标签:des android style blog http io color ar os
方法注册好后要经过哪些路
Android一个异常捕获项目 https://github.com/xroche/coffeecatch
CoffeeCatch, a tiny native POSIX signal catcher (especially useful for JNI code on Android/Dalvik, but it can be used in non-Java projects)
It allows to "gracefully" recover from a signal (SIGSEGV, SIGBUS...) as if it was an exception. It will not gracefully recover from allocator/mutexes corruption etc., however, but at least "most" gentle crashes (null pointer dereferencing, integer division, stack overflow etc.) should be handled without too much troubles.
/** Enter protected section. **/
COFFEE_TRY() {
/** Try to call ‘call_some_native_function‘. **/
call_some_protected_function();
} COFFEE_CATCH() {
/** Caught a signal: throw Java exception. **/
/** In pure C projects, you may print an error message (coffeecatch_get_message()). **/
coffeecatch_throw_exception(env);
} COFFEE_END();
You may read the corresponding discussion about this project.
The handler is thread-safe, but client must have exclusive control on the signal handlers (ie. the library is installing its own signal handlers on top of the existing ones).
Libraries
If you want to get useful stack traces, you should build all your libraries with -funwind-tables (this adds unwinding information). On ARM, you may also use the --no-merge-exidx-entries linker switch, to solve certain issues with unwinding (the switch is possibly not needed anymore). On Android, this can be achieved by using this line in the Android.mk file in each library block:
LOCAL_CFLAGS := -funwind-tables -Wl,--no-merge-exidx-entries
Example
First, build the library, or just add the two files in the list of local files to be built:
LOCAL_SRC_FILES += coffeecatch.c coffeejni.c
then, use the COFFEE_TRY_JNI() macro to protect your call(s):
/** The potentially dangerous function. **/
jint call_dangerous_function(JNIEnv* env, jobject object) {
// ... do dangerous things!
return 42;
}
/** Protected function stub. **/
void foo_protected(JNIEnv* env, jobject object, jint *retcode) {
/* Try to call ‘call_dangerous_function‘, and raise proper Java Error upon
* fatal error (SEGV, etc.). **/
COFFEE_TRY_JNI(env, *retcode = call_dangerous_function(env, object));
}
/** Regular JNI entry point. **/
jint Java_com_example_android_MyNative_foo(JNIEnv* env, jobject object) {
jint retcode = 0;
foo_protected(env, object, &retcode);
return retcode;
}
and, in case of crash, get something like this (note: the last Exception with native backtrace is produced on Android >= 4.1.1):
FATAL EXCEPTION: AsyncTask #5
java.lang.RuntimeException: An error occured while executing doInBackground()
at android.os.AsyncTask$3.done(AsyncTask.java:299)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.finishCompletion(FutureTask.java:352)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.setException(FutureTask.java:219)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:239)
at android.os.AsyncTask$SerialExecutor$1.run(AsyncTask.java:230)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1080)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:573)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:841)
Caused by: java.lang.Error: signal 11 (Address not mapped to object) at address 0x42 [at libexample.so:0xa024]
at com.example.jni.ExampleLib.main(Native Method)
at com.example.ExampleActivity$Runner.runInternal(ExampleActivity.java:998)
at com.example.ExampleActivity$Runner.doInBackground(ExampleActivity.java:919)
at com.example.ExampleActivity$Runner.doInBackground(ExampleActivity.java:1)
at android.os.AsyncTask$2.call(AsyncTask.java:287)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:234)
... 4 more
Caused by: java.lang.Error: signal 11 (Address not mapped to object) at address 0x42 [at libexample.so:0xa024]
at data.app_lib.com_example.libexample_so.0xa024(Native Method)
at data.app_lib.com_example.libexample_so.0x705fc(hts_main2:0x8f74:0)
at data.app_lib.com_example.libexamplejni_so.0x4cc8(ExampleLib_main:0xf8:0)
at data.app_lib.com_example.libexamplejni_so.0x52d8(Java_com_example_jni_ExampleLib_main:0x64:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x1dc4c(dvmPlatformInvoke:0x70:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x4dcab(dvmCallJNIMethod(unsigned int const*, JValue*, Method const*, Thread*):0x18a:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x385e1(dvmCheckCallJNIMethod(unsigned int const*, JValue*, Method const*, Thread*):0x8:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x4f699(dvmResolveNativeMethod(unsigned int const*, JValue*, Method const*, Thread*):0xb8:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x27060(Native Method)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x2b580(dvmInterpret(Thread*, Method const*, JValue*):0xb8:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x5fcbd(dvmCallMethodV(Thread*, Method const*, Object*, bool, JValue*, std::__va_list):0x124:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x5fce7(dvmCallMethod(Thread*, Method const*, Object*, JValue*, ...):0x14:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x54a6f(Native Method)
at system.lib.libc_so.0xca58(__thread_entry:0x48:0)
at system.lib.libc_so.0xcbd4(pthread_create:0xd0:0)
The COFFEE_TRY()/COFFEE_CATCH()/COFFEE_END() syntax can be used:
void my_function() {
COFFEE_TRY() {
/** Try to call ‘call_some_native_function‘. **/
call_some_native_function();
} COFFEE_CATCH() {
/** Caught a signal. **/
const char*const message = coffeecatch_get_message();
fprintf(stderr, "**FATAL ERROR: %s\n", message);
} COFFEE_END();
}
If you wish to catch signals and continue running your program rather than ending it (this may be dangerous, especially if a crash was spotted within a C library function, such as malloc()), use thecoffeecatch_cancel_pending_alarm() function to cancel the default pending alarm triggered to avoid deadlocks.
dvmCallJNIMethod_general不知从哪个版本就没了,但从http://androidxref.com/这里看,Gingerbread - 2.3.7还有,ICS - 4.0.3就没了。
这里模拟器里导出的libdvm.so,符号,只有dvmCallJNIMethod,如下(4.4.2_API19):
File: /cygdrive/d/Developer/sdk/platforms/android-19/lib/libdvm.so
Symbol table ‘.dynsym‘ contains 1713 entries:
Num: Value Size Type Bind Vis Ndx Name
0: 00000000 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT UND
1: 00000000 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UND __cxa_finalize
394: 0004dd75 664 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 8 _Z16dvmCallJNIMethodPKjP6JValuePK6MethodP6Thread

1 //xref: 4.4.2_r2 /dalvik/vm/interp/Stack.cpp 2 //http://androidxref.com/4.4.2_r2/xref/dalvik/vm/interp/Stack.cpp 3 4 /* 5 * Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project 6 * 7 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 8 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 9 * You may obtain a copy of the License at 10 * 11 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 12 * 13 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 14 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 15 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 16 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 17 * limitations under the License. 18 */ 19 20 /* 21 * Stacks and their uses (e.g. native --> interpreted method calls). 22 * 23 * See the majestic ASCII art in Stack.h. 24 */ 25 #include "Dalvik.h" 26 #include "jni.h" 27 28 #include <stdlib.h> 29 #include <stdarg.h> 30 31 #ifdef HAVE_ANDROID_OS 32 #include <corkscrew/backtrace.h> 33 #endif 34 35 /* 36 * Initialize the interpreter stack in a new thread. 37 * 38 * Currently this doesn‘t do much, since we don‘t need to zero out the 39 * stack (and we really don‘t want to if it was created with mmap). 40 */ 41 bool dvmInitInterpStack(Thread* thread, int stackSize) 42 { 43 assert(thread->interpStackStart != NULL); 44 45 assert(thread->interpSave.curFrame == NULL); 46 47 return true; 48 } 49 50 /* 51 * We‘re calling an interpreted method from an internal VM function or 52 * via reflection. 53 * 54 * Push a frame for an interpreted method onto the stack. This is only 55 * used when calling into interpreted code from native code. (The 56 * interpreter does its own stack frame manipulation for interp-->interp 57 * calls.) 58 * 59 * The size we need to reserve is the sum of parameters, local variables, 60 * saved goodies, and outbound parameters. 61 * 62 * We start by inserting a "break" frame, which ensures that the interpreter 63 * hands control back to us after the function we call returns or an 64 * uncaught exception is thrown. 65 */ 66 static bool dvmPushInterpFrame(Thread* self, const Method* method) 67 { 68 StackSaveArea* saveBlock; 69 StackSaveArea* breakSaveBlock; 70 int stackReq; 71 u1* stackPtr; 72 73 assert(!dvmIsNativeMethod(method)); 74 assert(!dvmIsAbstractMethod(method)); 75 76 stackReq = method->registersSize * 4 // params + locals 77 + sizeof(StackSaveArea) * 2 // break frame + regular frame 78 + method->outsSize * 4; // args to other methods 79 80 if (self->interpSave.curFrame != NULL) 81 stackPtr = (u1*) SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame); 82 else 83 stackPtr = self->interpStackStart; 84 85 if (stackPtr - stackReq < self->interpStackEnd) { 86 /* not enough space */ 87 ALOGW("Stack overflow on call to interp " 88 "(req=%d top=%p cur=%p size=%d %s.%s)", 89 stackReq, self->interpStackStart, self->interpSave.curFrame, 90 self->interpStackSize, method->clazz->descriptor, method->name); 91 dvmHandleStackOverflow(self, method); 92 assert(dvmCheckException(self)); 93 return false; 94 } 95 96 /* 97 * Shift the stack pointer down, leaving space for the function‘s 98 * args/registers and save area. 99 */ 100 stackPtr -= sizeof(StackSaveArea); 101 breakSaveBlock = (StackSaveArea*)stackPtr; 102 stackPtr -= method->registersSize * 4 + sizeof(StackSaveArea); 103 saveBlock = (StackSaveArea*) stackPtr; 104 105 #if !defined(NDEBUG) && !defined(PAD_SAVE_AREA) 106 /* debug -- memset the new stack, unless we want valgrind‘s help */ 107 memset(stackPtr - (method->outsSize*4), 0xaf, stackReq); 108 #endif 109 #ifdef EASY_GDB 110 breakSaveBlock->prevSave = 111 (StackSaveArea*)FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(self->interpSave.curFrame); 112 saveBlock->prevSave = breakSaveBlock; 113 #endif 114 115 breakSaveBlock->prevFrame = self->interpSave.curFrame; 116 breakSaveBlock->savedPc = NULL; // not required 117 breakSaveBlock->xtra.localRefCookie = 0; // not required 118 breakSaveBlock->method = NULL; 119 saveBlock->prevFrame = FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(breakSaveBlock); 120 saveBlock->savedPc = NULL; // not required 121 saveBlock->xtra.currentPc = NULL; // not required? 122 saveBlock->method = method; 123 124 LOGVV("PUSH frame: old=%p new=%p (size=%d)", 125 self->interpSave.curFrame, FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock), 126 (u1*)self->interpSave.curFrame - (u1*)FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock)); 127 128 self->interpSave.curFrame = FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock); 129 130 return true; 131 } 132 133 /* 134 * We‘re calling a JNI native method from an internal VM fuction or 135 * via reflection. This is also used to create the "fake" native-method 136 * frames at the top of the interpreted stack. 137 * 138 * This actually pushes two frames; the first is a "break" frame. 139 * 140 * The top frame has additional space for JNI local reference tracking. 141 */ 142 bool dvmPushJNIFrame(Thread* self, const Method* method) 143 { 144 StackSaveArea* saveBlock; 145 StackSaveArea* breakSaveBlock; 146 int stackReq; 147 u1* stackPtr; 148 149 assert(dvmIsNativeMethod(method)); 150 151 stackReq = method->registersSize * 4 // params only 152 + sizeof(StackSaveArea) * 2; // break frame + regular frame 153 154 if (self->interpSave.curFrame != NULL) 155 stackPtr = (u1*) SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame); 156 else 157 stackPtr = self->interpStackStart; 158 159 if (stackPtr - stackReq < self->interpStackEnd) { 160 /* not enough space */ 161 ALOGW("Stack overflow on call to native " 162 "(req=%d top=%p cur=%p size=%d ‘%s‘)", 163 stackReq, self->interpStackStart, self->interpSave.curFrame, 164 self->interpStackSize, method->name); 165 dvmHandleStackOverflow(self, method); 166 assert(dvmCheckException(self)); 167 return false; 168 } 169 170 /* 171 * Shift the stack pointer down, leaving space for just the stack save 172 * area for the break frame, then shift down farther for the full frame. 173 * We leave space for the method args, which are copied in later. 174 */ 175 stackPtr -= sizeof(StackSaveArea); 176 breakSaveBlock = (StackSaveArea*)stackPtr; 177 stackPtr -= method->registersSize * 4 + sizeof(StackSaveArea); 178 saveBlock = (StackSaveArea*) stackPtr; 179 180 #if !defined(NDEBUG) && !defined(PAD_SAVE_AREA) 181 /* debug -- memset the new stack */ 182 memset(stackPtr, 0xaf, stackReq); 183 #endif 184 #ifdef EASY_GDB 185 if (self->interpSave.curFrame == NULL) 186 breakSaveBlock->prevSave = NULL; 187 else { 188 void* fp = FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(self->interpSave.curFrame); 189 breakSaveBlock->prevSave = (StackSaveArea*)fp; 190 } 191 saveBlock->prevSave = breakSaveBlock; 192 #endif 193 194 breakSaveBlock->prevFrame = self->interpSave.curFrame; 195 breakSaveBlock->savedPc = NULL; // not required 196 breakSaveBlock->xtra.localRefCookie = 0; // not required 197 breakSaveBlock->method = NULL; 198 saveBlock->prevFrame = FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(breakSaveBlock); 199 saveBlock->savedPc = NULL; // not required 200 saveBlock->xtra.localRefCookie = self->jniLocalRefTable.segmentState.all; 201 saveBlock->method = method; 202 203 LOGVV("PUSH JNI frame: old=%p new=%p (size=%d)", 204 self->interpSave.curFrame, FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock), 205 (u1*)self->interpSave.curFrame - (u1*)FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock)); 206 207 self->interpSave.curFrame = FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock); 208 209 return true; 210 } 211 212 /* 213 * This is used by the JNI PushLocalFrame call. We push a new frame onto 214 * the stack that has no ins, outs, or locals, and no break frame above it. 215 * It‘s strictly used for tracking JNI local refs, and will be popped off 216 * by dvmPopFrame if it‘s not removed explicitly. 217 */ 218 bool dvmPushLocalFrame(Thread* self, const Method* method) 219 { 220 StackSaveArea* saveBlock; 221 int stackReq; 222 u1* stackPtr; 223 224 assert(dvmIsNativeMethod(method)); 225 226 stackReq = sizeof(StackSaveArea); // regular frame 227 228 assert(self->interpSave.curFrame != NULL); 229 stackPtr = (u1*) SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame); 230 231 if (stackPtr - stackReq < self->interpStackEnd) { 232 /* not enough space; let JNI throw the exception */ 233 ALOGW("Stack overflow on PushLocal " 234 "(req=%d top=%p cur=%p size=%d ‘%s‘)", 235 stackReq, self->interpStackStart, self->interpSave.curFrame, 236 self->interpStackSize, method->name); 237 dvmHandleStackOverflow(self, method); 238 assert(dvmCheckException(self)); 239 return false; 240 } 241 242 /* 243 * Shift the stack pointer down, leaving space for just the stack save 244 * area for the break frame, then shift down farther for the full frame. 245 */ 246 stackPtr -= sizeof(StackSaveArea); 247 saveBlock = (StackSaveArea*) stackPtr; 248 249 #if !defined(NDEBUG) && !defined(PAD_SAVE_AREA) 250 /* debug -- memset the new stack */ 251 memset(stackPtr, 0xaf, stackReq); 252 #endif 253 #ifdef EASY_GDB 254 saveBlock->prevSave = 255 (StackSaveArea*)FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(self->interpSave.curFrame); 256 #endif 257 258 saveBlock->prevFrame = self->interpSave.curFrame; 259 saveBlock->savedPc = NULL; // not required 260 saveBlock->xtra.localRefCookie = self->jniLocalRefTable.segmentState.all; 261 saveBlock->method = method; 262 263 LOGVV("PUSH JNI local frame: old=%p new=%p (size=%d)", 264 self->interpSave.curFrame, FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock), 265 (u1*)self->interpSave.curFrame - (u1*)FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock)); 266 267 self->interpSave.curFrame = FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock); 268 269 return true; 270 } 271 272 /* 273 * Pop one frame pushed on by JNI PushLocalFrame. 274 * 275 * If we‘ve gone too far, the previous frame is either a break frame or 276 * an interpreted frame. Either way, the method pointer won‘t match. 277 */ 278 bool dvmPopLocalFrame(Thread* self) 279 { 280 StackSaveArea* saveBlock = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame); 281 282 assert(!dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame)); 283 if (saveBlock->method != SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(saveBlock->prevFrame)->method) { 284 /* 285 * The previous frame doesn‘t have the same method pointer -- we‘ve 286 * been asked to pop too much. 287 */ 288 assert(dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)saveBlock->prevFrame) || 289 !dvmIsNativeMethod( 290 SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(saveBlock->prevFrame)->method)); 291 return false; 292 } 293 294 LOGVV("POP JNI local frame: removing %s, now %s", 295 saveBlock->method->name, 296 SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(saveBlock->prevFrame)->method->name); 297 dvmPopJniLocals(self, saveBlock); 298 self->interpSave.curFrame = saveBlock->prevFrame; 299 300 return true; 301 } 302 303 /* 304 * Pop a frame we added. There should be one method frame and one break 305 * frame. 306 * 307 * If JNI Push/PopLocalFrame calls were mismatched, we might end up 308 * popping multiple method frames before we find the break. 309 * 310 * Returns "false" if there was no frame to pop. 311 */ 312 static bool dvmPopFrame(Thread* self) 313 { 314 StackSaveArea* saveBlock; 315 316 if (self->interpSave.curFrame == NULL) 317 return false; 318 319 saveBlock = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame); 320 assert(!dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame)); 321 322 /* 323 * Remove everything up to the break frame. If this was a call into 324 * native code, pop the JNI local references table. 325 */ 326 while (saveBlock->prevFrame != NULL && saveBlock->method != NULL) { 327 /* probably a native->native JNI call */ 328 329 if (dvmIsNativeMethod(saveBlock->method)) { 330 LOGVV("Popping JNI stack frame for %s.%s%s", 331 saveBlock->method->clazz->descriptor, 332 saveBlock->method->name, 333 (SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(saveBlock->prevFrame)->method == NULL) ? 334 "" : " (JNI local)"); 335 dvmPopJniLocals(self, saveBlock); 336 } 337 338 saveBlock = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(saveBlock->prevFrame); 339 } 340 if (saveBlock->method != NULL) { 341 ALOGE("PopFrame missed the break"); 342 assert(false); 343 dvmAbort(); // stack trashed -- nowhere to go in this thread 344 } 345 346 LOGVV("POP frame: cur=%p new=%p", 347 self->interpSave.curFrame, saveBlock->prevFrame); 348 349 self->interpSave.curFrame = saveBlock->prevFrame; 350 return true; 351 } 352 353 /* 354 * Common code for dvmCallMethodV/A and dvmInvokeMethod. 355 * 356 * Pushes a call frame on, advancing self->interpSave.curFrame. 357 */ 358 static ClassObject* callPrep(Thread* self, const Method* method, Object* obj, 359 bool checkAccess) 360 { 361 ClassObject* clazz; 362 363 #ifndef NDEBUG 364 if (self->status != THREAD_RUNNING) { 365 ALOGW("threadid=%d: status=%d on call to %s.%s -", 366 self->threadId, self->status, 367 method->clazz->descriptor, method->name); 368 } 369 #endif 370 371 assert(self != NULL); 372 assert(method != NULL); 373 374 if (obj != NULL) 375 clazz = obj->clazz; 376 else 377 clazz = method->clazz; 378 379 IF_LOGVV() { 380 char* desc = dexProtoCopyMethodDescriptor(&method->prototype); 381 LOGVV("thread=%d native code calling %s.%s %s", self->threadId, 382 clazz->descriptor, method->name, desc); 383 free(desc); 384 } 385 386 if (checkAccess) { 387 /* needed for java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke */ 388 if (!dvmCheckMethodAccess(dvmGetCaller2Class(self->interpSave.curFrame), 389 method)) 390 { 391 /* note this throws IAException, not IAError */ 392 dvmThrowIllegalAccessException("access to method denied"); 393 return NULL; 394 } 395 } 396 397 /* 398 * Push a call frame on. If there isn‘t enough room for ins, locals, 399 * outs, and the saved state, it will throw an exception. 400 * 401 * This updates self->interpSave.curFrame. 402 */ 403 if (dvmIsNativeMethod(method)) { 404 /* native code calling native code the hard way */ 405 if (!dvmPushJNIFrame(self, method)) { 406 assert(dvmCheckException(self)); 407 return NULL; 408 } 409 } else { 410 /* native code calling interpreted code */ 411 if (!dvmPushInterpFrame(self, method)) { 412 assert(dvmCheckException(self)); 413 return NULL; 414 } 415 } 416 417 return clazz; 418 } 419 420 /* 421 * Issue a method call. 422 * 423 * Pass in NULL for "obj" on calls to static methods. 424 * 425 * (Note this can‘t be inlined because it takes a variable number of args.) 426 */ 427 void dvmCallMethod(Thread* self, const Method* method, Object* obj, 428 JValue* pResult, ...) 429 { 430 va_list args; 431 va_start(args, pResult); 432 dvmCallMethodV(self, method, obj, false, pResult, args); 433 va_end(args); 434 } 435 436 /* 437 * Issue a method call with a variable number of arguments. We process 438 * the contents of "args" by scanning the method signature. 439 * 440 * Pass in NULL for "obj" on calls to static methods. 441 * 442 * We don‘t need to take the class as an argument because, in Dalvik, 443 * we don‘t need to worry about static synchronized methods. 444 */ 445 void dvmCallMethodV(Thread* self, const Method* method, Object* obj, 446 bool fromJni, JValue* pResult, va_list args) 447 { 448 const char* desc = &(method->shorty[1]); // [0] is the return type. 449 int verifyCount = 0; 450 ClassObject* clazz; 451 u4* ins; 452 453 clazz = callPrep(self, method, obj, false); 454 if (clazz == NULL) 455 return; 456 457 /* "ins" for new frame start at frame pointer plus locals */ 458 ins = ((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame) + 459 (method->registersSize - method->insSize); 460 461 //ALOGD(" FP is %p, INs live at >= %p", self->interpSave.curFrame, ins); 462 463 /* put "this" pointer into in0 if appropriate */ 464 if (!dvmIsStaticMethod(method)) { 465 #ifdef WITH_EXTRA_OBJECT_VALIDATION 466 assert(obj != NULL && dvmIsHeapAddress(obj)); 467 #endif 468 *ins++ = (u4) obj; 469 verifyCount++; 470 } 471 472 while (*desc != ‘\0‘) { 473 switch (*(desc++)) { 474 case ‘D‘: case ‘J‘: { 475 u8 val = va_arg(args, u8); 476 memcpy(ins, &val, 8); // EABI prevents direct store 477 ins += 2; 478 verifyCount += 2; 479 break; 480 } 481 case ‘F‘: { 482 /* floats were normalized to doubles; convert back */ 483 float f = (float) va_arg(args, double); 484 *ins++ = dvmFloatToU4(f); 485 verifyCount++; 486 break; 487 } 488 case ‘L‘: { /* ‘shorty‘ descr uses L for all refs, incl array */ 489 void* arg = va_arg(args, void*); 490 assert(obj == NULL || dvmIsHeapAddress(obj)); 491 jobject argObj = reinterpret_cast<jobject>(arg); 492 if (fromJni) 493 *ins++ = (u4) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(self, argObj); 494 else 495 *ins++ = (u4) argObj; 496 verifyCount++; 497 break; 498 } 499 default: { 500 /* Z B C S I -- all passed as 32-bit integers */ 501 *ins++ = va_arg(args, u4); 502 verifyCount++; 503 break; 504 } 505 } 506 } 507 508 #ifndef NDEBUG 509 if (verifyCount != method->insSize) { 510 ALOGE("Got vfycount=%d insSize=%d for %s.%s", verifyCount, 511 method->insSize, clazz->descriptor, method->name); 512 assert(false); 513 goto bail; 514 } 515 #endif 516 517 //dvmDumpThreadStack(dvmThreadSelf()); 518 519 if (dvmIsNativeMethod(method)) { 520 TRACE_METHOD_ENTER(self, method); 521 /* 522 * Because we leave no space for local variables, "curFrame" points 523 * directly at the method arguments. 