标签:android style blog http io ar color os 使用
为了实现广告轮播功能,在网上找了很多方法,有的效果很好,但是代码太麻烦,并且大多是用的viewpager,总之不是很满意。
于是看了一下sdk有个控件是ViewFlipper,使用比较方便,于是尝试了一下,最终实现了所需效果。在这里与大家分享。
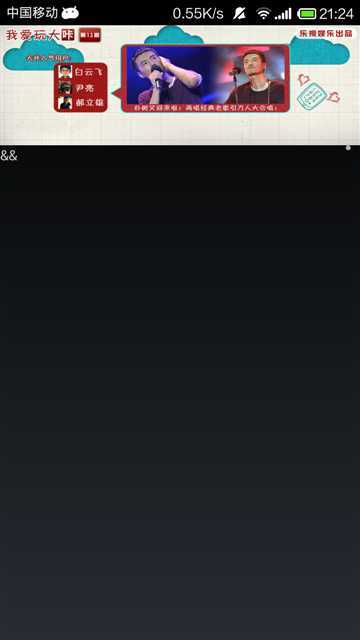
首先看一下效果(主要是布局方面的效果,毕竟手势识别和滑动不太好显示,懒得弄成gif了):
1、布局文件.xml
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<ViewFlipper
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="120dp"
android:id="@+id/details"
>
</ViewFlipper>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="16dp"
>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="16dp"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:gravity="right"
>
<View
android:id="@+id/v_dot0"
style="@style/dot_style"
android:background="@drawable/dot_focused"
/>
<View
android:id="@+id/v_dot1"
style="@style/dot_style"
/>
<View
android:id="@+id/v_dot2"
style="@style/dot_style"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="left"
android:text="hello"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
</LinearLayout>
我来解释一下这个布局
首先,最外层是一个LinearLayout布局来填充整个屏幕。
第二层就是控件ViewFlipper与RelativeLayout并列。其中ViewFlipper是实现图片轮播的,RelationLayout是图片下面的信息,比如图片的标题(如图中的&&)和图片在所有图片中的位置(表现形式为最右边的白色小点)
第三层其实就是把第二层的RelativeLayout展开,里面有一个TextView控件来显示标题,和三个View控件来显示小点。
下面是要用到的一些style和drawable代码(该部分代码来自网络):
前5个放在res/drawable文件夹下
1、btn_back_selector.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:drawable="@drawable/btn_top_pressed" android:state_focused="true"></item>
<item android:drawable="@drawable/btn_top_pressed" android:state_pressed="true"></item>
<item android:drawable="@drawable/btn_top_pressed" android:state_selected="true"></item>
<item android:drawable="@drawable/title_bk"></item>
</selector>
2、btn_top_pressed.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="rectangle" >
<gradient
android:angle="270"
android:endColor="#009ad6"
android:startColor="#11264f" />
</shape>
3、dot_focused.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="oval" >
<solid android:color="#aaFFFFFF" />
<corners android:radius="5dip" />
</shape>
4、dot_normal.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="oval" >
<solid android:color="#33000000" />
<corners android:radius="5dip" />
</shape>
5、title_bk.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="rectangle" >
<gradient
android:angle="270"
android:endColor="#11264f"
android:startColor="#009ad6" />
</shape>
6、styles.xml(放在values文件夹之下)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<style name="dot_style">
<item name="android:layout_width">5dip</item>
<item name="android:layout_height">5dip</item>
<item name="android:background">@drawable/dot_normal</item>
<item name="android:layout_marginLeft">1.5dip</item>
<item name="android:layout_marginRight">1.5dip</item>
</style>
</resources>
这上面的代码我也不怎么懂,但是目的就是为了操作那些小点点。
下面问题来了,java代码呢。不要急,这就上来。
下面高能,胆小误入。
java代码(先全都发上来,容我慢慢解释)
package com.example.mynews;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnTouchListener;
import android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.ImageView.ScaleType;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
import android.widget.ViewFlipper;
public class MainActivity extends Activity{
private ViewFlipper viewFlipper;
private String[] titles;
private TextView tv_title;
private List<View> dots;
float startx;
float x = 0;
float y = 0;
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
viewFlipper = (ViewFlipper)findViewById(R.id.details);
tv_title = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.title);
int image[] = new int[]
{
R.drawable.a,R.drawable.b,R.drawable.c
};
for(int i=0;i<image.length;i++)
{
ImageView iv = new ImageView(getApplicationContext());
iv.setBackgroundResource(image[i]);
iv.setScaleType(ScaleType.CENTER_INSIDE);
iv.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT,LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
viewFlipper.addView(iv);
}
titles = new String[image.length];
titles[0] = "hello";
titles[1] = "&&";
titles[2] = "world";
dots = new ArrayList<View>();
dots.add(findViewById(R.id.v_dot0));
dots.add(findViewById(R.id.v_dot1));
dots.add(findViewById(R.id.v_dot2));
handler.sendMessageDelayed(new Message(), 5000);
viewFlipper.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@SuppressLint("ClickableViewAccessibility")
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
switch(event.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
{ x = event.getX();
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "down"+event.getX(), 1).show();
}break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
