标签:
1.Android是什么
手机设备的软件栈,包括一个完整的操作系统、中间件、关键的应用程序,底层是linux内核,安全管理、内存管理、进程管理、电源管理、硬件驱动
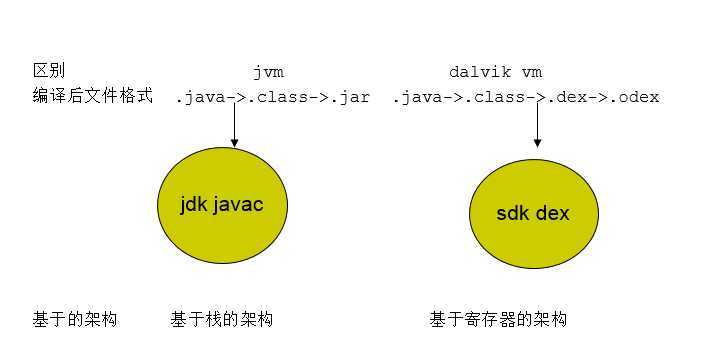
2.Dalvik VM 和 JVM 的比较
3.常见adb指令
platform-tools/adb.exe
adb.exe : android debug bridge android调试桥
adb devices:列出所以连接的设备
adb kill-server :杀死adb调试桥
adb start-server :启动adb调试桥
adb install xxx.apk 如果有多个设备,我们可以指定设备 adb install –s emulator-5554 D:/xxx.apk
adb uninstall 包名 : 卸载应用
adb pull 源文件 目标文件 : 导出文件
adb push 源文件 目标文件 : 导入文件
4.Android应用程序架构

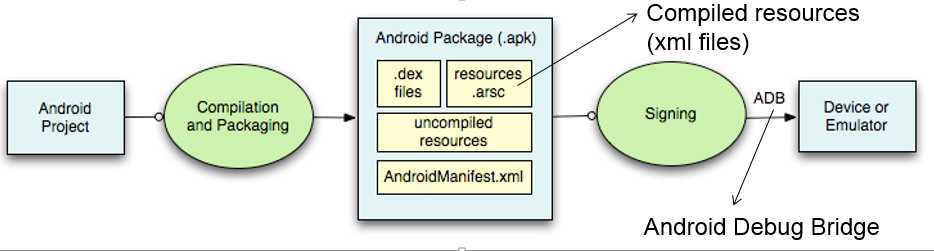
5.程序打包&安装的过程
6.电话拨号器
代码提示键:Alt+/
出现黄色的解决方式:Ctrl+1
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".PhoneActivity" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_number"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="phone"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_dail"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_below="@+id/et_number"
android:text="@string/dail" />
</RelativeLayout>
package com.example.demo1;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class PhoneActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private EditText dt_number = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_phone);
Button bt_dail = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.bt_dail);
dt_number = (EditText)this.findViewById(R.id.et_number);
bt_dail.setOnClickListener(this);
}
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.bt_dail:
String number = dt_number.getText().toString().trim();
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(number)) {
Toast.makeText(PhoneActivity.this, "号码不能为空!",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
}
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_CALL);
intent.setData(Uri.parse("tel:" + number));
startActivity(intent);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
<activity
android:name="com.example.demo1.PhoneActivity"
android:label="@string/title_activity_phone" >
<!--决定启动哪个activity-->
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CALL_PHONE" />
7.点击事件的4种写法
(1).创建一个内部类定义点击事件
bt_dail.setOnClickListener(new MyListener());
private class MyListener implements OnClickListener
(2).采用匿名内部类创建点击事件
bt_dail.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
});
(3).让类实现点击事件的接口,(常用)
public class PhoneActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.bt_dail:
default:
break;
}
(4).在布局文件中绑定一个点击(android:onClick="")
android:onClick="dail"
public void dail(View view) {}
8.短信发送器
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_number"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="请输入电话号码" >
<requestFocus />
</EditText>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="请输入内容"
android:lines="5" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_send"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="发送" />
</LinearLayout>
package com.example.demo1;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.telephony.SmsManager;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class SMSActivity extends Activity {
private EditText mEditTextNumber = null;
private EditText mEditTextContent = null;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_sms);
Button mButtonSend = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.bt_send);
this.mEditTextNumber = (EditText) this.findViewById(R.id.et_number);
this.mEditTextContent = (EditText) this.findViewById(R.id.et_content);
mButtonSend.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