524 */ 525 (*method->nativeFunc)((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame, pResult, 526 method, self); 527 TRACE_METHOD_EXIT(self, method); 528 } else { 529 dvmInterpret(self, method, pResult); 530 } 531 532 #ifndef NDEBUG 533 bail: 534 #endif 535 dvmPopFrame(self); 536 } 537 538 /* 539 * Issue a method call with arguments provided in an array. We process 540 * the contents of "args" by scanning the method signature. 541 * 542 * The values were likely placed into an uninitialized jvalue array using 543 * the field specifiers, which means that sub-32-bit fields (e.g. short, 544 * boolean) may not have 32 or 64 bits of valid data. This is different 545 * from the varargs invocation where the C compiler does a widening 546 * conversion when calling a function. As a result, we have to be a 547 * little more precise when pulling stuff out. 548 * 549 * "args" may be NULL if the method has no arguments. 550 */ 551 void dvmCallMethodA(Thread* self, const Method* method, Object* obj, 552 bool fromJni, JValue* pResult, const jvalue* args) 553 { 554 const char* desc = &(method->shorty[1]); // [0] is the return type. 555 int verifyCount = 0; 556 ClassObject* clazz; 557 u4* ins; 558 559 clazz = callPrep(self, method, obj, false); 560 if (clazz == NULL) 561 return; 562 563 /* "ins" for new frame start at frame pointer plus locals */ 564 ins = ((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame) + 565 (method->registersSize - method->insSize); 566 567 /* put "this" pointer into in0 if appropriate */ 568 if (!dvmIsStaticMethod(method)) { 569 assert(obj != NULL); 570 *ins++ = (u4) obj; /* obj is a "real" ref */ 571 verifyCount++; 572 } 573 574 while (*desc != ‘\0‘) { 575 switch (*desc++) { 576 case ‘D‘: /* 64-bit quantity; have to use */ 577 case ‘J‘: /* memcpy() in case of mis-alignment */ 578 memcpy(ins, &args->j, 8); 579 ins += 2; 580 verifyCount++; /* this needs an extra push */ 581 break; 582 case ‘L‘: /* includes array refs */ 583 if (fromJni) 584 *ins++ = (u4) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(self, args->l); 585 else 586 *ins++ = (u4) args->l; 587 break; 588 case ‘F‘: 589 case ‘I‘: 590 *ins++ = args->i; /* full 32 bits */ 591 break; 592 case ‘S‘: 593 *ins++ = args->s; /* 16 bits, sign-extended */ 594 break; 595 case ‘C‘: 596 *ins++ = args->c; /* 16 bits, unsigned */ 597 break; 598 case ‘B‘: 599 *ins++ = args->b; /* 8 bits, sign-extended */ 600 break; 601 case ‘Z‘: 602 *ins++ = args->z; /* 8 bits, zero or non-zero */ 603 break; 604 default: 605 ALOGE("Invalid char %c in short signature of %s.%s", 606 *(desc-1), clazz->descriptor, method->name); 607 assert(false); 608 goto bail; 609 } 610 611 verifyCount++; 612 args++; 613 } 614 615 #ifndef NDEBUG 616 if (verifyCount != method->insSize) { 617 ALOGE("Got vfycount=%d insSize=%d for %s.%s", verifyCount, 618 method->insSize, clazz->descriptor, method->name); 619 assert(false); 620 goto bail; 621 } 622 #endif 623 624 if (dvmIsNativeMethod(method)) { 625 TRACE_METHOD_ENTER(self, method); 626 /* 627 * Because we leave no space for local variables, "curFrame" points 628 * directly at the method arguments. 629 */ 630 (*method->nativeFunc)((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame, pResult, 631 method, self); 632 TRACE_METHOD_EXIT(self, method); 633 } else { 634 dvmInterpret(self, method, pResult); 635 } 636 637 bail: 638 dvmPopFrame(self); 639 } 640 641 static void throwArgumentTypeMismatch(int argIndex, ClassObject* expected, DataObject* arg) { 642 std::string expectedClassName(dvmHumanReadableDescriptor(expected->descriptor)); 643 std::string actualClassName = dvmHumanReadableType(arg); 644 dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exIllegalArgumentException, "argument %d should have type %s, got %s", 645 argIndex + 1, expectedClassName.c_str(), actualClassName.c_str()); 646 } 647 648 /* 649 * Invoke a method, using the specified arguments and return type, through 650 * one of the reflection interfaces. Could be a virtual or direct method 651 * (including constructors). Used for reflection. 652 * 653 * Deals with boxing/unboxing primitives and performs widening conversions. 654 * 655 * "invokeObj" will be null for a static method. 656 * 657 * If the invocation returns with an exception raised, we have to wrap it. 658 */ 659 Object* dvmInvokeMethod(Object* obj, const Method* method, 660 ArrayObject* argList, ArrayObject* params, ClassObject* returnType, 661 bool noAccessCheck) 662 { 663 ClassObject* clazz; 664 Object* retObj = NULL; 665 Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf(); 666 s4* ins; 667 int verifyCount, argListLength; 668 JValue retval; 669 bool needPop = false; 670 671 /* verify arg count */ 672 if (argList != NULL) 673 argListLength = argList->length; 674 else 675 argListLength = 0; 676 if (argListLength != (int) params->length) { 677 dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exIllegalArgumentException, 678 "wrong number of arguments; expected %d, got %d", 679 params->length, argListLength); 680 return NULL; 681 } 682 683 clazz = callPrep(self, method, obj, !noAccessCheck); 684 if (clazz == NULL) 685 return NULL; 686 needPop = true; 687 688 /* "ins" for new frame start at frame pointer plus locals */ 689 ins = ((s4*)self->interpSave.curFrame) + 690 (method->registersSize - method->insSize); 691 verifyCount = 0; 692 693 //ALOGD(" FP is %p, INs live at >= %p", self->interpSave.curFrame, ins); 694 695 /* put "this" pointer into in0 if appropriate */ 696 if (!dvmIsStaticMethod(method)) { 697 assert(obj != NULL); 698 *ins++ = (s4) obj; 699 verifyCount++; 700 } 701 702 /* 703 * Copy the args onto the stack. Primitive types are converted when 704 * necessary, and object types are verified. 705 */ 706 DataObject** args = (DataObject**)(void*)argList->contents; 707 ClassObject** types = (ClassObject**)(void*)params->contents; 708 for (int i = 0; i < argListLength; i++) { 709 int width = dvmConvertArgument(*args++, *types++, ins); 710 if (width < 0) { 711 dvmPopFrame(self); // throw wants to pull PC out of stack 712 needPop = false; 713 throwArgumentTypeMismatch(i, *(types-1), *(args-1)); 714 goto bail; 715 } 716 717 ins += width; 718 verifyCount += width; 719 } 720 721 #ifndef NDEBUG 722 if (verifyCount != method->insSize) { 723 ALOGE("Got vfycount=%d insSize=%d for %s.%s", verifyCount, 724 method->insSize, clazz->descriptor, method->name); 725 assert(false); 726 goto bail; 727 } 728 #endif 729 730 if (dvmIsNativeMethod(method)) { 731 TRACE_METHOD_ENTER(self, method); 732 /* 733 * Because we leave no space for local variables, "curFrame" points 734 * directly at the method arguments. 735 */ 736 (*method->nativeFunc)((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame, &retval, 737 method, self); 738 TRACE_METHOD_EXIT(self, method); 739 } else { 740 dvmInterpret(self, method, &retval); 741 } 742 743 /* 744 * Pop the frame immediately. The "wrap" calls below can cause 745 * allocations, and we don‘t want the GC to walk the now-dead frame. 746 */ 747 dvmPopFrame(self); 748 needPop = false; 749 750 /* 751 * If an exception is raised, wrap and replace. This is necessary 752 * because the invoked method could have thrown a checked exception 753 * that the caller wasn‘t prepared for. 754 * 755 * We might be able to do this up in the interpreted code, but that will 756 * leave us with a shortened stack trace in the top-level exception. 757 */ 758 if (dvmCheckException(self)) { 759 dvmWrapException("Ljava/lang/reflect/InvocationTargetException;"); 760 } else { 761 /* 762 * If this isn‘t a void method or constructor, convert the return type 763 * to an appropriate object. 764 * 765 * We don‘t do this when an exception is raised because the value 766 * in "retval" is undefined. 767 */ 768 if (returnType != NULL) { 769 retObj = (Object*)dvmBoxPrimitive(retval, returnType); 770 dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc(retObj, NULL); 771 } 772 } 773 774 bail: 775 if (needPop) { 776 dvmPopFrame(self); 777 } 778 return retObj; 779 } 780 781 struct LineNumFromPcContext { 782 u4 address; 783 u4 lineNum; 784 }; 785 786 static int lineNumForPcCb(void *cnxt, u4 address, u4 lineNum) 787 { 788 LineNumFromPcContext *pContext = (LineNumFromPcContext *)cnxt; 789 790 // We know that this callback will be called in 791 // ascending address order, so keep going until we find 792 // a match or we‘ve just gone past it. 793 794 if (address > pContext->address) { 795 // The line number from the previous positions callback 796 // wil be the final result. 797 return 1; 798 } 799 800 pContext->lineNum = lineNum; 801 802 return (address == pContext->address) ? 1 : 0; 803 } 804 805 /* 806 * Determine the source file line number based on the program counter. 807 * "pc" is an offset, in 16-bit units, from the start of the method‘s code. 808 * 809 * Returns -1 if no match was found (possibly because the source files were 810 * compiled without "-g", so no line number information is present). 811 * Returns -2 for native methods (as expected in exception traces). 812 */ 813 int dvmLineNumFromPC(const Method* method, u4 relPc) 814 { 815 const DexCode* pDexCode = dvmGetMethodCode(method); 816 817 if (pDexCode == NULL) { 818 if (dvmIsNativeMethod(method) && !dvmIsAbstractMethod(method)) 819 return -2; 820 return -1; /* can happen for abstract method stub */ 821 } 822 823 LineNumFromPcContext context; 824 memset(&context, 0, sizeof(context)); 825 context.address = relPc; 826 // A method with no line number info should return -1 827 context.lineNum = -1; 828 829 dexDecodeDebugInfo(method->clazz->pDvmDex->pDexFile, pDexCode, 830 method->clazz->descriptor, 831 method->prototype.protoIdx, 832 method->accessFlags, 833 lineNumForPcCb, NULL, &context); 834 835 return context.lineNum; 836 } 837 838 /* 839 * Compute the frame depth. 840 * 841 * Excludes "break" frames. 842 */ 843 int dvmComputeExactFrameDepth(const void* fp) 844 { 845 int count = 0; 846 847 for ( ; fp != NULL; fp = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(fp)->prevFrame) { 848 if (!dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)fp)) 849 count++; 850 } 851 852 return count; 853 } 854 855 /* 856 * Compute the "vague" frame depth, which is just a pointer subtraction. 857 * The result is NOT an overly generous assessment of the number of 858 * frames; the only meaningful use is to compare against the result of 859 * an earlier invocation. 860 * 861 * Useful for implementing single-step debugger modes, which may need to 862 * call this for every instruction. 863 */ 864 int dvmComputeVagueFrameDepth(Thread* thread, const void* fp) 865 { 866 const u1* interpStackStart = thread->interpStackStart; 867 868 assert((u1*) fp >= interpStackStart - thread->interpStackSize); 869 assert((u1*) fp < interpStackStart); 870 return interpStackStart - (u1*) fp; 871 } 872 873 /* 874 * Get the calling frame. Pass in the current fp. 875 * 876 * Skip "break" frames and reflection invoke frames. 877 */ 878 void* dvmGetCallerFP(const void* curFrame) 879 { 880 void* caller = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(curFrame)->prevFrame; 881 StackSaveArea* saveArea; 882 883 retry: 884 if (dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)caller)) { 885 /* pop up one more */ 886 caller = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(caller)->prevFrame; 887 if (caller == NULL) 888 return NULL; /* hit the top */ 889 890 /* 891 * If we got here by java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(), we don‘t 892 * want to return Method‘s class loader. Shift up one and try 893 * again. 894 */ 895 saveArea = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(caller); 896 if (dvmIsReflectionMethod(saveArea->method)) { 897 caller = saveArea->prevFrame; 898 assert(caller != NULL); 899 goto retry; 900 } 901 } 902 903 return caller; 904 } 905 906 /* 907 * Get the caller‘s class. Pass in the current fp. 908 * 909 * This is used by e.g. java.lang.Class. 910 */ 911 ClassObject* dvmGetCallerClass(const void* curFrame) 912 { 913 void* caller; 914 915 caller = dvmGetCallerFP(curFrame); 916 if (caller == NULL) 917 return NULL; 918 919 return SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(caller)->method->clazz; 920 } 921 922 /* 923 * Get the caller‘s caller‘s class. Pass in the current fp. 924 * 925 * This is used by e.g. java.lang.Class, which wants to know about the 926 * class loader of the method that called it. 927 */ 928 ClassObject* dvmGetCaller2Class(const void* curFrame) 929 { 930 void* caller = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(curFrame)->prevFrame; 931 void* callerCaller; 932 933 /* at the top? */ 934 if (dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)caller) && 935 SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(caller)->prevFrame == NULL) 936 return NULL; 937 938 /* go one more */ 939 callerCaller = dvmGetCallerFP(caller); 940 if (callerCaller == NULL) 941 return NULL; 942 943 return SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(callerCaller)->method->clazz; 944 } 945 946 /* 947 * Get the caller‘s caller‘s caller‘s class. Pass in the current fp. 948 * 949 * This is used by e.g. java.lang.Class, which wants to know about the 950 * class loader of the method that called it. 951 */ 952 ClassObject* dvmGetCaller3Class(const void* curFrame) 953 { 954 void* caller = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(curFrame)->prevFrame; 955 int i; 956 957 /* at the top? */ 958 if (dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)caller) && 959 SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(caller)->prevFrame == NULL) 960 return NULL; 961 962 /* Walk up two frames if possible. */ 963 for (i = 0; i < 2; i++) { 964 caller = dvmGetCallerFP(caller); 965 if (caller == NULL) 966 return NULL; 967 } 968 969 return SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(caller)->method->clazz; 970 } 971 972 /* 973 * Fill a flat array of methods that comprise the current interpreter 974 * stack trace. Pass in the current frame ptr. Break frames are 975 * skipped, but reflection invocations are not. 976 * 977 * The current frame will be in element 0. 978 */ 979 void dvmFillStackTraceArray(const void* fp, const Method** array, size_t length) 980 { 981 assert(fp != NULL); 982 assert(array != NULL); 983 size_t i = 0; 984 while (fp != NULL) { 985 if (!dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)fp)) { 986 assert(i < length); 987 array[i++] = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(fp)->method; 988 } 989 fp = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(fp)->prevFrame; 990 } 991 } 992 993 /* 994 * Open up the reserved area and throw an exception. The reserved area 995 * should only be needed to create and initialize the exception itself. 996 * 997 * If we already opened it and we‘re continuing to overflow, abort the VM. 998 * 999 * We have to leave the "reserved" area open until the "catch" handler has 1000 * finished doing its processing. This is because the catch handler may 1001 * need to resolve classes, which requires calling into the class loader if 1002 * the classes aren‘t already in the "initiating loader" list. 1003 */ 1004 void dvmHandleStackOverflow(Thread* self, const Method* method) 1005 { 1006 /* 1007 * Can we make the reserved area available? 1008 */ 1009 if (self->stackOverflowed) { 1010 /* 1011 * Already did, nothing to do but bail. 1012 */ 1013 ALOGE("DalvikVM: double-overflow of stack in threadid=%d; aborting", 1014 self->threadId); 1015 dvmDumpThread(self, false); 1016 dvmAbort(); 1017 } 1018 1019 /* open it up to the full range */ 1020 ALOGI("threadid=%d: stack overflow on call to %s.%s:%s", 1021 self->threadId, 1022 method->clazz->descriptor, method->name, method->shorty); 1023 StackSaveArea* saveArea = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame); 1024 ALOGI(" method requires %d+%d+%d=%d bytes, fp is %p (%d left)", 1025 method->registersSize * 4, sizeof(StackSaveArea), method->outsSize * 4, 1026 (method->registersSize + method->outsSize) * 4 + sizeof(StackSaveArea), 1027 saveArea, (u1*) saveArea - self->interpStackEnd); 1028 ALOGI(" expanding stack end (%p to %p)", self->interpStackEnd, 1029 self->interpStackStart - self->interpStackSize); 1030 //dvmDumpThread(self, false); 1031 self->interpStackEnd = self->interpStackStart - self->interpStackSize; 1032 self->stackOverflowed = true; 1033 1034 /* 1035 * If we were trying to throw an exception when the stack overflowed, 1036 * we will blow up when doing the class lookup on StackOverflowError 1037 * because of the pending exception. So, we clear it and make it 1038 * the cause of the SOE. 1039 */ 1040 Object* excep = dvmGetException(self); 1041 if (excep != NULL) { 1042 ALOGW("Stack overflow while throwing exception"); 1043 dvmClearException(self); 1044 } 1045 dvmThrowChainedException(gDvm.exStackOverflowError, NULL, excep); 1046 } 1047 1048 /* 1049 * Reduce the available stack size. By this point we should have finished 1050 * our overflow processing. 1051 */ 1052 void dvmCleanupStackOverflow(Thread* self, const Object* exception) 1053 { 1054 const u1* newStackEnd; 1055 1056 assert(self->stackOverflowed); 1057 1058 if (exception->clazz != gDvm.exStackOverflowError) { 1059 /* exception caused during SOE, not the SOE itself */ 1060 return; 1061 } 1062 1063 newStackEnd = (self->interpStackStart - self->interpStackSize) 1064 + STACK_OVERFLOW_RESERVE; 1065 if ((u1*)self->interpSave.curFrame <= newStackEnd) { 1066 ALOGE("Can‘t shrink stack: curFrame is in reserved area (%p %p)", 1067 self->interpStackEnd, self->interpSave.curFrame); 1068 dvmDumpThread(self, false); 1069 dvmAbort(); 1070 } 1071 1072 self->interpStackEnd = newStackEnd; 1073 self->stackOverflowed = false; 1074 1075 ALOGI("Shrank stack (to %p, curFrame is %p)", self->interpStackEnd, 1076 self->interpSave.curFrame); 1077 } 1078 1079 1080 /* 1081 * Extract the object that is the target of a monitor-enter instruction 1082 * in the top stack frame of "thread". 1083 * 1084 * The other thread might be alive, so this has to work carefully. 1085 * 1086 * The thread list lock must be held. 1087 * 1088 * Returns "true" if we successfully recover the object. "*pOwner" will 1089 * be NULL if we can‘t determine the owner for some reason (e.g. race 1090 * condition on ownership transfer). 1091 */ 1092 static bool extractMonitorEnterObject(Thread* thread, Object** pLockObj, 1093 Thread** pOwner) 1094 { 1095 void* framePtr = thread->interpSave.curFrame; 1096 1097 if (framePtr == NULL || dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)framePtr)) 1098 return false; 1099 1100 const StackSaveArea* saveArea = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(framePtr); 1101 const Method* method = saveArea->method; 1102 const u2* currentPc = saveArea->xtra.currentPc; 1103 1104 /* check Method* */ 1105 if (!dvmLinearAllocContains(method, sizeof(Method))) { 1106 ALOGD("ExtrMon: method %p not valid", method); 1107 return false; 1108 } 1109 1110 /* check currentPc */ 1111 u4 insnsSize = dvmGetMethodInsnsSize(method); 1112 if (currentPc < method->insns || 1113 currentPc >= method->insns + insnsSize) 1114 { 1115 ALOGD("ExtrMon: insns %p not valid (%p - %p)", 1116 currentPc, method->insns, method->insns + insnsSize); 1117 return false; 1118 } 1119 1120 /* check the instruction */ 1121 if ((*currentPc & 0xff) != OP_MONITOR_ENTER) { 1122 ALOGD("ExtrMon: insn at %p is not monitor-enter (0x%02x)", 1123 currentPc, *currentPc & 0xff); 1124 return false; 1125 } 1126 1127 /* get and check the register index */ 1128 unsigned int reg = *currentPc >> 8; 1129 if (reg >= method->registersSize) { 1130 ALOGD("ExtrMon: invalid register %d (max %d)", 1131 reg, method->registersSize); 1132 return false; 1133 } 1134 1135 /* get and check the object in that register */ 1136 u4* fp = (u4*) framePtr; 1137 Object* obj = (Object*) fp[reg]; 1138 if (obj != NULL && !dvmIsHeapAddress(obj)) { 1139 ALOGD("ExtrMon: invalid object %p at %p[%d]", obj, fp, reg); 1140 return false; 1141 } 1142 *pLockObj = obj; 1143 1144 /* 1145 * Try to determine the object‘s lock holder; it‘s okay if this fails. 1146 * 1147 * We‘re assuming the thread list lock is already held by this thread. 1148 * If it‘s not, we may be living dangerously if we have to scan through 1149 * the thread list to find a match. (The VM will generally be in a 1150 * suspended state when executing here, so this is a minor concern 1151 * unless we‘re dumping while threads are running, in which case there‘s 1152 * a good chance of stuff blowing up anyway.) 1153 */ 1154 *pOwner = dvmGetObjectLockHolder(obj); 1155 1156 return true; 1157 } 1158 1159 static void printWaitMessage(const DebugOutputTarget* target, const char* detail, Object* obj, 1160 Thread* thread) 1161 { 1162 std::string msg(StringPrintf(" - waiting %s <%p> ", detail, obj)); 1163 1164 if (obj->clazz != gDvm.classJavaLangClass) { 1165 // I(16573) - waiting on <0xf5feda38> (a java.util.LinkedList) 1166 // I(16573) - waiting on <0xf5ed54f8> (a java.lang.Class<java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue>) 1167 msg += "(a " + dvmHumanReadableType(obj) + ")"; 1168 } 1169 1170 if (thread != NULL) { 1171 std::string threadName(dvmGetThreadName(thread)); 1172 StringAppendF(&msg, " held by tid=%d (%s)", thread->threadId, threadName.c_str()); 1173 } 1174 1175 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "%s\n", msg.c_str()); 1176 } 1177 1178 /* 1179 * Dump stack frames, starting from the specified frame and moving down. 1180 * 1181 * Each frame holds a pointer to the currently executing method, and the 1182 * saved program counter from the caller ("previous" frame). This means 1183 * we don‘t have the PC for the current method on the stack, which is 1184 * pretty reasonable since it‘s in the "PC register" for the VM. Because 1185 * exceptions need to show the correct line number we actually *do* have 1186 * an updated version in the fame‘s "xtra.currentPc", but it‘s unreliable. 1187 * 1188 * Note "framePtr" could be NULL in rare circumstances. 1189 */ 1190 static void dumpFrames(const DebugOutputTarget* target, void* framePtr, 1191 Thread* thread) 1192 { 1193 const StackSaveArea* saveArea; 1194 const Method* method; 1195 int checkCount = 0; 1196 const u2* currentPc = NULL; 1197 bool first = true; 1198 1199 /* 1200 * We call functions that require us to be holding the thread list lock. 1201 * It‘s probable that the caller has already done so, but it‘s not 1202 * guaranteed. If it‘s not locked, lock it now. 1203 */ 1204 bool needThreadUnlock = dvmTryLockThreadList(); 1205 1206 /* 1207 * The "currentPc" is updated whenever we execute an instruction that 1208 * might throw an exception. Show it here. 1209 */ 1210 if (framePtr != NULL && !dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)framePtr)) { 1211 saveArea = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(framePtr); 1212 1213 if (saveArea->xtra.currentPc != NULL) 1214 currentPc = saveArea->xtra.currentPc; 1215 } 1216 1217 while (framePtr != NULL) { 1218 saveArea = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(framePtr); 1219 method = saveArea->method; 1220 1221 if (dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)framePtr)) { 1222 //dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " (break frame)\n"); 1223 } else { 1224 int relPc; 1225 1226 if (currentPc != NULL) 1227 relPc = currentPc - saveArea->method->insns; 1228 else 1229 relPc = -1; 1230 1231 std::string methodName(dvmHumanReadableMethod(method, false)); 1232 if (dvmIsNativeMethod(method)) { 1233 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " at %s(Native Method)\n", 1234 methodName.c_str()); 1235 } else { 1236 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " at %s(%s:%s%d)\n", 1237 methodName.c_str(), dvmGetMethodSourceFile(method), 1238 (relPc >= 0 && first) ? "~" : "", 1239 relPc < 0 ? -1 : dvmLineNumFromPC(method, relPc)); 1240 } 1241 1242 if (first) { 1243 /* 1244 * Decorate WAIT and MONITOR threads with some detail on 1245 * the first frame. 