标签:zone 做什么 期望 注册 reac run 实体类 code log
Ribbbon虽然现在已经进入维护模式了,但是使用的还是很多的。
1.官网
https://github.com/Netflix/ribbon/wiki/Getting-Started
2.Ribbon是什么
Ribbon是Netflix发布的开源项目,主要功能是提供客户端的软件负载均衡算法,是一个具有负载均衡等功能的http客户端
3.Ribbon能做什么
做负载均衡LB(进程内的LB)
4.负载均衡(LB)
目前主流的LB方案可分成两类:一种是集中式LB,另一种是进程内LB
集中式LB:即在服务的消费方和提供方之间使用独立的LB设施(可以是硬件,如F5, 也可以是软件,如nginx), 由该设施负责把访问请求通过某种策略转发至服务的提供方,消费者的请求先到这个中间设施,有中间设施来选择把这个请求转发到哪个服务提供者那里。消费者发送请求时还不知道请求会被发到具体哪个服务提供者,经过负载均衡中间件决定把请求转发到具体的那个服务提供者
进程内LB:将LB逻辑集成到消费方。消费者获取服务提供者的地址,由负载均衡(如Ribbon)来选择一个服务提供者,消费者再发送请求到这个服务提供者。Ribbon就属于后者,它只是一个类库,集成于消费方进程,消费方通过它来获取到服务提供方的地址并且选择发送请求到哪个服务提供者。消费者这边先靠负载均衡(如Ribbon)选择发送请求到哪个具体的服务提供者,再发送请求。在发送请求时已经确定了具体的服务提供者。
5.Ribbon的核心组件IRule
IRule是负载均衡的算法的顶级接口,它有很多具体的负载均衡算法的实现
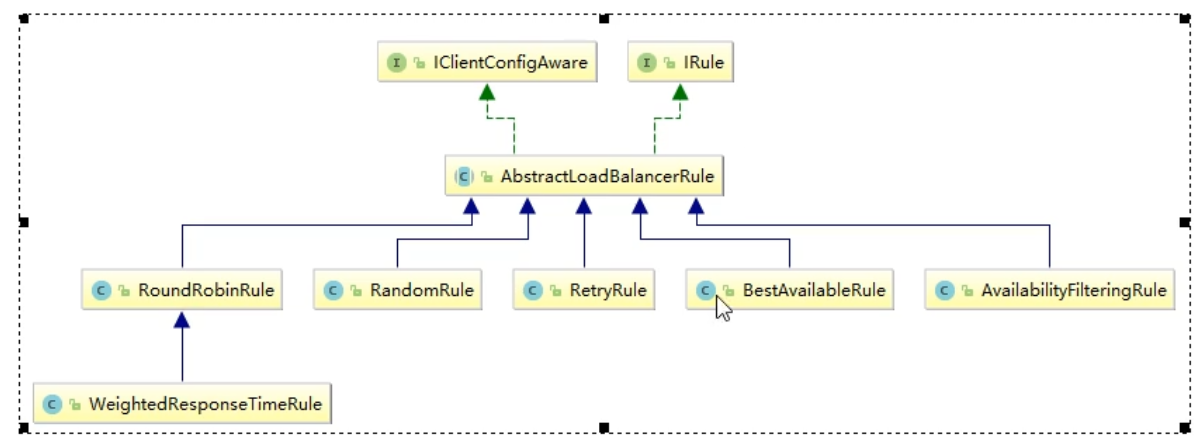
(1)RoundRobinRule:轮询;
(2)RandomRule:随机;
(3)AvailabilityFilteringRule:会先过滤掉由于多次访问故障而处于断路器状态的服务,还有并发的连接数量超过阈值的服务,然后对剩余的服务列表按照轮询策略进行访问;
(4)WeightedResponseTimeRule:根据平均响应时间计算所有服务的权重,响应时间越快的服务权重越大被选中的概率越大。刚启动时如果统计信息不足,则使用RoundRobinRule(轮询)策略,等统计信息足够,会切换到WeightedResponseTimeRule;
(5)RetryRule:先按照RoundRobinRule(轮询)策略获取服务,如果获取服务失败则在指定时间内进行重试,获取可用的服务;
(6)BestAvailableRule:会先过滤掉由于多次访问故障而处于断路器跳闸状态的服务,然后选择一个并发量最小的服务;
(7)ZoneAvoidanceRule:复合判断Server所在区域的性能和Server的可用性选择服务器
6.Ribbon使用实例
这是采用的是Euraka来使用Ribbon,因为Eureka自带Ribbon
关于Eureka的使用 https://www.cnblogs.com/jthr/p/14607318.html
6.1现在我们有一个项目
按照上面的文档构建一个Eureka的项目
服务:cloud-consumer-order80 (服务消费者)
cloud-provider-payment8001(服务提供者)、cloud-provider-payment8002(服务提供者)[8001和8002是同一个服务的集群]
注册中心(集群):cloud-eureka-server7001、cloud-eureka-server7002
公共commom:cloud-api-commons(存放公共的实体类、工具类...)
