标签:android style blog http io ar color os 使用
App Widget是一些桌面的小插件,比如说天气和某些音乐播放应用,放到桌面去的那部分;
例如:
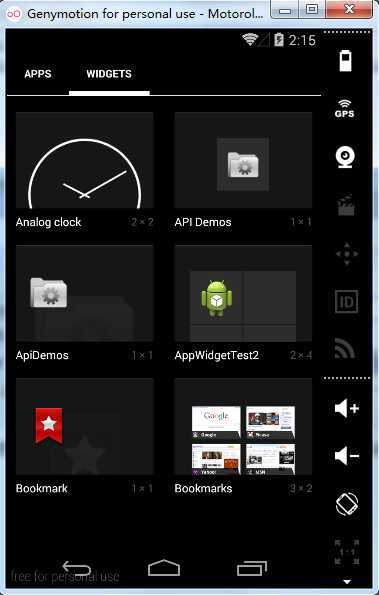
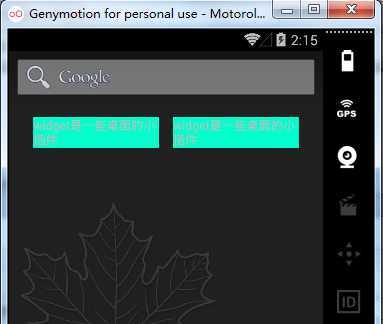
实现步骤及代码如下:
(1)首先,在AndroidManifest.xml中声明一个App Widget;
(1)定义AppWidgetProviderInfo对象:为App Widget提供元数据,包括布局、更新频率等,这个对象定义在XML文件当中;
在res/xml文件夹中定义一个名为example_appwidget_info.xml的文件;
(2)为App Widget指定样式和布局:
定义一个新的布局文件example_appwidget.xml;
(3)实现AppWidgetProvider:定义了App Widget的基本生命周期函数;
onUpdate:在到达指定的更新时间之后或当前用户向桌面添加App Widget时调用该方法;
onDeleted:当App Widget被删除时,会调用该方法;
onEnabled:当一个App Widget的实例第一次被创建时,会调用该方法;
onDisabled:当最后一个App Widget实例被删除后,会调用该方法;
onReveice:接收广播事件;
详细实现步骤可参考官方文档,讲解的十分详细:
http://android.toolib.net/guide/topics/appwidgets/index.html
http://developers.androidcn.com/guide/topics/appwidgets/index.html#Providers
代码:
AndroidManifest.xml中声明 App Widget:
<receiver android:name="ExampleAppWidgetProvider" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.appwidget.action.APPWIDGET_UPDATE" />
</intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.appwidget.provider"
android:resource="@xml/example_appwidget_info" />
</receiver>
res/xml目录下的example_appwidget_info.xml:
<appwidget-provider xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:initialLayout="@layout/example_appwidget"
android:minHeight="294dp"
android:minWidth="72dp"
android:updatePeriodMillis="86400000" >
</appwidget-provider>
新的布局文件 example_appwidget.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/widgetTextId"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#00FFCC"
android:text="widget是一些桌面的小插件" />
</LinearLayout>
定义类ExampleAppWidgetProvider继承AppWidgetProvider:
package com.example.appwidgettest2;
import android.appwidget.AppWidgetManager;
import android.appwidget.AppWidgetProvider;
import android.content.Context;
public class ExampleAppWidgetProvider extends AppWidgetProvider {
@Override
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,
int[] appWidgetIds) {
System.out.println("onUpdate");
super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds);
}
@Override
public void onDeleted(Context context, int[] appWidgetIds) {
System.out.println("onDeleted");
super.onDeleted(context, appWidgetIds);
}
@Override
public void onDisabled(Context context) {
System.out.println("onDisabled");
super.onDisabled(context);
}
@Override
public void onEnabled(Context context) {
System.out.println("onEnabled");
super.onEnabled(context);
}
}
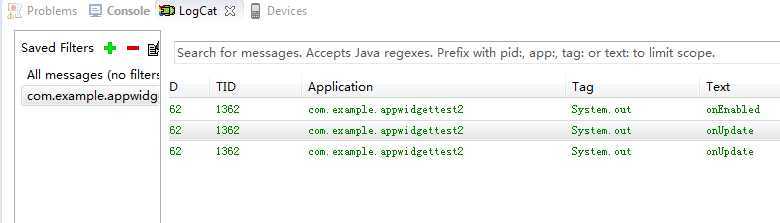
删除一个App Widget:
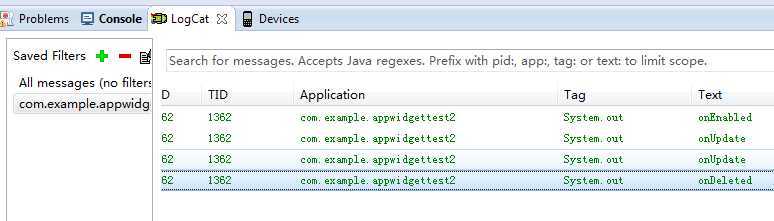
全部删除:
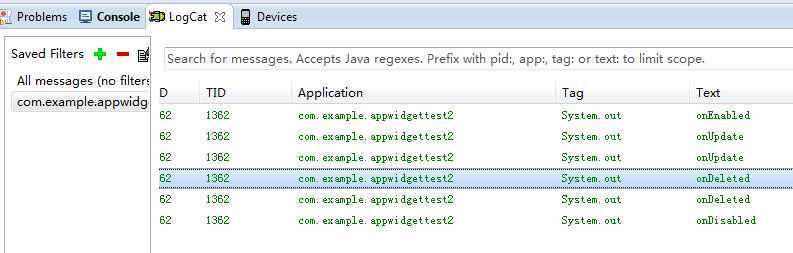
