标签:
1.k近邻算法的思想
给定一个训练集,对于新的输入实例,在训练集中找到与该实例最近的k个实例,这k个实例中的多数属于某个类,就把该输入实例分为这个类。
因为要找到最近的k个实例,所以计算输入实例与训练集中实例之间的距离是关键!
k近邻算法最简单的方法是线性扫描,这时要计算输入实例与每一个训练实例的距离,当训练集很大时,非常耗时,这种方法不可行,为了提高k近邻的搜索效率,常常考虑使用特殊的存储结构存储训练数据,以减少计算距离的次数,具体方法很多,这里介绍实现经典的kd树方法。
2.构造kd树
kd树是一种对k维空间中的实例点进行存储以便对其进行快速检索的树形数据结构,kd树是二叉树。
下面举例说明:
给定一个二维空间的数据集: T = {(2,3), (5,4), (9,6), (4,7), (8,1), (7,2)},构造一个平衡kd树。
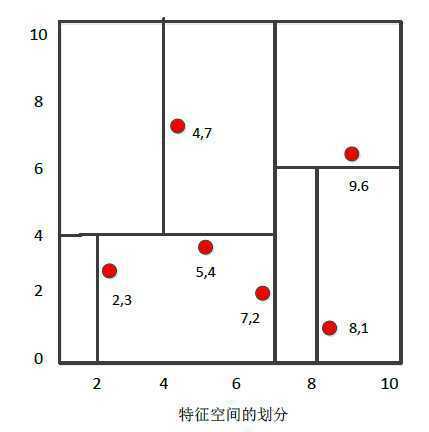
构造的kd树如下:
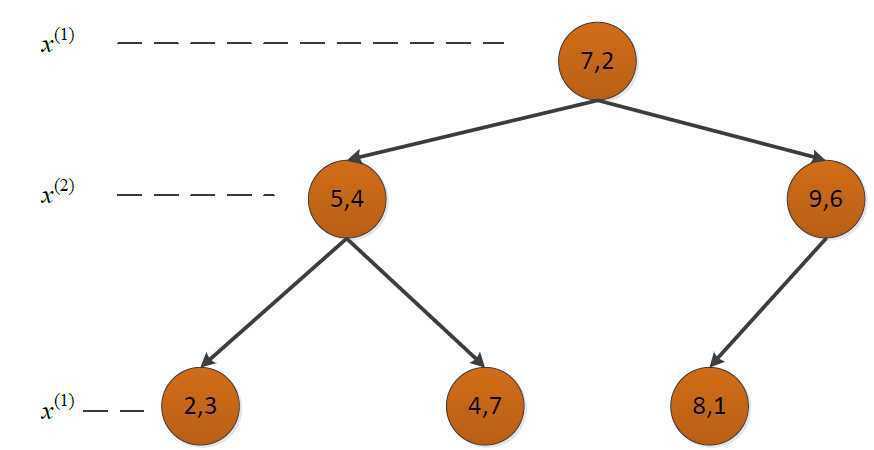
3.利用kd树搜索最近邻
输入:已构造的kd树;目标点x;
输出:x的最近邻
(b)当前最近点一定存在于某结点一个子结点对应的区域,检查该子结点的父结点的另
一子结点对应区域是否有更近的点(即检查另一子结点对应的区域是否与以目标点为球
心、以目标点与“当前最近点”间的距离为半径的球体相交);如果相交,可能在另一
个子结点对应的区域内存在距目标点更近的点,移动到另一个子结点,接着递归进行最
近邻搜索;如果不相交,向上回退
4.C++实现
1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <vector>
3 #include <algorithm>
4 #include <string>
5 #include <cmath>
6 using namespace std;
7
8
9
10
11 struct KdTree{
12 vector<double> root;
13 KdTree* parent;
14 KdTree* leftChild;
15 KdTree* rightChild;
16 //默认构造函数
17 KdTree(){parent = leftChild = rightChild = NULL;}
18 //判断kd树是否为空
19 bool isEmpty()
20 {
21 return root.empty();
22 }
23 //判断kd树是否只是一个叶子结点
24 bool isLeaf()
25 {
26 return (!root.empty()) &&
27 rightChild == NULL && leftChild == NULL;
28 }
29 //判断是否是树的根结点
30 bool isRoot()
31 {
32 return (!isEmpty()) && parent == NULL;
33 }
34 //判断该子kd树的根结点是否是其父kd树的左结点
35 bool isLeft()
36 {
37 return parent->leftChild->root == root;
38 }
39 //判断该子kd树的根结点是否是其父kd树的右结点
40 bool isRight()
41 {
42 return parent->rightChild->root == root;
43 }
44 };
45
46 int data[6][2] = {{2,3},{5,4},{9,6},{4,7},{8,1},{7,2}};
47
48 template<typename T>
49 vector<vector<T> > Transpose(vector<vector<T> > Matrix)
50 {
51 unsigned row = Matrix.size();
52 unsigned col = Matrix[0].size();
53 vector<vector<T> > Trans(col,vector<T>(row,0));
54 for (unsigned i = 0; i < col; ++i)
55 {
56 for (unsigned j = 0; j < row; ++j)
57 {
58 Trans[i][j] = Matrix[j][i];
59 }
60 }
61 return Trans;
62 }
63
64 template <typename T>
65 T findMiddleValue(vector<T> vec)
66 {
67 sort(vec.begin(),vec.end());
68 auto pos = vec.size() / 2;
69 return vec[pos];
70 }
71
72
73 //构建kd树
74 void buildKdTree(KdTree* tree, vector<vector<double> > data, unsigned depth)
75 {
76
77 //样本的数量
78 unsigned samplesNum = data.size();
79 //终止条件
80 if (samplesNum == 0)
81 {