1246 * 1247 * warning: wait status not stable, even in suspend 1248 */ 1249 if (thread->status == THREAD_WAIT || 1250 thread->status == THREAD_TIMED_WAIT) 1251 { 1252 Monitor* mon = thread->waitMonitor; 1253 Object* obj = dvmGetMonitorObject(mon); 1254 if (obj != NULL) { 1255 Thread* joinThread = NULL; 1256 if (obj->clazz == gDvm.classJavaLangVMThread) { 1257 joinThread = dvmGetThreadFromThreadObject(obj); 1258 } 1259 if (joinThread == NULL) { 1260 joinThread = dvmGetObjectLockHolder(obj); 1261 } 1262 printWaitMessage(target, "on", obj, joinThread); 1263 } 1264 } else if (thread->status == THREAD_MONITOR) { 1265 Object* obj; 1266 Thread* owner; 1267 if (extractMonitorEnterObject(thread, &obj, &owner)) { 1268 printWaitMessage(target, "to lock", obj, owner); 1269 } 1270 } 1271 } 1272 } 1273 1274 /* 1275 * Get saved PC for previous frame. There‘s no savedPc in a "break" 1276 * frame, because that represents native or interpreted code 1277 * invoked by the VM. The saved PC is sitting in the "PC register", 1278 * a local variable on the native stack. 1279 */ 1280 currentPc = saveArea->savedPc; 1281 1282 first = false; 1283 1284 if (saveArea->prevFrame != NULL && saveArea->prevFrame <= framePtr) { 1285 ALOGW("Warning: loop in stack trace at frame %d (%p -> %p)", 1286 checkCount, framePtr, saveArea->prevFrame); 1287 break; 1288 } 1289 framePtr = saveArea->prevFrame; 1290 1291 checkCount++; 1292 if (checkCount > 300) { 1293 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, 1294 " ***** printed %d frames, not showing any more\n", 1295 checkCount); 1296 break; 1297 } 1298 } 1299 1300 if (needThreadUnlock) { 1301 dvmUnlockThreadList(); 1302 } 1303 } 1304 1305 1306 /* 1307 * Dump the stack for the specified thread. 1308 */ 1309 void dvmDumpThreadStack(const DebugOutputTarget* target, Thread* thread) 1310 { 1311 dumpFrames(target, thread->interpSave.curFrame, thread); 1312 } 1313 1314 /* 1315 * Dump the stack for the specified thread, which is still running. 1316 * 1317 * This is very dangerous, because stack frames are being pushed on and 1318 * popped off, and if the thread exits we‘ll be looking at freed memory. 1319 * The plan here is to take a snapshot of the stack and then dump that 1320 * to try to minimize the chances of catching it mid-update. This should 1321 * work reasonably well on a single-CPU system. 1322 * 1323 * There is a small chance that calling here will crash the VM. 1324 */ 1325 void dvmDumpRunningThreadStack(const DebugOutputTarget* target, Thread* thread) 1326 { 1327 StackSaveArea* saveArea; 1328 const u1* origStack; 1329 u1* stackCopy = NULL; 1330 int origSize, fpOffset; 1331 void* fp; 1332 int depthLimit = 200; 1333 1334 if (thread == NULL || thread->interpSave.curFrame == NULL) { 1335 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, 1336 "DumpRunning: Thread at %p has no curFrame (threadid=%d)\n", 1337 thread, (thread != NULL) ? thread->threadId : 0); 1338 return; 1339 } 1340 1341 /* wait for a full quantum */ 1342 sched_yield(); 1343 1344 /* copy the info we need, then the stack itself */ 1345 origSize = thread->interpStackSize; 1346 origStack = (const u1*) thread->interpStackStart - origSize; 1347 stackCopy = (u1*) malloc(origSize); 1348 fpOffset = (u1*) thread->interpSave.curFrame - origStack; 1349 memcpy(stackCopy, origStack, origSize); 1350 1351 /* 1352 * Run through the stack and rewrite the "prev" pointers. 1353 */ 1354 //ALOGI("DR: fpOff=%d (from %p %p)",fpOffset, origStack, 1355 // thread->interpSave.curFrame); 1356 fp = stackCopy + fpOffset; 1357 while (true) { 1358 int prevOffset; 1359 1360 if (depthLimit-- < 0) { 1361 /* we‘re probably screwed */ 1362 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "DumpRunning: depth limit hit\n"); 1363 dvmAbort(); 1364 } 1365 saveArea = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(fp); 1366 if (saveArea->prevFrame == NULL) 1367 break; 1368 1369 prevOffset = (u1*) saveArea->prevFrame - origStack; 1370 if (prevOffset < 0 || prevOffset > origSize) { 1371 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, 1372 "DumpRunning: bad offset found: %d (from %p %p)\n", 1373 prevOffset, origStack, saveArea->prevFrame); 1374 saveArea->prevFrame = NULL; 1375 break; 1376 } 1377 1378 saveArea->prevFrame = (u4*)(stackCopy + prevOffset); 1379 fp = saveArea->prevFrame; 1380 } 1381 1382 /* 1383 * We still need to pass the Thread for some monitor wait stuff. 1384 */ 1385 dumpFrames(target, stackCopy + fpOffset, thread); 1386 free(stackCopy); 1387 } 1388 1389 /* 1390 * Dump the native stack for the specified thread. 1391 */ 1392 void dvmDumpNativeStack(const DebugOutputTarget* target, pid_t tid) 1393 { 1394 #ifdef HAVE_ANDROID_OS 1395 const size_t MAX_DEPTH = 32; 1396 backtrace_frame_t backtrace[MAX_DEPTH]; 1397 ssize_t frames = unwind_backtrace_thread(tid, backtrace, 0, MAX_DEPTH); 1398 if (frames > 0) { 1399 backtrace_symbol_t backtrace_symbols[MAX_DEPTH]; 1400 get_backtrace_symbols(backtrace, frames, backtrace_symbols); 1401 1402 for (size_t i = 0; i < size_t(frames); i++) { 1403 char line[MAX_BACKTRACE_LINE_LENGTH]; 1404 format_backtrace_line(i, &backtrace[i], &backtrace_symbols[i], 1405 line, MAX_BACKTRACE_LINE_LENGTH); 1406 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " %s\n", line); 1407 } 1408 1409 free_backtrace_symbols(backtrace_symbols, frames); 1410 } else { 1411 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " (native backtrace unavailable)\n"); 1412 } 1413 #endif 1414 }

1 //xref : /dalvik/vm/Jni.cpp 2 //http://androidxref.com/4.4.2_r2/xref/dalvik/vm/Jni.cpp 3 4 /* 5 * Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project 6 * 7 * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); 8 * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. 9 * You may obtain a copy of the License at 10 * 11 * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 12 * 13 * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software 14 * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, 15 * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. 16 * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and 17 * limitations under the License. 18 */ 19 20 /* 21 * Dalvik implementation of JNI interfaces. 22 */ 23 #include "Dalvik.h" 24 #include "JniInternal.h" 25 #include "Misc.h" 26 #include "ScopedPthreadMutexLock.h" 27 #include "UniquePtr.h" 28 29 #include <stdlib.h> 30 #include <stdarg.h> 31 #include <limits.h> 32 33 /* 34 Native methods and interaction with the GC 35 36 All JNI methods must start by changing their thread status to 37 THREAD_RUNNING, and finish by changing it back to THREAD_NATIVE before 38 returning to native code. The switch to "running" triggers a thread 39 suspension check. 40 41 With a rudimentary GC we should be able to skip the status change for 42 simple functions, e.g. IsSameObject, GetJavaVM, GetStringLength, maybe 43 even access to fields with primitive types. Our options are more limited 44 with a compacting GC. 45 46 For performance reasons we do as little error-checking as possible here. 47 For example, we don‘t check to make sure the correct type of Object is 48 passed in when setting a field, and we don‘t prevent you from storing 49 new values in a "final" field. Such things are best handled in the 50 "check" version. For actions that are common, dangerous, and must be 51 checked at runtime, such as array bounds checks, we do the tests here. 52 53 54 General notes on local/global reference tracking 55 56 JNI provides explicit control over natively-held references that the GC 57 needs to know about. These can be local, in which case they‘re released 58 when the native method returns into the VM, or global, which are held 59 until explicitly released. (There are also weak-global references, 60 which have the lifespan and visibility of global references, but the 61 object they refer to may be collected.) 62 63 The references can be created with explicit JNI NewLocalRef / NewGlobalRef 64 calls. The former is very unusual, the latter is reasonably common 65 (e.g. for caching references to class objects). 66 67 Local references are most often created as a side-effect of JNI functions. 68 For example, the AllocObject/NewObject functions must create local 69 references to the objects returned, because nothing else in the GC root 70 set has a reference to the new objects. 71 72 The most common mode of operation is for a method to create zero or 73 more local references and return. Explicit "local delete" operations 74 are expected to be exceedingly rare, except when walking through an 75 object array, and the Push/PopLocalFrame calls are expected to be used 76 infrequently. For efficient operation, we want to add new local refs 77 with a simple store/increment operation; to avoid infinite growth in 78 pathological situations, we need to reclaim the space used by deleted 79 entries. 80 81 If we just want to maintain a list for the GC root set, we can use an 82 expanding append-only array that compacts when objects are deleted. 83 In typical situations, e.g. running through an array of objects, we will 84 be deleting one of the most recently added entries, so we can minimize 85 the number of elements moved (or avoid having to move any). 86 87 If we want to conceal the pointer values from native code, which is 88 necessary to allow the GC to move JNI-referenced objects around, then we 89 have to use a more complicated indirection mechanism. 90 91 The spec says, "Local references are only valid in the thread in which 92 they are created. The native code must not pass local references from 93 one thread to another." 94 95 96 Pinned objects 97 98 For some large chunks of data, notably primitive arrays and String data, 99 JNI allows the VM to choose whether it wants to pin the array object or 100 make a copy. We currently pin the memory for better execution performance. 101 102 TODO: we‘re using simple root set references to pin primitive array data, 103 because they have the property we need (i.e. the pointer we return is 104 guaranteed valid until we explicitly release it). However, if we have a 105 compacting GC and don‘t want to pin all memory held by all global refs, 106 we need to treat these differently. 107 108 109 Global reference tracking 110 111 There should be a small "active" set centered around the most-recently 112 added items. 113 114 Because it‘s global, access to it has to be synchronized. Additions and 115 removals require grabbing a mutex. If the table serves as an indirection 116 mechanism (i.e. it‘s not just a list for the benefit of the garbage 117 collector), reference lookups may also require grabbing a mutex. 118 119 The JNI spec does not define any sort of limit, so the list must be able 120 to expand to a reasonable size. It may be useful to log significant 121 increases in usage to help identify resource leaks. 122 123 124 Weak-global reference tracking 125 126 [TBD] 127 128 129 Local reference tracking 130 131 Each Thread/JNIEnv points to an IndirectRefTable. 132 133 We implement Push/PopLocalFrame with actual stack frames. Before a JNI 134 frame gets popped, we set "nextEntry" to the "top" pointer of the current 135 frame, effectively releasing the references. 136 137 The GC will scan all references in the table. 138 139 */ 140 141 static void ReportJniError() { 142 dvmDumpThread(dvmThreadSelf(), false); 143 dvmAbort(); 144 } 145 146 #ifdef WITH_JNI_STACK_CHECK 147 # define COMPUTE_STACK_SUM(_self) computeStackSum(_self); 148 # define CHECK_STACK_SUM(_self) checkStackSum(_self); 149 150 /* 151 * Compute a CRC on the entire interpreted stack. 152 * 153 * Would be nice to compute it on "self" as well, but there are parts of 154 * the Thread that can be altered by other threads (e.g. prev/next pointers). 155 */ 156 static void computeStackSum(Thread* self) { 157 const u1* low = (const u1*)SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame); 158 u4 crc = dvmInitCrc32(); 159 self->stackCrc = 0; 160 crc = dvmComputeCrc32(crc, low, self->interpStackStart - low); 161 self->stackCrc = crc; 162 } 163 164 /* 165 * Compute a CRC on the entire interpreted stack, and compare it to what 166 * we previously computed. 167 * 168 * We can execute JNI directly from native code without calling in from 169 * interpreted code during VM initialization and immediately after JNI 170 * thread attachment. Another opportunity exists during JNI_OnLoad. Rather 171 * than catching these cases we just ignore them here, which is marginally 172 * less accurate but reduces the amount of code we have to touch with #ifdefs. 173 */ 174 static void checkStackSum(Thread* self) { 175 const u1* low = (const u1*)SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame); 176 u4 stackCrc = self->stackCrc; 177 self->stackCrc = 0; 178 u4 crc = dvmInitCrc32(); 179 crc = dvmComputeCrc32(crc, low, self->interpStackStart - low); 180 if (crc != stackCrc) { 181 const Method* meth = dvmGetCurrentJNIMethod(); 182 if (dvmComputeExactFrameDepth(self->interpSave.curFrame) == 1) { 183 ALOGD("JNI: bad stack CRC (0x%08x) -- okay during init", stackCrc); 184 } else if (strcmp(meth->name, "nativeLoad") == 0 && 185 (strcmp(meth->clazz->descriptor, "Ljava/lang/Runtime;") == 0)) { 186 ALOGD("JNI: bad stack CRC (0x%08x) -- okay during JNI_OnLoad", stackCrc); 187 } else { 188 ALOGW("JNI: bad stack CRC (%08x vs %08x)", crc, stackCrc); 189 ReportJniError(); 190 } 191 } 192 self->stackCrc = (u4) -1; /* make logic errors more noticeable */ 193 } 194 195 #else 196 # define COMPUTE_STACK_SUM(_self) ((void)0) 197 # define CHECK_STACK_SUM(_self) ((void)0) 198 #endif 199 200 201 /* 202 * =========================================================================== 203 * Utility functions 204 * =========================================================================== 205 */ 206 207 /* 208 * Entry/exit processing for all JNI calls. 209 * 210 * We skip the (curiously expensive) thread-local storage lookup on our Thread*. 211 * If the caller has passed the wrong JNIEnv in, we‘re going to be accessing unsynchronized 212 * structures from more than one thread, and things are going to fail 213 * in bizarre ways. This is only sensible if the native code has been 214 * fully exercised with CheckJNI enabled. 215 */ 216 class ScopedJniThreadState { 217 public: 218 explicit ScopedJniThreadState(JNIEnv* env) { 219 mSelf = ((JNIEnvExt*) env)->self; 220 221 if (UNLIKELY(gDvmJni.workAroundAppJniBugs)) { 222 // When emulating direct pointers with indirect references, it‘s critical 223 // that we use the correct per-thread indirect reference table. 224 Thread* self = gDvmJni.workAroundAppJniBugs ? dvmThreadSelf() : mSelf; 225 if (self != mSelf) { 226 ALOGE("JNI ERROR: env->self != thread-self (%p vs. %p); auto-correcting", mSelf, self); 227 mSelf = self; 228 } 229 } 230 231 CHECK_STACK_SUM(mSelf); 232 dvmChangeStatus(mSelf, THREAD_RUNNING); 233 } 234 235 ~ScopedJniThreadState() { 236 dvmChangeStatus(mSelf, THREAD_NATIVE); 237 COMPUTE_STACK_SUM(mSelf); 238 } 239 240 inline Thread* self() { 241 return mSelf; 242 } 243 244 private: 245 Thread* mSelf; 246 247 // Disallow copy and assignment. 248 ScopedJniThreadState(const ScopedJniThreadState&); 249 void operator=(const ScopedJniThreadState&); 250 }; 251 252 #define kGlobalRefsTableInitialSize 512 253 #define kGlobalRefsTableMaxSize 51200 /* arbitrary, must be < 64K */ 254 255 #define kWeakGlobalRefsTableInitialSize 16 256 257 #define kPinTableInitialSize 16 258 #define kPinTableMaxSize 1024 259 #define kPinComplainThreshold 10 260 261 bool dvmJniStartup() { 262 if (!gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.init(kGlobalRefsTableInitialSize, 263 kGlobalRefsTableMaxSize, 264 kIndirectKindGlobal)) { 265 return false; 266 } 267 if (!gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable.init(kWeakGlobalRefsTableInitialSize, 268 kGlobalRefsTableMaxSize, 269 kIndirectKindWeakGlobal)) { 270 return false; 271 } 272 273 dvmInitMutex(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefLock); 274 dvmInitMutex(&gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefLock); 275 276 if (!dvmInitReferenceTable(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable, kPinTableInitialSize, kPinTableMaxSize)) { 277 return false; 278 } 279 280 dvmInitMutex(&gDvm.jniPinRefLock); 281 282 return true; 283 } 284 285 void dvmJniShutdown() { 286 gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.destroy(); 287 gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable.destroy(); 288 dvmClearReferenceTable(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable); 289 } 290 291 bool dvmIsBadJniVersion(int version) { 292 // We don‘t support JNI_VERSION_1_1. These are the only other valid versions. 293 return version != JNI_VERSION_1_2 && version != JNI_VERSION_1_4 && version != JNI_VERSION_1_6; 294 } 295 296 /* 297 * Find the JNIEnv associated with the current thread. 298 * 299 * Currently stored in the Thread struct. Could also just drop this into 300 * thread-local storage. 301 */ 302 JNIEnvExt* dvmGetJNIEnvForThread() { 303 Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf(); 304 if (self == NULL) { 305 return NULL; 306 } 307 return (JNIEnvExt*) dvmGetThreadJNIEnv(self); 308 } 309 310 /* 311 * Convert an indirect reference to an Object reference. The indirect 312 * reference may be local, global, or weak-global. 313 * 314 * If "jobj" is NULL, or is a weak global reference whose reference has 315 * been cleared, this returns NULL. If jobj is an invalid indirect 316 * reference, kInvalidIndirectRefObject is returned. 317 * 318 * Note "env" may be NULL when decoding global references. 319 */ 320 Object* dvmDecodeIndirectRef(Thread* self, jobject jobj) { 321 if (jobj == NULL) { 322 return NULL; 323 } 324 325 switch (indirectRefKind(jobj)) { 326 case kIndirectKindLocal: 327 { 328 Object* result = self->jniLocalRefTable.get(jobj); 329 if (UNLIKELY(result == NULL)) { 330 ALOGE("JNI ERROR (app bug): use of deleted local reference (%p)", jobj); 331 ReportJniError(); 332 } 333 return result; 334 } 335 case kIndirectKindGlobal: 336 { 337 // TODO: find a way to avoid the mutex activity here 338 IndirectRefTable* pRefTable = &gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable; 339 ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefLock); 340 Object* result = pRefTable->get(jobj); 341 if (UNLIKELY(result == NULL)) { 342 ALOGE("JNI ERROR (app bug): use of deleted global reference (%p)", jobj); 343 ReportJniError(); 344 } 345 return result; 346 } 347 case kIndirectKindWeakGlobal: 348 { 349 // TODO: find a way to avoid the mutex activity here 350 IndirectRefTable* pRefTable = &gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable; 351 ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefLock); 352 Object* result = pRefTable->get(jobj); 353 if (result == kClearedJniWeakGlobal) { 354 result = NULL; 355 } else if (UNLIKELY(result == NULL)) { 356 ALOGE("JNI ERROR (app bug): use of deleted weak global reference (%p)", jobj); 357 ReportJniError(); 358 } 359 return result; 360 } 361 case kIndirectKindInvalid: 362 default: 363 if (UNLIKELY(gDvmJni.workAroundAppJniBugs)) { 364 // Assume an invalid local reference is actually a direct pointer. 365 return reinterpret_cast<Object*>(jobj); 366 } 367 ALOGW("Invalid indirect reference %p in decodeIndirectRef", jobj); 368 ReportJniError(); 369 return kInvalidIndirectRefObject; 370 } 371 } 372 373 static void AddLocalReferenceFailure(IndirectRefTable* pRefTable) { 374 pRefTable->dump("JNI local"); 375 ALOGE("Failed adding to JNI local ref table (has %zd entries)", pRefTable->capacity()); 376 ReportJniError(); // spec says call FatalError; this is equivalent 377 } 378 379 /* 380 * Add a local reference for an object to the current stack frame. When 381 * the native function returns, the reference will be discarded. 382 * 383 * We need to allow the same reference to be added multiple times. 384 * 385 * This will be called on otherwise unreferenced objects. We cannot do 386 * GC allocations here, and it‘s best if we don‘t grab a mutex. 387 */ 388 static inline jobject addLocalReference(Thread* self, Object* obj) { 389 if (obj == NULL) { 390 return NULL; 391 } 392 393 IndirectRefTable* pRefTable = &self->jniLocalRefTable; 394 void* curFrame = self->interpSave.curFrame; 395 u4 cookie = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(curFrame)->xtra.localRefCookie; 396 jobject jobj = (jobject) pRefTable->add(cookie, obj); 397 if (UNLIKELY(jobj == NULL)) { 398 AddLocalReferenceFailure(pRefTable); 399 } 400 401 if (UNLIKELY(gDvmJni.workAroundAppJniBugs)) { 402 // Hand out direct pointers to support broken old apps. 403 return reinterpret_cast<jobject>(obj); 404 } 405 return jobj; 406 } 407 408 /* 409 * Ensure that at least "capacity" references can be held in the local 410 * refs table of the current thread. 411 */ 412 static bool ensureLocalCapacity(Thread* self, int capacity) { 413 int numEntries = self->jniLocalRefTable.capacity(); 414 // TODO: this isn‘t quite right, since "numEntries" includes holes 415 return ((kJniLocalRefMax - numEntries) >= capacity); 416 } 417 418 /* 419 * Explicitly delete a reference from the local list. 420 */ 421 static void deleteLocalReference(Thread* self, jobject jobj) { 422 if (jobj == NULL) { 423 return; 424 } 425 426 IndirectRefTable* pRefTable = &self->jniLocalRefTable; 427 void* curFrame = self->interpSave.curFrame; 428 u4 cookie = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(curFrame)->xtra.localRefCookie; 429 if (!pRefTable->remove(cookie, jobj)) { 430 /* 431 * Attempting to delete a local reference that is not in the 432 * topmost local reference frame is a no-op. DeleteLocalRef returns 433 * void and doesn‘t throw any exceptions, but we should probably 434 * complain about it so the user will notice that things aren‘t 435 * going quite the way they expect. 436 */ 437 ALOGW("JNI WARNING: DeleteLocalRef(%p) failed to find entry", jobj); 438 } 439 } 440 441 /* 442 * Add a global reference for an object. 443 * 444 * We may add the same object more than once. Add/remove calls are paired, 445 * so it needs to appear on the list multiple times. 446 */ 447 static jobject addGlobalReference(Object* obj) { 448 if (obj == NULL) { 449 return NULL; 450 } 451 452 //ALOGI("adding obj=%p", obj); 453 //dvmDumpThread(dvmThreadSelf(), false); 454 455 if (false && dvmIsClassObject((Object*)obj)) { 456 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) obj; 457 ALOGI("-------"); 458 ALOGI("Adding global ref on class %s", clazz->descriptor); 459 dvmDumpThread(dvmThreadSelf(), false); 460 } 461 if (false && ((Object*)obj)->clazz == gDvm.classJavaLangString) { 462 StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) obj; 463 char* str = dvmCreateCstrFromString(strObj); 464 if (strcmp(str, "sync-response") == 0) { 465 ALOGI("-------"); 466 ALOGI("Adding global ref on string ‘%s‘", str); 467 dvmDumpThread(dvmThreadSelf(), false); 468 //dvmAbort(); 469 } 470 free(str); 471 } 472 if (false && ((Object*)obj)->clazz == gDvm.classArrayByte) { 473 ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) obj; 474 if (arrayObj->length == 8192 /*&& 475 dvmReferenceTableEntries(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable) > 400*/) 476 { 477 ALOGI("Adding global ref on byte array %p (len=%d)", 478 arrayObj, arrayObj->length); 479 dvmDumpThread(dvmThreadSelf(), false); 480 } 481 } 482 483 ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefLock); 484 485 /* 486 * Throwing an exception on failure is problematic, because JNI code 487 * may not be expecting an exception, and things sort of cascade. We 488 * want to have a hard limit to catch leaks during debugging, but this 489 * otherwise needs to expand until memory is consumed. As a practical 490 * matter, if we have many thousands of global references, chances are 491 * we‘re either leaking global ref table entries or we‘re going to 492 * run out of space in the GC heap. 493 */ 494 jobject jobj = (jobject) gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.add(IRT_FIRST_SEGMENT, obj); 495 if (jobj == NULL) { 496 gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.dump("JNI global"); 497 ALOGE("Failed adding to JNI global ref table (%zd entries)", 498 gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.capacity()); 499 ReportJniError(); 500 } 501 502 LOGVV("GREF add %p (%s.