标签:
1、 软件开发:
*什么是软件?
软件是一系列按照特定顺序组织的计算机数据和指令的集合。程序设计的最终结果是软件
系统软件:系统软件为计算机使用提供最基本的功能:如:DOS,Windows,Linux,Unix,Mac,Android,IOS
2、人机交互
图形化界面:
命令行方式
3、Java语言特征(跨平台)
Java通过java虚拟机跨平台(JVM)
4、JDK、JRE、JVM之间的关系
JDK是整个java和核心,包括java的运行环境、java工具、java基础类库
JRE,运行JAVA程序所必须的环境的集合,保护JVM标准实现及java核心类库
JVM是java虚拟机,是一种用于计算设备的规范,他是一个虚构出来的计算机,是通过在实际的计算机上仿真模拟平台
相关信息,使jva程序只需生产在java虚拟机上运行的目标代码,就可以在多种平台上不加修改地运行。
5:JDK安装:
官网:www.oracle.com java.sun.com
在JDK里面就有JRE,所以提示安装JRE时可以不装
6.在我的电脑-熟悉=高级=环境变量设置java工具即bin所在路径就可以了
注:%%代表调用,需要用;分割
临时配置,在dos中输入set path=你携带的U盘就JRE中的bin的路径
1、进制的转换
实例:
1 import java.util.LinkedList; 2 3 import javax.swing.text.html.HTMLDocument.Iterator; 4 5 //查表法转换进制 6 public class jinZhi { 7 public static void main(String [] args){ 8 9 int num=6; 10 11 tobin(num); 12 13 toOct(num); 14 15 toHex(num); 16 } 17 private static void toHex(int num) { 18 con(num,15,4); 19 20 } 21 22 private static void toOct(int num) { 23 con(num,7,3); 24 25 } 26 27 private static void tobin(int num) { 28 con(num,1,1); 29 30 } 31 //列表法结合集合运用实例 32 private static void con(int num, int diwei, int yiwei) { 33 if(num==0){ 34 System.out.println("num="+0); 35 return; 36 } 37 38 // 表格法 39 char[] chs={‘0‘,‘1‘,‘2‘,‘3‘,‘4‘,‘5‘,‘6‘,‘7‘, 40 ‘8‘,‘9‘,‘a‘,‘b‘,‘c‘,‘d‘,‘e‘,‘f‘}; 41 42 LinkedList<Character> list=new LinkedList<Character>(); 43 44 while(num!=0){ 45 list.addFirst(chs[num&diwei]); 46 num>>>=yiwei; 47 } 48 while(!list.isEmpty()){ 49 System.out.print(list.removeFirst()); 50 } 51 System.out.println(); 52 } 53 }
直接转换的快捷方法:
1 Integer.toHexString(int num); 2 10进制——16进制 3 Integer.toOctalString(int num); 4 10进制——8进制 5 Integer.toBinaryString(int num); 6 10进制——2进制
2.数据类型
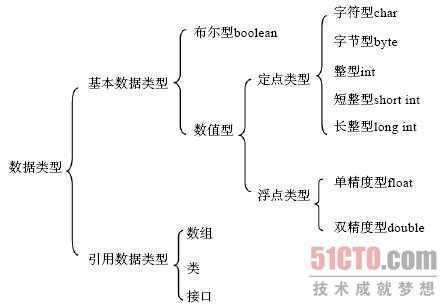
注意:String是类不是基本数据类型
当出现Object数组Object[],可以看出是引用数据类型,是不能放入基本数据类型的;
概述:
面向过程强调过程、执行者、强调功能行为;
面向对象强调功能、指挥者、将功能封装进对象,强调具备功能的对象
面向对象思想的特点:问题简单化,执行者变指挥者
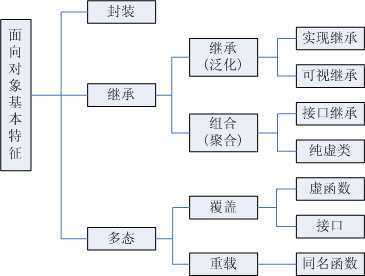
三大特征:封装、继承、多态
重写(override)和重载(overload)的区别:
重载的特点:
重载在同一类中。
重载方法名相同,参数列表不同。
重写的特点:
重写要有继承关系。在子父类中
重写方法的声明相同。(方法名和参数列表都相同)
子类覆盖时,子类方法权限一定要大于等于父类方法权限
父类的权限不能是私有的
父类静态只能覆盖静态。当一个类中所有的方法都是抽象的时候,你没必要定义为抽象类,定义为接口就可以了。
(2)成员特点:所以不能被创建,只能被继承
一、String
1、String方法
int length():获得长度 char charAt(index):获得指定角标的字符返回字节
int indexOf(int ch(ASCII码)):返回ch在字符中第一次出现的位置的角标,没有则返回-1
int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex):从fromIndex位置开始,获取ch在字符串中位置
int indexOf(String Str):获取str的第一次出现位置
int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex):获取从fromIndex后第一次出现的位置角标
boolean contains(str):判断是否包含___常用
isEmpty():判断是否空——常用
startsWith(str):头部有某字符串
endsWith(str):尾巴有某字符串
equals:判断字符串是否相同——常用——也经常被复写
equalsIgnoreCase:忽略大小写的判断字符串是否相同
2、String转换
构造函数:String(char[])
String(char[],offset,count)//讲字符数组一部分转换为字符串
3
char[] tocharArray():将字符串转换为字符数组
String(byte[]);将字符数组转换为字符串
String(byte[],offset,count)
byte[] getBytes();将字符串装好为字符数组
String valueOf(int):int变String
String valueOf(double):double变字符串
4、替换:String replace(older,newer)
5切割:String[] split("");切割括号捏的字符串,分成若干字符串组成字符串数组
6、获得字符串的一部分 String subString(begin,end)
7、大写:UpperCase() 小写:toLowerCase()
compareTo:字符串的自然顺序排序:常用
实例:判断字符串key在字符串Str出现的次数:
1 public static int count(String str,String key){ 2 int count=0; 3 int index=0; 4 5 while( (index=str.indexOf(key,index))!=-1){ 6 index=index+key.length(); 7 count++; 8 } 9 return count; 10 }
实例:反转字符串数组:
1 class ReverString{ 2 3 4 public static String reverseString(String s){ 5 return reverseString(s,0,s.length()); 6 } 7 8 public static String reverseString(String s, int start, int end) { 9 // 变字符数组 10 char[] ch=s.toCharArray(); 11 // 将数组反转,已经得到ch的对象的反转字符数组 12 charRecerse(ch,start,end); 13 14 return new String().valueOf(ch); 15 } 16 17 public static void charRecerse(char[] ch, int start, int end) { 18 for(int x=start,y=end-1;x<y;x++,y--){ 19 swap(ch,x,y); 20 } 21 } 22 private static void swap(char[] ch,int x,int y){ 23 char t=ch[x]; 24 ch[x]=ch[y]; 25 ch[y]=t; 26 } 27 }
实例:寻找相同子字符串
1 /* 2 * 需求:获取连个字符串中最大的相同子串 3 */ 4 5 public static String getMaxSubString(String s1,String s2){ 6 String max,min; 7 max=(s1.length()>s2.length())?s1:s2; 8 min=(max==s1)?s2:s1; 9 10 for(int x=0;x<min.length();x++){ 11 for(int y=0,z=min.length()-x;z<min.length()+1;y++,z++){ 12 String tenp=min.substring(y,z); 13 if(max.contains(tenp)){ 14 return tenp; 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 return "没有字符串"; 19 20 }
二、StirngBuffer
1、 一个长度可变的,可以操作多个数据类型的、可以通过toString方法变成字符串的容器
2方法:
append():添加
insert(数据,index):指定位置添加
delete(start,end)删除
delexteCharAt(index):删除指定位置
charAt(index):获取并返回char
indexOf(Str):返回字符串的位置
length():长度
subString(start,end):获取指定位置返回String
setCharAt(index,char ch):
反转: reverse()
三、基本数据类型的包装类
将基本数据类型封装成对象的好处:可以在对象中定义许多功能方法操作该数据
byte---Byte short———Short int——Integer long——Long
boolean——Boolean float——Float double——Double char——Character
包装类的常用方法:
static int parseInt(String str):将数组字符串转换成数组
Integer.toBinaryString();10转2
Integer.toOctalString():10转8
Integer.toHexSfring():10转16
实例:
1 private static String StringSort(String s) { 2 // 分割 3 String[] str=s.split(" "); 4 // 转成int型 5 int[] arr=new int[str.length]; 6 for(int x=0;x<str.length;x++){ 7 // 使用Interger.parseInt方法将字符数组变Int数组 8 arr[x]=Integer.parseInt(str[x]); 9 } 10 Arrays.sort(arr); 11 12 StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder(); 13 for(int x=0;x<arr.length;x++){ 14 sb.append(arr[x]+""); 15 } 16 sb.append(arr[arr.length-1]+""); 17 18 return sb.toString(); 19 }
Arrays工具类:
static int |
binarySearch(byte[] a, byte key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 byte 型数组,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(byte[] a,
int fromIndex, int toIndex, byte key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 byte 型数组的范围,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(char[] a,
char key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 char 型数组,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(char[] a,
int fromIndex, int toIndex, char key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 char 型数组的范围,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(double[] a,
double key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 double 型数组,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(double[] a,
int fromIndex, int toIndex, double key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 double 型数组的范围,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(float[] a,
float key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 float 型数组,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(float[] a,
int fromIndex, int toIndex, float key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 float 型数组的范围,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(int[] a,