{
y = event.getX();
if(y>x)
{
Log.v(null, "result:y>x");
showPre();
}
else if(x==y)
{
Log.v(null, "result:y=x");
showDetail();
}
else
{
Log.v(null, "result:x>y");
showNext();
}
}break;
}
return true;
}
});
}
private Handler handler = new Handler()
{
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg)
{
super.handleMessage(msg);
showNext();
handler.sendMessageDelayed(new Message(), 5000);
}
};
private void showNext()
{
viewFlipper.showNext();
int cur = viewFlipper.getDisplayedChild();
if(cur == 0)
{
dots.get(2).setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.dot_normal);
}
else
{
dots.get(cur-1).setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.dot_normal);
}
dots.get(cur).setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.dot_focused);
tv_title.setText(titles[cur]);
}
private void showPre()
{
viewFlipper.showPrevious();
int cur = viewFlipper.getDisplayedChild();
if(cur == 2)
{
dots.get(0).setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.dot_normal);
}
else
{
dots.get(cur+1).setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.dot_normal);
}
dots.get(cur).setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.dot_focused);
tv_title.setText(titles[cur]);
}
private void showDetail()
{
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"x=y", 1).show();
}
}
1、先准备图片,这里我准备了三张,初始化代码如下:
int image[] = new int[]//用int型数组来储存三张照片的编号
{
R.drawable.a,R.drawable.b,R.drawable.c
};
for(int i=0;i<image.length;i++)//将三张照片加入viewflipper里
{
ImageView iv = new ImageView(getApplicationContext());
iv.setBackgroundResource(image[i]);
iv.setScaleType(ScaleType.CENTER_INSIDE);//这里设置图片变换格式
iv.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT,LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
viewFlipper.addView(iv);
}
2、对ViewFlipper设置监听事件(进行手势操作的核心),注意,这里的监听不是onclicklistener,而是ontouchlistener
viewFlipper.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@SuppressLint("ClickableViewAccessibility")
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
switch(event.getAction())
{
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN://手指按下
{ x = event.getX();//全局变量,接收按下是的手指坐标
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "down"+event.getX(), 1).show();
}break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP://手指松开
{
y = event.getX();//全局变量,接收松开是的手指坐标
//下面就是简单的逻辑判断,从而区分向左滑、向右滑以及不滑(也就是点击事件)
if(y>x)
{
Log.v(null, "result:y>x");
showPre();
}
else if(x==y)
{
Log.v(null, "result:y=x");
showDetail();
}
else
{
Log.v(null, "result:x>y");
showNext();
}
}break;
}
return true;
}
});
这里要重点说下,本来我采用的不是这种方法,而是将activity使用ontouch接口、ViewFlipper使用onclicklistener,而且还要声明一个gesturedetector变量,这样会出现一个问题,就是ontouch与onclick的事件会相互影响,具体怎么回事,我也没搞明白。有事件会仔细研究研究。此外,如果使用gesturedetector又会增加复杂度。
然后是图片切换动作,也就是上段代码中的showPre()、showNext()、showDetail()方法。作用分别是向左滑、向右滑、不滑(这里可以用来实现点击事件)代码如下:
private void showNext()
{
viewFlipper.showNext();//sdk封装好的,使用非常方便
int cur = viewFlipper.getDisplayedChild();
if(cur == 0)
{
dots.get(2).setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.dot_normal);//这是控制那些小点点的,逻辑应该能看懂,就不解释了
}
else
{
dots.get(cur-1).setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.dot_normal);
}
dots.get(cur).setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.dot_focused);
tv_title.setText(titles[cur]);
}
private void showPre()
{
viewFlipper.showPrevious();//sdk封装好的,使用非常方便
int cur = viewFlipper.getDisplayedChild();
if(cur == 2)
{
dots.get(0).setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.dot_normal);
}
else
{
dots.get(cur+1).setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.dot_normal);
}
dots.get(cur).setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.dot_focused);
tv_title.setText(titles[cur]);
}
private void showDetail()
{
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),"x=y", 1).show();
}
下面又到了另外一个重点,handler机制,其实和定时器差不多(至少在这里是)
handler.sendMessageDelayed(new Message(), 5000);
没5000ms也就是5s发送一次消息,这个消息是干嘛的?请看下端代码
private Handler handler = new Handler()
{
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg)
{
super.handleMessage(msg);
showNext();
handler.sendMessageDelayed(new Message(), 5000);
}
};
简单的讲,它是给他自己发消息,提醒自己时间到了,该吃药了(该做某件事了)。然后做完之后还要告诉自己,过5s还要吃药,就这样一直吃药,不放弃治疗。
我想,说到这里,应该明白,这段代码的功能就是实现图片的自动切换。
至此,代码的重点部分解释完了。至于标题和那些小点点怎么处理,都在那三个方法里写好了,肯定可以看明白,就不多赘述了。
附:
1、代码出问题尽量不要找我,虽然是我写的,但是它自己长歪了。
2、转载请注明出处。
谢谢阅读,欢迎批评指正。
Android 通过ViewFlipper实现广告轮播功能并可以通过手势滑动进行广告切换
标签:android style blog http io ar color os 使用
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hearzeus/p/4109309.html