text.");
System.out.println("Enter ‘end‘ to quit.");
do {
str = br.readLine();
System.out.println(str);
} while (!str.equals("end"));
}
}
【FileInputStream】
选择一个现有文件作为输入流,这个路径可以在文件的“属性”里面复制,另外当文件处在原程序的文件夹里面,可以只写文件名不用写全部路径
InputStreamf = new FileInputStream("C:/java/hello");
或者
File f = new File("C:/java/hello");
InputStreamout = new FileInputStream(f);
FileInputStream中的一些方法
public void close() throws IOException{}
protected void finalize()throws IOException{}
public int read(int r)throws IOException{}
public int read(byte[] r) throws IOException{}
public int available() throws IOException{}
【FileOutputStream】
有Input就有Output
OutputStream f= new FileOutputStream("C:/java/hello");
或者
File f= new File("C:/java/hello");
OutputStream f= new FileOutputStream(f);
FileOutputStream中的一些方法
public void close() throws IOException{}
protected void finalize()throws IOException{}
public void write(int w)throws IOException{}
【一些实例代码】
A
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
File f = new File("C:/Users/zhang/eclipse-workspace/HelloWord/src/lecture13/a1.txt");
// Make sure the path is correct!
// path coped from windows is C:\Users\zhang\eclipse-workspace\HelloWord\src\lecture13
FileOutputStream fop = new FileOutputStream(f);
// Create FileOutputStream object, a new file will be created if it does not exist.
OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(fop, "gbk");
// Create OutputStreamWriter object, second argument is data format, gbk for windows, UTF-8 for Linux
writer.append("Hello");
// Appends the specified character sequence to this writer.
writer.append("\n");
// Appends a line return to this writer.
writer.append("CS161FZ");
// Appends the specified character sequence to this writer.
writer.close();
//Closes the stream, flushing it first.
fop.close();
// Closes this file output stream and releases any system resources associated with this stream.
FileInputStream fip = new FileInputStream(f);
// Create a FileInputStream对 object
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(fip, "gbk");
// Create a InputStreamReader object, same data format with the above
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
while (reader.ready()) {
sb.append((char) reader.read());
// convert to char, and add to StringBuffer object
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
reader.close();
// close read stream
fip.close();
// Closes this file input stream and releases any system resources associated with the stream.
}
B
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File f = new File("C:/Users/zhang/eclipse-workspace/HelloWord/src/lecture13/test.txt");
FileOutputStream fop = new FileOutputStream(f);
OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(fop, "gbk");
int datatoWrite[] = {11, 21, 3, 40, 5, 74, 89};
for (int i = 0; i < datatoWrite.length; i++) {
writer.append(Integer.toString(datatoWrite[i])); // writes the ints
writer.append("\n");
}
writer.close();
// If you forget to close the writer, YOU CAN NOT SUCESSFULLY WRITER!
fop.close();
FileInputStream fip = new FileInputStream(f);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fip, "gbk"));
while(br.ready()) {
System.out.println(br.readLine());
}
br.close();
fip.close();
}
标签:lips convert ase 文本 argument 阶段 读取文本 选择 load
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/RetenQ/p/14660409.html