int key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 int 型数组,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(int[] a,
int fromIndex, int toIndex, int key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 int 型数组的范围,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(long[] a,
int fromIndex, int toIndex, long key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 long 型数组的范围,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(long[] a,
long key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 long 型数组,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(Object[] a,
int fromIndex, int toIndex, Object key)
使用二分搜索法来搜索指定数组的范围,以获得指定对象。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(Object[] a, Object key)
使用二分搜索法来搜索指定数组,以获得指定对象。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(short[] a,
int fromIndex, int toIndex, short key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 short 型数组的范围,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static int |
binarySearch(short[] a,
short key) 使用二分搜索法来搜索指定的 short 型数组,以获得指定的值。 |
|
static
|
binarySearch(T[] a,
int fromIndex, int toIndex, T key, Comparator<? super T> c)
使用二分搜索法来搜索指定数组的范围,以获得指定对象。 |
|
static
|
binarySearch(T[] a,
T key, Comparator<? super T> c)
使用二分搜索法来搜索指定数组,以获得指定对象。 |
一个进程又多个线程同时操控,从而达到同时运行的效果:
1两种方式
extend Thread方式:首先类继承Thread,然后复写run;创建这个类,使用start()方法启动
inplements Runnable:类implements Runnable,复写run;创建类,创建线程Thread一类对象为参数,使用startt(0启动
2、买票练习:
1 import java.util.Arrays; 2 //买票 3 public class StringSort { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args){ 6 Ticket tk = new Ticket();//建立票信息对象 7 sealCentre tsc = new sealCentre(tk);// 创建售票中心。 8 tsc.set(200);//售票中心分配一定数量的票 9 new Thread(new windowsSeal(tk,"一号窗口")).start();// 创建、启动线程,开始卖票。 10 new Thread(new windowsSeal(tk,"二号窗口")).start(); 11 new Thread(new windowsSeal(tk,"三号窗口")).start(); 12 new Thread(new windowsSeal(tk,"四号窗口")).start(); 13 } 14 15 } 16 17 18 class Ticket{ 19 private int ticket; 20 21 public int getTicket() { 22 return ticket; 23 } 24 25 public void setTicket(int ticket) { 26 this.ticket = ticket; 27 } 28 29 30 } 31 32 33 class sealCentre{ 34 private Ticket tk; 35 sealCentre(Ticket tk){ 36 this.tk=tk; 37 } 38 public void set(int t){ 39 tk.setTicket(t); 40 } 41 } 42 43 class windowsSeal implements Runnable{ 44 private Ticket tk; 45 private String name; 46 windowsSeal(Ticket tk,String name){ 47 this.tk=tk; 48 this.name=name; 49 } 50 @Override 51 public void run() { 52 53 while(true){ 54 synchronized (tk) { 55 int t=tk.getTicket(); 56 if(t>0){ 57 System.out.println(name+"第"+(t--)+"张票卖出"); 58 tk.setTicket(t); 59 }else{ 60 System.out.println(name+"票已经售完"); 61 // System.exit(0); 62 break; 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 }
在Java当中,线程通常都有五种状态,创建、就绪、运行、阻塞和死亡。
第一是创建状态。在生成线程对象,并没有调用该对象的start方法,这是线程处于创建状态。
第二是就绪状态。当调用了线程对象的start方法之后,该线程就进入了就绪状态,但是此时线程调度程序还没有把该线程设置为当前线程,此时处于就绪状态。在线程运行之后,从等待或者睡眠中回来之后,也会处于就绪状态。
第三是运行状态。线程调度程序将处于就绪状态的线程设置为当前线程,此时线程就进入了运行状态,开始运行run函数当中的代码。
第四是阻塞状态。线程正在运行的时候,被暂停,通常是为了等待某个时间的发生(比如说某项资源就绪)之后再继续运行。sleep,join(),wait(),yield等方法都可以导致线程阻塞。
第五是死亡状态。如果一个线程的run方法执行结束或者调用stop方法后,该线程就会死亡。对于已经死亡的线程,无法再使用start方法令其进入就绪。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/shuiyinmeizi/p/4204393.html