String number = mEditTextNumber.getText().toString().trim();
String content = mEditTextContent.getText().toString().trim();
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(number) || TextUtils.isEmpty(content)) {
Toast.makeText(SMSActivity.this, "电话号码或内容不能为空!", 0).show();
} else {
PendingIntent sentIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(SMSActivity.this, 0, new Intent(), 0);
SmsManager smsManager = SmsManager.getDefault();
//如果字数超过70,需拆分成多条短信发送
ArrayList<String> contents = smsManager.divideMessage(content);
for (String str : contents) {
//最后二个参数为短信已发送的广播意图,最后一个参数为短信对方已收到短信的广播意图
smsManager.sendTextMessage(number, null, str, sentIntent,null);
}
Toast.makeText(SMSActivity.this, "短信发送完成", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
});
}
}
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.SEND_SMS"/>
9. Android 中各种布局
<!-- LinearLayout - 线形布局。
orientation - 容器内元素的排列方式。vertical: 子元素们垂直排列;horizontal: 子元素们水平排列
gravity - 内容的排列形式。常用的有 top, bottom, left, right, center 等,详见文档 -->
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:gravity="right"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<!-- FrameLayout - 层叠式布局。以左上角为起点,将 FrameLayout 内的元素一层覆盖一层地显示 -->
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="FrameLayout" >
</TextView>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Frame Layout" >
</TextView>
</FrameLayout>
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<!--
TableLayout - 表格式布局。
TableRow - 表格内的行,行内每一个元素算作一列
collapseColumns - 设置 TableLayout 内的 TableRow 中需要隐藏的列的列索引,多个用“,”隔开
stretchColumns - 设置 TableLayout 内的 TableRow 中需要拉伸(该列会拉伸到所有可用空间)的列的列索引,多个用“,”隔开
shrinkColumns - 设置 TableLayout 内的 TableRow 中需要收缩(为了使其他列不会被挤到屏幕外,此列会自动收缩)的列的列索引,多个用“,”隔开
-->
<TableLayout android:id="@+id/TableLayout01"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:collapseColumns="1">
<TableRow android:id="@+id/TableRow01" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="行1列1" />
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="行1列2" />
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="行1列3" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow android:id="@+id/TableRow01" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="行2列1" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
<!--
AbsoluteLayout - 绝对定位布局。
layout_x - x 坐标。以左上角为顶点
layout_y - y 坐标。以左上角为顶点
-->
<AbsoluteLayout android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent">
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="AbsoluteLayout"
android:layout_x="100px"
android:layout_y="100px" />
</AbsoluteLayout>
<!--
RelativeLayout - 相对定位布局。
layout_centerInParent - 将当前元素放置到其容器内的水平方向和垂直方向的中央位置(类似的属性有 :layout_centerHorizontal, layout_alignParentLeft 等)
layout_marginLeft - 设置当前元素相对于其容器的左侧边缘的距离
layout_below - 放置当前元素到指定的元素的下面
layout_alignRight - 当前元素与指定的元素右对齐
-->
<RelativeLayout android:id="@+id/RelativeLayout01"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/abc"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="centerInParent=true"
android:layout_centerInParent="true" />
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="marginLeft=20dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp" />
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="xxx"
android:layout_below="@id/abc" android:layout_alignRight="@id/abc" />
</RelativeLayout>
</LinearLayout>
无废话Android之常见adb指令、电话拨号器、点击事件的4种写法、短信发送器、Android 中各种布局(1)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yxlblogs/p/4209756.html