标签:方式 expand 必须 数组 运行 ado ons div 属性
1、用偶判断,不用奇判断
System.out.println(-1%2==1?"奇数":"偶数");
---偶数
原因:java计算余数:a/b -> a-a/b*b 所以-1/2余数为-1,不等于1.
2、不要只替换一个类
常量类中的属性final修饰。其他类引用时,final常量会被直接将值写到类中。当只替换编译好的常量class时,引用的类不重新编译,则还是用老的常量值。
3、浮点精度问题
10进制小数转成二进制时,存在除不尽问题。小数转换方法:乘以2取整数部分。如 0.4-> 0.4*2=0.8(0) ->0.8*2=1.6(1) -> 0.6*2=1.2(1) ->0.2*2=0.4(0) ..............最终结果为(011001100110......)
4、包装类型进行比较不能使用==
包装类型使用==进行比较时,是比较对象的地址。可以使用compareTo
5、整型池
-128-127之间的数字放到整型池中。
Integer i1 = 128; Integer i2 = 128; System.out.println(i1 == i2); --false i1 = 127; i2 = 127; System.out.println(i1 == i2); --true
6、深拷贝
通过流方式实现(重点是类必须可序列化实现Serializable接口)
import java.io.*; /** * 深拷贝 * 序列化方式 */ public class TestClone implements Serializable{ public static void main(String[] args) { TestClone testClone = new TestClone(); testClone.test(); } public void test() { A a = new A("张三"); B b = new B("李四"); a.setB(b); try { A aClone = a.clone(); b.setName("李四改名"); System.out.println(aClone); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } class A implements Cloneable, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public A(String name) { this.name = name; } private String name; private B b; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public B getB() { return b; } public void setB(B b) { this.b = b; } @Override public A clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { /** * 序列化方式拷贝 */ ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); try { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos); oos.writeObject(this); oos.close(); ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray()); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis); return (A)ois.readObject(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return (A) super.clone(); } @Override public String toString() { return "A{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ", b=" + b + ‘}‘; } } class B implements Serializable{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public B(String name) { this.name = name; } private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "B{" + "name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ + ‘}‘; } } }
7、String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder
String不可变
StringBuffer:可变,线程安全
StringBuilder:可变,线程不安全
8、尽量使用数组代替集合
9、使用变长数组
public void test() { int[] arr = new int[8]; int size = 4000; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (i == arr.length) { arr = expand(arr, arr.length * 2); } arr[i] = i; } System.out.println(arr.length); } public int[] expand(int[] arr, int size) { size = size < 0 ? 0 : size; return Arrays.copyOf(arr, size); }
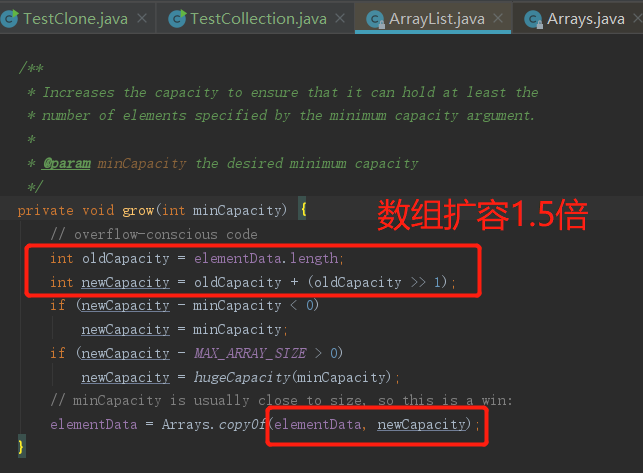
10、集合设置默认初始长度
ArrayList 默认初始值10,扩容机制为不够用时,扩充大小到原来的1.5倍。如果程序中可以评估出数量个数字,可以在创建数组对象是,设置初始值,减少扩容带来的性能损耗。
List arr = new ArrayList(100);
11、基本数据类型转换列表
基本数据类型转换,会将数组当作一个对象封装到列表里。

int[] arr1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; List arrList = Arrays.asList(arr1); System.out.println(arrList.size()); --结果:1