%s)", obj, 503 dvmGetCurrentJNIMethod()->clazz->descriptor, 504 dvmGetCurrentJNIMethod()->name); 505 506 return jobj; 507 } 508 509 static jobject addWeakGlobalReference(Object* obj) { 510 if (obj == NULL) { 511 return NULL; 512 } 513 514 ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefLock); 515 IndirectRefTable *table = &gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable; 516 jobject jobj = (jobject) table->add(IRT_FIRST_SEGMENT, obj); 517 if (jobj == NULL) { 518 gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable.dump("JNI weak global"); 519 ALOGE("Failed adding to JNI weak global ref table (%zd entries)", table->capacity()); 520 ReportJniError(); 521 } 522 return jobj; 523 } 524 525 static void deleteWeakGlobalReference(jobject jobj) { 526 if (jobj == NULL) { 527 return; 528 } 529 530 ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefLock); 531 IndirectRefTable *table = &gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable; 532 if (!table->remove(IRT_FIRST_SEGMENT, jobj)) { 533 ALOGW("JNI: DeleteWeakGlobalRef(%p) failed to find entry", jobj); 534 } 535 } 536 537 /* 538 * Remove a global reference. In most cases it‘s the entry most recently 539 * added, which makes this pretty quick. 540 * 541 * Thought: if it‘s not the most recent entry, just null it out. When we 542 * fill up, do a compaction pass before we expand the list. 543 */ 544 static void deleteGlobalReference(jobject jobj) { 545 if (jobj == NULL) { 546 return; 547 } 548 549 ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefLock); 550 if (!gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.remove(IRT_FIRST_SEGMENT, jobj)) { 551 ALOGW("JNI: DeleteGlobalRef(%p) failed to find entry", jobj); 552 return; 553 } 554 } 555 556 /* 557 * Objects don‘t currently move, so we just need to create a reference 558 * that will ensure the array object isn‘t collected. 559 * 560 * We use a separate reference table, which is part of the GC root set. 561 */ 562 static void pinPrimitiveArray(ArrayObject* arrayObj) { 563 if (arrayObj == NULL) { 564 return; 565 } 566 567 ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniPinRefLock); 568 569 if (!dvmAddToReferenceTable(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable, (Object*)arrayObj)) { 570 dvmDumpReferenceTable(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable, "JNI pinned array"); 571 ALOGE("Failed adding to JNI pinned array ref table (%d entries)", 572 (int) dvmReferenceTableEntries(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable)); 573 ReportJniError(); 574 } 575 576 /* 577 * The total number of pinned primitive arrays should be pretty small. 578 * A single array should not be pinned more than once or twice; any 579 * more than that is a strong indicator that a Release function is 580 * not being called. 581 */ 582 int count = 0; 583 Object** ppObj = gDvm.jniPinRefTable.table; 584 while (ppObj < gDvm.jniPinRefTable.nextEntry) { 585 if (*ppObj++ == (Object*) arrayObj) { 586 count++; 587 } 588 } 589 590 if (count > kPinComplainThreshold) { 591 ALOGW("JNI: pin count on array %p (%s) is now %d", 592 arrayObj, arrayObj->clazz->descriptor, count); 593 /* keep going */ 594 } 595 } 596 597 /* 598 * Un-pin the array object. If an object was pinned twice, it must be 599 * unpinned twice before it‘s free to move. 600 */ 601 static void unpinPrimitiveArray(ArrayObject* arrayObj) { 602 if (arrayObj == NULL) { 603 return; 604 } 605 606 ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniPinRefLock); 607 if (!dvmRemoveFromReferenceTable(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable, 608 gDvm.jniPinRefTable.table, (Object*) arrayObj)) 609 { 610 ALOGW("JNI: unpinPrimitiveArray(%p) failed to find entry (valid=%d)", 611 arrayObj, dvmIsHeapAddress((Object*) arrayObj)); 612 return; 613 } 614 } 615 616 /* 617 * Dump the contents of the JNI reference tables to the log file. 618 * 619 * We only dump the local refs associated with the current thread. 620 */ 621 void dvmDumpJniReferenceTables() { 622 Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf(); 623 self->jniLocalRefTable.dump("JNI local"); 624 gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.dump("JNI global"); 625 dvmDumpReferenceTable(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable, "JNI pinned array"); 626 } 627 628 void dvmDumpJniStats(DebugOutputTarget* target) { 629 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "JNI: CheckJNI is %s", gDvmJni.useCheckJni ? "on" : "off"); 630 if (gDvmJni.forceCopy) { 631 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " (with forcecopy)"); 632 } 633 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "; workarounds are %s", gDvmJni.workAroundAppJniBugs ? "on" : "off"); 634 635 dvmLockMutex(&gDvm.jniPinRefLock); 636 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "; pins=%d", dvmReferenceTableEntries(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable)); 637 dvmUnlockMutex(&gDvm.jniPinRefLock); 638 639 dvmLockMutex(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefLock); 640 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "; globals=%d", gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.capacity()); 641 dvmUnlockMutex(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefLock); 642 643 dvmLockMutex(&gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefLock); 644 size_t weaks = gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable.capacity(); 645 if (weaks > 0) { 646 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " (plus %d weak)", weaks); 647 } 648 dvmUnlockMutex(&gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefLock); 649 650 dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "\n\n"); 651 } 652 653 /* 654 * Verify that a reference passed in from native code is one that the 655 * code is allowed to have. 656 * 657 * It‘s okay for native code to pass us a reference that: 658 * - was passed in as an argument when invoked by native code (and hence 659 * is in the JNI local refs table) 660 * - was returned to it from JNI (and is now in the local refs table) 661 * - is present in the JNI global refs table 662 * 663 * Used by -Xcheck:jni and GetObjectRefType. 664 */ 665 jobjectRefType dvmGetJNIRefType(Thread* self, jobject jobj) { 666 /* 667 * IndirectRefKind is currently defined as an exact match of 668 * jobjectRefType, so this is easy. We have to decode it to determine 669 * if it‘s a valid reference and not merely valid-looking. 670 */ 671 assert(jobj != NULL); 672 673 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(self, jobj); 674 if (obj == reinterpret_cast<Object*>(jobj) && gDvmJni.workAroundAppJniBugs) { 675 // If we‘re handing out direct pointers, check whether ‘jobj‘ is a direct reference 676 // to a local reference. 677 return self->jniLocalRefTable.contains(obj) ? JNILocalRefType : JNIInvalidRefType; 678 } else if (obj == kInvalidIndirectRefObject) { 679 return JNIInvalidRefType; 680 } else { 681 return (jobjectRefType) indirectRefKind(jobj); 682 } 683 } 684 685 static void dumpMethods(Method* methods, size_t methodCount, const char* name) { 686 size_t i; 687 for (i = 0; i < methodCount; ++i) { 688 Method* method = &methods[i]; 689 if (strcmp(name, method->name) == 0) { 690 char* desc = dexProtoCopyMethodDescriptor(&method->prototype); 691 ALOGE("Candidate: %s.%s:%s", method->clazz->descriptor, name, desc); 692 free(desc); 693 } 694 } 695 } 696 697 static void dumpCandidateMethods(ClassObject* clazz, const char* methodName, const char* signature) { 698 ALOGE("ERROR: couldn‘t find native method"); 699 ALOGE("Requested: %s.%s:%s", clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature); 700 dumpMethods(clazz->virtualMethods, clazz->virtualMethodCount, methodName); 701 dumpMethods(clazz->directMethods, clazz->directMethodCount, methodName); 702 } 703 704 static void throwNoSuchMethodError(ClassObject* c, const char* name, const char* sig, const char* kind) { 705 std::string msg(StringPrintf("no %s method \"%s.%s%s\"", kind, c->descriptor, name, sig)); 706 dvmThrowNoSuchMethodError(msg.c_str()); 707 } 708 709 /* 710 * Register a method that uses JNI calling conventions. 711 */ 712 static bool dvmRegisterJNIMethod(ClassObject* clazz, const char* methodName, 713 const char* signature, void* fnPtr) 714 { 715 if (fnPtr == NULL) { 716 return false; 717 } 718 719 // If a signature starts with a ‘!‘, we take that as a sign that the native code doesn‘t 720 // need the extra JNI arguments (the JNIEnv* and the jclass). 721 bool fastJni = false; 722 if (*signature == ‘!‘) { 723 fastJni = true; 724 ++signature; 725 ALOGV("fast JNI method %s.%s:%s detected", clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature); 726 } 727 728 Method* method = dvmFindDirectMethodByDescriptor(clazz, methodName, signature); 729 if (method == NULL) { 730 method = dvmFindVirtualMethodByDescriptor(clazz, methodName, signature); 731 } 732 if (method == NULL) { 733 dumpCandidateMethods(clazz, methodName, signature); 734 throwNoSuchMethodError(clazz, methodName, signature, "static or non-static"); 735 return false; 736 } 737 738 if (!dvmIsNativeMethod(method)) { 739 ALOGW("Unable to register: not native: %s.%s:%s", clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature); 740 throwNoSuchMethodError(clazz, methodName, signature, "native"); 741 return false; 742 } 743 744 if (fastJni) { 745 // In this case, we have extra constraints to check... 746 if (dvmIsSynchronizedMethod(method)) { 747 // Synchronization is usually provided by the JNI bridge, 748 // but we won‘t have one. 749 ALOGE("fast JNI method %s.%s:%s cannot be synchronized", 750 clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature); 751 return false; 752 } 753 if (!dvmIsStaticMethod(method)) { 754 // There‘s no real reason for this constraint, but since we won‘t 755 // be supplying a JNIEnv* or a jobject ‘this‘, you‘re effectively 756 // static anyway, so it seems clearer to say so. 757 ALOGE("fast JNI method %s.%s:%s cannot be non-static", 758 clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature); 759 return false; 760 } 761 } 762 763 if (method->nativeFunc != dvmResolveNativeMethod) { 764 /* this is allowed, but unusual */ 765 ALOGV("Note: %s.%s:%s was already registered", clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature); 766 } 767 768 method->fastJni = fastJni; 769 dvmUseJNIBridge(method, fnPtr); 770 771 ALOGV("JNI-registered %s.%s:%s", clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature); 772 return true; 773 } 774 775 static const char* builtInPrefixes[] = { 776 "Landroid/", 777 "Lcom/android/", 778 "Lcom/google/android/", 779 "Ldalvik/", 780 "Ljava/", 781 "Ljavax/", 782 "Llibcore/", 783 "Lorg/apache/harmony/", 784 }; 785 786 static bool shouldTrace(Method* method) { 787 const char* className = method->clazz->descriptor; 788 // Return true if the -Xjnitrace setting implies we should trace ‘method‘. 789 if (gDvm.jniTrace && strstr(className, gDvm.jniTrace)) { 790 return true; 791 } 792 // Return true if we‘re trying to log all third-party JNI activity and ‘method‘ doesn‘t look 793 // like part of Android. 794 if (gDvmJni.logThirdPartyJni) { 795 for (size_t i = 0; i < NELEM(builtInPrefixes); ++i) { 796 if (strstr(className, builtInPrefixes[i]) == className) { 797 return false; 798 } 799 } 800 return true; 801 } 802 return false; 803 } 804 805 /* 806 * Point "method->nativeFunc" at the JNI bridge, and overload "method->insns" 807 * to point at the actual function. 808 */ 809 void dvmUseJNIBridge(Method* method, void* func) { 810 method->shouldTrace = shouldTrace(method); 811 812 // Does the method take any reference arguments? 813 method->noRef = true; 814 const char* cp = method->shorty; 815 while (*++cp != ‘\0‘) { // Pre-increment to skip return type. 816 if (*cp == ‘L‘) { 817 method->noRef = false; 818 break; 819 } 820 } 821 822 DalvikBridgeFunc bridge = gDvmJni.useCheckJni ? dvmCheckCallJNIMethod : dvmCallJNIMethod; 823 dvmSetNativeFunc(method, bridge, (const u2*) func); 824 } 825 826 // TODO: rewrite this to share code with CheckJNI‘s tracing... 827 static void appendValue(char type, const JValue value, char* buf, size_t n, bool appendComma) 828 { 829 size_t len = strlen(buf); 830 if (len >= n - 32) { // 32 should be longer than anything we could append. 831 buf[len - 1] = ‘.‘; 832 buf[len - 2] = ‘.‘; 833 buf[len - 3] = ‘.‘; 834 return; 835 } 836 char* p = buf + len; 837 switch (type) { 838 case ‘B‘: 839 if (value.b >= 0 && value.b < 10) { 840 sprintf(p, "%d", value.b); 841 } else { 842 sprintf(p, "%#x (%d)", value.b, value.b); 843 } 844 break; 845 case ‘C‘: 846 if (value.c < 0x7f && value.c >= ‘ ‘) { 847 sprintf(p, "U+%x (‘%c‘)", value.c, value.c); 848 } else { 849 sprintf(p, "U+%x", value.c); 850 } 851 break; 852 case ‘D‘: 853 sprintf(p, "%g", value.d); 854 break; 855 case ‘F‘: 856 sprintf(p, "%g", value.f); 857 break; 858 case ‘I‘: 859 sprintf(p, "%d", value.i); 860 break; 861 case ‘L‘: 862 sprintf(p, "%#x", value.i); 863 break; 864 case ‘J‘: 865 sprintf(p, "%lld", value.j); 866 break; 867 case ‘S‘: 868 sprintf(p, "%d", value.s); 869 break; 870 case ‘V‘: 871 strcpy(p, "void"); 872 break; 873 case ‘Z‘: 874 strcpy(p, value.z ? "true" : "false"); 875 break; 876 default: 877 sprintf(p, "unknown type ‘%c‘", type); 878 break; 879 } 880 881 if (appendComma) { 882 strcat(p, ", "); 883 } 884 } 885 886 static void logNativeMethodEntry(const Method* method, const u4* args) 887 { 888 char thisString[32] = { 0 }; 889 const u4* sp = args; 890 if (!dvmIsStaticMethod(method)) { 891 sprintf(thisString, "this=0x%08x ", *sp++); 892 } 893 894 char argsString[128]= { 0 }; 895 const char* desc = &method->shorty[1]; 896 while (*desc != ‘\0‘) { 897 char argType = *desc++; 898 JValue value; 899 if (argType == ‘D‘ || argType == ‘J‘) { 900 value.j = dvmGetArgLong(sp, 0); 901 sp += 2; 902 } else { 903 value.i = *sp++; 904 } 905 appendValue(argType, value, argsString, sizeof(argsString), 906 *desc != ‘\0‘); 907 } 908 909 std::string className(dvmHumanReadableDescriptor(method->clazz->descriptor)); 910 char* signature = dexProtoCopyMethodDescriptor(&method->prototype); 911 ALOGI("-> %s %s%s %s(%s)", className.c_str(), method->name, signature, thisString, argsString); 912 free(signature); 913 } 914 915 static void logNativeMethodExit(const Method* method, Thread* self, const JValue returnValue) 916 { 917 std::string className(dvmHumanReadableDescriptor(method->clazz->descriptor)); 918 char* signature = dexProtoCopyMethodDescriptor(&method->prototype); 919 if (dvmCheckException(self)) { 920 Object* exception = dvmGetException(self); 921 std::string exceptionClassName(dvmHumanReadableDescriptor(exception->clazz->descriptor)); 922 ALOGI("<- %s %s%s threw %s", className.c_str(), 923 method->name, signature, exceptionClassName.c_str()); 924 } else { 925 char returnValueString[128] = { 0 }; 926 char returnType = method->shorty[0]; 927 appendValue(returnType, returnValue, returnValueString, sizeof(returnValueString), false); 928 ALOGI("<- %s %s%s returned %s", className.c_str(), 929 method->name, signature, returnValueString); 930 } 931 free(signature); 932 } 933 934 /* 935 * Get the method currently being executed by examining the interp stack. 936 */ 937 const Method* dvmGetCurrentJNIMethod() { 938 assert(dvmThreadSelf() != NULL); 939 940 void* fp = dvmThreadSelf()->interpSave.curFrame; 941 const Method* meth = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(fp)->method; 942 943 assert(meth != NULL); 944 assert(dvmIsNativeMethod(meth)); 945 return meth; 946 } 947 948 /* 949 * Track a JNI MonitorEnter in the current thread. 950 * 951 * The goal is to be able to "implicitly" release all JNI-held monitors 952 * when the thread detaches. 953 * 954 * Monitors may be entered multiple times, so we add a new entry for each 955 * enter call. It would be more efficient to keep a counter. At present 956 * there‘s no real motivation to improve this however. 957 */ 958 static void trackMonitorEnter(Thread* self, Object* obj) { 959 static const int kInitialSize = 16; 960 ReferenceTable* refTable = &self->jniMonitorRefTable; 961 962 /* init table on first use */ 963 if (refTable->table == NULL) { 964 assert(refTable->maxEntries == 0); 965 966 if (!dvmInitReferenceTable(refTable, kInitialSize, INT_MAX)) { 967 ALOGE("Unable to initialize monitor tracking table"); 968 ReportJniError(); 969 } 970 } 971 972 if (!dvmAddToReferenceTable(refTable, obj)) { 973 /* ran out of memory? could throw exception instead */ 974 ALOGE("Unable to add entry to monitor tracking table"); 975 ReportJniError(); 976 } else { 977 LOGVV("--- added monitor %p", obj); 978 } 979 } 980 981 /* 982 * Track a JNI MonitorExit in the current thread. 983 */ 984 static void trackMonitorExit(Thread* self, Object* obj) { 985 ReferenceTable* pRefTable = &self->jniMonitorRefTable; 986 987 if (!dvmRemoveFromReferenceTable(pRefTable, pRefTable->table, obj)) { 988 ALOGE("JNI monitor %p not found in tracking list", obj); 989 /* keep going? */ 990 } else { 991 LOGVV("--- removed monitor %p", obj); 992 } 993 } 994 995 /* 996 * Release all monitors held by the jniMonitorRefTable list. 997 */ 998 void dvmReleaseJniMonitors(Thread* self) { 999 ReferenceTable* pRefTable = &self->jniMonitorRefTable; 1000 Object** top = pRefTable->table; 1001 1002 if (top == NULL) { 1003 return; 1004 } 1005 Object** ptr = pRefTable->nextEntry; 1006 while (--ptr >= top) { 1007 if (!dvmUnlockObject(self, *ptr)) { 1008 ALOGW("Unable to unlock monitor %p at thread detach", *ptr); 1009 } else { 1010 LOGVV("--- detach-releasing monitor %p", *ptr); 1011 } 1012 } 1013 1014 /* zap it */ 1015 pRefTable->nextEntry = pRefTable->table; 1016 } 1017 1018 /* 1019 * Determine if the specified class can be instantiated from JNI. This 1020 * is used by AllocObject / NewObject, which are documented as throwing 1021 * an exception for abstract and interface classes, and not accepting 1022 * array classes. We also want to reject attempts to create new Class 1023 * objects, since only DefineClass should do that. 1024 */ 1025 static bool canAllocClass(ClassObject* clazz) { 1026 if (dvmIsAbstractClass(clazz) || dvmIsInterfaceClass(clazz)) { 1027 /* JNI spec defines what this throws */ 1028 dvmThrowInstantiationException(clazz, "abstract class or interface"); 1029 return false; 1030 } else if (dvmIsArrayClass(clazz) || dvmIsTheClassClass(clazz)) { 1031 /* spec says "must not" for arrays, ignores Class */ 1032 dvmThrowInstantiationException(clazz, "wrong JNI function"); 1033 return false; 1034 } 1035 return true; 1036 } 1037 1038 1039 /* 1040 * =========================================================================== 1041 * JNI call bridge 1042 * =========================================================================== 1043 */ 1044 1045 /* 1046 * The functions here form a bridge between interpreted code and JNI native 1047 * functions. The basic task is to convert an array of primitives and 1048 * references into C-style function arguments. This is architecture-specific 1049 * and usually requires help from assembly code. 1050 * 1051 * The bridge takes four arguments: the array of parameters, a place to 1052 * store the function result (if any), the method to call, and a pointer 1053 * to the current thread. 1054 * 1055 * These functions aren‘t called directly from elsewhere in the VM. 1056 * A pointer in the Method struct points to one of these, and when a native 1057 * method is invoked the interpreter jumps to it. 1058 * 1059 * (The "internal native" methods are invoked the same way, but instead 1060 * of calling through a bridge, the target method is called directly.) 1061 * 1062 * The "args" array should not be modified, but we do so anyway for 1063 * performance reasons. We know that it points to the "outs" area on 1064 * the current method‘s interpreted stack. This area is ignored by the 1065 * precise GC, because there is no register map for a native method (for 1066 * an interpreted method the args would be listed in the argument set). 1067 * We know all of the values exist elsewhere on the interpreted stack, 1068 * because the method call setup copies them right before making the call, 1069 * so we don‘t have to worry about concealing stuff from the GC. 1070 * 1071 * If we don‘t want to modify "args", we either have to create a local 1072 * copy and modify it before calling dvmPlatformInvoke, or we have to do 1073 * the local reference replacement within dvmPlatformInvoke. The latter 1074 * has some performance advantages, though if we can inline the local 1075 * reference adds we may win when there‘s a lot of reference args (unless 1076 * we want to code up some local ref table manipulation in assembly. 1077 */ 1078 1079 /* 1080 * If necessary, convert the value in pResult from a local/global reference 1081 * to an object pointer. 1082 * 1083 * If the returned reference is invalid, kInvalidIndirectRefObject will 1084 * be returned in pResult. 1085 */ 1086 static inline void convertReferenceResult(JNIEnv* env, JValue* pResult, 1087 const Method* method, Thread* self) 1088 { 1089 if (method->shorty[0] == ‘L‘ && !dvmCheckException(self) && pResult->l != NULL) { 1090 pResult->l = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(self, (jobject) pResult->l); 1091 } 1092 } 1093 1094 /* 1095 * General form, handles all cases. 1096 */ 1097 void dvmCallJNIMethod(const u4* args, JValue* pResult, const Method* method, Thread* self) { 1098 u4* modArgs = (u4*) args; 1099 jclass staticMethodClass = NULL; 1100 1101 u4 accessFlags = method->accessFlags; 1102 bool isSynchronized = (accessFlags & ACC_SYNCHRONIZED) != 0; 1103 1104 //ALOGI("JNI calling %p (%s.%s:%s):", method->insns, 1105 // method->clazz->descriptor, method->name, method->shorty); 1106 1107 /* 1108 * Walk the argument list, creating local references for appropriate 1109 * arguments. 1110 */ 1111 int idx = 0; 1112 Object* lockObj; 1113 if ((accessFlags & ACC_STATIC) != 0) { 1114 lockObj = (Object*) method->clazz; 1115 /* add the class object we pass in */ 1116 staticMethodClass = (jclass) addLocalReference(self, (Object*) method->clazz); 1117 } else { 1118 lockObj = (Object*) args[0]; 1119 /* add "this" */ 1120 modArgs[idx++] = (u4) addLocalReference(self, (Object*) modArgs[0]); 1121 } 1122 1123 if (!method->noRef) { 1124 const char* shorty = &method->shorty[1]; /* skip return type */ 1125 while (*shorty != ‘\0‘) { 1126 switch (*shorty++) { 1127 case ‘L‘: 1128 //ALOGI(" local %d: 0x%08x", idx, modArgs[idx]); 1129 if (modArgs[idx] != 0) { 1130 modArgs[idx] = (u4) addLocalReference(self, (Object*) modArgs[idx]); 1131 } 1132 break; 1133 case ‘D‘: 1134 case ‘J‘: 1135 idx++; 1136 break; 1137 default: 1138 /* Z B C S I -- do nothing */ 1139 break; 1140 } 1141 idx++; 1142 } 1143 } 1144 1145 if (UNLIKELY(method->shouldTrace)) { 1146 logNativeMethodEntry(method, args); 1147 } 1148 if (UNLIKELY(isSynchronized)) { 1149 dvmLockObject(self, lockObj); 1150 } 1151 1152 ThreadStatus oldStatus = dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_NATIVE); 1153 1154 ANDROID_MEMBAR_FULL(); /* guarantee ordering on method->insns */ 1155 assert(method->insns != NULL); 1156 1157 JNIEnv* env = self->jniEnv; 1158 COMPUTE_STACK_SUM(self); 1159 dvmPlatformInvoke(env, 1160 (ClassObject*) staticMethodClass, 1161 method->jniArgInfo, method->insSize, modArgs, method->shorty, 1162 (void*) method->insns, pResult); 1163 CHECK_STACK_SUM(self); 1164 1165 dvmChangeStatus(self, oldStatus); 1166 1167 convertReferenceResult(env, pResult, method, self); 1168 1169 if (UNLIKELY(isSynchronized)) { 1170 dvmUnlockObject(self, lockObj); 1171 } 1172 if (UNLIKELY(method->shouldTrace)) { 1173 logNativeMethodExit(method, self, *pResult); 1174 } 1175 } 1176 1177 /* 1178 * =========================================================================== 1179 * JNI implementation 1180 * =========================================================================== 1181 */ 1182 1183 /* 1184 * Return the version of the native method interface. 