6.2在cloud-consumer-order80使用负载均衡
调用服务是采用RestTemplate来调用的,只需要在RestTemplate的Bean这里加上注解@LoadBalanced即可打开负载均衡,默认是轮询
package com.atguigu.springcloud.config; import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; @Configuration public class ApplicationContextConfig { //创建RestTemplate的bean @Bean @LoadBalanced //设置负载均衡 让它可以同为微服务名称调用服务 - 默认调用同名服务集群是才去轮询调用 public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){ return new RestTemplate(); } }
6.3怎么用其它的负载均衡算法替换默认的轮询算法
1)配置类
里面返回一个IRule负载均衡算法的实现类
/** * @Classname MyRule * @Description TODO * @Date 2021/4/23 0023 下午 2:27 * @Created by jcc */ @Configuration public class MyLoadBalanced { @Bean public IRule myRule(){ return new RandomRule();//定义为随机 } }
需要注意的是,这个配置类的位置有要求。

而启动类的注解@SpringBootApplication是包含了这个注解的
所以,这个类要放在启动类所在包及子包外,如下图
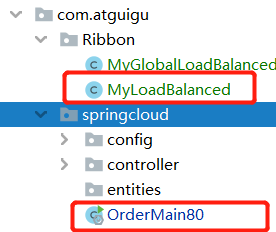
2)在主启动类加上配置@RibbonClient

参数:name:服务的名称 configuration:刚才的配置类
如果需要设置多个@RibbonClient 注解,可以使用 @RibbonClients 注解,value 可以设置多个 @RibbonClient 注解,多个@RibbonClient用逗号隔开
@SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaClient @RibbonClients(value = {@RibbonClient(name = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE",configuration = MyGlobalLoadBalanced.class)}) public class OrderMain80 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderMain80.class,args); } }
6.4自定义负载均衡算法
1)创建一个类实现IRule,里面写算法的具体实现
下面是一个自定义的轮询,和默认的实现差不多,就是作为一个例子
package com.atguigu.springcloud.config; import com.netflix.loadbalancer.ILoadBalancer; import com.netflix.loadbalancer.IRule; import com.netflix.loadbalancer.Server; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; /** * @Classname GlobalRule * @Description TODO * @Date 2021/4/23 0023 下午 3:25 * @Created by jcc */ public class GlobalRule implements IRule { private ILoadBalancer iLoadBalancer; private AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(0); @Override public Server choose(Object o) { List<Server> reachableServers = iLoadBalancer.getReachableServers(); int index = getAndIncrement() % reachableServers.size(); //得到服务器的下标位置 return reachableServers.get(index); } @Override public void setLoadBalancer(ILoadBalancer iLoadBalancer) { this.iLoadBalancer = iLoadBalancer; } @Override public ILoadBalancer getLoadBalancer() { return this.iLoadBalancer; } //坐标 private final int getAndIncrement(){ int current; int next; do { current = this.atomicInteger.get(); next = current >= 2147483647 ? 0 : current + 1; }while (!this.atomicInteger.compareAndSet(current,next));//(这里是CAS和自旋锁的知识)第一个参数是期望值,第二个参数是修改值是 System.out.println("Global*******第几次访问,次数next: "+next); return next; } }
2)配置类
和6.3的第一步是一样的
package com.atguigu.Ribbon; import com.atguigu.springcloud.config.GlobalRule; import com.netflix.loadbalancer.IRule; import com.netflix.loadbalancer.RandomRule; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; /** * @Classname MyRule * @Description TODO * @Date 2021/4/23 0023 下午 2:27 * @Created by jcc */ @Configuration public class MyGlobalLoadBalanced { @Bean public IRule myRule(){ return new GlobalRule(); } }
3)在主启动类加上配置@RibbonClient
和6.3的第二步是一样的
package com.atguigu.springcloud; import com.atguigu.Ribbon.MyGlobalLoadBalanced; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EnableEurekaClient; import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonClient; @SpringBootApplication @EnableEurekaClient @RibbonClient(name = "CLOUD-PAYMENT-SERVICE",configuration = MyGlobalLoadBalanced.class) //表示使用MyRule的算法来做负载均衡 public class OrderMain80 { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(OrderMain80.class,args); } }
标签:zone 做什么 期望 注册 reac run 实体类 code log
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/jthr/p/14694632.html