Integer[] arr1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; List arrList = Arrays.asList(arr1); System.out.println(arrList.size()); --结果:6
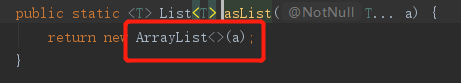
12、asList后列表不可变
List arr2 = Arrays.asList("一", "二");
arr2.add("三");
--结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException
at java.util.AbstractList.add(AbstractList.java:148)
at java.util.AbstractList.add(AbstractList.java:108)
at com.example.test.TestCollection.main(TestCollection.java:12)
原因:final修饰
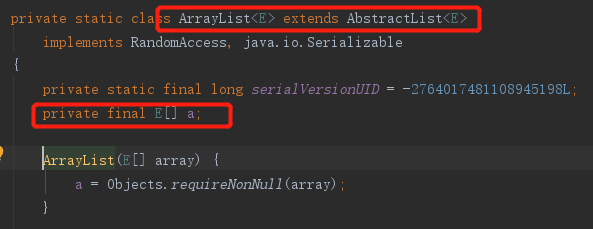
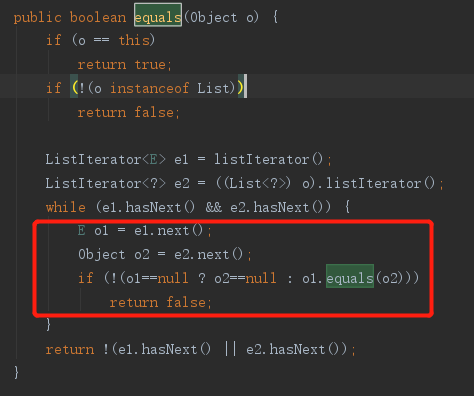
13、列表比较只比较内容
List arr01 = new ArrayList(){{add(1);add(2);add(3);add(4);}}; List arr02 = new LinkedList(){{add(1);add(2);add(3);add(4);}}; System.out.println(arr01.equals(arr02));----true List arr01 = new ArrayList(){{add(1);add(2);add(3);add(4);}}; List arr02 = new LinkedList(){{add(1);add(2);add(4);add(3);}}; System.out.println(arr01.equals(arr02));----false
源码解析:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
查看AbstractList.equals 方法:比较相同位置的对象是否相等
14、subList为原列表的视图
对子列表的操作就是直接操作原列表
15、泛型擦除
JAVA的泛型是在编译期有效,运行期将被擦除。(即泛型在代码编译成class时,擦除掉泛型定义)下面代码编译时就进行了校验。
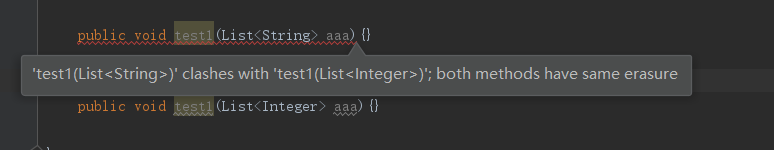
16、受检异常/非受检异常
非受检异常:继承RuntimeException
受检异常:继承其他Exception,调用代码必须处理该异常(try...catch)
public class CheckedException extends Exception { String code; String message; /** * Constructs a new exception with {@code null} as its detail message. * The cause is not initialized, and may subsequently be initialized by a * call to {@link #initCause}. */ public CheckedException(String code, String message) { this.code = code; this.message = message; } public String getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(String code) { this.code = code; } @Override public String getMessage() { return message; } public void setMessage(String message) { this.message = message; } }
public class UncheckedException extends RuntimeException { /** * Constructs a new runtime exception with {@code null} as its * detail message. The cause is not initialized, and may subsequently be * initialized by a call to {@link #initCause}. */ public UncheckedException(String code, String message) { this.code = code; this.message = message; } String code; String message; public String getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(String code) { this.code = code; } @Override public String getMessage() { return message; } public void setMessage(String message) { this.message = message; } }
public class TestException { public static void main(String[] args) { TestException testException = new TestException(); try { testException.testCheck(); } catch (CheckedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } testException.testUnCheck(); } public void testCheck() throws CheckedException{ throw new CheckedException("9999", "我错了"); } public void testUnCheck() throws UncheckedException{ throw new UncheckedException("9999", "我错了啊啊啊啊"); } }
标签:方式 expand 必须 数组 运行 ado ons div 属性
原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/guanhao0114/p/14793962.html