在此基础上,来看另一个例子:
给原先的App Widget添加一个按钮,点击后能跳转到另一个Activity;
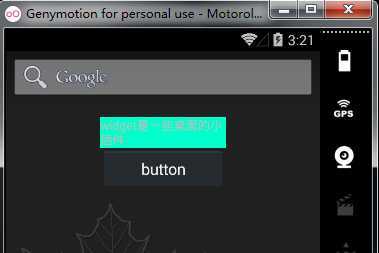
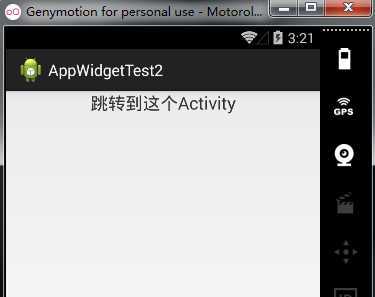
实现方式为:
使用PendingIntent和RemoteViews来实现;
(1)创建PendingIntent的方法有3种;
getActivity(Context context, int requestCode, Intent intent, int flags)
getBroadcast(Context context, int requestCode, Intent intent, int flags)
getService(Context context, int requestCode, Intent intent, int flags)
(2)RemoteViews的作用:
RemoteViews对象表示了一系列的View对象;
RemoteViews所代表的对象运行在另外的线程当中;
(3)因为App Widget和我们的应用程序运行在不同的进程当中(App Widget当中的View运行在Home Screen进程当中),所以无法按照之前那种方式绑定监听器;
而是应该使用remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.widgetButtonId,pendingIntent)来实现;
TargetActivity.java
package com.example.appwidgettest2;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class TargetActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.target_activity);
}
}
target_activity.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="跳转到这个Activity" />
</LinearLayout>
而ExampleAppWidgetProvider修改为:
package com.example.appwidgettest2;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.appwidget.AppWidgetManager;
import android.appwidget.AppWidgetProvider;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.widget.RemoteViews;
public class ExampleAppWidgetProvider extends AppWidgetProvider {
@Override
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,
int[] appWidgetIds) {
System.out.println("onUpdate");
for (int i = 0; i < appWidgetIds.length; i++) {
System.out.println(appWidgetIds[i]);
// 创建一个Intent对象
Intent intent = new Intent(context, TargetActivity.class);
// 创建一个PendingIntent
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(context, 0,
intent, 0);
RemoteViews remoteViews = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(),
R.layout.example_appwidget);
// 为按钮绑定事件处理器,
// 第一个参数用来指定被绑定处理器控件的ID;
// 第二个参数用来指定当事件发生时,哪个PendingIntent将会被指定;
remoteViews.setOnClickPendingIntent(R.id.widgetButtonId,
pendingIntent);
// 更新AppWidget
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetIds[i], remoteViews);
}
super.onUpdate(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetIds);
}
@Override
public void onDeleted(Context context, int[] appWidgetIds) {
super.onDeleted(context, appWidgetIds);
}
@Override
public void onDisabled(Context context) {
super.onDisabled(context);
}
@Override
public void onEnabled(Context context) {
super.onEnabled(context);
}
}
标签:android style blog http io ar color os 使用
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaozhang2014/p/4164299.html