1185 */ 1186 static jint GetVersion(JNIEnv* env) { 1187 /* 1188 * There is absolutely no need to toggle the mode for correct behavior. 1189 * However, it does provide native code with a simple "suspend self 1190 * if necessary" call. 1191 */ 1192 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1193 return JNI_VERSION_1_6; 1194 } 1195 1196 /* 1197 * Create a new class from a bag of bytes. 1198 * 1199 * This is not currently supported within Dalvik. 1200 */ 1201 static jclass DefineClass(JNIEnv* env, const char *name, jobject loader, 1202 const jbyte* buf, jsize bufLen) 1203 { 1204 UNUSED_PARAMETER(name); 1205 UNUSED_PARAMETER(loader); 1206 UNUSED_PARAMETER(buf); 1207 UNUSED_PARAMETER(bufLen); 1208 1209 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1210 ALOGW("JNI DefineClass is not supported"); 1211 return NULL; 1212 } 1213 1214 /* 1215 * Find a class by name. 1216 * 1217 * We have to use the "no init" version of FindClass here, because we might 1218 * be getting the class prior to registering native methods that will be 1219 * used in <clinit>. 1220 * 1221 * We need to get the class loader associated with the current native 1222 * method. If there is no native method, e.g. we‘re calling this from native 1223 * code right after creating the VM, the spec says we need to use the class 1224 * loader returned by "ClassLoader.getBaseClassLoader". There is no such 1225 * method, but it‘s likely they meant ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader. 1226 * We can‘t get that until after the VM has initialized though. 1227 */ 1228 static jclass FindClass(JNIEnv* env, const char* name) { 1229 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1230 1231 const Method* thisMethod = dvmGetCurrentJNIMethod(); 1232 assert(thisMethod != NULL); 1233 1234 Object* loader; 1235 Object* trackedLoader = NULL; 1236 if (ts.self()->classLoaderOverride != NULL) { 1237 /* hack for JNI_OnLoad */ 1238 assert(strcmp(thisMethod->name, "nativeLoad") == 0); 1239 loader = ts.self()->classLoaderOverride; 1240 } else if (thisMethod == gDvm.methDalvikSystemNativeStart_main || 1241 thisMethod == gDvm.methDalvikSystemNativeStart_run) { 1242 /* start point of invocation interface */ 1243 if (!gDvm.initializing) { 1244 loader = trackedLoader = dvmGetSystemClassLoader(); 1245 } else { 1246 loader = NULL; 1247 } 1248 } else { 1249 loader = thisMethod->clazz->classLoader; 1250 } 1251 1252 char* descriptor = dvmNameToDescriptor(name); 1253 if (descriptor == NULL) { 1254 return NULL; 1255 } 1256 ClassObject* clazz = dvmFindClassNoInit(descriptor, loader); 1257 free(descriptor); 1258 1259 jclass jclazz = (jclass) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*) clazz); 1260 dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc(trackedLoader, ts.self()); 1261 return jclazz; 1262 } 1263 1264 /* 1265 * Return the superclass of a class. 1266 */ 1267 static jclass GetSuperclass(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz) { 1268 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1269 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 1270 return (jclass) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*)clazz->super); 1271 } 1272 1273 /* 1274 * Determine whether an object of clazz1 can be safely cast to clazz2. 1275 * 1276 * Like IsInstanceOf, but with a pair of class objects instead of obj+class. 1277 */ 1278 static jboolean IsAssignableFrom(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz1, jclass jclazz2) { 1279 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1280 ClassObject* clazz1 = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz1); 1281 ClassObject* clazz2 = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz2); 1282 return dvmInstanceof(clazz1, clazz2); 1283 } 1284 1285 /* 1286 * Given a java.lang.reflect.Method or .Constructor, return a methodID. 1287 */ 1288 static jmethodID FromReflectedMethod(JNIEnv* env, jobject jmethod) { 1289 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1290 Object* method = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jmethod); 1291 return (jmethodID) dvmGetMethodFromReflectObj(method); 1292 } 1293 1294 /* 1295 * Given a java.lang.reflect.Field, return a fieldID. 1296 */ 1297 static jfieldID FromReflectedField(JNIEnv* env, jobject jfield) { 1298 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1299 Object* field = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jfield); 1300 return (jfieldID) dvmGetFieldFromReflectObj(field); 1301 } 1302 1303 /* 1304 * Convert a methodID to a java.lang.reflect.Method or .Constructor. 1305 * 1306 * (The "isStatic" field does not appear in the spec.) 1307 * 1308 * Throws OutOfMemory and returns NULL on failure. 1309 */ 1310 static jobject ToReflectedMethod(JNIEnv* env, jclass jcls, jmethodID methodID, jboolean isStatic) { 1311 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1312 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jcls); 1313 Object* obj = dvmCreateReflectObjForMethod(clazz, (Method*) methodID); 1314 dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc(obj, NULL); 1315 return addLocalReference(ts.self(), obj); 1316 } 1317 1318 /* 1319 * Convert a fieldID to a java.lang.reflect.Field. 1320 * 1321 * (The "isStatic" field does not appear in the spec.) 1322 * 1323 * Throws OutOfMemory and returns NULL on failure. 1324 */ 1325 static jobject ToReflectedField(JNIEnv* env, jclass jcls, jfieldID fieldID, jboolean isStatic) { 1326 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1327 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jcls); 1328 Object* obj = dvmCreateReflectObjForField(clazz, (Field*) fieldID); 1329 dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc(obj, NULL); 1330 return addLocalReference(ts.self(), obj); 1331 } 1332 1333 /* 1334 * Take this exception and throw it. 1335 */ 1336 static jint Throw(JNIEnv* env, jthrowable jobj) { 1337 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1338 if (jobj != NULL) { 1339 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 1340 dvmSetException(ts.self(), obj); 1341 return JNI_OK; 1342 } 1343 return JNI_ERR; 1344 } 1345 1346 /* 1347 * Constructs an exception object from the specified class with the message 1348 * specified by "message", and throws it. 1349 */ 1350 static jint ThrowNew(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, const char* message) { 1351 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1352 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 1353 dvmThrowException(clazz, message); 1354 // TODO: should return failure if this didn‘t work (e.g. OOM) 1355 return JNI_OK; 1356 } 1357 1358 /* 1359 * If an exception is being thrown, return the exception object. Otherwise, 1360 * return NULL. 1361 * 1362 * TODO: if there is no pending exception, we should be able to skip the 1363 * enter/exit checks. If we find one, we need to enter and then re-fetch 1364 * the exception (in case it got moved by a compacting GC). 1365 */ 1366 static jthrowable ExceptionOccurred(JNIEnv* env) { 1367 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1368 Object* exception = dvmGetException(ts.self()); 1369 jthrowable localException = (jthrowable) addLocalReference(ts.self(), exception); 1370 if (localException == NULL && exception != NULL) { 1371 /* 1372 * We were unable to add a new local reference, and threw a new 1373 * exception. We can‘t return "exception", because it‘s not a 1374 * local reference. So we have to return NULL, indicating that 1375 * there was no exception, even though it‘s pretty much raining 1376 * exceptions in here. 1377 */ 1378 ALOGW("JNI WARNING: addLocal/exception combo"); 1379 } 1380 return localException; 1381 } 1382 1383 /* 1384 * Print an exception and stack trace to stderr. 1385 */ 1386 static void ExceptionDescribe(JNIEnv* env) { 1387 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1388 Object* exception = dvmGetException(ts.self()); 1389 if (exception != NULL) { 1390 dvmPrintExceptionStackTrace(); 1391 } else { 1392 ALOGI("Odd: ExceptionDescribe called, but no exception pending"); 1393 } 1394 } 1395 1396 /* 1397 * Clear the exception currently being thrown. 1398 * 1399 * TODO: we should be able to skip the enter/exit stuff. 1400 */ 1401 static void ExceptionClear(JNIEnv* env) { 1402 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1403 dvmClearException(ts.self()); 1404 } 1405 1406 /* 1407 * Kill the VM. This function does not return. 1408 */ 1409 static void FatalError(JNIEnv* env, const char* msg) { 1410 //dvmChangeStatus(NULL, THREAD_RUNNING); 1411 ALOGE("JNI posting fatal error: %s", msg); 1412 ReportJniError(); 1413 } 1414 1415 /* 1416 * Push a new JNI frame on the stack, with a new set of locals. 1417 * 1418 * The new frame must have the same method pointer. (If for no other 1419 * reason than FindClass needs it to get the appropriate class loader.) 1420 */ 1421 static jint PushLocalFrame(JNIEnv* env, jint capacity) { 1422 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1423 if (!ensureLocalCapacity(ts.self(), capacity) || 1424 !dvmPushLocalFrame(ts.self(), dvmGetCurrentJNIMethod())) 1425 { 1426 /* yes, OutOfMemoryError, not StackOverflowError */ 1427 dvmClearException(ts.self()); 1428 dvmThrowOutOfMemoryError("out of stack in JNI PushLocalFrame"); 1429 return JNI_ERR; 1430 } 1431 return JNI_OK; 1432 } 1433 1434 /* 1435 * Pop the local frame off. If "jresult" is not null, add it as a 1436 * local reference on the now-current frame. 1437 */ 1438 static jobject PopLocalFrame(JNIEnv* env, jobject jresult) { 1439 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1440 Object* result = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jresult); 1441 if (!dvmPopLocalFrame(ts.self())) { 1442 ALOGW("JNI WARNING: too many PopLocalFrame calls"); 1443 dvmClearException(ts.self()); 1444 dvmThrowRuntimeException("too many PopLocalFrame calls"); 1445 } 1446 return addLocalReference(ts.self(), result); 1447 } 1448 1449 /* 1450 * Add a reference to the global list. 1451 */ 1452 static jobject NewGlobalRef(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) { 1453 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1454 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 1455 return addGlobalReference(obj); 1456 } 1457 1458 /* 1459 * Delete a reference from the global list. 1460 */ 1461 static void DeleteGlobalRef(JNIEnv* env, jobject jglobalRef) { 1462 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1463 deleteGlobalReference(jglobalRef); 1464 } 1465 1466 1467 /* 1468 * Add a reference to the local list. 1469 */ 1470 static jobject NewLocalRef(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) { 1471 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1472 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 1473 return addLocalReference(ts.self(), obj); 1474 } 1475 1476 /* 1477 * Delete a reference from the local list. 1478 */ 1479 static void DeleteLocalRef(JNIEnv* env, jobject jlocalRef) { 1480 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1481 deleteLocalReference(ts.self(), jlocalRef); 1482 } 1483 1484 /* 1485 * Ensure that the local references table can hold at least this many 1486 * references. 1487 */ 1488 static jint EnsureLocalCapacity(JNIEnv* env, jint capacity) { 1489 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1490 bool okay = ensureLocalCapacity(ts.self(), capacity); 1491 if (!okay) { 1492 dvmThrowOutOfMemoryError("can‘t ensure local reference capacity"); 1493 } 1494 return okay ? 0 : -1; 1495 } 1496 1497 1498 /* 1499 * Determine whether two Object references refer to the same underlying object. 1500 */ 1501 static jboolean IsSameObject(JNIEnv* env, jobject jref1, jobject jref2) { 1502 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1503 Object* obj1 = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jref1); 1504 Object* obj2 = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jref2); 1505 return (obj1 == obj2); 1506 } 1507 1508 /* 1509 * Allocate a new object without invoking any constructors. 1510 */ 1511 static jobject AllocObject(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz) { 1512 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1513 1514 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 1515 if (!canAllocClass(clazz) || 1516 (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz))) 1517 { 1518 assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self())); 1519 return NULL; 1520 } 1521 1522 Object* newObj = dvmAllocObject(clazz, ALLOC_DONT_TRACK); 1523 return addLocalReference(ts.self(), newObj); 1524 } 1525 1526 /* 1527 * Allocate a new object and invoke the supplied constructor. 1528 */ 1529 static jobject NewObject(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, jmethodID methodID, ...) { 1530 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1531 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 1532 1533 if (!canAllocClass(clazz) || (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz))) { 1534 assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self())); 1535 return NULL; 1536 } 1537 1538 Object* newObj = dvmAllocObject(clazz, ALLOC_DONT_TRACK); 1539 jobject result = addLocalReference(ts.self(), newObj); 1540 if (newObj != NULL) { 1541 JValue unused; 1542 va_list args; 1543 va_start(args, methodID); 1544 dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), (Method*) methodID, newObj, true, &unused, args); 1545 va_end(args); 1546 } 1547 return result; 1548 } 1549 1550 static jobject NewObjectV(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, jmethodID methodID, va_list args) { 1551 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1552 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 1553 1554 if (!canAllocClass(clazz) || (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz))) { 1555 assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self())); 1556 return NULL; 1557 } 1558 1559 Object* newObj = dvmAllocObject(clazz, ALLOC_DONT_TRACK); 1560 jobject result = addLocalReference(ts.self(), newObj); 1561 if (newObj != NULL) { 1562 JValue unused; 1563 dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), (Method*) methodID, newObj, true, &unused, args); 1564 } 1565 return result; 1566 } 1567 1568 static jobject NewObjectA(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, jmethodID methodID, jvalue* args) { 1569 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1570 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 1571 1572 if (!canAllocClass(clazz) || (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz))) { 1573 assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self())); 1574 return NULL; 1575 } 1576 1577 Object* newObj = dvmAllocObject(clazz, ALLOC_DONT_TRACK); 1578 jobject result = addLocalReference(ts.self(), newObj); 1579 if (newObj != NULL) { 1580 JValue unused; 1581 dvmCallMethodA(ts.self(), (Method*) methodID, newObj, true, &unused, args); 1582 } 1583 return result; 1584 } 1585 1586 /* 1587 * Returns the class of an object. 1588 * 1589 * JNI spec says: obj must not be NULL. 1590 */ 1591 static jclass GetObjectClass(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) { 1592 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1593 1594 assert(jobj != NULL); 1595 1596 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 1597 return (jclass) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*) obj->clazz); 1598 } 1599 1600 /* 1601 * Determine whether "obj" is an instance of "clazz". 1602 */ 1603 static jboolean IsInstanceOf(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, jclass jclazz) { 1604 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1605 1606 assert(jclazz != NULL); 1607 if (jobj == NULL) { 1608 return true; 1609 } 1610 1611 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 1612 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 1613 return dvmInstanceof(obj->clazz, clazz); 1614 } 1615 1616 /* 1617 * Get a method ID for an instance method. 1618 * 1619 * While Dalvik bytecode has distinct instructions for virtual, super, 1620 * static, direct, and interface method invocation, JNI only provides 1621 * two functions for acquiring a method ID. This call handles everything 1622 * but static methods. 1623 * 1624 * JNI defines <init> as an instance method, but Dalvik considers it a 1625 * "direct" method, so we have to special-case it here. 1626 * 1627 * Dalvik also puts all private methods into the "direct" list, so we 1628 * really need to just search both lists. 1629 */ 1630 static jmethodID GetMethodID(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, const char* name, const char* sig) { 1631 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1632 1633 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 1634 if (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz)) { 1635 assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self())); 1636 } else if (dvmIsInterfaceClass(clazz)) { 1637 Method* meth = dvmFindInterfaceMethodHierByDescriptor(clazz, name, sig); 1638 if (meth == NULL) { 1639 dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exNoSuchMethodError, 1640 "no method with name=‘%s‘ signature=‘%s‘ in interface %s", 1641 name, sig, clazz->descriptor); 1642 } 1643 return (jmethodID) meth; 1644 } 1645 Method* meth = dvmFindVirtualMethodHierByDescriptor(clazz, name, sig); 1646 if (meth == NULL) { 1647 /* search private methods and constructors; non-hierarchical */ 1648 meth = dvmFindDirectMethodByDescriptor(clazz, name, sig); 1649 } 1650 if (meth != NULL && dvmIsStaticMethod(meth)) { 1651 IF_ALOGD() { 1652 char* desc = dexProtoCopyMethodDescriptor(&meth->prototype); 1653 ALOGD("GetMethodID: not returning static method %s.%s %s", 1654 clazz->descriptor, meth->name, desc); 1655 free(desc); 1656 } 1657 meth = NULL; 1658 } 1659 if (meth == NULL) { 1660 dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exNoSuchMethodError, 1661 "no method with name=‘%s‘ signature=‘%s‘ in class %s", 1662 name, sig, clazz->descriptor); 1663 } else { 1664 /* 1665 * The method‘s class may not be the same as clazz, but if 1666 * it isn‘t this must be a virtual method and the class must 1667 * be a superclass (and, hence, already initialized). 1668 */ 1669 assert(dvmIsClassInitialized(meth->clazz) || dvmIsClassInitializing(meth->clazz)); 1670 } 1671 return (jmethodID) meth; 1672 } 1673 1674 /* 1675 * Get a field ID (instance fields). 1676 */ 1677 static jfieldID GetFieldID(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, const char* name, const char* sig) { 1678 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1679 1680 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 1681 1682 if (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz)) { 1683 assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self())); 1684 return NULL; 1685 } 1686 1687 jfieldID id = (jfieldID) dvmFindInstanceFieldHier(clazz, name, sig); 1688 if (id == NULL) { 1689 dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exNoSuchFieldError, 1690 "no field with name=‘%s‘ signature=‘%s‘ in class %s", 1691 name, sig, clazz->descriptor); 1692 } 1693 return id; 1694 } 1695 1696 /* 1697 * Get the method ID for a static method in a class. 1698 */ 1699 static jmethodID GetStaticMethodID(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, const char* name, const char* sig) { 1700 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1701 1702 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 1703 if (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz)) { 1704 assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self())); 1705 return NULL; 1706 } 1707 1708 Method* meth = dvmFindDirectMethodHierByDescriptor(clazz, name, sig); 1709 1710 /* make sure it‘s static, not virtual+private */ 1711 if (meth != NULL && !dvmIsStaticMethod(meth)) { 1712 IF_ALOGD() { 1713 char* desc = dexProtoCopyMethodDescriptor(&meth->prototype); 1714 ALOGD("GetStaticMethodID: not returning nonstatic method %s.%s %s", 1715 clazz->descriptor, meth->name, desc); 1716 free(desc); 1717 } 1718 meth = NULL; 1719 } 1720 1721 jmethodID id = (jmethodID) meth; 1722 if (id == NULL) { 1723 dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exNoSuchMethodError, 1724 "no static method with name=‘%s‘ signature=‘%s‘ in class %s", 1725 name, sig, clazz->descriptor); 1726 } 1727 return id; 1728 } 1729 1730 /* 1731 * Get a field ID (static fields). 1732 */ 1733 static jfieldID GetStaticFieldID(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, const char* name, const char* sig) { 1734 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1735 1736 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 1737 if (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz)) { 1738 assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self())); 1739 return NULL; 1740 } 1741 1742 jfieldID id = (jfieldID) dvmFindStaticFieldHier(clazz, name, sig); 1743 if (id == NULL) { 1744 dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exNoSuchFieldError, 1745 "no static field with name=‘%s‘ signature=‘%s‘ in class %s", 1746 name, sig, clazz->descriptor); 1747 } 1748 return id; 1749 } 1750 1751 /* 1752 * Get a static field. 1753 * 1754 * If we get an object reference, add it to the local refs list. 1755 */ 1756 #define GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(_ctype, _jname, _isref) 1757 static _ctype GetStatic##_jname##Field(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, 1758 jfieldID fieldID) 1759 { 1760 UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); 1761 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1762 StaticField* sfield = (StaticField*) fieldID; 1763 _ctype value; 1764 if (dvmIsVolatileField(sfield)) { 1765 if (_isref) { /* only when _ctype==jobject */ 1766 Object* obj = dvmGetStaticFieldObjectVolatile(sfield); 1767 value = (_ctype)(u4)addLocalReference(ts.self(), obj); 1768 } else { 1769 value = (_ctype) dvmGetStaticField##_jname##Volatile(sfield);1770 } 1771 } else { 1772 if (_isref) { 1773 Object* obj = dvmGetStaticFieldObject(sfield); 1774 value = (_ctype)(u4)addLocalReference(ts.self(), obj); 1775 } else { 1776 value = (_ctype) dvmGetStaticField##_jname(sfield); 1777 } 1778 } 1779 return value; 1780 } 1781 GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jobject, Object, true); 1782 GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jboolean, Boolean, false); 1783 GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jbyte, Byte, false); 1784 GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jchar, Char, false); 1785 GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jshort, Short, false); 1786 GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jint, Int, false); 1787 GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jlong, Long, false); 1788 GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jfloat, Float, false); 1789 GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jdouble, Double, false); 1790 1791 /* 1792 * Set a static field. 