标签:多个 天气 launch tco content 代码 icon 步骤 ati
本文力求用最简的描述,演示C#开发和调用webapi。
所用的例子在.net5以及vs2019 v16.9.3中调试通过。
mvc框架实现的webapi和webapi框架的对比:
学过.net MVC的同学都知道,MVC中,c是可以返回字符串(多数是json字符串)的。因此,在不计体量的情况下,完全可以用mvc来开发webapi。
webapi相对于mvc,最大的好处就是轻量。因为它不用考虑视图等等内容。当然,配置也略微麻烦一点。
webapi实现步骤:
1、新建项目。如下图:
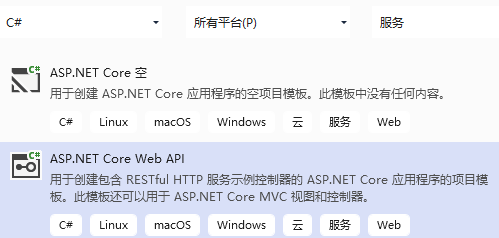
之后的项目配置界面,选择最简内容:

如需勾选什么,自己负责研究清楚。
2、创建项目之后,添加自己的控制器“HomeController”(原有的天气系统可以删除)

此处添加两个方法:index和index1
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace WebApplication1.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]/[action]")]
public class HomeController :ControllerBase
{
public string Index()
{
return "Hello Katty.";
}
[HttpGet("{x}")]
public string Index1(string x)
{
return x+ ",Hello Katty.";
}
}
}
要点:
(1)、“[ApiController]”必须有,否则方法不会被识别为webapi方法。加了它以后,“[Route("[controller]/[action]")]”也就必须有了。它表示使用什么样的格式访问对应方法。
想要在多个控制器上使用ApiController属性,微软的建议是:
[ApiController] public class MyControllerBase : ControllerBase { }
然后
[Produces(MediaTypeNames.Application.Json)] [Route("[controller]")] public class PetsController : MyControllerBase
(见:https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/web-api/?view=aspnetcore-5.0)
(2)、参数可以用示例代码的方式添加。
(3)、控制器继承自ControllerBase而不是Controller。前者是后者的父类,更轻便,没有处理视图的代码。
(4)、要返回json,也可以返回类型是 ActionResult<T> 类型。 ASP.NET Core 自动将对象序列化为 JSON,并将 JSON 写入响应消息的正文中。 此返回类型的响应代码为 200 OK(假设没有未处理的异常)。
(见:https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/web-api/?view=aspnetcore-5.0)这一点和mvc相同。
3、配置启动文档" Properties\launchSettings.json" 。添加了对新控制器的支持。
{ "$schema": "http://json.schemastore.org/launchsettings.json", "iisSettings": { "windowsAuthentication": false, "anonymousAuthentication": true, "iisExpress": { "applicationUrl": "http://localhost:28916", "sslPort": 0 } }, "profiles": { "IIS Express": { "commandName": "IISExpress", "launchBrowser": true, "launchUrl": "WeatherForecast", "environmentVariables": { "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development" } }, "myapi": { "commandName": "test", "dotnetRunMessages": "true", "launchBrowser": true, "launchUrl": "Home", //"applicationUrl": "http://localhost:5000", "environmentVariables": { "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development" } //"WebApplication1": { // "commandName": "Project", // "dotnetRunMessages": "true", // "launchBrowser": true, // "launchUrl": "Home", // "applicationUrl": "http://localhost:5000", // "environmentVariables": { // "ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development" // } } } }
至此,webapi完成。
调用此webapi:
简单起见,采用控制台方式调用。
****
考虑到日后使用方便,参考了CSDN博主「大海中一粒沙子」的原创文章(原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u013730110/article/details/98941934)
新建了restClient类,代码如下:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.IO; using System.Net; using System.Web; namespace ConsoleApp1 { public class RestClient { /// <summary> /// 请求服务器地址 /// </summary> private string BaseUri; public RestClient(string baseUri) { this.BaseUri = baseUri; } #region Get请求 public string Get(string uri) { //先根据用户请求的uri构造请求地址 string serviceUrl = string.Format("{0}/{1}", this.BaseUri, uri); //创建Web访问对 象 HttpWebRequest myRequest = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(serviceUrl); //通过Web访问对象获取响应内容 HttpWebResponse myResponse = (HttpWebResponse)myRequest.GetResponse(); //通过响应内容流创建StreamReader对象,因为StreamReader更高级更快 StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(myResponse.GetResponseStream(), Encoding.UTF8); //string returnXml = HttpUtility.UrlDecode(reader.ReadToEnd());//解决编码问题 string returnXml = reader.ReadToEnd();//利用StreamReader就可以从响应内容从头读到尾 reader.Close(); myResponse.Close(); return returnXml; } #endregion #region Post请求 public string Post(string data, string