82 return;
83 }
84 if (samplesNum == 1)
85 {
86 tree->root = data[0];
87 return;
88 }
89 //样本的维度
90 unsigned k = data[0].size();
91 vector<vector<double> > transData = Transpose(data);
92 //选择切分属性
93 unsigned splitAttribute = depth % k;
94 vector<double> splitAttributeValues = transData[splitAttribute];
95 //选择切分值
96 double splitValue = findMiddleValue(splitAttributeValues);
97 //cout << "splitValue" << splitValue << endl;
98
99 // 根据选定的切分属性和切分值,将数据集分为两个子集
100 vector<vector<double> > subset1;
101 vector<vector<double> > subset2;
102 for (unsigned i = 0; i < samplesNum; ++i)
103 {
104 if (splitAttributeValues[i] == splitValue && tree->root.empty())
105 tree->root = data[i];
106 else
107 {
108 if (splitAttributeValues[i] < splitValue)
109 subset1.push_back(data[i]);
110 else
111 subset2.push_back(data[i]);
112 }
113 }
114
115 //子集递归调用buildKdTree函数
116
117 tree->leftChild = new KdTree;
118 tree->leftChild->parent = tree;
119 tree->rightChild = new KdTree;
120 tree->rightChild->parent = tree;
121 buildKdTree(tree->leftChild, subset1, depth + 1);
122 buildKdTree(tree->rightChild, subset2, depth + 1);
123 }
124
125 //逐层打印kd树
126 void printKdTree(KdTree *tree, unsigned depth)
127 {
128 for (unsigned i = 0; i < depth; ++i)
129 cout << "\t";
130
131 for (vector<double>::size_type j = 0; j < tree->root.size(); ++j)
132 cout << tree->root[j] << ",";
133 cout << endl;
134 if (tree->leftChild == NULL && tree->rightChild == NULL )//叶子节点
135 return;
136 else //非叶子节点
137 {
138 if (tree->leftChild != NULL)
139 {
140 for (unsigned i = 0; i < depth + 1; ++i)
141 cout << "\t";
142 cout << " left:";
143 printKdTree(tree->leftChild, depth + 1);
144 }
145
146 cout << endl;
147 if (tree->rightChild != NULL)
148 {
149 for (unsigned i = 0; i < depth + 1; ++i)
150 cout << "\t";
151 cout << "right:";
152 printKdTree(tree->rightChild, depth + 1);
153 }
154 cout << endl;
155 }
156 }
157
158
159 //计算空间中两个点的距离
160 double measureDistance(vector<double> point1, vector<double> point2, unsigned method)
161 {
162 if (point1.size() != point2.size())
163 {
164 cerr << "Dimensions don‘t match!!" ;
165 exit(1);
166 }
167 switch (method)
168 {
169 case 0://欧氏距离
170 {
171 double res = 0;
172 for (vector<double>::size_type i = 0; i < point1.size(); ++i)
173 {