1793 */ 1794 #define SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(_ctype, _ctype2, _jname, _isref) 1795 static void SetStatic##_jname##Field(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, 1796 jfieldID fieldID, _ctype value) 1797 { 1798 UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); 1799 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1800 StaticField* sfield = (StaticField*) fieldID; 1801 if (dvmIsVolatileField(sfield)) { 1802 if (_isref) { /* only when _ctype==jobject */ 1803 Object* valObj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), (jobject)(u4)value); 1804 dvmSetStaticFieldObjectVolatile(sfield, valObj); 1805 } else { 1806 dvmSetStaticField##_jname##Volatile(sfield, (_ctype2)value);1807 } 1808 } else { 1809 if (_isref) { 1810 Object* valObj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), (jobject)(u4)value); 1811 dvmSetStaticFieldObject(sfield, valObj); 1812 } else { 1813 dvmSetStaticField##_jname(sfield, (_ctype2)value); 1814 } 1815 } 1816 } 1817 SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jobject, Object*, Object, true); 1818 SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jboolean, bool, Boolean, false); 1819 SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jbyte, s1, Byte, false); 1820 SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jchar, u2, Char, false); 1821 SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jshort, s2, Short, false); 1822 SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jint, s4, Int, false); 1823 SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jlong, s8, Long, false); 1824 SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jfloat, float, Float, false); 1825 SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jdouble, double, Double, false); 1826 1827 /* 1828 * Get an instance field. 1829 * 1830 * If we get an object reference, add it to the local refs list. 1831 */ 1832 #define GET_TYPE_FIELD(_ctype, _jname, _isref) 1833 static _ctype Get##_jname##Field(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, 1834 jfieldID fieldID) 1835 { 1836 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1837 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 1838 InstField* field = (InstField*) fieldID; 1839 _ctype value; 1840 if (dvmIsVolatileField(field)) { 1841 if (_isref) { /* only when _ctype==jobject */ 1842 Object* valObj = 1843 dvmGetFieldObjectVolatile(obj, field->byteOffset); 1844 value = (_ctype)(u4)addLocalReference(ts.self(), valObj); 1845 } else { 1846 value = (_ctype) 1847 dvmGetField##_jname##Volatile(obj, field->byteOffset); 1848 } 1849 } else { 1850 if (_isref) { 1851 Object* valObj = dvmGetFieldObject(obj, field->byteOffset); 1852 value = (_ctype)(u4)addLocalReference(ts.self(), valObj); 1853 } else { 1854 value = (_ctype) dvmGetField##_jname(obj, field->byteOffset);1855 } 1856 } 1857 return value; 1858 } 1859 GET_TYPE_FIELD(jobject, Object, true); 1860 GET_TYPE_FIELD(jboolean, Boolean, false); 1861 GET_TYPE_FIELD(jbyte, Byte, false); 1862 GET_TYPE_FIELD(jchar, Char, false); 1863 GET_TYPE_FIELD(jshort, Short, false); 1864 GET_TYPE_FIELD(jint, Int, false); 1865 GET_TYPE_FIELD(jlong, Long, false); 1866 GET_TYPE_FIELD(jfloat, Float, false); 1867 GET_TYPE_FIELD(jdouble, Double, false); 1868 1869 /* 1870 * Set an instance field. 1871 */ 1872 #define SET_TYPE_FIELD(_ctype, _ctype2, _jname, _isref) 1873 static void Set##_jname##Field(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, 1874 jfieldID fieldID, _ctype value) 1875 { 1876 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1877 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 1878 InstField* field = (InstField*) fieldID; 1879 if (dvmIsVolatileField(field)) { 1880 if (_isref) { /* only when _ctype==jobject */ 1881 Object* valObj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), (jobject)(u4)value); 1882 dvmSetFieldObjectVolatile(obj, field->byteOffset, valObj); 1883 } else { 1884 dvmSetField##_jname##Volatile(obj, 1885 field->byteOffset, (_ctype2)value); 1886 } 1887 } else { 1888 if (_isref) { 1889 Object* valObj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), (jobject)(u4)value); 1890 dvmSetFieldObject(obj, field->byteOffset, valObj); 1891 } else { 1892 dvmSetField##_jname(obj, 1893 field->byteOffset, (_ctype2)value); 1894 } 1895 } 1896 } 1897 SET_TYPE_FIELD(jobject, Object*, Object, true); 1898 SET_TYPE_FIELD(jboolean, bool, Boolean, false); 1899 SET_TYPE_FIELD(jbyte, s1, Byte, false); 1900 SET_TYPE_FIELD(jchar, u2, Char, false); 1901 SET_TYPE_FIELD(jshort, s2, Short, false); 1902 SET_TYPE_FIELD(jint, s4, Int, false); 1903 SET_TYPE_FIELD(jlong, s8, Long, false); 1904 SET_TYPE_FIELD(jfloat, float, Float, false); 1905 SET_TYPE_FIELD(jdouble, double, Double, false); 1906 1907 /* 1908 * Make a virtual method call. 1909 * 1910 * Three versions (..., va_list, jvalue[]) for each return type. If we‘re 1911 * returning an Object, we have to add it to the local references table. 1912 */ 1913 #define CALL_VIRTUAL(_ctype, _jname, _retfail, _retok, _isref) 1914 static _ctype Call##_jname##Method(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, 1915 jmethodID methodID, ...) 1916 { 1917 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1918 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 1919 const Method* meth; 1920 va_list args; 1921 JValue result; 1922 meth = dvmGetVirtualizedMethod(obj->clazz, (Method*)methodID); 1923 if (meth == NULL) { 1924 return _retfail; 1925 } 1926 va_start(args, methodID); 1927 dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), meth, obj, true, &result, args); 1928 va_end(args); 1929 if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) 1930 result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); 1931 return _retok; 1932 } 1933 static _ctype Call##_jname##MethodV(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, 1934 jmethodID methodID, va_list args) 1935 { 1936 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1937 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 1938 const Method* meth; 1939 JValue result; 1940 meth = dvmGetVirtualizedMethod(obj->clazz, (Method*)methodID); 1941 if (meth == NULL) { 1942 return _retfail; 1943 } 1944 dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), meth, obj, true, &result, args); 1945 if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) 1946 result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); 1947 return _retok; 1948 } 1949 static _ctype Call##_jname##MethodA(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, 1950 jmethodID methodID, jvalue* args) 1951 { 1952 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1953 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 1954 const Method* meth; 1955 JValue result; 1956 meth = dvmGetVirtualizedMethod(obj->clazz, (Method*)methodID); 1957 if (meth == NULL) { 1958 return _retfail; 1959 } 1960 dvmCallMethodA(ts.self(), meth, obj, true, &result, args); 1961 if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) 1962 result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); 1963 return _retok; 1964 } 1965 CALL_VIRTUAL(jobject, Object, NULL, (jobject) result.l, true); 1966 CALL_VIRTUAL(jboolean, Boolean, 0, result.z, false); 1967 CALL_VIRTUAL(jbyte, Byte, 0, result.b, false); 1968 CALL_VIRTUAL(jchar, Char, 0, result.c, false); 1969 CALL_VIRTUAL(jshort, Short, 0, result.s, false); 1970 CALL_VIRTUAL(jint, Int, 0, result.i, false); 1971 CALL_VIRTUAL(jlong, Long, 0, result.j, false); 1972 CALL_VIRTUAL(jfloat, Float, 0.0f, result.f, false); 1973 CALL_VIRTUAL(jdouble, Double, 0.0, result.d, false); 1974 CALL_VIRTUAL(void, Void, , , false); 1975 1976 /* 1977 * Make a "non-virtual" method call. We‘re still calling a virtual method, 1978 * but this time we‘re not doing an indirection through the object‘s vtable. 1979 * The "clazz" parameter defines which implementation of a method we want. 1980 * 1981 * Three versions (..., va_list, jvalue[]) for each return type. 1982 */ 1983 #define CALL_NONVIRTUAL(_ctype, _jname, _retfail, _retok, _isref) 1984 static _ctype CallNonvirtual##_jname##Method(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, 1985 jclass jclazz, jmethodID methodID, ...) 1986 { 1987 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 1988 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 1989 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 1990 const Method* meth; 1991 va_list args; 1992 JValue result; 1993 meth = dvmGetVirtualizedMethod(clazz, (Method*)methodID); 1994 if (meth == NULL) { 1995 return _retfail; 1996 } 1997 va_start(args, methodID); 1998 dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), meth, obj, true, &result, args); 1999 if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) 2000 result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); 2001 va_end(args); 2002 return _retok; 2003 } 2004 static _ctype CallNonvirtual##_jname##MethodV(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj,2005 jclass jclazz, jmethodID methodID, va_list args) 2006 { 2007 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2008 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 2009 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 2010 const Method* meth; 2011 JValue result; 2012 meth = dvmGetVirtualizedMethod(clazz, (Method*)methodID); 2013 if (meth == NULL) { 2014 return _retfail; 2015 } 2016 dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), meth, obj, true, &result, args); 2017 if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) 2018 result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); 2019 return _retok; 2020 } 2021 static _ctype CallNonvirtual##_jname##MethodA(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj,2022 jclass jclazz, jmethodID methodID, jvalue* args) 2023 { 2024 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2025 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 2026 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 2027 const Method* meth; 2028 JValue result; 2029 meth = dvmGetVirtualizedMethod(clazz, (Method*)methodID); 2030 if (meth == NULL) { 2031 return _retfail; 2032 } 2033 dvmCallMethodA(ts.self(), meth, obj, true, &result, args); 2034 if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) 2035 result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); 2036 return _retok; 2037 } 2038 CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jobject, Object, NULL, (jobject) result.l, true); 2039 CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jboolean, Boolean, 0, result.z, false); 2040 CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jbyte, Byte, 0, result.b, false); 2041 CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jchar, Char, 0, result.c, false); 2042 CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jshort, Short, 0, result.s, false); 2043 CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jint, Int, 0, result.i, false); 2044 CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jlong, Long, 0, result.j, false); 2045 CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jfloat, Float, 0.0f, result.f, false); 2046 CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jdouble, Double, 0.0, result.d, false); 2047 CALL_NONVIRTUAL(void, Void, , , false); 2048 2049 2050 /* 2051 * Call a static method. 2052 */ 2053 #define CALL_STATIC(_ctype, _jname, _retfail, _retok, _isref) 2054 static _ctype CallStatic##_jname##Method(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, 2055 jmethodID methodID, ...) 2056 { 2057 UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); 2058 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2059 JValue result; 2060 va_list args; 2061 va_start(args, methodID); 2062 dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), (Method*)methodID, NULL, true, &result, args);2063 va_end(args); 2064 if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) 2065 result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); 2066 return _retok; 2067 } 2068 static _ctype CallStatic##_jname##MethodV(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, 2069 jmethodID methodID, va_list args) 2070 { 2071 UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); 2072 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2073 JValue result; 2074 dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), (Method*)methodID, NULL, true, &result, args);2075 if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) 2076 result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); 2077 return _retok; 2078 } 2079 static _ctype CallStatic##_jname##MethodA(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, 2080 jmethodID methodID, jvalue* args) 2081 { 2082 UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); 2083 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2084 JValue result; 2085 dvmCallMethodA(ts.self(), (Method*)methodID, NULL, true, &result, args);2086 if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) 2087 result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); 2088 return _retok; 2089 } 2090 CALL_STATIC(jobject, Object, NULL, (jobject) result.l, true); 2091 CALL_STATIC(jboolean, Boolean, 0, result.z, false); 2092 CALL_STATIC(jbyte, Byte, 0, result.b, false); 2093 CALL_STATIC(jchar, Char, 0, result.c, false); 2094 CALL_STATIC(jshort, Short, 0, result.s, false); 2095 CALL_STATIC(jint, Int, 0, result.i, false); 2096 CALL_STATIC(jlong, Long, 0, result.j, false); 2097 CALL_STATIC(jfloat, Float, 0.0f, result.f, false); 2098 CALL_STATIC(jdouble, Double, 0.0, result.d, false); 2099 CALL_STATIC(void, Void, , , false); 2100 2101 /* 2102 * Create a new String from Unicode data. 2103 * 2104 * If "len" is zero, we will return an empty string even if "unicodeChars" 2105 * is NULL. (The JNI spec is vague here.) 2106 */ 2107 static jstring NewString(JNIEnv* env, const jchar* unicodeChars, jsize len) { 2108 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2109 StringObject* jstr = dvmCreateStringFromUnicode(unicodeChars, len); 2110 if (jstr == NULL) { 2111 return NULL; 2112 } 2113 dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc((Object*) jstr, NULL); 2114 return (jstring) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*) jstr); 2115 } 2116 2117 /* 2118 * Return the length of a String in Unicode character units. 2119 */ 2120 static jsize GetStringLength(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr) { 2121 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2122 StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr); 2123 return strObj->length(); 2124 } 2125 2126 2127 /* 2128 * Get a string‘s character data. 2129 * 2130 * The result is guaranteed to be valid until ReleaseStringChars is 2131 * called, which means we have to pin it or return a copy. 2132 */ 2133 static const jchar* GetStringChars(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, jboolean* isCopy) { 2134 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2135 2136 StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr); 2137 ArrayObject* strChars = strObj->array(); 2138 2139 pinPrimitiveArray(strChars); 2140 2141 const u2* data = strObj->chars(); 2142 if (isCopy != NULL) { 2143 *isCopy = JNI_FALSE; 2144 } 2145 return (jchar*) data; 2146 } 2147 2148 /* 2149 * Release our grip on some characters from a string. 2150 */ 2151 static void ReleaseStringChars(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, const jchar* chars) { 2152 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2153 StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr); 2154 ArrayObject* strChars = strObj->array(); 2155 unpinPrimitiveArray(strChars); 2156 } 2157 2158 /* 2159 * Create a new java.lang.String object from chars in modified UTF-8 form. 2160 * 2161 * The spec doesn‘t say how to handle a NULL string. Popular desktop VMs 2162 * accept it and return a NULL pointer in response. 2163 */ 2164 static jstring NewStringUTF(JNIEnv* env, const char* bytes) { 2165 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2166 if (bytes == NULL) { 2167 return NULL; 2168 } 2169 /* note newStr could come back NULL on OOM */ 2170 StringObject* newStr = dvmCreateStringFromCstr(bytes); 2171 jstring result = (jstring) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*) newStr); 2172 dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc((Object*)newStr, NULL); 2173 return result; 2174 } 2175 2176 /* 2177 * Return the length in bytes of the modified UTF-8 form of the string. 2178 */ 2179 static jsize GetStringUTFLength(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr) { 2180 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2181 StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr); 2182 if (strObj == NULL) { 2183 return 0; // Should we throw something or assert? 2184 } 2185 return strObj->utfLength(); 2186 } 2187 2188 /* 2189 * Convert "string" to modified UTF-8 and return a pointer. The returned 2190 * value must be released with ReleaseStringUTFChars. 2191 * 2192 * According to the JNI reference, "Returns a pointer to a UTF-8 string, 2193 * or NULL if the operation fails. Returns NULL if and only if an invocation 2194 * of this function has thrown an exception." 2195 * 2196 * The behavior here currently follows that of other open-source VMs, which 2197 * quietly return NULL if "string" is NULL. We should consider throwing an 2198 * NPE. (The CheckJNI code blows up if you try to pass in a NULL string, 2199 * which should catch this sort of thing during development.) Certain other 2200 * VMs will crash with a segmentation fault. 2201 */ 2202 static const char* GetStringUTFChars(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, jboolean* isCopy) { 2203 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2204 if (jstr == NULL) { 2205 /* this shouldn‘t happen; throw NPE? */ 2206 return NULL; 2207 } 2208 if (isCopy != NULL) { 2209 *isCopy = JNI_TRUE; 2210 } 2211 StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr); 2212 char* newStr = dvmCreateCstrFromString(strObj); 2213 if (newStr == NULL) { 2214 /* assume memory failure */ 2215 dvmThrowOutOfMemoryError("native heap string alloc failed"); 2216 } 2217 return newStr; 2218 } 2219 2220 /* 2221 * Release a string created by GetStringUTFChars(). 2222 */ 2223 static void ReleaseStringUTFChars(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, const char* utf) { 2224 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2225 free((char*) utf); 2226 } 2227 2228 /* 2229 * Return the capacity of the array. 2230 */ 2231 static jsize GetArrayLength(JNIEnv* env, jarray jarr) { 2232 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2233 ArrayObject* arrObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); 2234 return arrObj->length; 2235 } 2236 2237 /* 2238 * Construct a new array that holds objects from class "elementClass". 2239 */ 2240 static jobjectArray NewObjectArray(JNIEnv* env, jsize length, 2241 jclass jelementClass, jobject jinitialElement) 2242 { 2243 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2244 2245 if (jelementClass == NULL) { 2246 dvmThrowNullPointerException("JNI NewObjectArray elementClass == NULL"); 2247 return NULL; 2248 } 2249 2250 ClassObject* elemClassObj = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jelementClass); 2251 ClassObject* arrayClass = dvmFindArrayClassForElement(elemClassObj); 2252 ArrayObject* newObj = dvmAllocArrayByClass(arrayClass, length, ALLOC_DEFAULT); 2253 if (newObj == NULL) { 2254 assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self())); 2255 return NULL; 2256 } 2257 jobjectArray newArray = (jobjectArray) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*) newObj); 2258 dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc((Object*) newObj, NULL); 2259 2260 /* 2261 * Initialize the array. 2262 */ 2263 if (jinitialElement != NULL) { 2264 Object* initialElement = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jinitialElement); 2265 Object** arrayData = (Object**) (void*) newObj->contents; 2266 for (jsize i = 0; i < length; ++i) { 2267 arrayData[i] = initialElement; 2268 } 2269 } 2270 2271 return newArray; 2272 } 2273 2274 static bool checkArrayElementBounds(ArrayObject* arrayObj, jsize index) { 2275 assert(arrayObj != NULL); 2276 if (index < 0 || index >= (int) arrayObj->length) { 2277 dvmThrowArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(arrayObj->length, index); 2278 return false; 2279 } 2280 return true; 2281 } 2282 2283 /* 2284 * Get one element of an Object array. 2285 * 2286 * Add the object to the local references table in case the array goes away. 2287 */ 2288 static jobject GetObjectArrayElement(JNIEnv* env, jobjectArray jarr, jsize index) { 2289 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2290 2291 ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); 2292 if (!checkArrayElementBounds(arrayObj, index)) { 2293 return NULL; 2294 } 2295 2296 Object* value = ((Object**) (void*) arrayObj->contents)[index]; 2297 return addLocalReference(ts.self(), value); 2298 } 2299 2300 /* 2301 * Set one element of an Object array. 2302 */ 2303 static void SetObjectArrayElement(JNIEnv* env, jobjectArray jarr, jsize index, jobject jobj) { 2304 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2305 2306 ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); 2307 if (!checkArrayElementBounds(arrayObj, index)) { 2308 return; 2309 } 2310 2311 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 2312 2313 if (obj != NULL && !dvmCanPutArrayElement(obj->clazz, arrayObj->clazz)) { 2314 ALOGV("Can‘t put a ‘%s‘(%p) into array type=‘%s‘(%p)", 2315 obj->clazz->descriptor, obj, 2316 arrayObj->clazz->descriptor, arrayObj); 2317 dvmThrowArrayStoreExceptionIncompatibleElement(obj->clazz, arrayObj->clazz); 2318 return; 2319 } 2320 2321 //ALOGV("JNI: set element %d in array %p to %p", index, array, value); 2322 2323 dvmSetObjectArrayElement(arrayObj, index, obj); 2324 } 2325 2326 /* 2327 * Create a new array of primitive elements. 2328 */ 2329 #define NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(_artype, _jname, _typechar) 2330 static _artype New##_jname##Array(JNIEnv* env, jsize length) { 2331 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2332 ArrayObject* arrayObj = dvmAllocPrimitiveArray(_typechar, length, ALLOC_DEFAULT); 2333 if (arrayObj == NULL) { 2334 return NULL; 2335 } 2336 _artype result = (_artype) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*) arrayObj); 2337 dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc((Object*) arrayObj, NULL); 2338 return result; 2339 } 2340 NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jbooleanArray, Boolean, ‘Z‘); 2341 NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jbyteArray, Byte, ‘B‘); 2342 NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jcharArray, Char, ‘C‘); 2343 NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jshortArray, Short, ‘S‘); 2344 NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jintArray, Int, ‘I‘); 2345 NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jlongArray, Long, ‘J‘); 2346 NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jfloatArray, Float, ‘F‘); 2347 NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jdoubleArray, Double, ‘D‘); 2348 2349 /* 2350 * Get a pointer to a C array of primitive elements from an array object 2351 * of the matching type. 2352 * 2353 * In a compacting GC, we either need to return a copy of the elements or 2354 * "pin" the memory. Otherwise we run the risk of native code using the 2355 * buffer as the destination of e.g. a blocking read() call that wakes up 2356 * during a GC. 2357 */ 2358 #define GET_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_ELEMENTS(_ctype, _jname) 2359 static _ctype* Get##_jname##ArrayElements(JNIEnv* env, 2360 _ctype##Array jarr, jboolean* isCopy) 2361 { 2362 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2363 ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); 2364 pinPrimitiveArray(arrayObj); 2365 _ctype* data = (_ctype*) (void*) arrayObj->contents; 2366 if (isCopy != NULL) { 2367 *isCopy = JNI_FALSE; 2368 } 2369 return data; 2370 } 2371 2372 /* 2373 * Release the storage locked down by the "get" function. 