标签:
Android Runtime使得直接调用底层Linux下的可执行程序或脚本成为可能
比如Linux下写个测试工具,直接编译后apk中通过Runtime来调用
或者写个脚本,apk中直接调用,省去中间层或者JNI
这个至少效率应该比较高吧

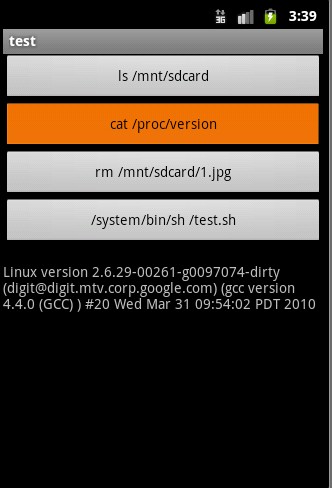

代码:
[java] view plaincopy
public class test extends Activity {
TextView text;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text);
Button btn_ls = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_ls);
btn_ls.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
do_exec("ls /mnt/sdcard");
}
});
Button btn_cat = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_cat);
btn_cat.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
do_exec("cat /proc/version");
}
});
Button btn_rm = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_rm);
btn_rm.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
do_exec("rm /mnt/sdcard/1.jpg");
}
});
Button btn_sh = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_sh);
btn_sh.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
do_exec("/system/bin/sh /mnt/sdcard/test.sh 123");
}
});
}
String do_exec(String cmd) {
String s = "/n";
try {
Process p = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(p.getInputStream()));
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
s += line + "/n";
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
text.setText(s);
return cmd;
}
}
test.sh:
echo test.sh
echo $1
需要注意:
1. exec不等于console命令
2. exec的输入输出流需要自己处理
3. exec执行时阻塞、非阻塞,返回结果问题
4. 注意权限问题
通过Runtime.getRuntime().exec调用底层Linux下的程序或脚本
标签:
原文地址:http://my.oschina.net/u/994235/blog/365218