174 res += pow((point1[i] - point2[i]), 2);
175 }
176 return sqrt(res);
177 }
178 case 1://曼哈顿距离
179 {
180 double res = 0;
181 for (vector<double>::size_type i = 0; i < point1.size(); ++i)
182 {
183 res += abs(point1[i] - point2[i]);
184 }
185 return res;
186 }
187 default:
188 {
189 cerr << "Invalid method!!" << endl;
190 return -1;
191 }
192 }
193 }
194 //在kd树tree中搜索目标点goal的最近邻
195 //输入:目标点;已构造的kd树
196 //输出:目标点的最近邻
197 vector<double> searchNearestNeighbor(vector<double> goal, KdTree *tree)
198 {
199 /*第一步:在kd树中找出包含目标点的叶子结点:从根结点出发,
200 递归的向下访问kd树,若目标点的当前维的坐标小于切分点的
201 坐标,则移动到左子结点,否则移动到右子结点,直到子结点为
202 叶结点为止,以此叶子结点为“当前最近点”
203 */
204 unsigned k = tree->root.size();//计算出数据的维数
205 unsigned d = 0;//维度初始化为0,即从第1维开始
206 KdTree* currentTree = tree;
207 vector<double> currentNearest = currentTree->root;
208 while(!currentTree->isLeaf())
209 {
210 unsigned index = d % k;//计算当前维
211 if (currentTree->rightChild->isEmpty() || goal[index] < currentNearest[index])
212 {
213 currentTree = currentTree->leftChild;
214 }
215 else
216 {
217 currentTree = currentTree->rightChild;
218 }
219 ++d;
220 }
221 currentNearest = currentTree->root;
222
223 /*第二步:递归地向上回退, 在每个结点进行如下操作:
224 (a)如果该结点保存的实例比当前最近点距离目标点更近,则以该例点为“当前最近点”
225 (b)当前最近点一定存在于某结点一个子结点对应的区域,检查该子结点的父结点的另
226 一子结点对应区域是否有更近的点(即检查另一子结点对应的区域是否与以目标点为球
227 心、以目标点与“当前最近点”间的距离为半径的球体相交);如果相交,可能在另一
228 个子结点对应的区域内存在距目标点更近的点,移动到另一个子结点,接着递归进行最
229 近邻搜索;如果不相交,向上回退*/
230
231 //当前最近邻与目标点的距离
232 double currentDistance = measureDistance(goal, currentNearest, 0);
233
234 //如果当前子kd树的根结点是其父结点的左孩子,则搜索其父结点的右孩子结点所代表
235 //的区域,反之亦反
236 KdTree* searchDistrict;
237 if (currentTree->isLeft())
238 {
239 if (currentTree->parent->rightChild == NULL)
240 searchDistrict = currentTree;
241 else
242 searchDistrict = currentTree->parent->rightChild;
243 }
244 else
245 {
246 searchDistrict = currentTree->parent->leftChild;
247 }
248
249 //如果搜索区域对应的子kd树的根结点不是整个kd树的根结点,继续回退搜索
250 while (searchDistrict->parent != NULL)
251 {
252 //搜索区域与目标点的最近距离
253 double districtDistance = abs(goal[(d+1)%k] - searchDistrict->parent->root[(d+1)%k]);
254
255 //如果“搜索区域与目标点的最近距离”比“当前最近邻与目标点的距离”短,表明搜索
256 //区域内可能存在距离目标点更近的点
257 if (districtDistance < currentDistance )//&& !searchDistrict->isEmpty()
258 {
259
260 double parentDistance = measureDistance(goal, searchDistrict->parent->root, 0);
