标签:
android 小游戏 ---- 数独(三)
好的,既然要把数独棋盘中初始提示数字绘制出来,我们就要先了解数独的一些特点。
数独棋盘中总共是81个数字,那我们是否可以用一个数组来代表整个棋盘对应的数字呢
想象我们初始化一个9x9的数组,
private int[] sudoku = new int[9*9]
//初始化数据 private int[] sudoku = new int[9*9];
这里使用一维数组,当然使用二维数组更加明了直接,这个随个人喜好。
那么我们可以让 sudoku[0] 对应数独棋盘上第一个方格的数字(左上角),
sudoku[1]对应第一个行第二个方格数字,以此类推。
数独的81个数字是有规律的,这个可以在网上找到初始化的数字和填好棋盘的数字。
我们找一个这样的数据,以String字符串的形式初始化,在通过分解让其填充到int数组中
//数独初始化谜题数据的字符串 private final String init_str = "061030020050008107000007034" +"009006078003209500570300900" +"190700000802400060040010250"; //正确答案字符串 private final String correct_str = "761934825354628197928157634" +"219546378483279516576381942" +"195762483832495761647813259";
/** *根据一个字符串数据 生成一个整形数组 数独游戏的初始化数据 */ protected int[] fromPuzzleString(String str){ int[] sudo = new int[str.length()]; for(int i=0;i<sudo.length;i++){ //charAt()返回指定索引处的 char值 分解字符串填充到数组 //减去0 做类型转换 使之成为int类型 sudo[i]=str.charAt(i)-‘0‘; } return sudo; }
/** * 根据九宫格中当中的坐标 返回此位置的所应该填写的数据字符串 */ public String getTileString(int x,int y){ int v = getTileInteger(x, y); if(v == 0){ return ""; } else { return String.valueOf(v); } }
有了getTileString(int x,int y)这个方法,我们就可以根据棋盘方格的位置代表的坐标
的到当前方格应该填充的数字。
如何的到我们绘制棋盘方格所代表的坐标呢?
首先我们重写SurfaveView的onSizeChanged方法,不重写也可以,主要目的是确定棋盘方格的高度和宽度。
@Override protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) { /* * 计算单元格的宽度和高度 * 设置方块的宽度和高度为屏幕w宽度的1/9 正方形 */ this.width = w/9f; this.height = w/9f; super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh); }
这里我们设置宽高都为宽度的1/9,这样看就是完整的正方形了。
当用户点击屏幕时,根据点击事件得到点击的坐标,在做一下运算就可得到当前所点击
的方格所代表的坐标了。
//用户点击的屏幕的坐标点 selectedX = (int)(event.getX() / width); selectedY = (int)(event.getY() / height);
绘制初始数据,则不需要知道方格代表的坐标,
如下,用嵌套循环,便利sudoku数组,如果匹配到空则不绘制
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) { if(!game.getTileString(i, j).equals("")){ paint.setColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.shudu_init_number_bg)); canvas.drawRect(i*width, j*height, i*width+width, j*height+width, paint); } } }
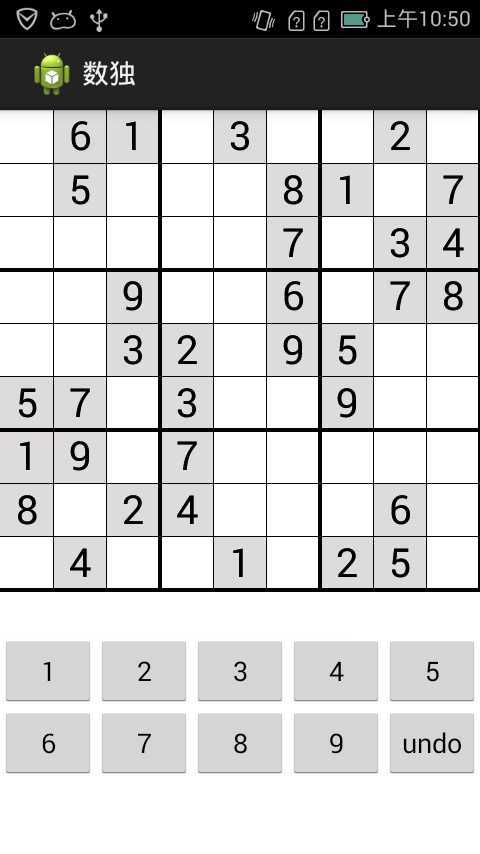
棋盘下方的数字键盘,是在xml中布局的,keypad.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center" android:orientation="vertical" > <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:id="@+id/num_1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/num_1" android:layout_weight="1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/num_2" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/num_2" android:layout_weight="1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/num_3" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/num_3" android:layout_weight="1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/num_4" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/num_4" android:layout_weight="1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/num_5" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/num_5" android:layout_weight="1" /> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:id="@+id/num_6" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/num_6" android:layout_weight="1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/num_7" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/num_7" android:layout_weight="1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/num_8" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/num_8" android:layout_weight="1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/num_9" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/num_9" android:layout_weight="1" /> <Button android:id="@+id/undo" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="undo" android:layout_weight="1" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
然后在main.xml include进来
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" android:background="@android:color/white" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <FrameLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="350dp" > <com.sphere.shudu.GameSFView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/panelSurfaceView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> </FrameLayout> <include android:id="@+id/keyPadView" layout="@layout/keypad" /> </LinearLayout>
这里使用了350dip,适用于hdpi的设备,如果是其他类型请自行配置高度大小。
最后在Activity的setContentView中传R.layout.main即可
这样,Activity中就同时包含surfaceview的显示和操作的按钮区域了。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/sphere/p/4177923.html