uri) { //先根据用户请求的uri构造请求地址 string serviceUrl = string.Format("{0}/{1}", this.BaseUri, uri); //创建Web访问对象 HttpWebRequest myRequest = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(serviceUrl); //数据转成“UTF-8”的字节流 byte[] buf = System.Text.Encoding.GetEncoding("UTF-8").GetBytes(data); myRequest.Method = "POST"; myRequest.ContentLength = buf.Length; myRequest.ContentType = "application/json"; myRequest.MaximumAutomaticRedirections = 1; myRequest.AllowAutoRedirect = true; //发送请求 Stream stream = myRequest.GetRequestStream(); stream.Write(buf, 0, buf.Length); stream.Close(); //获取接口返回值 //通过Web访问对象获取响应内容 HttpWebResponse myResponse = (HttpWebResponse)myRequest.GetResponse(); //通过响应内容流创建StreamReader对象,因为StreamReader更高级更快 StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(myResponse.GetResponseStream(), Encoding.UTF8); //string returnXml = HttpUtility.UrlDecode(reader.ReadToEnd());//解决编码问题 string returnXml = reader.ReadToEnd();//利用StreamReader就可以从响应内容从头读到尾 reader.Close(); myResponse.Close(); return returnXml; } #endregion #region Put请求 public string Put(string data, string uri) { //先根据用户请求的uri构造请求地址 string serviceUrl = string.Format("{0}/{1}", this.BaseUri, uri); //创建Web访问对象 HttpWebRequest myRequest = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(serviceUrl); //把用户传过来的数据转成“UTF-8”的字节流 byte[] buf = System.Text.Encoding.GetEncoding("UTF-8").GetBytes(data); myRequest.Method = "PUT"; myRequest.ContentLength = buf.Length; myRequest.ContentType = "application/json"; myRequest.MaximumAutomaticRedirections = 1; myRequest.AllowAutoRedirect = true; //发送请求 Stream stream = myRequest.GetRequestStream(); stream.Write(buf, 0, buf.Length); stream.Close(); //获取接口返回值 //通过Web访问对象获取响应内容 HttpWebResponse myResponse = (HttpWebResponse)myRequest.GetResponse(); //通过响应内容流创建StreamReader对象,因为StreamReader更高级更快 StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(myResponse.GetResponseStream(), Encoding.UTF8); //string returnXml = HttpUtility.UrlDecode(reader.ReadToEnd());//解决编码问题 string returnXml = reader.ReadToEnd();//利用StreamReader就可以从响应内容从头读到尾 reader.Close(); myResponse.Close(); return returnXml; } #endregion #region Delete请求 public string Delete(string data, string uri) { //先根据用户请求的uri构造请求地址 string serviceUrl = string.Format("{0}/{1}", this.BaseUri, uri); //创建Web访问对象 HttpWebRequest myRequest = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(serviceUrl); //把用户传过来的数据转成“UTF-8”的字节流 byte[] buf = System.Text.Encoding.GetEncoding("UTF-8").GetBytes(data); myRequest.Method = "DELETE"; myRequest.ContentLength = buf.Length; myRequest.ContentType = "application/json"; myRequest.MaximumAutomaticRedirections = 1; myRequest.AllowAutoRedirect = true; //发送请求 Stream stream = myRequest.GetRequestStream(); stream.Write(buf, 0, buf.Length); stream.Close(); //获取接口返回值 //通过Web访问对象获取响应内容 HttpWebResponse myResponse = (HttpWebResponse)myRequest.GetResponse(); //通过响应内容流创建StreamReader对象,因为StreamReader更高级更快 StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(myResponse.GetResponseStream(), Encoding.UTF8); //string returnXml = HttpUtility.UrlDecode(reader.ReadToEnd());//解决编码问题 string returnXml = reader.ReadToEnd();//利用StreamReader就可以从响应内容从头读到尾 reader.Close(); myResponse.Close(); return returnXml; } #endregion } }
实质:利用HttpWebRequest、HttpWebResponse发送和返回内容,由流来读写,自行研究,不再赘述。
****
代码为:
string s; RestClient restClient = new("http://localhost:28916"); s=restClient.Get("home/index"); Console.WriteLine(s); s = restClient.Get("home/index1/zs"); Console.WriteLine(s);
运行效果:
webapi:
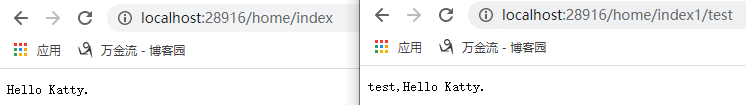
控制台:
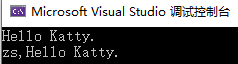
(完)
标签:多个 天气 launch tco content 代码 icon 步骤 ati
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/wanjinliu/p/14672559.html