261
262 if (parentDistance < currentDistance)
263 {
264 currentDistance = parentDistance;
265 currentTree = searchDistrict->parent;
266 currentNearest = currentTree->root;
267 }
268 if (!searchDistrict->isEmpty())
269 {
270 double rootDistance = measureDistance(goal, searchDistrict->root, 0);
271 if (rootDistance < currentDistance)
272 {
273 currentDistance = rootDistance;
274 currentTree = searchDistrict;
275 currentNearest = currentTree->root;
276 }
277 }
278 if (searchDistrict->leftChild != NULL)
279 {
280 double leftDistance = measureDistance(goal, searchDistrict->leftChild->root, 0);
281 if (leftDistance < currentDistance)
282 {
283 currentDistance = leftDistance;
284 currentTree = searchDistrict;
285 currentNearest = currentTree->root;
286 }
287 }
288 if (searchDistrict->rightChild != NULL)
289 {
290 double rightDistance = measureDistance(goal, searchDistrict->rightChild->root, 0);
291 if (rightDistance < currentDistance)
292 {
293 currentDistance = rightDistance;
294 currentTree = searchDistrict;
295 currentNearest = currentTree->root;
296 }
297 }
298 }//end if
299
300 if (searchDistrict->parent->parent != NULL)
301 {
302 searchDistrict = searchDistrict->parent->isLeft()?
303 searchDistrict->parent->parent->rightChild:
304 searchDistrict->parent->parent->leftChild;
305 }
306 else
307 {
308 searchDistrict = searchDistrict->parent;
309 }
310 ++d;
311 }//end while
312 return currentNearest;
313 }
314
315 int main()
316 {
317 vector<vector<double> > train(6, vector<double>(2, 0));
318 for (unsigned i = 0; i < 6; ++i)
319 for (unsigned j = 0; j < 2; ++j)
320 train[i][j] = data[i][j];
321
322 KdTree* kdTree = new KdTree;
323 buildKdTree(kdTree, train, 0);
324
325 printKdTree(kdTree, 0);
326
327 vector<double> goal;
328 goal.push_back(3);
329 goal.push_back(4.5);
330 vector<double> nearestNeighbor = searchNearestNeighbor(goal, kdTree);
331 vector<double>::iterator beg = nearestNeighbor.begin();
332 cout << "The nearest neighbor is: ";
333 while(beg != nearestNeighbor.end()) cout << *beg++ << ",";
334 cout << endl;
335 return 0;
336 }
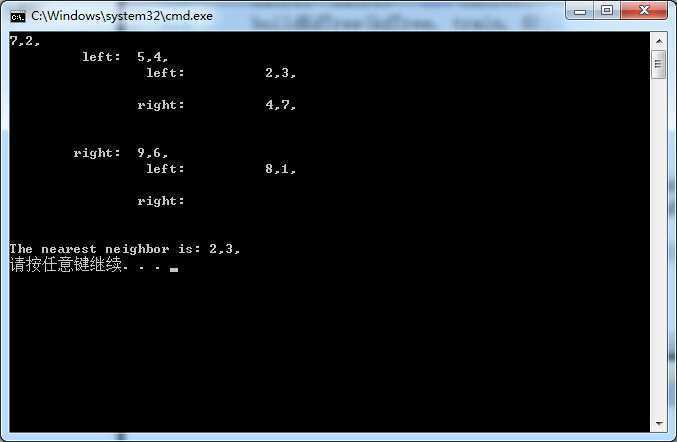
5. 运行
下面是用上面举例构造的kd树求点(3,4.5)的最近邻:
参考文献:李航《统计学习方法》,维基百科
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/90zeng/p/kdtree.html