标签:blog http io ar 使用 sp for java strong
Java中的流程控制结构主要有三种:
顺序结构
选择结构
if语句(二路选择结构)、switch语句(多路选择结构)
循环结构
for语句、while语句、do-while语句
跑个程序:
public class test
{
public static void main(String[ ] args) throws IOException {
int year;
boolean IsLeapYear;
System.out.println("Enter the year:");
BufferedReader in =new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
year=(new Integer(in.readLine())).intValue();
IsLeapYear=((year%4==0 && year%100 != 0)||(year%400 == 0));
if (IsLeapYear) {
System.out.print(year);
System.out.println( "is a leap year");
} else {
System.out.print(year);
System.out.println( "is not a leap year");
}
}
}
由于java相关循环控制与C语言类似,所以不加赘述
异常的基本概念:
又称为例外,是特殊的运行错误对象;是面向对象规范的一部分,是异常类的对象;Java中声明了很多异常类,每个异常类都代表了一种运行错误,类中包含了该运行错误的信息
处理错误的方法:
每当Java程序运行过程中发生一个可识别的运行错误时,即该错误有一个异常类与之相对应时,系统都会产生一个相应的该异常类的对象,即产生一个异常
异常处理示意图:
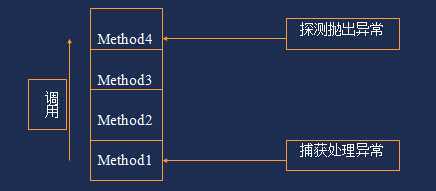
将错误处理代码从常规代码中分离出来
按错误类型和差别分组
对无法预测的错误的捕获和处理
克服了传统方法的错误信息有限的问题
把错误传播给调用堆栈
程序运行过程中发生的异常事件,根据错误的严重程度不同,可分为两类
错误
致命性的,用户程序无法处理
Error类是所有错误类的父类
异常
非致命性的,可编制程序捕获和处理
Exception类是所有异常类的父类
异常和错误类的层次结构:
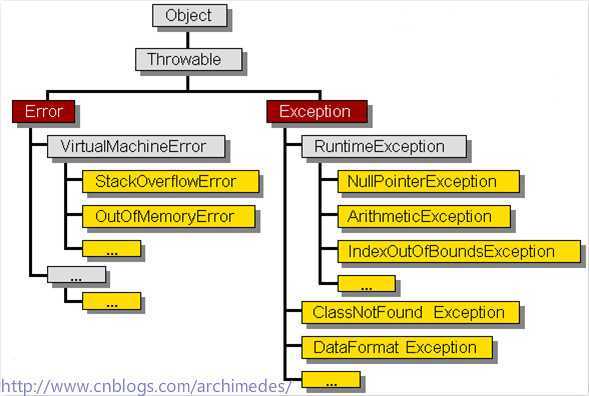
ArithmeticException:整数除法中除数为0
NullPointerException:访问的对象还没有实例化
NegativeArraySizeException:创建数组时元素个数是负数
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:访问数组元素时,数组下标越界
ArrayStoreException:程序试图向数组中存取错误类型的数据
FileNotFoundException:试图存取一个并不存在的文件
IOException:通常的I/O错误
异常的处理:
对于检查型异常,Java强迫程序必须进行处理。处理方法有两种:声明抛出异常
不在当前方法内处理异常,而是把异常抛出到调用方法中捕获异常,使用try{} catch() {}块,捕获到所发生的异常,并进行相应的处理
声明抛出异常
如果程序员不想在当前方法内处理异常,可以使用throws子句声明将异常抛出到调用方法中
如果所有的方法都选择了抛出此异常,最后JVM将捕获它,输出相关的错误信息,并终止程序的运行。在异常被抛出的过程中, 任何方法都可以捕获它并进行相应的处理
举个例子:
public void openThisFile(String fileName) throws java.io.FileNotFoundException {
//code for method
}
public void getCustomerInfo() throws java.io.FileNotFoundException {
// do something
this.openThisFile("customer.txt");
// do something
}
如果在openThisFile中抛出了FileNotfoundException异常,getCustomerInfo将停止执行,并将此异常传送给它的调用者
捕获异常
try {
statement(s)
} catch (exceptiontype name) {
statement(s)
} finally {
statement(s)
}
说明
try 语句,其后跟随可能产生异常的代码块
catch语句,其后跟随异常处理语句,通常用到两个方法
getMessage(),返回一个字符串对发生的异常进行描述。
printStackTrace(),给出方法的调用序列,一直到异常的产生位置
finally语句,不论在try代码段是否产生异常,finally 后的程序代码段都会被执行。通常在这里释放内存以外的其他资源
注意事项
在类层次树中,一般的异常类型放在后面,特殊的放在前面
举个例子:
import java.io.*;
public class ExceptionTester {
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Enter the first number:");
int number1 = Keyboard.getInteger();
System.out.println("Enter the second number:");
int number2 = Keyboard.getInteger();
System.out.print(number1 + " / " + number2 + "=");
int result = number1 / number2;
System.out.println(result);
}
}
其中,Keyboard类的声明如下:
import java.io.*;
public class Keyboard{
static BufferedReader inputStream = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static int getInteger() {
try {
return (Integer.valueOf(inputStream.readLine().trim()).intValue());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
public static String getString() {
try {
return (inputStream.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
return "0";
}
}
}
Enter the first number:
140
Enter the second number:
abc
java.lang.NumberFormatException: abc
at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:426)
at java.lang.Integer.valueOf(Integer.java:532)
at Keyboard.getInteger(Keyboard.java:10)
at ExceptionTester.main(ExceptionTester.java:7)
140 / 0=Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at ExceptionTester.main(ExceptionTester.java:10)
一个类中名字相同的多个方法,这些方法的参数必须不同,Java可通过参数列表的不同来辨别重载的方法:或者参数个数不同、或者参数类型不同
返回值可以相同,也可以不同;重载的价值在于它允许通过使用一个方法名来访问多个方法
举个例子:
class MethodOverloading {
public void receive(int i){
System.out.println("Receive one int parameter. ");
System.out.println("i="+i);
}
public void receive(double d){
System.out.println("Receive one double parameter. ");
System.out.println("d="+d);
}
public void receive(String s){
System.out.println("Receive one String parameter. ");
System.out.println("s="+s);
}
public void receive(int i,int j){
System.out.println("Receive two int parameters. ");
System.out.println("i=" + i + " j=" + j);
}
public void receive(int i,double d){
System.out.println("Receive one int parameter and one double parameter. ");
System.out.println("i=" + i + " d=" + d);
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(String args[]){
MethodOverloading m = new MethodOverloading();
m.receive(2);
m.receive(5.6);
m.receive(3,4);
m.receive(7,8.2);
m.receive("Is it fun?");
}
}
Receive one int parameter.
i=2
Receive one double parameter.
d=5.6
Receive two int parameters.
i=3 j=4
Receive one int parameter and one double parameter.
i=7 d=8.2
Receive one String parameter.
s=Is it fun?
标签:blog http io ar 使用 sp for java strong
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zampo/p/4155987.html