2374 * 2375 * The spec says, "‘mode‘ has no effect if ‘elems‘ is not a copy of the 2376 * elements in ‘array‘." They apparently did not anticipate the need to 2377 * un-pin memory. 2378 */ 2379 #define RELEASE_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_ELEMENTS(_ctype, _jname) 2380 static void Release##_jname##ArrayElements(JNIEnv* env, 2381 _ctype##Array jarr, _ctype* elems, jint mode) 2382 { 2383 UNUSED_PARAMETER(elems); 2384 if (mode != JNI_COMMIT) { 2385 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2386 ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); 2387 unpinPrimitiveArray(arrayObj); 2388 } 2389 } 2390 2391 static void throwArrayRegionOutOfBounds(ArrayObject* arrayObj, jsize start, 2392 jsize len, const char* arrayIdentifier) 2393 { 2394 dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException, 2395 "%s offset=%d length=%d %s.length=%d", 2396 arrayObj->clazz->descriptor, start, len, arrayIdentifier, 2397 arrayObj->length); 2398 } 2399 2400 /* 2401 * Copy a section of a primitive array to a buffer. 2402 */ 2403 #define GET_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_REGION(_ctype, _jname) 2404 static void Get##_jname##ArrayRegion(JNIEnv* env, 2405 _ctype##Array jarr, jsize start, jsize len, _ctype* buf) 2406 { 2407 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2408 ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); 2409 _ctype* data = (_ctype*) (void*) arrayObj->contents; 2410 if (start < 0 || len < 0 || start + len > (int) arrayObj->length) { 2411 throwArrayRegionOutOfBounds(arrayObj, start, len, "src"); 2412 } else { 2413 memcpy(buf, data + start, len * sizeof(_ctype)); 2414 } 2415 } 2416 2417 /* 2418 * Copy a section of a primitive array from a buffer. 2419 */ 2420 #define SET_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_REGION(_ctype, _jname) 2421 static void Set##_jname##ArrayRegion(JNIEnv* env, 2422 _ctype##Array jarr, jsize start, jsize len, const _ctype* buf) 2423 { 2424 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2425 ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); 2426 _ctype* data = (_ctype*) (void*) arrayObj->contents; 2427 if (start < 0 || len < 0 || start + len > (int) arrayObj->length) { 2428 throwArrayRegionOutOfBounds(arrayObj, start, len, "dst"); 2429 } else { 2430 memcpy(data + start, buf, len * sizeof(_ctype)); 2431 } 2432 } 2433 2434 /* 2435 * 4-in-1: 2436 * Get<Type>ArrayElements 2437 * Release<Type>ArrayElements 2438 * Get<Type>ArrayRegion 2439 * Set<Type>ArrayRegion 2440 */ 2441 #define PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(_ctype, _jname) 2442 GET_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_ELEMENTS(_ctype, _jname); 2443 RELEASE_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_ELEMENTS(_ctype, _jname); 2444 GET_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_REGION(_ctype, _jname); 2445 SET_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_REGION(_ctype, _jname); 2446 2447 PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jboolean, Boolean); 2448 PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jbyte, Byte); 2449 PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jchar, Char); 2450 PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jshort, Short); 2451 PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jint, Int); 2452 PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jlong, Long); 2453 PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jfloat, Float); 2454 PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jdouble, Double); 2455 2456 /* 2457 * Register one or more native functions in one class. 2458 * 2459 * This can be called multiple times on the same method, allowing the 2460 * caller to redefine the method implementation at will. 2461 */ 2462 static jint RegisterNatives(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, 2463 const JNINativeMethod* methods, jint nMethods) 2464 { 2465 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2466 2467 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 2468 2469 if (gDvm.verboseJni) { 2470 ALOGI("[Registering JNI native methods for class %s]", 2471 clazz->descriptor); 2472 } 2473 2474 for (int i = 0; i < nMethods; i++) { 2475 if (!dvmRegisterJNIMethod(clazz, methods[i].name, 2476 methods[i].signature, methods[i].fnPtr)) 2477 { 2478 return JNI_ERR; 2479 } 2480 } 2481 return JNI_OK; 2482 } 2483 2484 /* 2485 * Un-register all native methods associated with the class. 2486 * 2487 * The JNI docs refer to this as a way to reload/relink native libraries, 2488 * and say it "should not be used in normal native code". In particular, 2489 * there is no need to do this during shutdown, and you do not need to do 2490 * this before redefining a method implementation with RegisterNatives. 2491 * 2492 * It‘s chiefly useful for a native "plugin"-style library that wasn‘t 2493 * loaded with System.loadLibrary() (since there‘s no way to unload those). 2494 * For example, the library could upgrade itself by: 2495 * 2496 * 1. call UnregisterNatives to unbind the old methods 2497 * 2. ensure that no code is still executing inside it (somehow) 2498 * 3. dlclose() the library 2499 * 4. dlopen() the new library 2500 * 5. use RegisterNatives to bind the methods from the new library 2501 * 2502 * The above can work correctly without the UnregisterNatives call, but 2503 * creates a window of opportunity in which somebody might try to call a 2504 * method that is pointing at unmapped memory, crashing the VM. In theory 2505 * the same guards that prevent dlclose() from unmapping executing code could 2506 * prevent that anyway, but with this we can be more thorough and also deal 2507 * with methods that only exist in the old or new form of the library (maybe 2508 * the lib wants to try the call and catch the UnsatisfiedLinkError). 2509 */ 2510 static jint UnregisterNatives(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz) { 2511 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2512 2513 ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); 2514 if (gDvm.verboseJni) { 2515 ALOGI("[Unregistering JNI native methods for class %s]", 2516 clazz->descriptor); 2517 } 2518 dvmUnregisterJNINativeMethods(clazz); 2519 return JNI_OK; 2520 } 2521 2522 /* 2523 * Lock the monitor. 2524 * 2525 * We have to track all monitor enters and exits, so that we can undo any 2526 * outstanding synchronization before the thread exits. 2527 */ 2528 static jint MonitorEnter(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) { 2529 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2530 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 2531 dvmLockObject(ts.self(), obj); 2532 trackMonitorEnter(ts.self(), obj); 2533 return JNI_OK; 2534 } 2535 2536 /* 2537 * Unlock the monitor. 2538 * 2539 * Throws an IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread 2540 * doesn‘t own the monitor. (dvmUnlockObject() takes care of the throw.) 2541 * 2542 * According to the 1.6 spec, it‘s legal to call here with an exception 2543 * pending. If this fails, we‘ll stomp the original exception. 2544 */ 2545 static jint MonitorExit(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) { 2546 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2547 Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 2548 bool success = dvmUnlockObject(ts.self(), obj); 2549 if (success) { 2550 trackMonitorExit(ts.self(), obj); 2551 } 2552 return success ? JNI_OK : JNI_ERR; 2553 } 2554 2555 /* 2556 * Return the JavaVM interface associated with the current thread. 2557 */ 2558 static jint GetJavaVM(JNIEnv* env, JavaVM** vm) { 2559 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2560 *vm = gDvmJni.jniVm; 2561 return (*vm == NULL) ? JNI_ERR : JNI_OK; 2562 } 2563 2564 /* 2565 * Copies "len" Unicode characters, from offset "start". 2566 */ 2567 static void GetStringRegion(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, jsize start, jsize len, jchar* buf) { 2568 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2569 StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr); 2570 int strLen = strObj->length(); 2571 if (((start|len) < 0) || (start + len > strLen)) { 2572 dvmThrowStringIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionWithRegion(strLen, start, len); 2573 return; 2574 } 2575 memcpy(buf, strObj->chars() + start, len * sizeof(u2)); 2576 } 2577 2578 /* 2579 * Translates "len" Unicode characters, from offset "start", into 2580 * modified UTF-8 encoding. 2581 */ 2582 static void GetStringUTFRegion(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, jsize start, jsize len, char* buf) { 2583 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2584 StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr); 2585 int strLen = strObj->length(); 2586 if (((start|len) < 0) || (start + len > strLen)) { 2587 dvmThrowStringIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionWithRegion(strLen, start, len); 2588 return; 2589 } 2590 dvmGetStringUtfRegion(strObj, start, len, buf); 2591 } 2592 2593 /* 2594 * Get a raw pointer to array data. 2595 * 2596 * The caller is expected to call "release" before doing any JNI calls 2597 * or blocking I/O operations. 2598 * 2599 * We need to pin the memory or block GC. 2600 */ 2601 static void* GetPrimitiveArrayCritical(JNIEnv* env, jarray jarr, jboolean* isCopy) { 2602 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2603 ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); 2604 pinPrimitiveArray(arrayObj); 2605 void* data = arrayObj->contents; 2606 if (UNLIKELY(isCopy != NULL)) { 2607 *isCopy = JNI_FALSE; 2608 } 2609 return data; 2610 } 2611 2612 /* 2613 * Release an array obtained with GetPrimitiveArrayCritical. 2614 */ 2615 static void ReleasePrimitiveArrayCritical(JNIEnv* env, jarray jarr, void* carray, jint mode) { 2616 if (mode != JNI_COMMIT) { 2617 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2618 ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); 2619 unpinPrimitiveArray(arrayObj); 2620 } 2621 } 2622 2623 /* 2624 * Like GetStringChars, but with restricted use. 2625 */ 2626 static const jchar* GetStringCritical(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, jboolean* isCopy) { 2627 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2628 2629 StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr); 2630 ArrayObject* strChars = strObj->array(); 2631 2632 pinPrimitiveArray(strChars); 2633 2634 const u2* data = strObj->chars(); 2635 if (isCopy != NULL) { 2636 *isCopy = JNI_FALSE; 2637 } 2638 return (jchar*) data; 2639 } 2640 2641 /* 2642 * Like ReleaseStringChars, but with restricted use. 2643 */ 2644 static void ReleaseStringCritical(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, const jchar* carray) { 2645 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2646 StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr); 2647 ArrayObject* strChars = strObj->array(); 2648 unpinPrimitiveArray(strChars); 2649 } 2650 2651 /* 2652 * Create a new weak global reference. 2653 */ 2654 static jweak NewWeakGlobalRef(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) { 2655 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2656 Object *obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); 2657 return (jweak) addWeakGlobalReference(obj); 2658 } 2659 2660 /* 2661 * Delete the specified weak global reference. 2662 */ 2663 static void DeleteWeakGlobalRef(JNIEnv* env, jweak wref) { 2664 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2665 deleteWeakGlobalReference(wref); 2666 } 2667 2668 /* 2669 * Quick check for pending exceptions. 2670 * 2671 * TODO: we should be able to skip the enter/exit macros here. 2672 */ 2673 static jboolean ExceptionCheck(JNIEnv* env) { 2674 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2675 return dvmCheckException(ts.self()); 2676 } 2677 2678 /* 2679 * Returns the type of the object referred to by "obj". It can be local, 2680 * global, or weak global. 2681 * 2682 * In the current implementation, references can be global and local at 2683 * the same time, so while the return value is accurate it may not tell 2684 * the whole story. 2685 */ 2686 static jobjectRefType GetObjectRefType(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) { 2687 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2688 return dvmGetJNIRefType(ts.self(), jobj); 2689 } 2690 2691 /* 2692 * Allocate and return a new java.nio.ByteBuffer for this block of memory. 2693 */ 2694 static jobject NewDirectByteBuffer(JNIEnv* env, void* address, jlong capacity) { 2695 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2696 2697 if (capacity < 0) { 2698 ALOGE("JNI ERROR (app bug): negative buffer capacity: %lld", capacity); 2699 ReportJniError(); 2700 } 2701 if (address == NULL && capacity != 0) { 2702 ALOGE("JNI ERROR (app bug): non-zero capacity for NULL pointer: %lld", capacity); 2703 ReportJniError(); 2704 } 2705 2706 /* create an instance of java.nio.DirectByteBuffer */ 2707 ClassObject* bufferClazz = gDvm.classJavaNioDirectByteBuffer; 2708 if (!dvmIsClassInitialized(bufferClazz) && !dvmInitClass(bufferClazz)) { 2709 return NULL; 2710 } 2711 Object* newObj = dvmAllocObject(bufferClazz, ALLOC_DONT_TRACK); 2712 if (newObj == NULL) { 2713 return NULL; 2714 } 2715 /* call the constructor */ 2716 jobject result = addLocalReference(ts.self(), newObj); 2717 JValue unused; 2718 dvmCallMethod(ts.self(), gDvm.methJavaNioDirectByteBuffer_init, 2719 newObj, &unused, (jlong) address, (jint) capacity); 2720 if (dvmGetException(ts.self()) != NULL) { 2721 deleteLocalReference(ts.self(), result); 2722 return NULL; 2723 } 2724 return result; 2725 } 2726 2727 /* 2728 * Get the starting address of the buffer for the specified java.nio.Buffer. 2729 * 2730 * If this is not a "direct" buffer, we return NULL. 2731 */ 2732 static void* GetDirectBufferAddress(JNIEnv* env, jobject jbuf) { 2733 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2734 2735 // All Buffer objects have an effectiveDirectAddress field. 2736 Object* bufObj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jbuf); 2737 return (void*) dvmGetFieldLong(bufObj, gDvm.offJavaNioBuffer_effectiveDirectAddress); 2738 } 2739 2740 /* 2741 * Get the capacity of the buffer for the specified java.nio.Buffer. 2742 * 2743 * Returns -1 if the object is not a direct buffer. (We actually skip 2744 * this check, since it‘s expensive to determine, and just return the 2745 * capacity regardless.) 2746 */ 2747 static jlong GetDirectBufferCapacity(JNIEnv* env, jobject jbuf) { 2748 ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); 2749 2750 /* 2751 * The capacity is always in the Buffer.capacity field. 2752 * 2753 * (The "check" version should verify that this is actually a Buffer, 2754 * but we‘re not required to do so here.) 2755 */ 2756 Object* buf = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jbuf); 2757 return dvmGetFieldInt(buf, gDvm.offJavaNioBuffer_capacity); 2758 } 2759 2760 2761 /* 2762 * =========================================================================== 2763 * JNI invocation functions 2764 * =========================================================================== 2765 */ 2766 2767 /* 2768 * Handle AttachCurrentThread{AsDaemon}. 2769 * 2770 * We need to make sure the VM is actually running. For example, if we start 2771 * up, issue an Attach, and the VM exits almost immediately, by the time the 2772 * attaching happens the VM could already be shutting down. 2773 * 2774 * It‘s hard to avoid a race condition here because we don‘t want to hold 2775 * a lock across the entire operation. What we can do is temporarily 2776 * increment the thread count to prevent a VM exit. 2777 * 2778 * This could potentially still have problems if a daemon thread calls here 2779 * while the VM is shutting down. dvmThreadSelf() will work, since it just 2780 * uses pthread TLS, but dereferencing "vm" could fail. Such is life when 2781 * you shut down a VM while threads are still running inside it. 2782 * 2783 * Remember that some code may call this as a way to find the per-thread 2784 * JNIEnv pointer. Don‘t do excess work for that case. 2785 */ 2786 static jint attachThread(JavaVM* vm, JNIEnv** p_env, void* thr_args, bool isDaemon) { 2787 JavaVMAttachArgs* args = (JavaVMAttachArgs*) thr_args; 2788 2789 /* 2790 * Return immediately if we‘re already one with the VM. 2791 */ 2792 Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf(); 2793 if (self != NULL) { 2794 *p_env = self->jniEnv; 2795 return JNI_OK; 2796 } 2797 2798 /* 2799 * No threads allowed in zygote mode. 2800 */ 2801 if (gDvm.zygote) { 2802 return JNI_ERR; 2803 } 2804 2805 /* increment the count to keep the VM from bailing while we run */ 2806 dvmLockThreadList(NULL); 2807 if (gDvm.nonDaemonThreadCount == 0) { 2808 // dead or dying 2809 ALOGV("Refusing to attach thread ‘%s‘ -- VM is shutting down", 2810 (thr_args == NULL) ? "(unknown)" : args->name); 2811 dvmUnlockThreadList(); 2812 return JNI_ERR; 2813 } 2814 gDvm.nonDaemonThreadCount++; 2815 dvmUnlockThreadList(); 2816 2817 /* tweak the JavaVMAttachArgs as needed */ 2818 JavaVMAttachArgs argsCopy; 2819 if (args == NULL) { 2820 /* allow the v1.1 calling convention */ 2821 argsCopy.version = JNI_VERSION_1_2; 2822 argsCopy.name = NULL; 2823 argsCopy.group = (jobject) dvmGetMainThreadGroup(); 2824 } else { 2825 if (dvmIsBadJniVersion(args->version)) { 2826 ALOGE("Bad JNI version passed to %s: %d", 2827 (isDaemon ? "AttachCurrentThreadAsDaemon" : "AttachCurrentThread"), 2828 args->version); 2829 return JNI_EVERSION; 2830 } 2831 2832 argsCopy.version = args->version; 2833 argsCopy.name = args->name; 2834 if (args->group != NULL) { 2835 argsCopy.group = (jobject) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(NULL, args->group); 2836 } else { 2837 argsCopy.group = (jobject) dvmGetMainThreadGroup(); 2838 } 2839 } 2840 2841 bool result = dvmAttachCurrentThread(&argsCopy, isDaemon); 2842 2843 /* restore the count */ 2844 dvmLockThreadList(NULL); 2845 gDvm.nonDaemonThreadCount--; 2846 dvmUnlockThreadList(); 2847 2848 /* 2849 * Change the status to indicate that we‘re out in native code. This 2850 * call is not guarded with state-change macros, so we have to do it 2851 * by hand. 2852 */ 2853 if (result) { 2854 self = dvmThreadSelf(); 2855 assert(self != NULL); 2856 dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_NATIVE); 2857 *p_env = self->jniEnv; 2858 return JNI_OK; 2859 } else { 2860 return JNI_ERR; 2861 } 2862 } 2863 2864 /* 2865 * Attach the current thread to the VM. If the thread is already attached, 2866 * this is a no-op. 2867 */ 2868 static jint AttachCurrentThread(JavaVM* vm, JNIEnv** p_env, void* thr_args) { 2869 return attachThread(vm, p_env, thr_args, false); 2870 } 2871 2872 /* 2873 * Like AttachCurrentThread, but set the "daemon" flag. 2874 */ 2875 static jint AttachCurrentThreadAsDaemon(JavaVM* vm, JNIEnv** p_env, void* thr_args) 2876 { 2877 return attachThread(vm, p_env, thr_args, true); 2878 } 2879 2880 /* 2881 * Dissociate the current thread from the VM. 2882 */ 2883 static jint DetachCurrentThread(JavaVM* vm) { 2884 Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf(); 2885 if (self == NULL) { 2886 /* not attached, can‘t do anything */ 2887 return JNI_ERR; 2888 } 2889 2890 /* switch to "running" to check for suspension */ 2891 dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_RUNNING); 2892 2893 /* detach the thread */ 2894 dvmDetachCurrentThread(); 2895 2896 /* (no need to change status back -- we have no status) */ 2897 return JNI_OK; 2898 } 2899 2900 /* 2901 * If current thread is attached to VM, return the associated JNIEnv. 2902 * Otherwise, stuff NULL in and return JNI_EDETACHED. 2903 * 2904 * JVMTI overloads this by specifying a magic value for "version", so we 2905 * do want to check that here. 2906 */ 2907 static jint GetEnv(JavaVM* vm, void** env, jint version) { 2908 Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf(); 2909 2910 // GetEnv also accepts JNI_VERSION_1_1, but always returns a JNIEnv* 2911 // corresponding to the most current supported JNI version. 2912 if (dvmIsBadJniVersion(version) && version != JNI_VERSION_1_1) { 2913 ALOGE("Bad JNI version passed to GetEnv: %d", version); 2914 return JNI_EVERSION; 2915 } 2916 2917 if (self == NULL) { 2918 *env = NULL; 2919 } else { 2920 /* TODO: status change is probably unnecessary */ 2921 dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_RUNNING); 2922 *env = (void*) dvmGetThreadJNIEnv(self); 2923 dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_NATIVE); 2924 } 2925 return (*env != NULL) ? JNI_OK : JNI_EDETACHED; 2926 } 2927 2928 /* 2929 * Destroy the VM. This may be called from any thread. 2930 * 2931 * If the current thread is attached, wait until the current thread is 2932 * the only non-daemon user-level thread. If the current thread is not 2933 * attached, we attach it and do the processing as usual. (If the attach 2934 * fails, it‘s probably because all the non-daemon threads have already 2935 * exited and the VM doesn‘t want to let us back in.) 2936 * 2937 * TODO: we don‘t really deal with the situation where more than one thread 2938 * has called here. One thread wins, the other stays trapped waiting on 2939 * the condition variable forever. Not sure this situation is interesting 2940 * in real life. 2941 */ 2942 static jint DestroyJavaVM(JavaVM* vm) { 2943 JavaVMExt* ext = (JavaVMExt*) vm; 2944 if (ext == NULL) { 2945 return JNI_ERR; 2946 } 2947 2948 if (gDvm.verboseShutdown) { 2949 ALOGD("DestroyJavaVM waiting for non-daemon threads to exit"); 2950 } 2951 2952 /* 2953 * Sleep on a condition variable until it‘s okay to exit. 2954 */ 2955 Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf(); 2956 if (self == NULL) { 2957 JNIEnv* tmpEnv; 2958 if (AttachCurrentThread(vm, &tmpEnv, NULL) != JNI_OK) { 2959 ALOGV("Unable to reattach main for Destroy; assuming VM is shutting down (count=%d)", 2960 gDvm.nonDaemonThreadCount); 2961 goto shutdown; 2962 } else { 2963 ALOGV("Attached to wait for shutdown in Destroy"); 2964 } 2965 } 2966 dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_VMWAIT); 2967 2968 dvmLockThreadList(self); 2969 gDvm.nonDaemonThreadCount--; // remove current thread from count 2970 2971 while (gDvm.nonDaemonThreadCount > 0) { 2972 pthread_cond_wait(&gDvm.vmExitCond, &gDvm.threadListLock); 2973 } 2974 2975 dvmUnlockThreadList(); 2976 self = NULL; 2977 2978 shutdown: 2979 // TODO: call System.exit() to run any registered shutdown hooks 2980 // (this may not return -- figure out how this should work) 2981 2982 if (gDvm.verboseShutdown) { 2983 ALOGD("DestroyJavaVM shutting VM down"); 2984 } 2985 dvmShutdown(); 2986 2987 // TODO - free resources associated with JNI-attached daemon threads 2988 free(ext->envList); 2989 free(ext); 2990 2991 return JNI_OK; 2992 } 2993 2994 2995 /* 2996 * =========================================================================== 2997 * Function tables 2998 * =========================================================================== 2999 */ 3000 3001 static const struct JNINativeInterface gNativeInterface = { 3002 NULL, 3003 NULL, 3004 NULL, 3005 NULL, 3006 3007 GetVersion, 3008 3009 DefineClass, 3010 FindClass, 3011 3012 FromReflectedMethod, 3013 FromReflectedField, 3014 ToReflectedMethod, 3015 3016 GetSuperclass, 3017 IsAssignableFrom, 3018 3019 ToReflectedField, 3020 3021 Throw, 3022 ThrowNew, 3023 ExceptionOccurred, 3024 ExceptionDescribe, 3025 ExceptionClear, 3026 FatalError, 3027 3028 PushLocalFrame, 3029 PopLocalFrame, 3030 3031 NewGlobalRef, 3032 DeleteGlobalRef, 3033 DeleteLocalRef, 3034 IsSameObject, 3035 NewLocalRef, 3036 EnsureLocalCapacity, 3037 3038 AllocObject, 3039 NewObject, 3040 NewObjectV, 3041 NewObjectA, 3042 3043 GetObjectClass, 3044 IsInstanceOf, 3045 3046 GetMethodID, 3047 3048 CallObjectMethod, 3049 CallObjectMethodV, 3050 CallObjectMethodA, 3051 CallBooleanMethod, 3052 CallBooleanMethodV, 3053 CallBooleanMethodA, 3054 CallByteMethod, 3055 CallByteMethodV, 3056 CallByteMethodA, 3057 CallCharMethod, 3058 CallCharMethodV, 3059 CallCharMethodA, 3060 CallShortMethod, 3061 CallShortMethodV, 3062 CallShortMethodA, 3063 CallIntMethod, 3064 CallIntMethodV, 3065 CallIntMethodA, 3066 CallLongMethod, 3067 CallLongMethodV, 3068 CallLongMethodA, 3069 CallFloatMethod, 3070 CallFloatMethodV, 3071 CallFloatMethodA, 3072 CallDoubleMethod, 3073 CallDoubleMethodV, 3074 CallDoubleMethodA, 3075 CallVoidMethod, 3076 CallVoidMethodV, 3077 CallVoidMethodA, 3078 3079 CallNonvirtualObjectMethod, 3080 CallNonvirtualObjectMethodV, 3081 CallNonvirtualObjectMethodA, 3082 CallNonvirtualBooleanMethod, 3083 CallNonvirtualBooleanMethodV, 3084 CallNonvirtualBooleanMethodA, 3085 CallNonvirtualByteMethod, 3086 CallNonvirtualByteMethodV, 3087 CallNonvirtualByteMethodA, 3088 CallNonvirtualCharMethod, 3089 CallNonvirtualCharMethodV, 3090 CallNonvirtualCharMethodA, 3091 CallNonvirtualShortMethod, 3092 CallNonvirtualShortMethodV, 3093 CallNonvirtualShortMethodA, 3094 CallNonvirtualIntMethod, 3095 CallNonvirtualIntMethodV, 3096 CallNonvirtualIntMethodA, 3097 CallNonvirtualLongMethod, 3098 CallNonvirtualLongMethodV, 3099 CallNonvirtualLongMethodA, 3100 CallNonvirtualFloatMethod, 3101 CallNonvirtualFloatMethodV, 3102 CallNonvirtualFloatMethodA, 3103 CallNonvirtualDoubleMethod, 3104 CallNonvirtualDoubleMethodV, 3105 CallNonvirtualDoubleMethodA, 3106 CallNonvirtualVoidMethod, 3107 CallNonvirtualVoidMethodV, 3108 CallNonvirtualVoidMethodA, 3109 3110 GetFieldID, 3111 3112 GetObjectField, 3113 GetBooleanField, 3114 GetByteField, 3115 GetCharField, 3116 GetShortField, 3117 GetIntField, 3118 GetLongField, 3119 GetFloatField, 3120 GetDoubleField, 3121 SetObjectField, 3122 SetBooleanField, 3123 SetByteField, 3124 SetCharField, 3125 SetShortField, 3126 SetIntField, 3127 SetLongField, 3128 SetFloatField, 3129 SetDoubleField, 3130 3131 GetStaticMethodID, 3132 3133 CallStaticObjectMethod, 3134 CallStaticObjectMethodV, 3135 CallStaticObjectMethodA, 3136 CallStaticBooleanMethod, 3137 CallStaticBooleanMethodV, 3138 CallStaticBooleanMethodA, 3139 CallStaticByteMethod, 3140 CallStaticByteMethodV, 3141 CallStaticByteMethodA, 3142 CallStaticCharMethod, 3143 CallStaticCharMethodV, 3144 CallStaticCharMethodA, 3145 CallStaticShortMethod, 3146 CallStaticShortMethodV, 3147 CallStaticShortMethodA, 3148 CallStaticIntMethod, 3149 CallStaticIntMethodV, 3150 CallStaticIntMethodA, 3151 CallStaticLongMethod, 3152 CallStaticLongMethodV, 3153 CallStaticLongMethodA, 3154 CallStaticFloatMethod, 3155 CallStaticFloatMethodV, 3156 CallStaticFloatMethodA, 3157 CallStaticDoubleMethod, 3158 CallStaticDoubleMethodV, 3159 CallStaticDoubleMethodA, 3160 CallStaticVoidMethod, 3161 CallStaticVoidMethodV, 3162 CallStaticVoidMethodA, 3163 3164 GetStaticFieldID, 3165 3166 GetStaticObjectField, 3167 GetStaticBooleanField, 3168 GetStaticByteField, 3169 GetStaticCharField, 3170 GetStaticShortField, 3171 GetStaticIntField, 3172 GetStaticLongField, 3173 GetStaticFloatField, 3174 GetStaticDoubleField, 3175 3176 SetStaticObjectField, 3177 SetStaticBooleanField, 3178 SetStaticByteField, 3179 SetStaticCharField, 3180 SetStaticShortField, 3181 SetStaticIntField, 3182 SetStaticLongField, 3183 SetStaticFloatField, 3184 SetStaticDoubleField, 3185 3186 NewString, 3187 3188 GetStringLength, 3189 GetStringChars, 3190 ReleaseStringChars, 3191 3192 NewStringUTF, 3193 GetStringUTFLength, 3194 GetStringUTFChars, 3195 ReleaseStringUTFChars, 3196 3197 GetArrayLength, 3198 NewObjectArray, 3199 GetObjectArrayElement, 3200 SetObjectArrayElement, 3201 3202 NewBooleanArray, 3203 NewByteArray, 3204 NewCharArray, 3205 NewShortArray, 3206 NewIntArray, 3207 NewLongArray, 3208 NewFloatArray, 3209 NewDoubleArray, 3210 3211 GetBooleanArrayElements, 3212 GetByteArrayElements, 3213 GetCharArrayElements, 3214 GetShortArrayElements, 3215 GetIntArrayElements, 3216 GetLongArrayElements, 3217 GetFloatArrayElements, 3218 GetDoubleArrayElements, 3219 3220 ReleaseBooleanArrayElements, 3221 ReleaseByteArrayElements, 3222 ReleaseCharArrayElements, 3223 ReleaseShortArrayElements, 3224 ReleaseIntArrayElements, 3225 ReleaseLongArrayElements, 3226 ReleaseFloatArrayElements, 3227 ReleaseDoubleArrayElements, 3228 3229 GetBooleanArrayRegion, 3230 GetByteArrayRegion, 3231 GetCharArrayRegion, 3232 GetShortArrayRegion, 3233 GetIntArrayRegion, 3234 GetLongArrayRegion, 3235 GetFloatArrayRegion, 3236 GetDoubleArrayRegion, 3237 SetBooleanArrayRegion, 3238 SetByteArrayRegion, 3239 SetCharArrayRegion, 3240 SetShortArrayRegion, 3241 SetIntArrayRegion, 3242 SetLongArrayRegion, 3243 SetFloatArrayRegion, 3244 SetDoubleArrayRegion, 3245 3246 RegisterNatives, 3247 UnregisterNatives, 3248 3249 MonitorEnter, 3250 MonitorExit, 3251 3252 GetJavaVM, 3253 3254 GetStringRegion, 3255 GetStringUTFRegion, 3256 3257 GetPrimitiveArrayCritical, 3258 ReleasePrimitiveArrayCritical, 3259 3260 GetStringCritical, 3261 ReleaseStringCritical, 3262 3263 NewWeakGlobalRef, 3264 DeleteWeakGlobalRef, 3265 3266 ExceptionCheck, 3267 3268 NewDirectByteBuffer, 3269 GetDirectBufferAddress, 3270 GetDirectBufferCapacity, 3271 3272 GetObjectRefType 3273 }; 3274 3275 static const struct JNIInvokeInterface gInvokeInterface = { 3276 NULL, 3277 NULL, 3278 NULL, 3279 3280 DestroyJavaVM, 3281 AttachCurrentThread, 3282 DetachCurrentThread, 3283 3284 GetEnv, 3285 3286 AttachCurrentThreadAsDaemon, 3287 }; 3288 3289 /* 3290 * =========================================================================== 3291 * VM/Env creation 3292 * =========================================================================== 3293 */ 3294 3295 /* 3296 * Create a new JNIEnv struct and add it to the VM‘s list. 3297 * 3298 * "self" will be NULL for the main thread, since the VM hasn‘t started 3299 * yet; the value will be filled in later. 3300 */ 3301 JNIEnv* dvmCreateJNIEnv(Thread* self) { 3302 JavaVMExt* vm = (JavaVMExt*) gDvmJni.jniVm; 3303 3304 //if (self != NULL) 3305 // ALOGI("Ent CreateJNIEnv: threadid=%d %p", self->threadId, self); 3306 3307 assert(vm != NULL); 3308 3309 JNIEnvExt* newEnv = (JNIEnvExt*) calloc(1, sizeof(JNIEnvExt)); 3310 newEnv->funcTable = &gNativeInterface; 3311 if (self != NULL) { 3312 dvmSetJniEnvThreadId((JNIEnv*) newEnv, self); 3313 assert(newEnv->envThreadId != 0); 3314 } else { 3315 /* make it obvious if we fail to initialize these later */ 3316 newEnv->envThreadId = 0x77777775; 3317 newEnv->self = (Thread*) 0x77777779; 3318 } 3319 if (gDvmJni.useCheckJni) { 3320 dvmUseCheckedJniEnv(newEnv); 3321 } 3322 3323 ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&vm->envListLock); 3324 3325 /* insert at head of list */ 3326 newEnv->next = vm->envList; 3327 assert(newEnv->prev == NULL); 3328 if (vm->envList == NULL) { 3329 // rare, but possible 3330 vm->envList = newEnv; 3331 } else { 3332 vm->envList->prev = newEnv; 3333 } 3334 vm->envList = newEnv; 3335 3336 //if (self != NULL) 3337 // ALOGI("Xit CreateJNIEnv: threadid=%d %p", self->threadId, self); 3338 return (JNIEnv*) newEnv; 3339 } 3340 3341 /* 3342 * Remove a JNIEnv struct from the list and free it. 3343 */ 3344 void dvmDestroyJNIEnv(JNIEnv* env) { 3345 if (env == NULL) { 3346 return; 3347 } 3348 3349 //ALOGI("Ent DestroyJNIEnv: threadid=%d %p", self->threadId, self); 3350 3351 JNIEnvExt* extEnv = (JNIEnvExt*) env; 3352 JavaVMExt* vm = (JavaVMExt*) gDvmJni.jniVm; 3353 3354 ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&vm->envListLock); 3355 3356 if (extEnv == vm->envList) { 3357 assert(extEnv->prev == NULL); 3358 vm->envList = extEnv->next; 3359 } else { 3360 assert(extEnv->prev != NULL); 3361 extEnv->prev->next = extEnv->next; 3362 } 3363 if (extEnv->next != NULL) { 3364 extEnv->next->prev = extEnv->prev; 3365 } 3366 3367 free(env); 3368 //ALOGI("Xit DestroyJNIEnv: threadid=%d %p", self->threadId, self); 3369 } 3370 3371 /* 3372 * Enable "checked JNI" after the VM has partially started. This must 3373 * only be called in "zygote" mode, when we have one thread running. 3374 * 3375 * This doesn‘t attempt to rewrite the JNI call bridge associated with 3376 * native methods, so we won‘t get those checks for any methods that have 3377 * already been resolved. 3378 */ 3379 void dvmLateEnableCheckedJni() { 3380 JNIEnvExt* extEnv = dvmGetJNIEnvForThread(); 3381 if (extEnv == NULL) { 3382 ALOGE("dvmLateEnableCheckedJni: thread has no JNIEnv"); 3383 return; 3384 } 3385 JavaVMExt* extVm = (JavaVMExt*) gDvmJni.jniVm; 3386 assert(extVm != NULL); 3387 3388 if (!gDvmJni.useCheckJni) { 3389 ALOGD("Late-enabling CheckJNI"); 3390 dvmUseCheckedJniVm(extVm); 3391 dvmUseCheckedJniEnv(extEnv); 3392 } else { 3393 ALOGD("Not late-enabling CheckJNI (already on)"); 3394 } 3395 } 3396 3397 /* 3398 * Not supported. 3399 */ 3400 jint JNI_GetDefaultJavaVMInitArgs(void* vm_args) { 3401 return JNI_ERR; 3402 } 3403 3404 /* 3405 * Return a buffer full of created VMs. 3406 * 3407 * We always have zero or one. 3408 */ 3409 jint JNI_GetCreatedJavaVMs(JavaVM** vmBuf, jsize bufLen, jsize* nVMs) { 3410 if (gDvmJni.jniVm != NULL) { 3411 *nVMs = 1; 3412 if (bufLen > 0) { 3413 *vmBuf++ = gDvmJni.jniVm; 3414 } 3415 } else { 3416 *nVMs = 0; 3417 } 3418 return JNI_OK; 3419 } 3420 3421 /* 3422 * Create a new VM instance. 3423 * 3424 * The current thread becomes the main VM thread. We return immediately, 3425 * which effectively means the caller is executing in a native method. 3426 */ 3427 jint JNI_CreateJavaVM(JavaVM** p_vm, JNIEnv** p_env, void* vm_args) { 3428 const JavaVMInitArgs* args = (JavaVMInitArgs*) vm_args; 3429 if (dvmIsBadJniVersion(args->version)) { 3430 ALOGE("Bad JNI version passed to CreateJavaVM: %d", args->version); 3431 return JNI_EVERSION; 3432 } 3433 3434 // TODO: don‘t allow creation of multiple VMs -- one per customer for now 3435 3436 /* zero globals; not strictly necessary the first time a VM is started */ 3437 memset(&gDvm, 0, sizeof(gDvm)); 3438 3439 /* 3440 * Set up structures for JNIEnv and VM. 3441 */ 3442 JavaVMExt* pVM = (JavaVMExt*) calloc(1, sizeof(JavaVMExt)); 3443 pVM->funcTable = &gInvokeInterface; 3444 pVM->envList = NULL; 3445 dvmInitMutex(&pVM->envListLock); 3446 3447 UniquePtr<const char*[]> argv(new const char*[args->nOptions]); 3448 memset(argv.get(), 0, sizeof(char*) * (args->nOptions)); 3449 3450 /* 3451 * Convert JNI args to argv. 3452 * 3453 * We have to pull out vfprintf/exit/abort, because they use the 3454 * "extraInfo" field to pass function pointer "hooks" in. We also 3455 * look for the -Xcheck:jni stuff here. 3456 */ 3457 int argc = 0; 3458 for (int i = 0; i < args->nOptions; i++) { 3459 const char* optStr = args->options[i].optionString; 3460 if (optStr == NULL) { 3461 dvmFprintf(stderr, "ERROR: CreateJavaVM failed: argument %d was NULL\n", i); 3462 return JNI_ERR; 3463 } else if (strcmp(optStr, "vfprintf") == 0) { 3464 gDvm.vfprintfHook = (int (*)(FILE *, const char*, va_list))args->options[i].extraInfo; 3465 } else if (strcmp(optStr, "exit") == 0) { 3466 gDvm.exitHook = (void (*)(int)) args->options[i].extraInfo; 3467 } else if (strcmp(optStr, "abort") == 0) { 3468 gDvm.abortHook = (void (*)(void))args->options[i].extraInfo; 3469 } else if (strcmp(optStr, "sensitiveThread") == 0) { 3470 gDvm.isSensitiveThreadHook = (bool (*)(void))args->options[i].extraInfo; 3471 } else if (strcmp(optStr, "-Xcheck:jni") == 0) { 3472 gDvmJni.useCheckJni = true; 3473 } else if (strncmp(optStr, "-Xjniopts:", 10) == 0) { 3474 char* jniOpts = strdup(optStr + 10); 3475 size_t jniOptCount = 1; 3476 for (char* p = jniOpts; *p != 0; ++p) { 3477 if (*p == ‘,‘) { 3478 ++jniOptCount; 3479 *p = 0; 3480 } 3481 } 3482 char* jniOpt = jniOpts; 3483 for (size_t i = 0; i < jniOptCount; ++i) { 3484 if (strcmp(jniOpt, "warnonly") == 0) { 3485 gDvmJni.warnOnly = true; 3486 } else if (strcmp(jniOpt, "forcecopy") == 0) { 3487 gDvmJni.forceCopy = true; 3488 } else if (strcmp(jniOpt, "logThirdPartyJni") == 0) { 3489 gDvmJni.logThirdPartyJni = true; 3490 } else { 3491 dvmFprintf(stderr, "ERROR: CreateJavaVM failed: unknown -Xjniopts option ‘%s‘\n", 3492 jniOpt); 3493 free(pVM); 3494 free(jniOpts); 3495 return JNI_ERR; 3496 } 3497 jniOpt += strlen(jniOpt) + 1; 3498 } 3499 free(jniOpts); 3500 } else { 3501 /* regular option */ 3502 argv[argc++] = optStr; 3503 } 3504 } 3505 3506 if (gDvmJni.useCheckJni) { 3507 dvmUseCheckedJniVm(pVM); 3508 } 3509 3510 if (gDvmJni.jniVm != NULL) { 3511 dvmFprintf(stderr, "ERROR: Dalvik only supports one VM per process\n"); 3512 free(pVM); 3513 return JNI_ERR; 3514 } 3515 gDvmJni.jniVm = (JavaVM*) pVM; 3516 3517 /* 3518 * Create a JNIEnv for the main thread. We need to have something set up 3519 * here because some of the class initialization we do when starting 3520 * up the VM will call into native code. 3521 */ 3522 JNIEnvExt* pEnv = (JNIEnvExt*) dvmCreateJNIEnv(NULL); 3523 3524 /* Initialize VM. */ 3525 gDvm.initializing = true; 3526 std::string status = 3527 dvmStartup(argc, argv.get(), args->ignoreUnrecognized, (JNIEnv*)pEnv); 3528 gDvm.initializing = false; 3529 3530 if (!status.empty()) { 3531 free(pEnv); 3532 free(pVM); 3533 ALOGW("CreateJavaVM failed: %s", status.c_str()); 3534 return JNI_ERR; 3535 } 3536 3537 /* 3538 * Success! Return stuff to caller. 3539 */ 3540 dvmChangeStatus(NULL, THREAD_NATIVE); 3541 *p_env = (JNIEnv*) pEnv; 3542 *p_vm = (JavaVM*) pVM; 3543 ALOGV("CreateJavaVM succeeded"); 3544 return JNI_OK; 3545 }
拿2.3.3的
print(GetString(R1,-1, ASCSTR_C)),使用0 * print(GetString(DbgDword(R2+0x10),-1, ASCSTR_C)) 跟踪而不断下来,虽然文档说‘void‘ means that function returns no meaningful value (always 0),但是还会段下来,乘以0就不一样,即运行语句又判断值。
IDA的帮助文档
// Print variables in the message window // This function print text representation of all its arguments to the output window. // This function can be used to debug IDC scripts void print (...);
Alphabetical list of IDC functions
The following conventions are used in the function descriptions:
‘ea‘ is a linear address ‘success‘ is 0 if a function fails, 1 otherwise ‘void‘ means that function returns no meaningful value (always 0) ‘anyvalue‘ means that function may return value of any type
下面一个截图跟踪方法调用,最后到我们的jni方法。
看这里http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/8923483,了解到注册jni方法以后再调用jni方法需要经过最直接看出的就是第一二参数变量等准备,这个来自注册时由Dalvik虚拟机的启动选项来为即将要注册的JNI选择一个合适的Bridge函数。以后通过这个Bridge函数(DalvikBridgeFunc)调用你的jni方法。但是这里有2类,每类4个。一般只有能选择1类,则对于jni方法调用存在4种调用过程。正如前面描述,从哪个版本开始就不会出现了,已经只有 一个了。
Dalvik虚拟机提供的Bridge函数主要是分为两类。第一类Bridge函数在调用完成JNI方法之后,会检查该JNI方法的返回结果是否与声明的一致,这是因为一个声明返回String的JNI方法在执行时返回的可能会是一个Byte Array。如果不一致,取决于Dalvik虚拟机的启动选项,它可能会停机。第二类Bridge函数不对JNI方法的返回结果进行上述检查。选择哪一类Bridge函数可以通过-Xcheck:jni选项来决定。不过由于检查一个JNI方法的返回结果是否与声明的一致是很耗时的,因此,我们一般都不会使用第一类Bridge函数。
此外,每一类Bridge函数又分为四个子类:Genernal、Sync、VirtualNoRef和StaticNoRef,它们的选择规则为:
1. 一个JNI方法的参数列表中如果包含有引用类型的参数,那么对应的Bridge函数就是Genernal类型的,即为dvmCallJNIMethod_general或者dvmCheckCallJNIMethod_general。
2. 一个JNI方法如果声明为同步方法,即带有synchronized修饰符,那么对应的Bridge函数就是Sync类型的,即为dvmCallJNIMethod_synchronized或者dvmCheckCallJNIMethod_synchronized。
3. 一个JNI方法的参数列表中如果不包含有引用类型的参数,并且它是一个虚成员函数,那么对应的Bridge函数就是kJNIVirtualNoRef类型的,即为dvmCallJNIMethod_virtualNoRef或者dvmCheckCallJNIMethod_virtualNoRef。
4. 一个JNI方法的参数列表中如果不包含有引用类型的参数,并且它是一个静态成员函数,那么对应的Bridge函数就是StaticNoRef类型的,即为dvmCallJNIMethod_staticNoRef或者dvmCheckCallJNIMethod_staticNoRef。
每一类Bridge函数之所以要划分为上述四个子类,是因为每一个子类的Bridge函数在调用真正的JNI方法之前,所要进行的准备工作是不一样的。例如,Genernal类型的Bridge函数需要为引用类型的参数增加一个本地引用,避免它在JNI方法执行的过程中被回收。又如,Sync类型的Bridge函数在调用JNI方法之前,需要执行同步原始,以避免多线程访问的竞争问题。
void dvmCallJNIMethod_general(const u4* args, JValue* pResult, const Method* method, Thread* self)
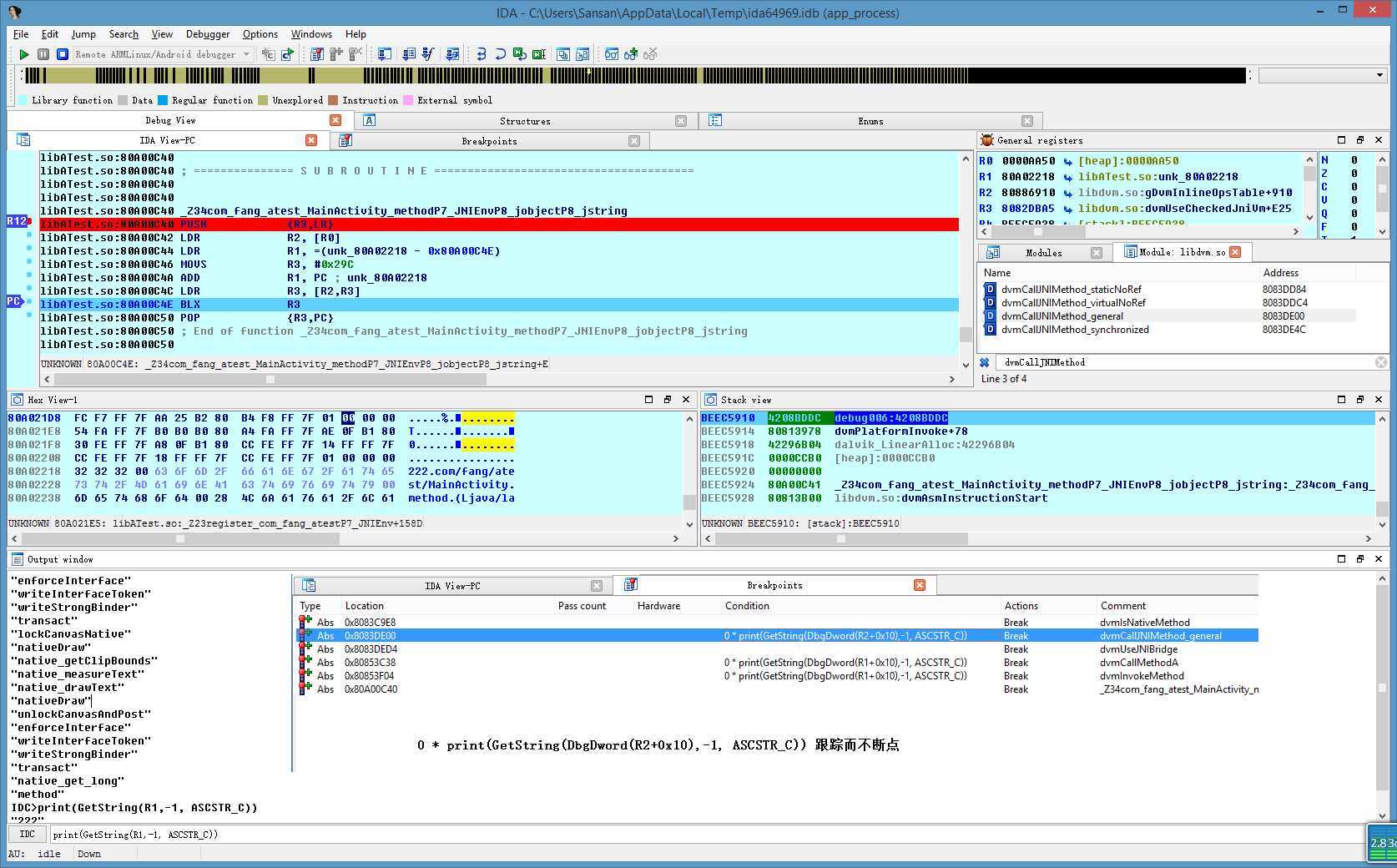
这样是不是说根据"method" == GetString(DbgDword(R2+0x10),-1, ASCSTR_C)条件断点,找到调用的函数地址。

//这个头可以选择VC++编译器直接导入到ida里 typedef void ClassObject; typedef void DexFile; typedef void JValue; typedef void RegisterMap; typedef int u4 ; typedef short u2; //xref: KitKat 4.4.2_r2 /dalvik/libdex/DexProto.h /* * Method prototype structure, which refers to a protoIdx in a * particular DexFile. */ struct DexProto { const DexFile* dexFile; /* file the idx refers to */ u4 protoIdx; /* index into proto_ids table of dexFile */ }; /* * Native function pointer type. * * "args[0]" holds the "this" pointer for virtual methods. * * The "Bridge" form is a super-set of the "Native" form; in many places * they are used interchangeably. Currently, all functions have all * arguments passed in, but some functions only care about the first two. * Passing extra arguments to a C function is (mostly) harmless. */ typedef void (*DalvikBridgeFunc)(const u4* args, JValue* pResult, const Method* method, void* self); /* * A method. We create one of these for every method in every class * we load, so try to keep the size to a minimum. * * Much of this comes from and could be accessed in the data held in shared * memory. We hold it all together here for speed. Everything but the * pointers could be held in a shared table generated by the optimizer; * if we‘re willing to convert them to offsets and take the performance * hit (e.g. "meth->insns" becomes "baseAddr + meth->insnsOffset") we * could move everything but "nativeFunc". */ struct Method { /* the class we are a part of */ ClassObject* clazz; /* access flags; low 16 bits are defined by spec (could be u2?) */ u4 accessFlags; /* * For concrete virtual methods, this is the offset of the method * in "vtable". * * For abstract methods in an interface class, this is the offset * of the method in "iftable[n]->methodIndexArray". */ u2 methodIndex; /* * Method bounds; not needed for an abstract method. * * For a native method, we compute the size of the argument list, and * set "insSize" and "registerSize" equal to it. */ u2 registersSize; /* ins + locals */ u2 outsSize; u2 insSize; /* method name, e.g. "<init>" or "eatLunch" */ const char* name; /* * Method prototype descriptor string (return and argument types). * * TODO: This currently must specify the DexFile as well as the proto_ids * index, because generated Proxy classes don‘t have a DexFile. We can * remove the DexFile* and reduce the size of this struct if we generate * a DEX for proxies. */ DexProto prototype; /* short-form method descriptor string */ const char* shorty; /* * The remaining items are not used for abstract or native methods. * (JNI is currently hijacking "insns" as a function pointer, set * after the first call. For internal-native this stays null.) */ /* the actual code */ const u2* insns; /* instructions, in memory-mapped .dex */ /* JNI: cached argument and return-type hints */ int jniArgInfo; /* * JNI: native method ptr; could be actual function or a JNI bridge. We * don‘t currently discriminate between DalvikBridgeFunc and * DalvikNativeFunc; the former takes an argument superset (i.e. two * extra args) which will be ignored. If necessary we can use * insns==NULL to detect JNI bridge vs. internal native. */ DalvikBridgeFunc nativeFunc; /* * JNI: true if this static non-synchronized native method (that has no * reference arguments) needs a JNIEnv* and jclass/jobject. Libcore * uses this. */ bool fastJni; /* * JNI: true if this method has no reference arguments. This lets the JNI * bridge avoid scanning the shorty for direct pointers that need to be * converted to local references. * * TODO: replace this with a list of indexes of the reference arguments. */ bool noRef; /* * JNI: true if we should log entry and exit. This is the only way * developers can log the local references that are passed into their code. * Used for debugging JNI problems in third-party code. */ bool shouldTrace; /* * Register map data, if available. This will point into the DEX file * if the data was computed during pre-verification, or into the * linear alloc area if not. */ const RegisterMap* registerMap; /* set if method was called during method profiling */ bool inProfile; };
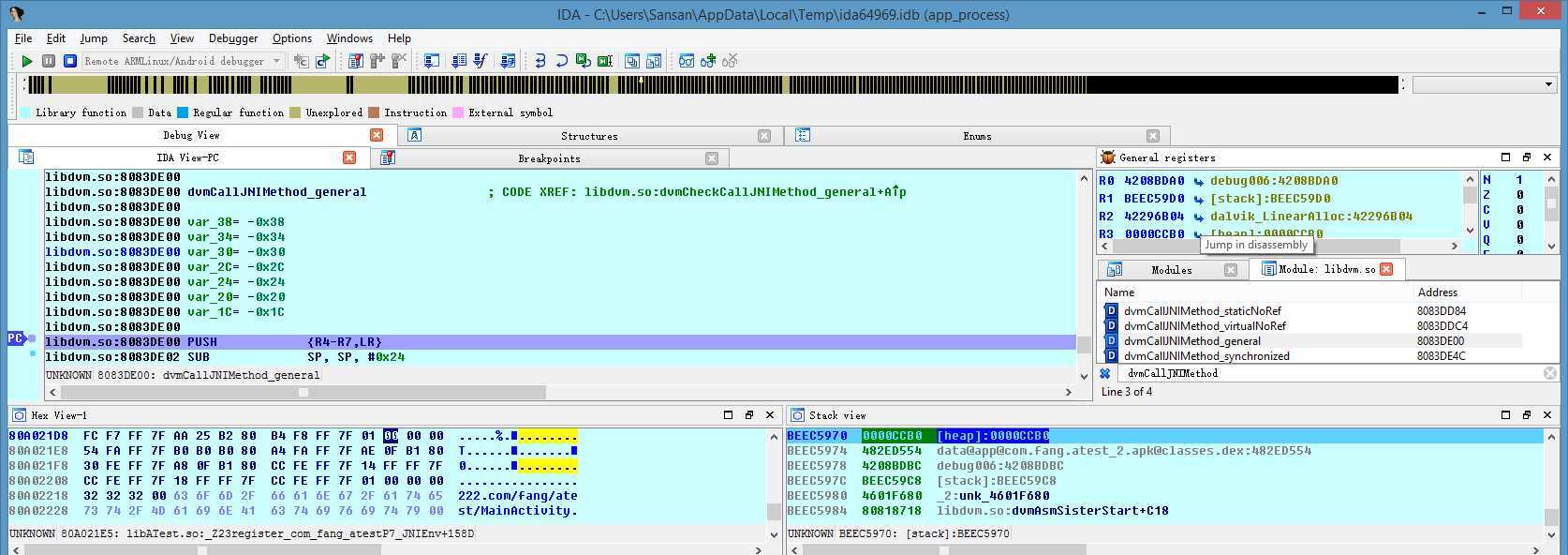
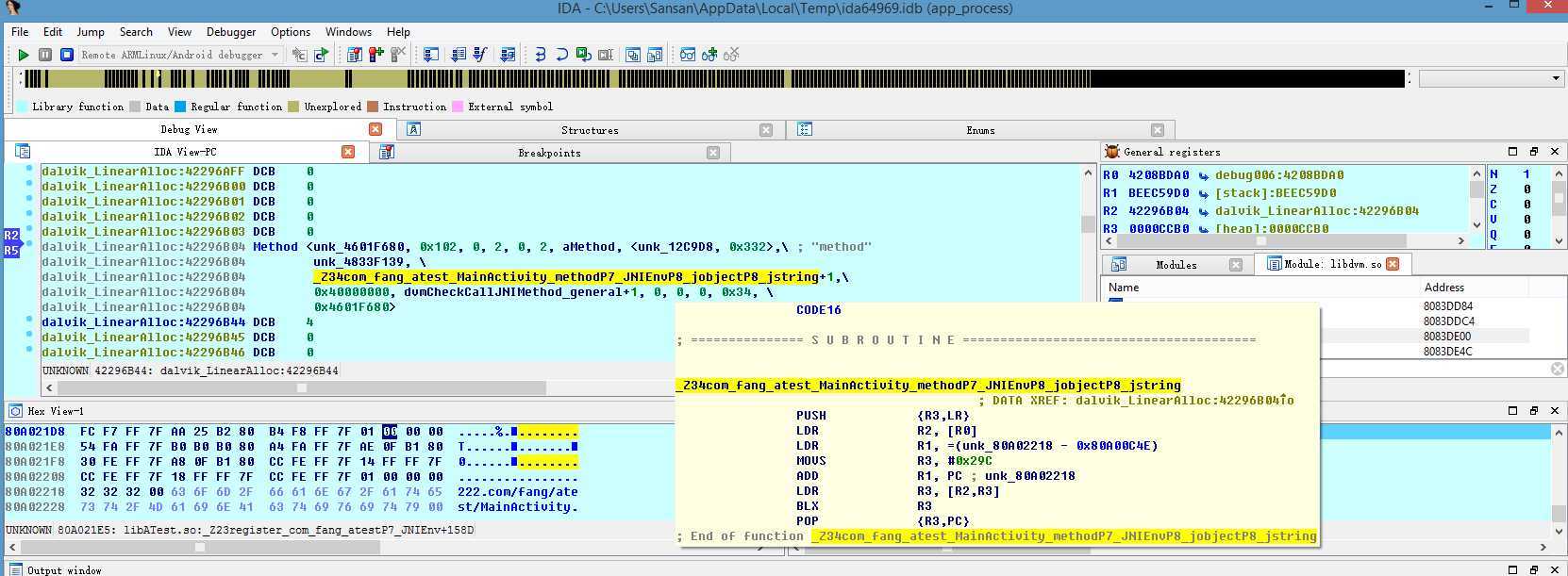
#include <jni.h> jstring com_fang_atest_MainActivity_method(JNIEnv *pEnv, jobject o, jstring param) { return pEnv->NewStringUTF("222"); } /* * 由于gMethods[]是一个<名称,函数指针>对照表,在程序执行时, * 可多次调用registerNativeMethods()函数来更换本地函数的指针, * 从而达到弹性调用本地函数的目的。 */ static JNINativeMethod gMethods[] = { /* name, signature, funcPtr */ { "method", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/String;", (void*) com_fang_atest_MainActivity_method }, }; static const char* const className = "com/fang/atest/MainActivity"; //在native 注册的时候首先保存java的调用方法:以便事件回调而不必每次获取,即在native里调用java对象,方法等。 int register_com_fang_atest(JNIEnv* pEnv) { jclass clazz; //ALOGI(TAG, "Registering %s natives\n", className); clazz = pEnv->FindClass(className); if (clazz == 0) { //ALOGE("Native registration unable to find class ‘%s‘\n", className); return -1; } if (pEnv->RegisterNatives(clazz, gMethods, 1) < 0) { //ALOGE("RegisterNatives failed for ‘%s‘\n", className); return -1; } return 0; } // Set some test stuff up. //Used by WithFramework to register native functions. //Returns the JNI version on success, -1 on failure. //Dalvik虚拟机加载C库时,第一件事是调用JNI_OnLoad()函数 extern "C" jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM* vm, void* reserved) { JNIEnv* env = 0; /*JavaVM::GetEnv 原型为 jint (*GetEnv)(JavaVM*, void**, jint); * GetEnv()函数返回的 Jni 环境对每个线程来说是不同的, * 由于Dalvik虚拟机通常是Multi-threading的。每一个线程调用JNI_OnLoad()时, * 所用的JNI Env是不同的,因此我们必须在每次进入函数时都要通过vm->GetEnv重新获取 */ //得到JNI Env if (vm->GetEnv(reinterpret_cast<void**>(&env), JNI_VERSION_1_4) != JNI_OK) { return JNI_ERR; } // Get jclass with env->FindClass. // Register methods with env->RegisterNatives //assert(env != NULL); register_com_fang_atest(env); // success -- return valid version number return JNI_VERSION_1_4; }
package com.fang.atest; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.io.StringWriter; import java.io.Writer; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.Menu; import android.view.MenuItem; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.TextView; public class MainActivity extends Activity { /* * static { // load library: libADemo.so try { System.loadLibrary("ATest"); * } catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError ule) { * System.err.println("WARNING: Could not load library!"); } * * } */ private native String method(String paramString1); TextView tv; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); tv = (TextView) MainActivity.this.findViewById(R.id.textView1); Button btnCall = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1); btnCall.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub try { tv.setText(method("888")); } catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError ule) { tv.setText(getStackTrace(ule)); ule.printStackTrace(); } } }); Button btnLoad = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button2); btnLoad.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub try { System.loadLibrary("ATest"); } catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError ule) { tv.setText(getStackTrace(ule)); System.err.println("WARNING: Could not load library!"); } } }); /* * Button btnUnLoad = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1); * btnLoad.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { * * @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method * stub try { System.loadLibrary("ATest"); } catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError * ule) { System.err.println("WARNING: Could not load library!"); } } * }); */ } /** * 将异常堆栈转换为字符串 * * @param aThrowable * 异常 * @return String */ public static String getStackTrace(Throwable aThrowable) { final Writer result = new StringWriter(); final PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(result); aThrowable.printStackTrace(printWriter); return result.toString(); } }
标签:des android style blog http io color ar os
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Fang3s/p/4096366.html